Open Tibia Fracture with Septic Nonunion and PTFJ Dislocation
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
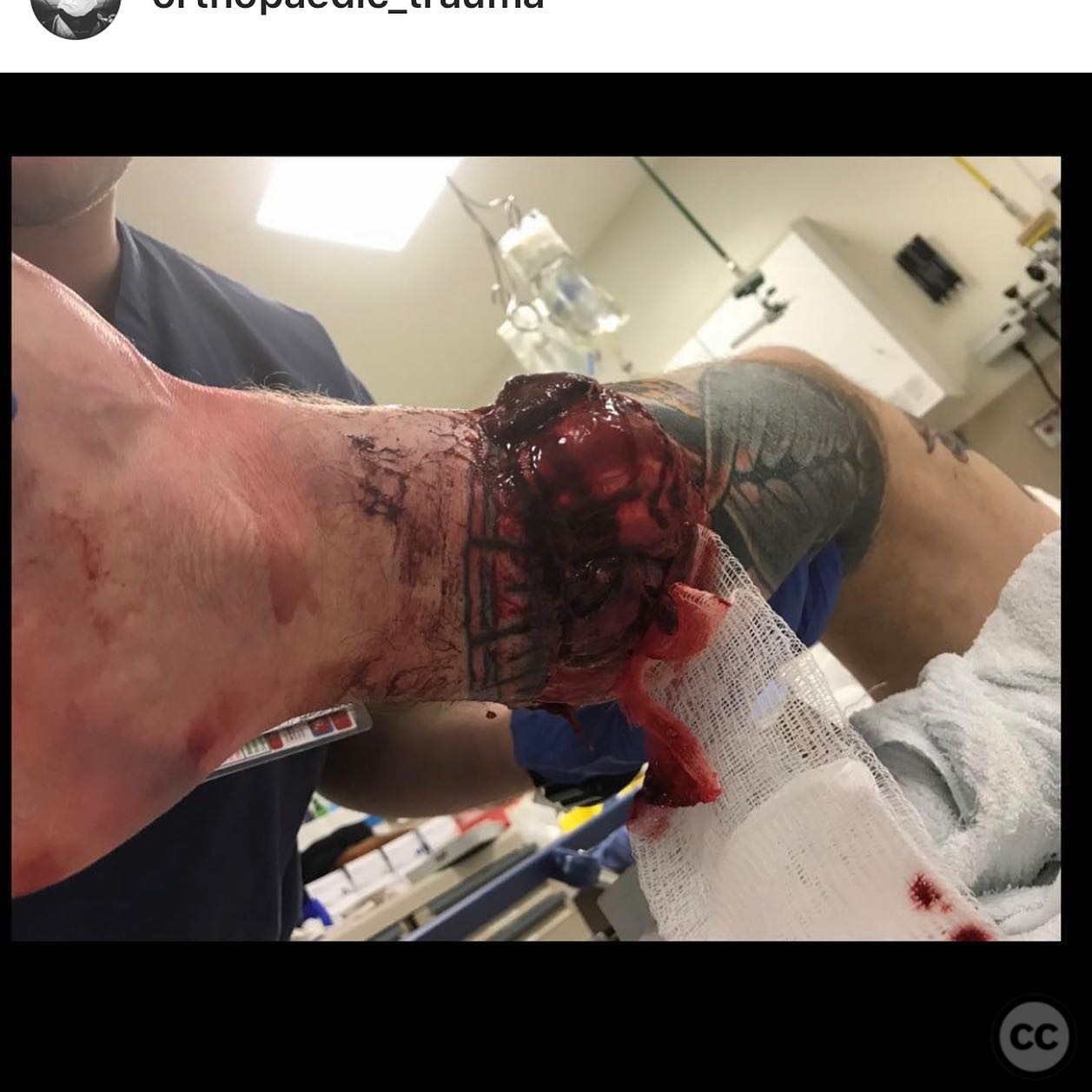
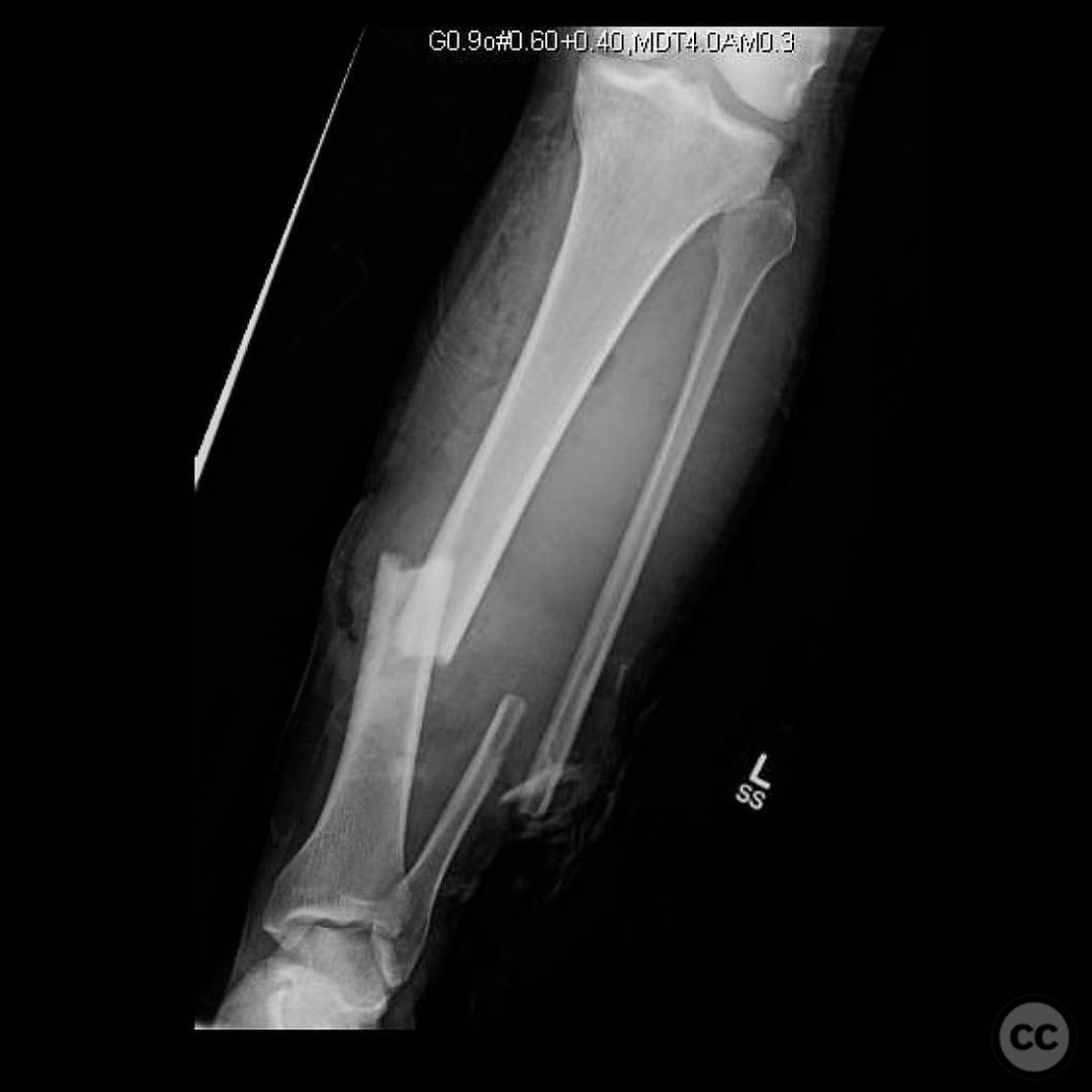
Clinical and radiological findings: The patient presented with a severe Gustilo-Anderson type IIIB open tibial fracture, accompanied by proximal tibiofibular joint (PTFJ) dislocation and interosseous membrane disruption. Initial management included intramedullary nailing (IMN), soft tissue flap coverage, and split-thickness skin grafting (STSG). The patient subsequently developed a septic nonunion.
Preoperative Plan
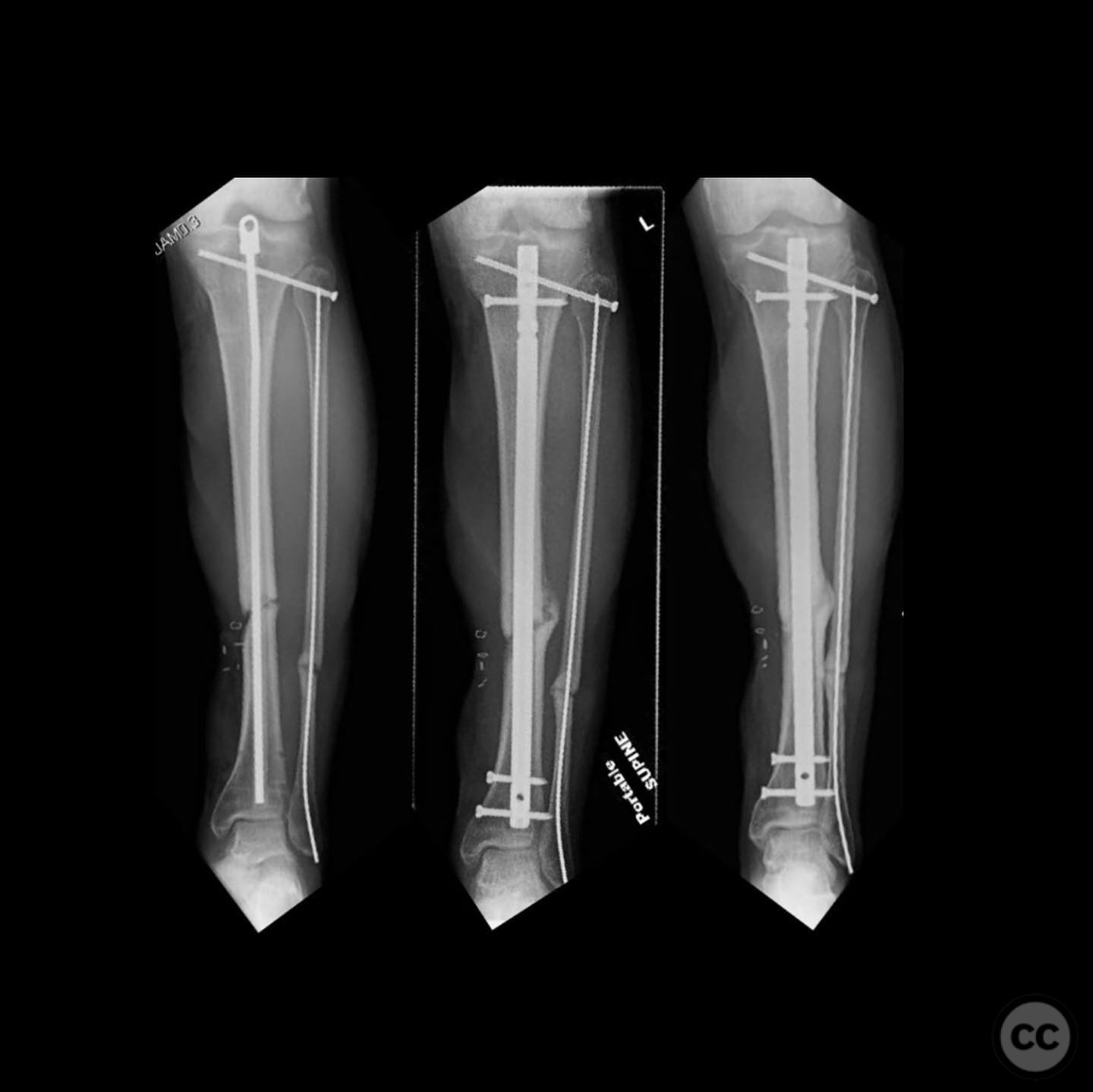
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved antibiotic-coated intramedullary nailing to address the infection, followed by an exchange nailing procedure to promote union.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine positioning was utilized for both the initial and subsequent surgical interventions.
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal incision was made over the anteromedial aspect of the tibia to access the site of nonunion. The previous IMN was removed, and the canal was reamed to accommodate an antibiotic-coated nail. In the exchange nailing procedure, the canal was re-reamed, and a larger diameter nail was inserted to achieve stability.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted the importance of addressing both the infection and mechanical stability to achieve union. The use of antibiotic nailing was crucial in controlling the infection, allowing for successful exchange nailing and eventual healing.
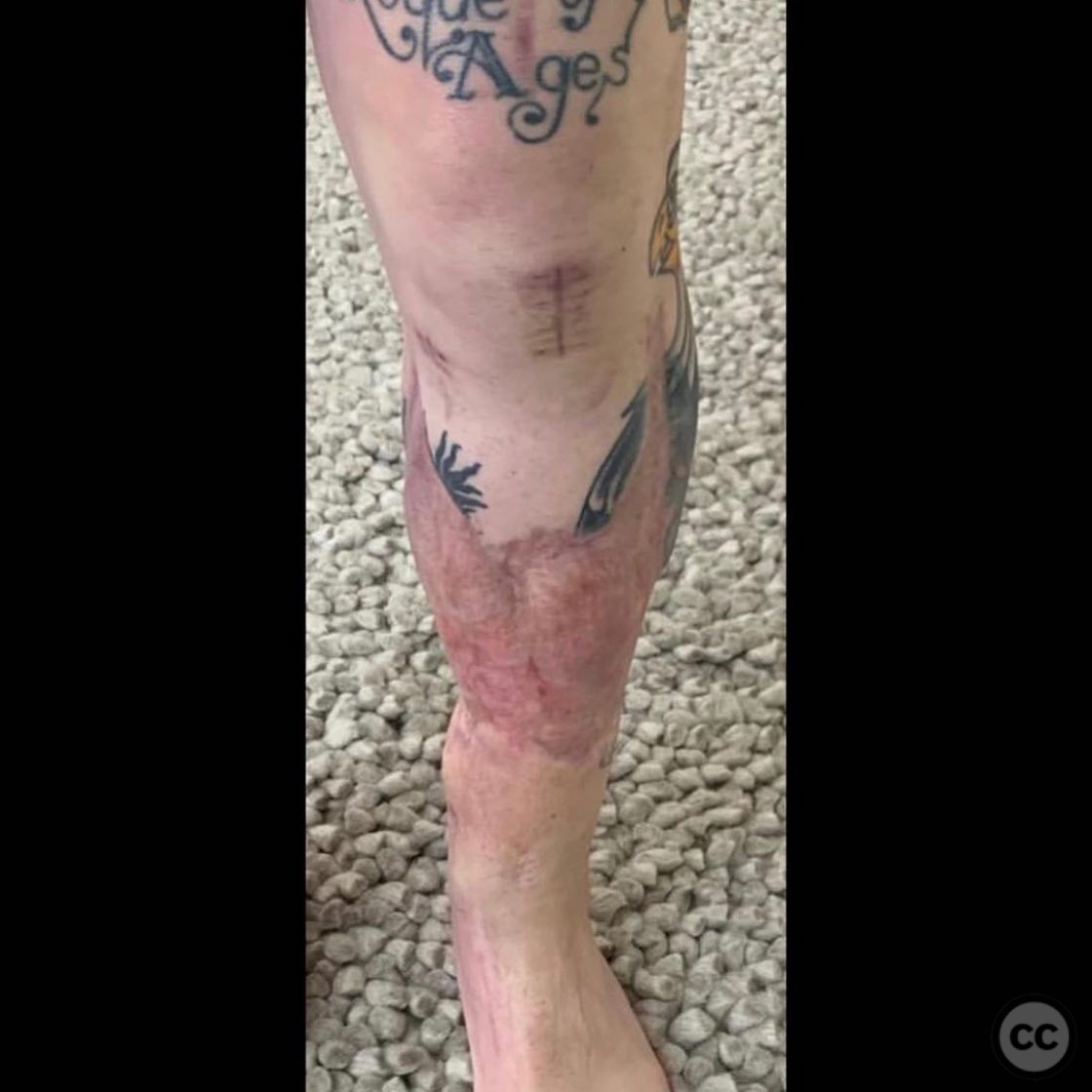
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included protected weight-bearing with crutches until radiographic evidence of union was observed. Gradual progression to full weight-bearing was implemented as tolerated.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Antibiotic-coated intramedullary nail, exchange intramedullary nail.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities



Article viewed 191 times
16 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Open Tibia Fracture with Septic Nonunion and PTFJ Dislocation. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 8613628 Published Online Jul 16 2025.