ORIF of Scapular Body and Glenoid Fracture via Modified Judet Approach
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
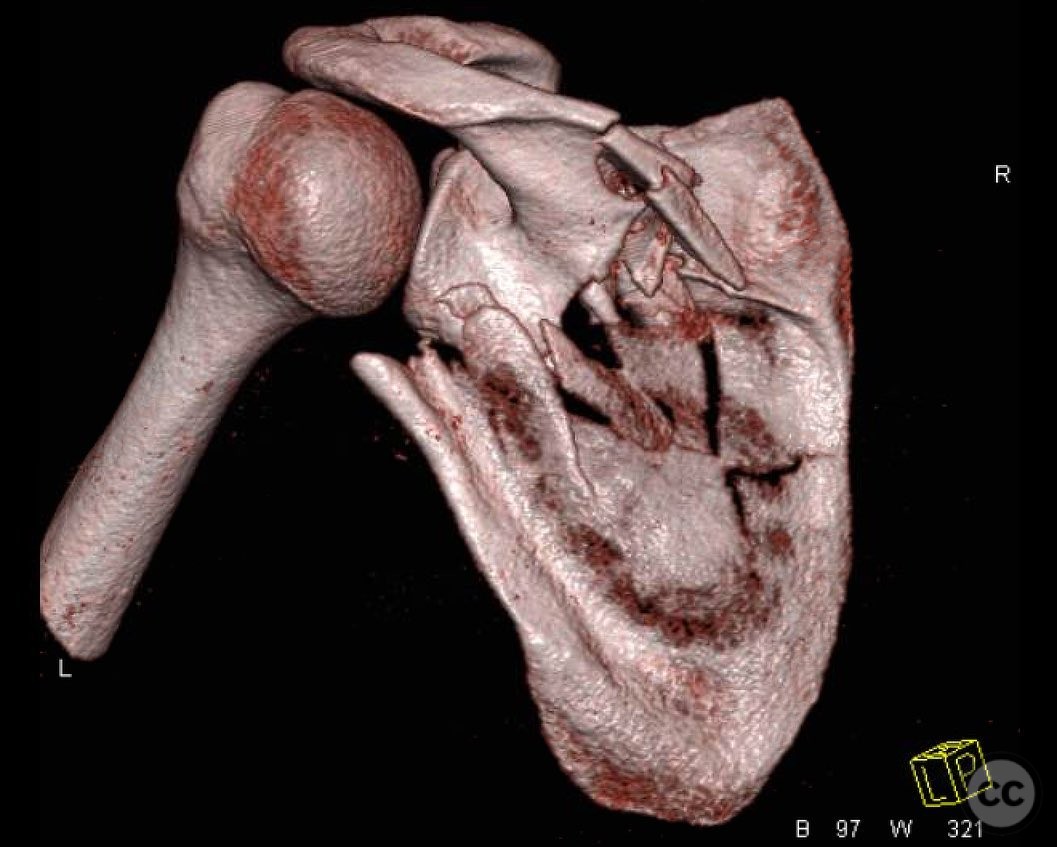
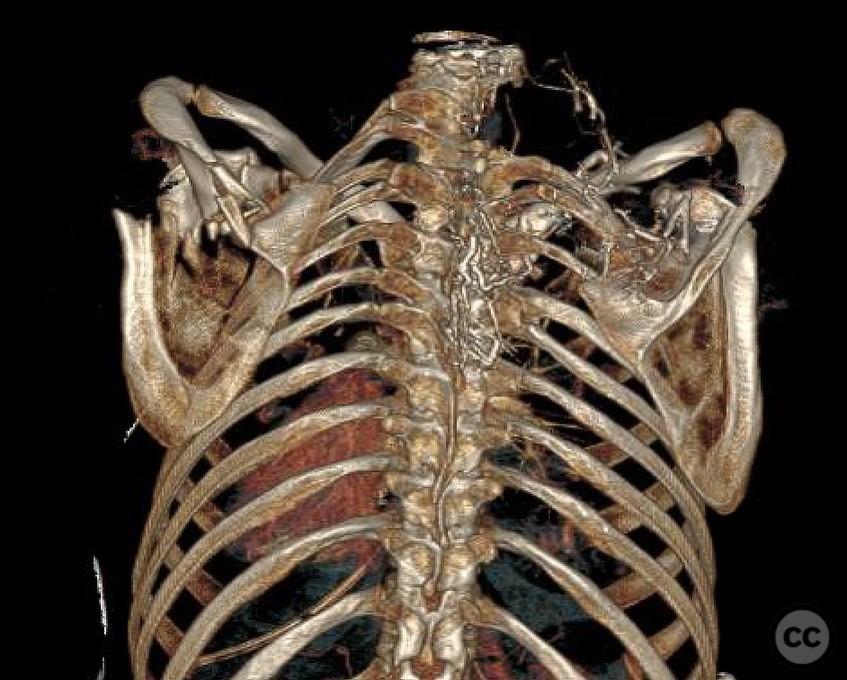
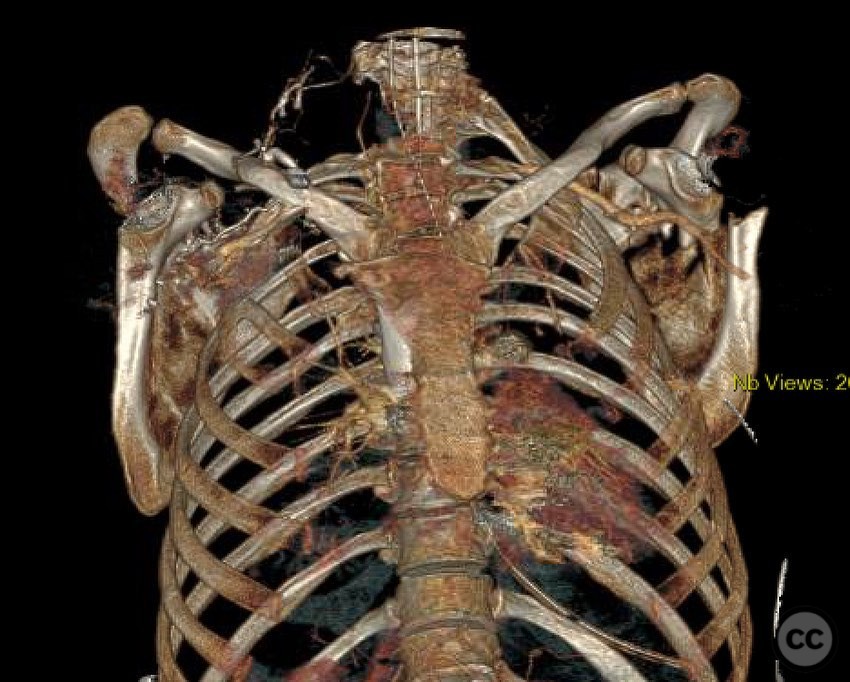
Clinical and radiological findings: The patient presented with a significant lateralization of the scapular body exceeding 5 cm, accompanied by notable angulation between the scapular body and the glenoid. Radiological assessment confirmed the displacement and angulation, indicating the need for surgical intervention. The neurovascular examination was unremarkable.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved an open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) using a modified Judet approach. The surgical objective was to address the lateralization of the scapular body and realign it with the glenoid, focusing on restoring proper anatomical alignment and rotator cuff mechanics.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned in a lateral decubitus position to facilitate access to the posterior aspect of the scapula, with the affected side up. This positioning allowed optimal exposure for the modified Judet approach.
Anatomical surgical approach: A modified Judet approach was utilized, involving a posterior incision along the scapular spine extending towards the lateral border of the scapula. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the scapular body and glenoid, allowing for direct visualization and manipulation of the fracture fragments.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that understanding the stable versus unstable segments was crucial for successful reduction. The reduction was achieved by aligning the scapular body to the glenoid neck, counteracting the deforming forces. Fixation was accomplished using plate and screw constructs to maintain stability and promote healing.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included immobilization in a sling for initial comfort, followed by gradual mobilization exercises. Passive range of motion exercises were initiated early, progressing to active-assisted and active range of motion as tolerated. Strengthening exercises were introduced once adequate healing was confirmed radiologically.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included plate and screw constructs for stabilization of the scapular body and glenoid alignment.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_2.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_4.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_1.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_3.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_6.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_5.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signifi_7.jpg)
 lateralization of the scapular body_ and signific(.jpg)
Article viewed 205 times
19 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). ORIF of Scapular Body and Glenoid Fracture via Modified Judet Approach. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 9106554 Published Online Jul 19 2025.