Pathological Femoral Fracture in an 11-Year-Old with Non-Ossifying Fibroma
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
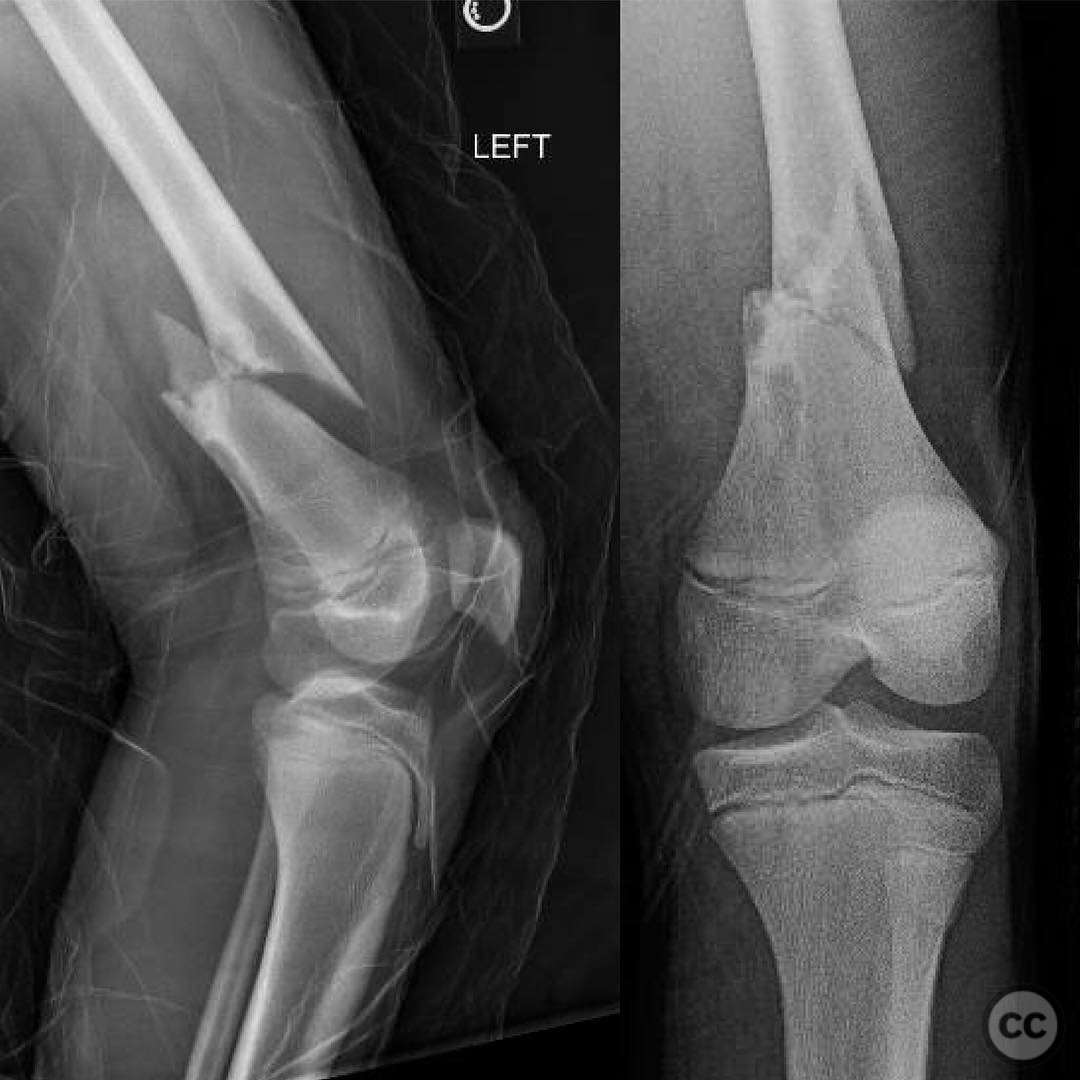
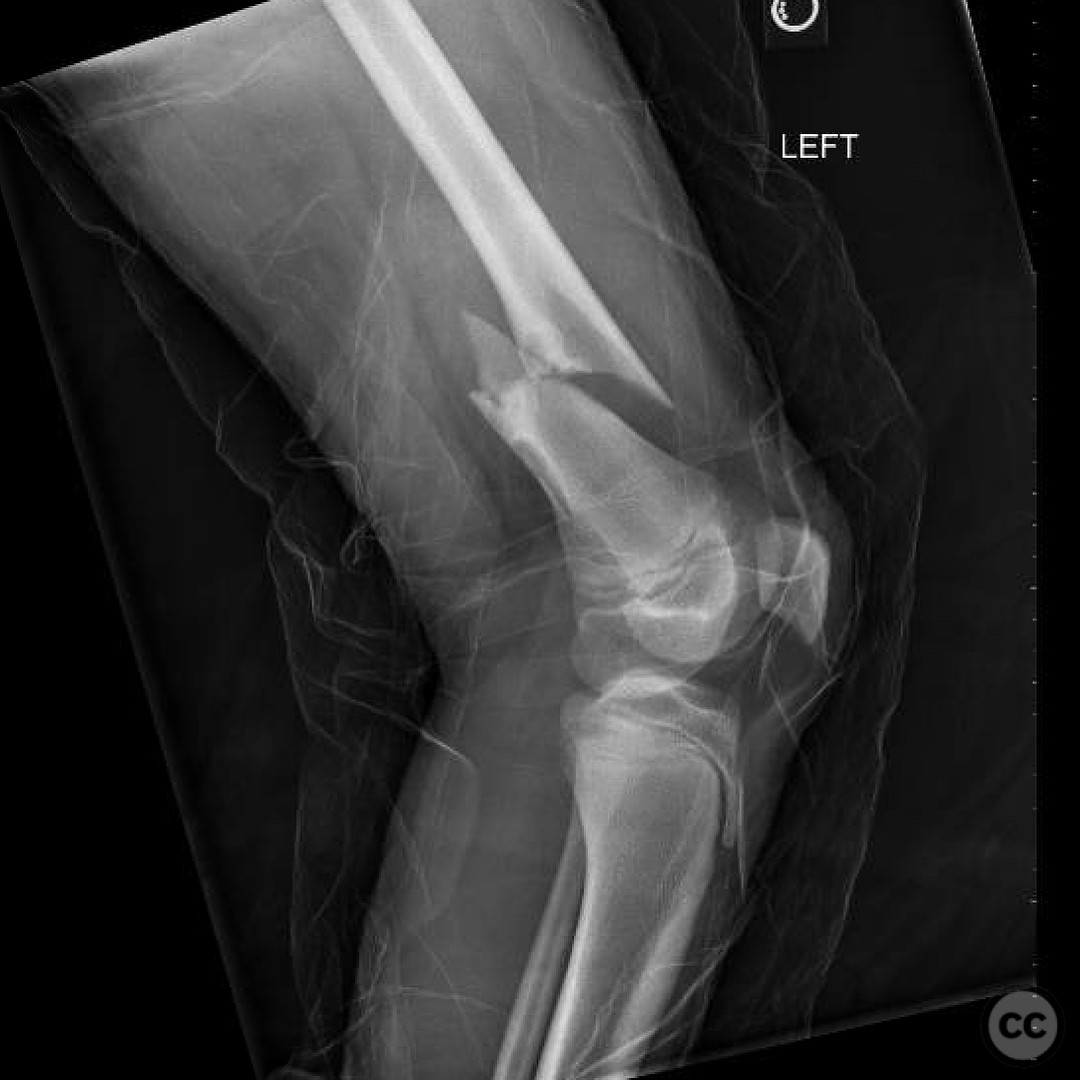
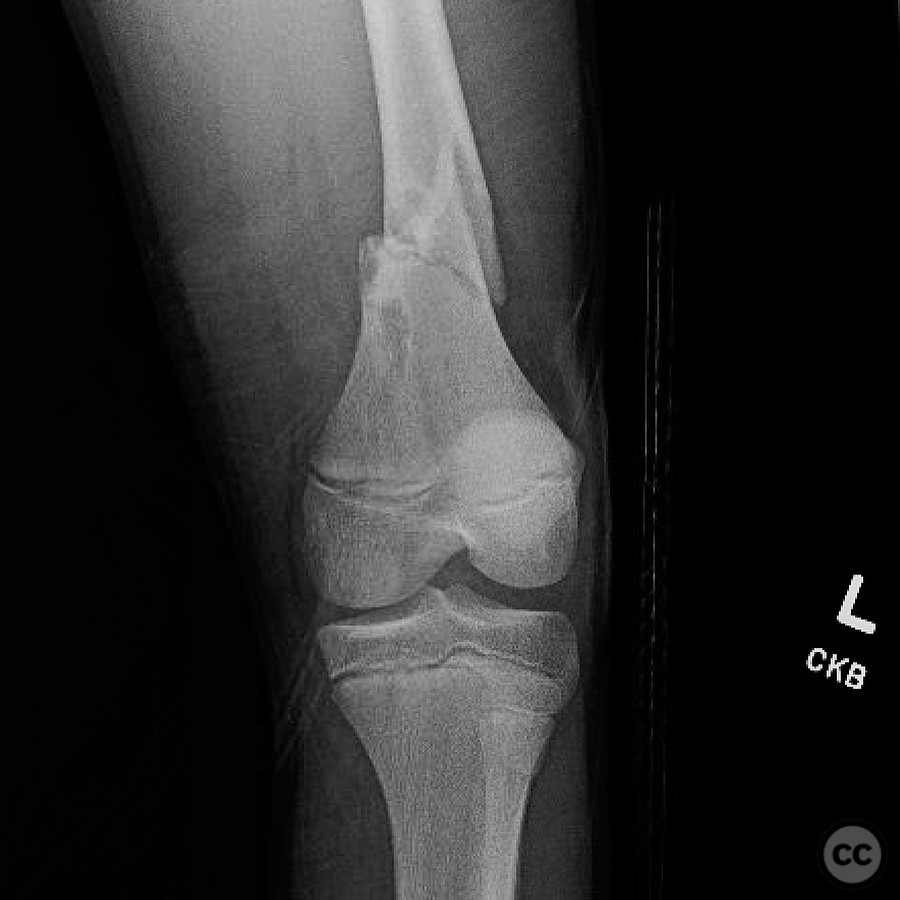
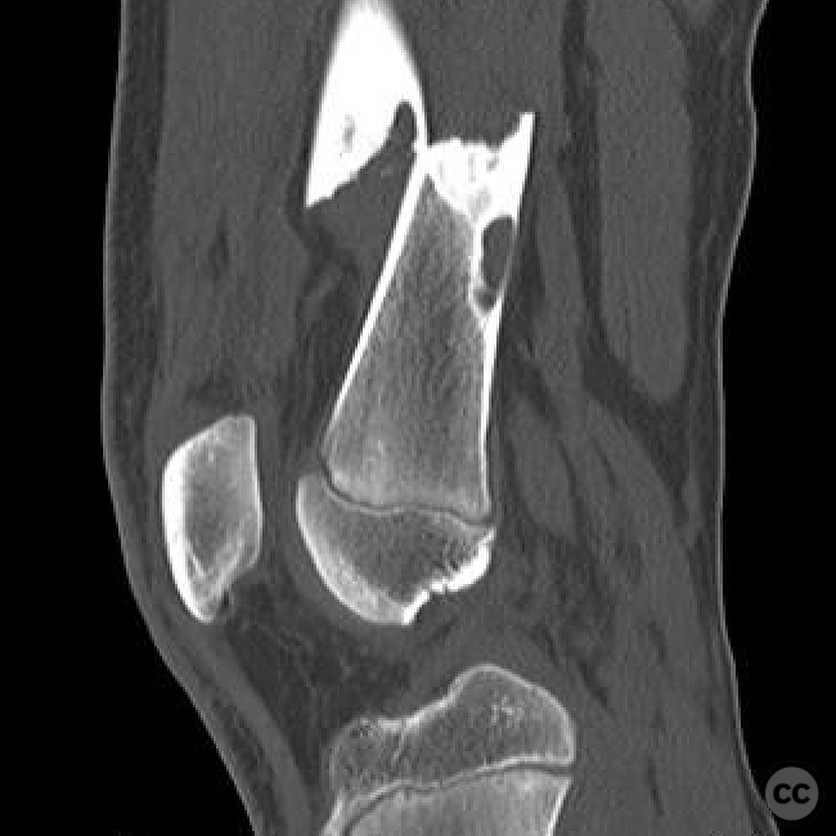
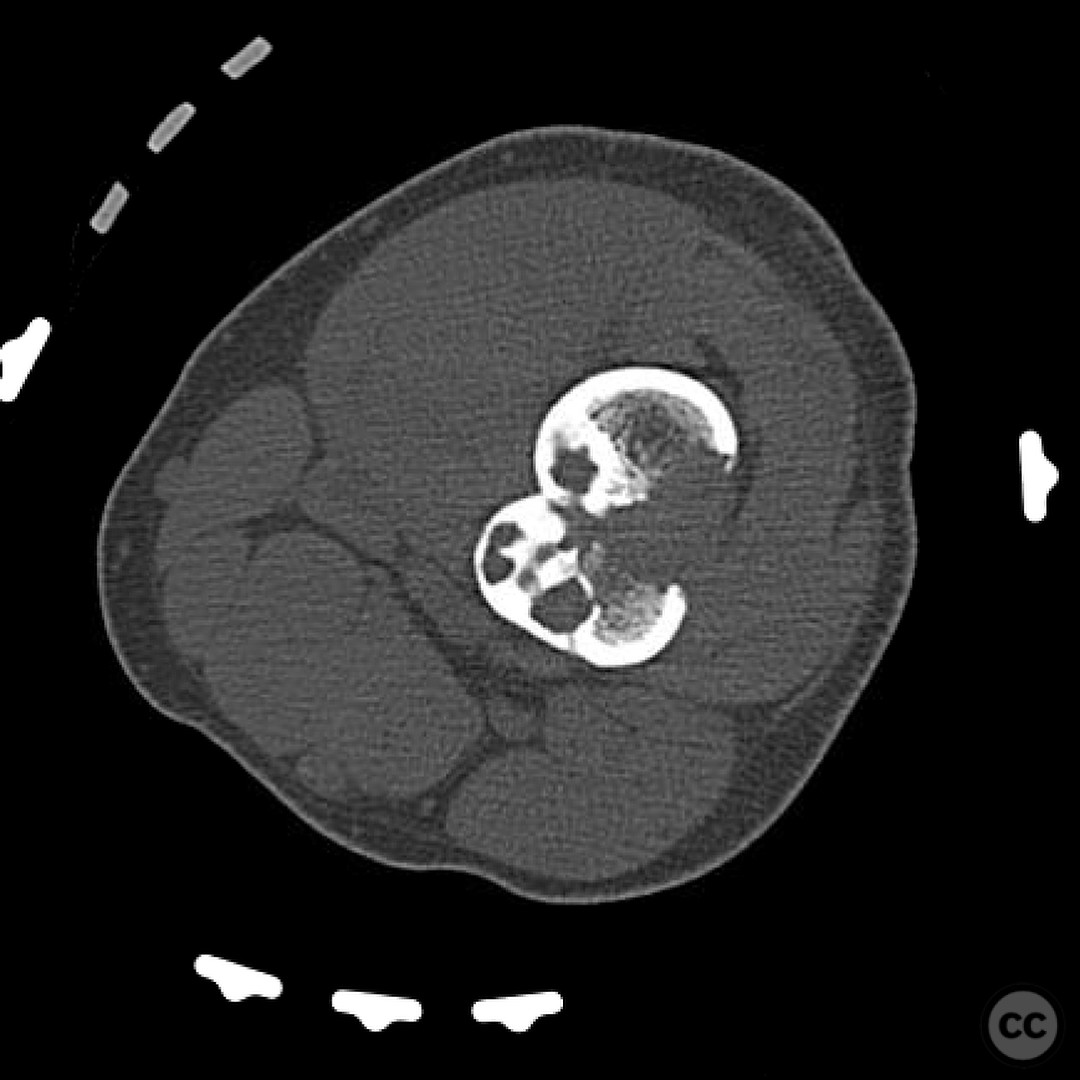
Clinical and radiological findings: An 11-year-old patient presented with a pathological fracture of the femur following a minor trauma involving a goat. Initial radiographs revealed a transverse fracture through a lytic lesion in the distal femoral metaphysis, consistent with a non-ossifying fibroma (NOF). The lesion was well-circumscribed with sclerotic margins, suggesting a benign nature. No significant soft tissue swelling or neurovascular compromise was noted.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved an open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of the femoral fracture. Given the presence of the NOF, an intraoperative biopsy was planned to rule out malignancy prior to definitive fixation. A lateral approach to the distal femur was chosen to allow for direct visualization and access to the lesion and fracture site.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with a radiolucent table to facilitate intraoperative imaging. A bump was placed under the ipsilateral hip to achieve slight external rotation of the limb.
Anatomical surgical approach: A lateral approach to the distal femur was performed. An incision was made along the lateral aspect of the thigh, followed by dissection through the subcutaneous tissue and fascia lata. The vastus lateralis muscle was elevated subperiosteally to expose the distal femur and the pathological lesion.
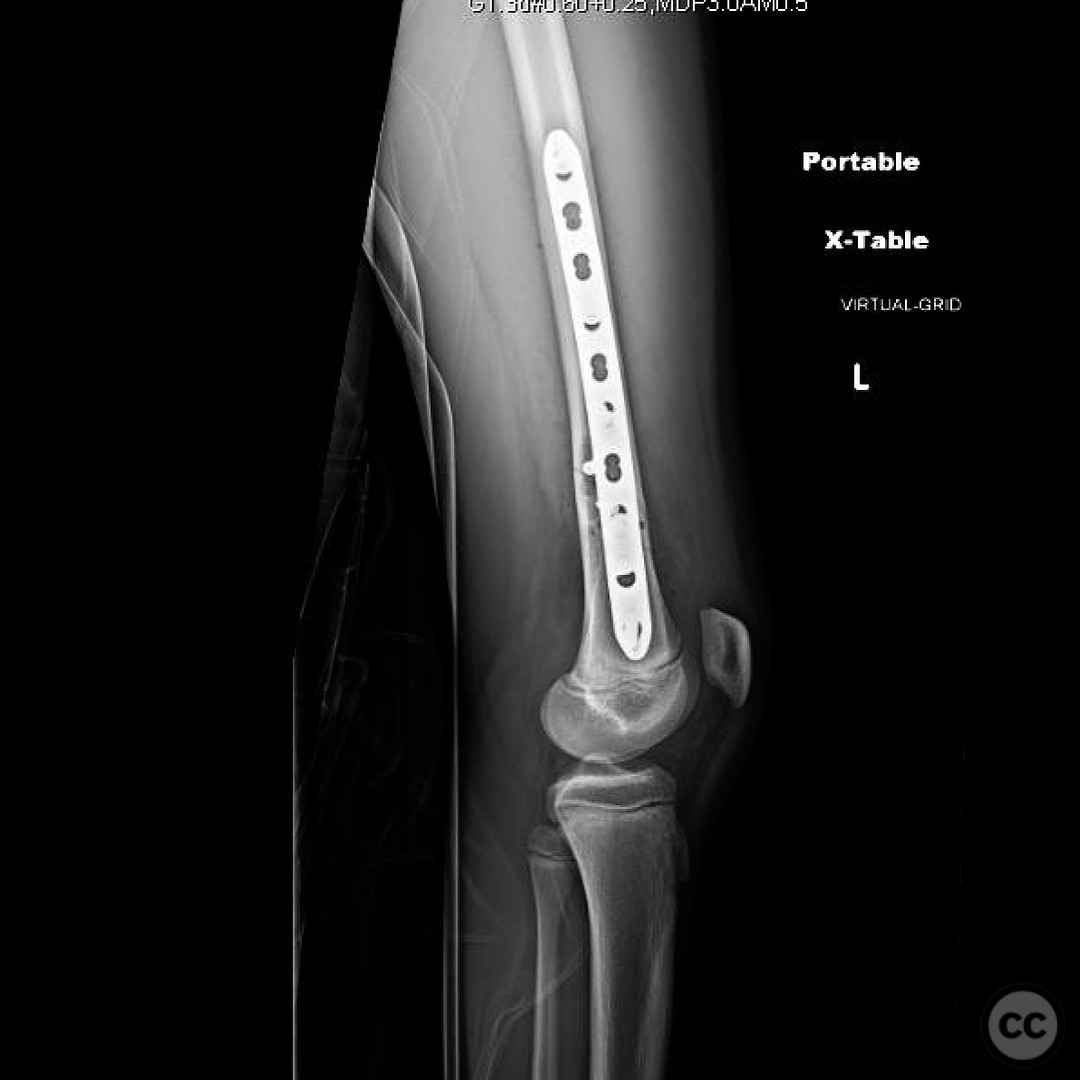
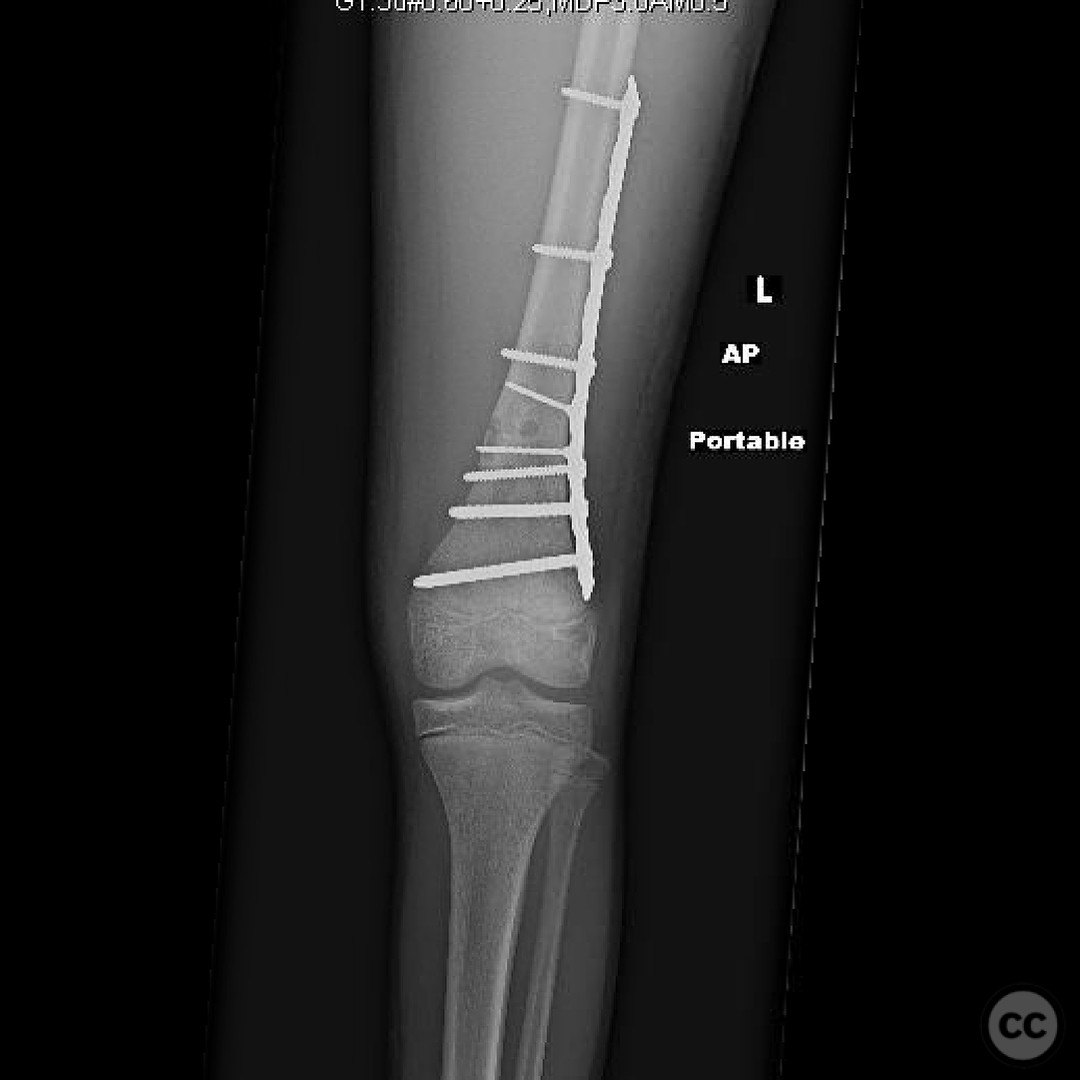
Operative remarks:Intraoperative frozen section pathology confirmed the lesion as a non-ossifying fibroma with no evidence of malignancy. ORIF was performed using a submuscular plate to avoid potential malreduction associated with intramedullary nailing due to the intracortical lesion. Care was taken to ensure that the plate did not extend within 1 cm of the physis to minimize the risk of growth disturbance and valgus deformity.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was placed in a knee immobilizer and instructed on non-weight bearing for 6 weeks. Progressive weight bearing was initiated at 6 weeks, with full weight bearing anticipated by 12 weeks post-surgery. Physical therapy focused on range of motion and strengthening exercises.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Submuscular locking compression plate (LCP) system.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 166 times
25 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Pathological Femoral Fracture in an 11-Year-Old with Non-Ossifying Fibroma. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 8643609 Published Online Jul 25 2025.