High-Energy Pilon Fracture with Intact Fibula Entrapment Behind Talus: A Bosworth-Type Injury
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
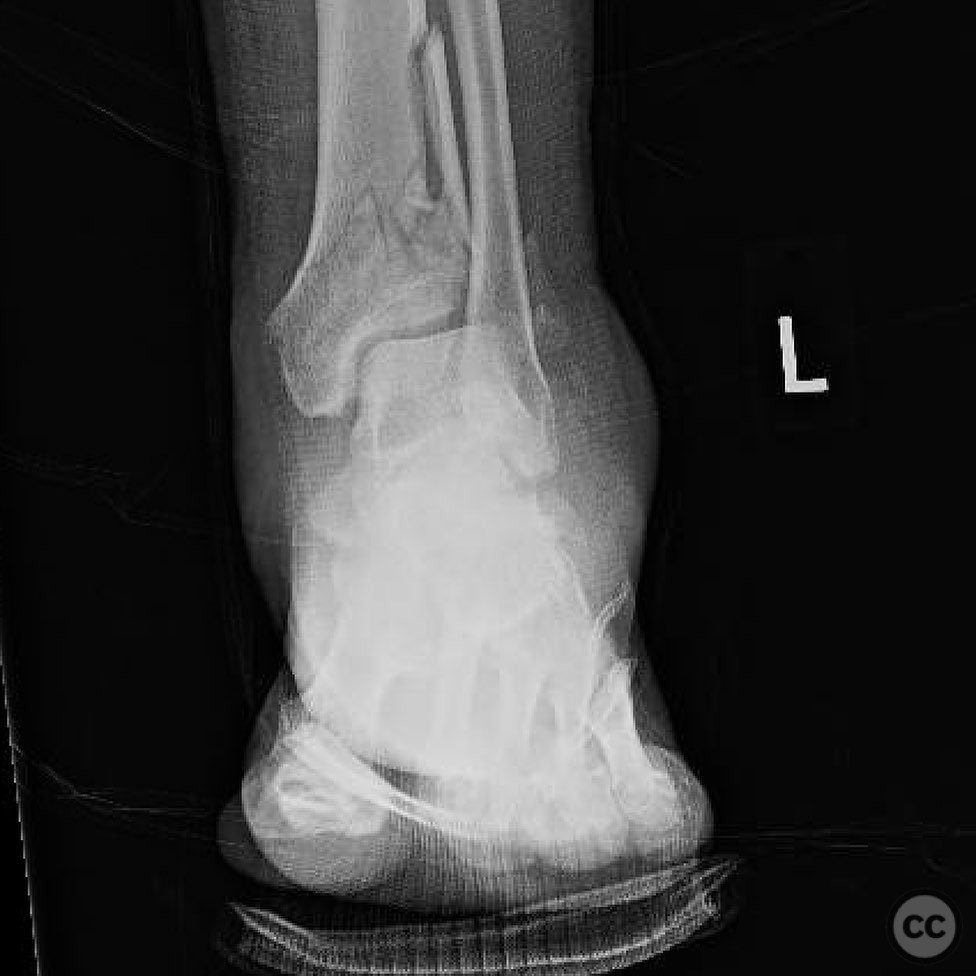
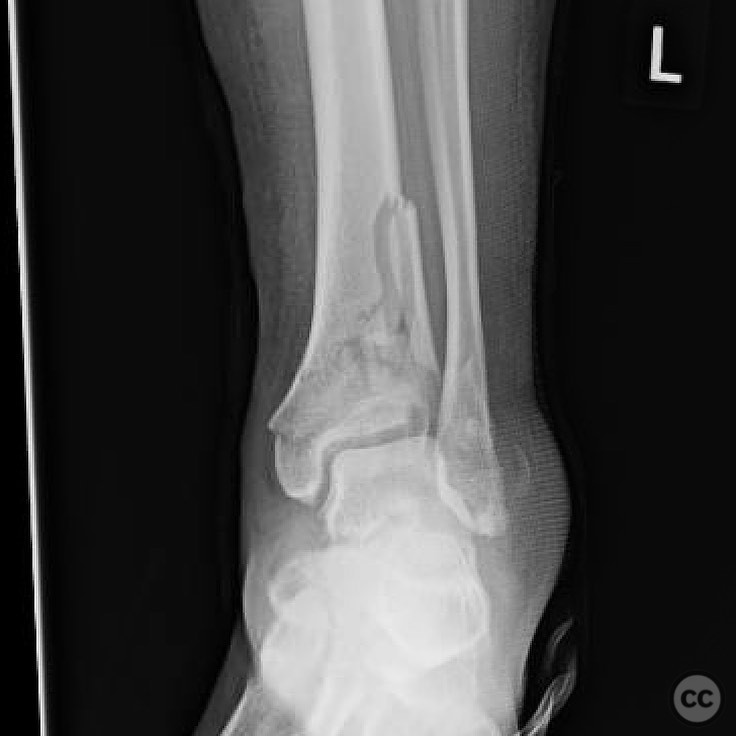
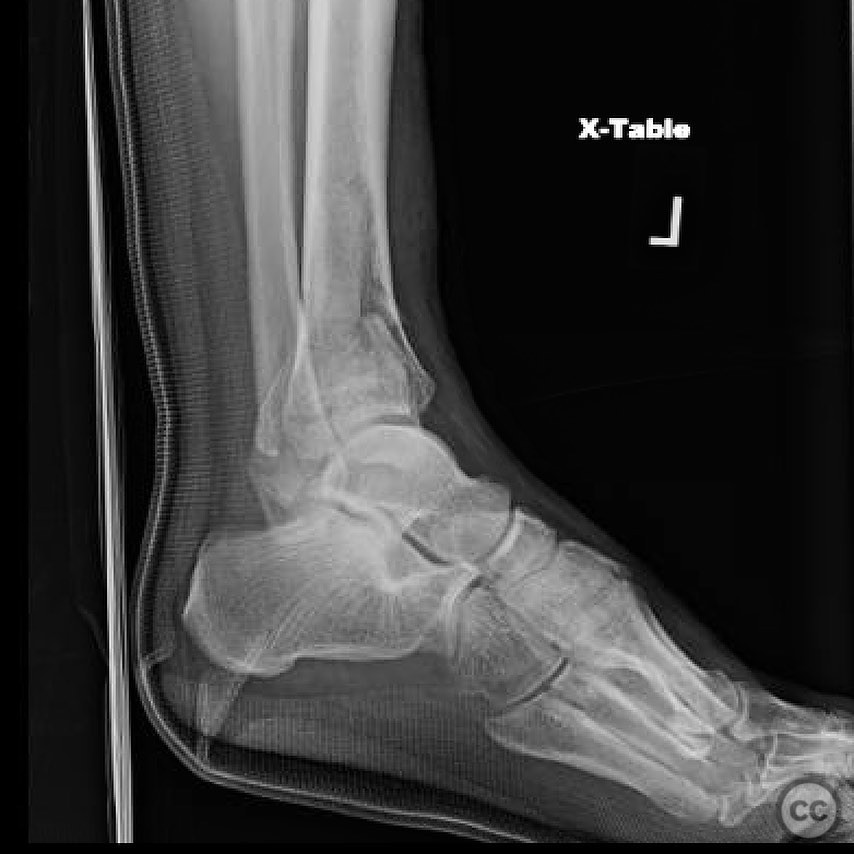
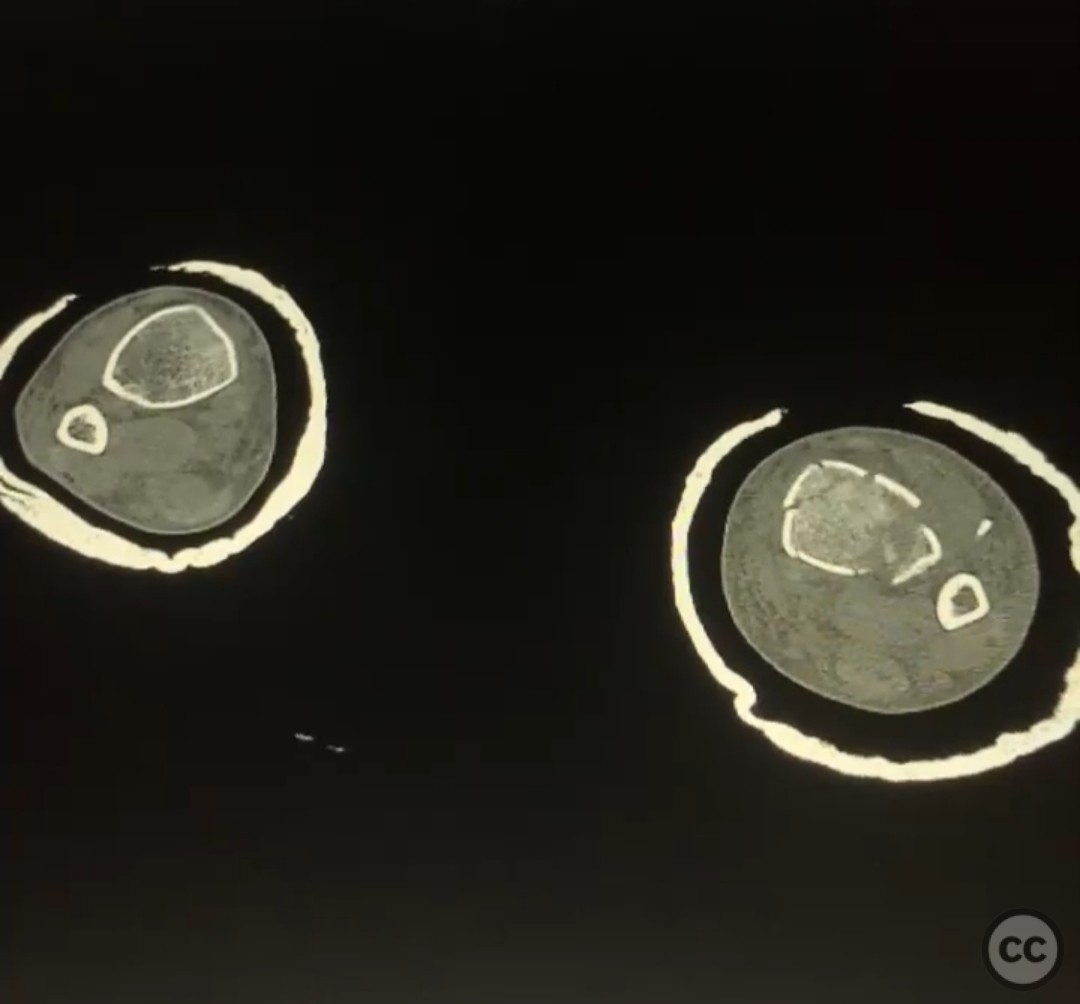
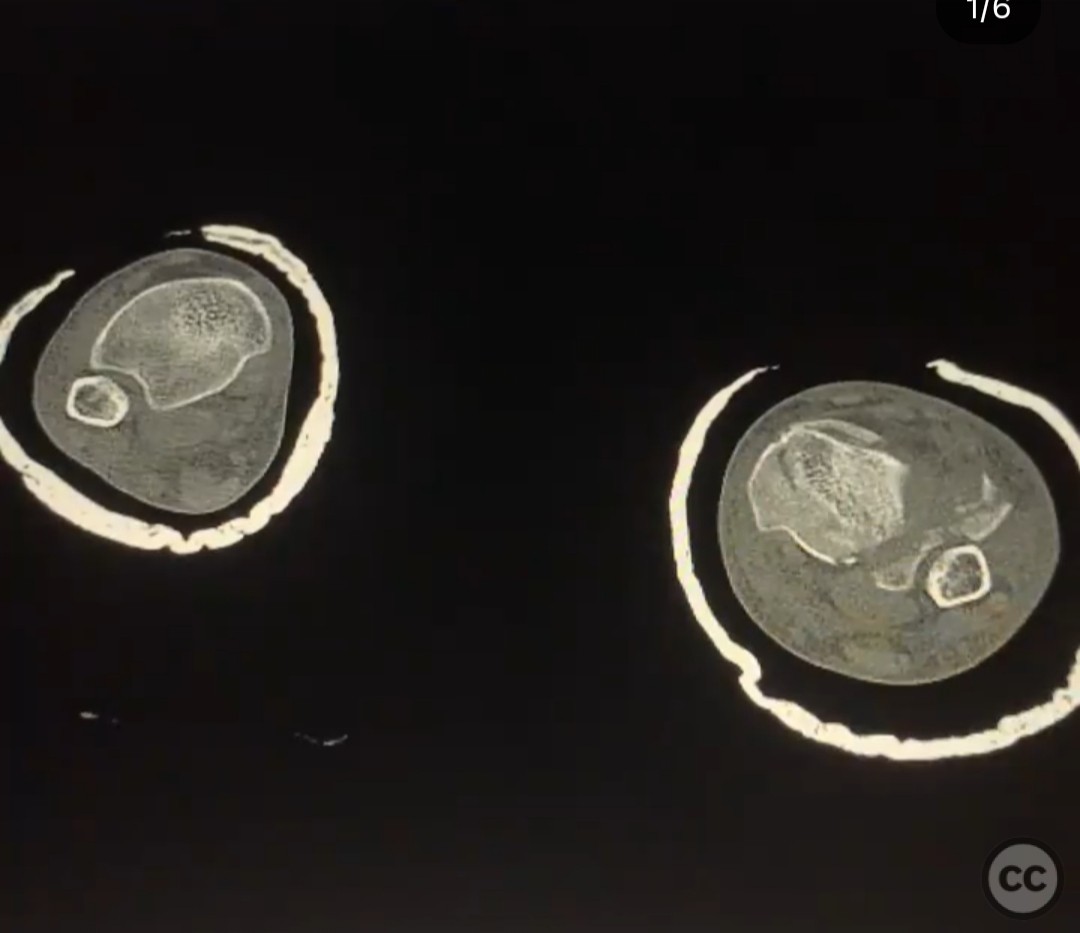
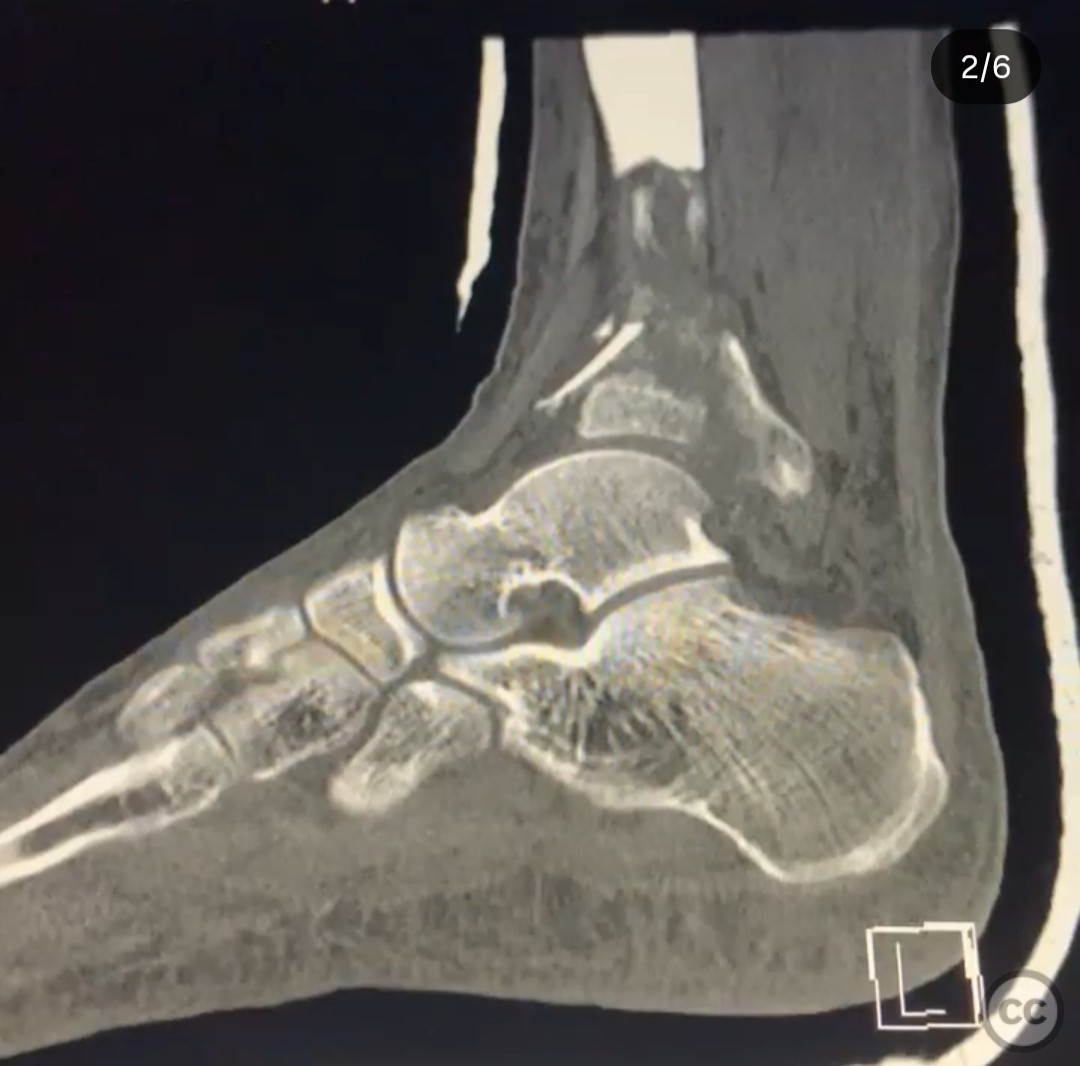
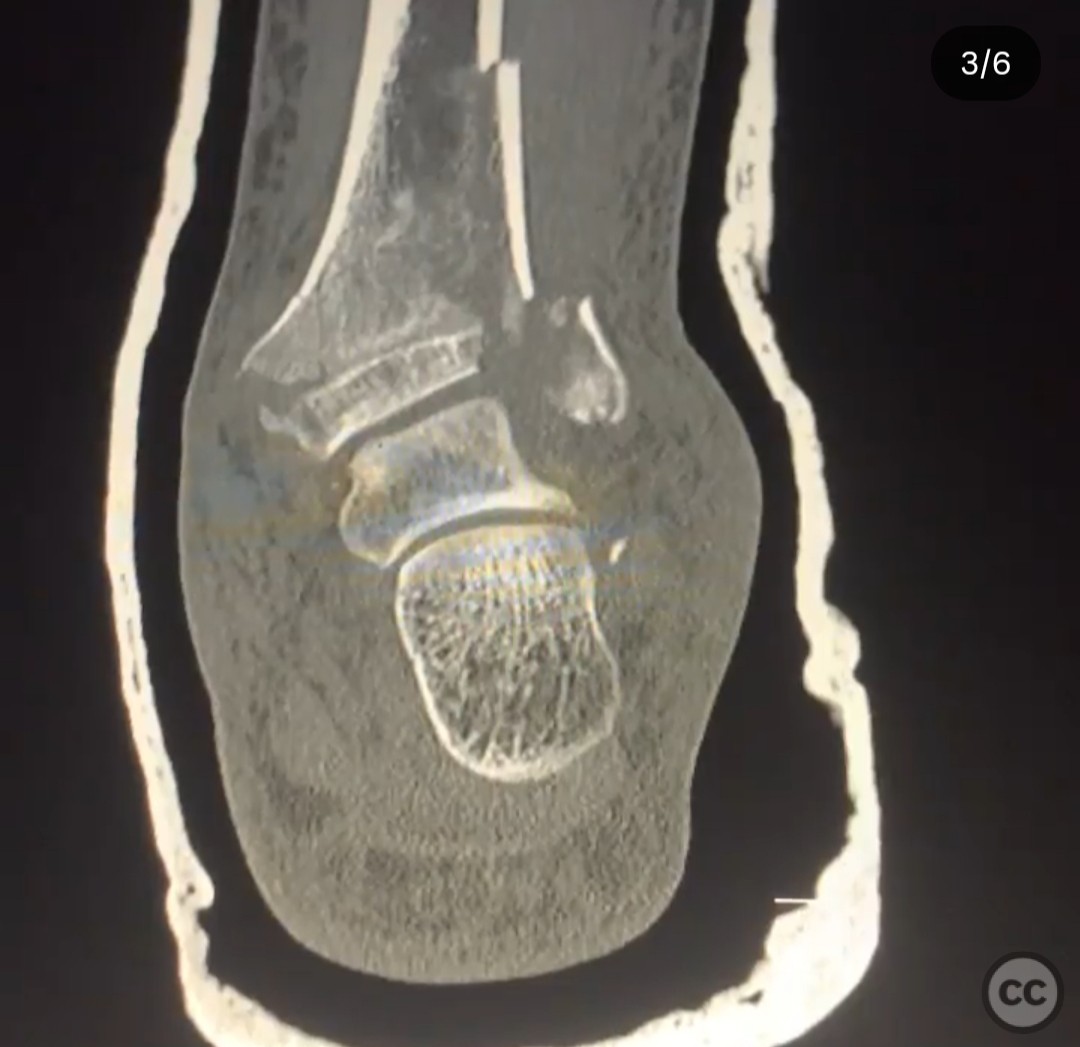
Clinical and radiological findings: A 26-year-old male presented after a fall from a height of approximately 30 feet while rock climbing. He sustained an axial load injury with the foot in a supinated position. Initial radiographs suggested a pilon fracture with valgus impaction, overlap of the talus and fibula on AP/mortise views, and posterior displacement of the intact fibula on lateral view. CT confirmed a C-type pilon fracture with the fibula locked behind the talus (Bosworth variant), associated with small Volkmann and Chaput fragments, syndesmotic disruption, and suspected peroneal tendon dislocation.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: Pre-operatively, the plan begins with obtaining a CT scan to confirm the suspected Bosworth-type injury, where the intact fibula is entrapped behind the talus. This imaging is crucial to understand the fracture complexity and guide the reduction strategy. The next step involves applying an ankle-spanning external fixator to restore tibial length and alignment while allowing the soft tissues to recover. Given the fibula is locked behind the talus, reduction is expected to be challenging—multi-vector distraction will likely be necessary to disengage the fibula. Intra-operatively, attention must be paid to the syndesmosis. If the Chaput or Volkmann fragments are too small to securely fix, syndesmotic stabilization using screws or a suture-button construct should be planned. Additionally, a small bony fleck from the fibula on imaging raises suspicion for peroneal tendon dislocation. After the fracture has been fixed, a dynamic examination should be performed to assess tendon stability. If dislocation persists, surgical stabilization of the tendons may be needed. Finally, implant planning should aim to avoid overlap with external fixator pin sites, as this may increase infection risk—even if data on this issue is limited.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient is positioned supine on a radiolucent table.
Anatomical surgical approach: External fixation is applied first to restore length and alignment, followed by open reduction and internal fixation through appropriate incisions, with special attention to avoiding interference between plates and external fixator pins.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the unique challenge posed by the Bosworth variant pilon fracture, noting the difficulty in reducing the intact fibula entrapped posterior to the talus. Initial application of an ankle-spanning external fixator provided provisional stability and allowed for gradual multi-vector distraction essential to disengage the fibula. Definitive fixation required a carefully sequenced approach to avoid further soft tissue injury and to address syndesmotic instability due to small Volkmann and Chaput fragments that were not amenable to direct fixation. The fibula was released from its locked position through a posterolateral window, followed by open reduction of the tibial plafond via an anterolateral approach. Locking plates were contoured and applied to restore articular congruity and provide stable fixation. After fracture fixation, a dynamic assessment of the peroneal tendons was performed, revealing instability that necessitated tendon stabilization procedures to prevent recurrent dislocation. Special attention was given to the placement of hardware to avoid overlap with external fixator pin sites, minimizing the risk of pin tract infection and facilitating postoperative care.
Postoperative protocol: Post-op care involves non-weight-bearing for 8–10 weeks, with early ankle motion exercises as tolerated. Monitor wound healing and pin sites. Gradual weight-bearing starts after evidence of healing. Follow-up includes assessing peroneal tendon stability and fracture union.
Follow up: Not specified.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_3.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_4.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_5.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about the(.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_1.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_2.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_7.jpg)
 don_t miss a syndesmotic injury or syndesmosis equivalent in pilon fractures_ We tend to think about th_6.jpg)
Article viewed 201 times
19 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). High-Energy Pilon Fracture with Intact Fibula Entrapment Behind Talus: A Bosworth-Type Injury. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 8646188 Published Online Jul 19 2025.