Complex Pilon Fracture with Haraguchi II Pattern and Syndesmotic Injury
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
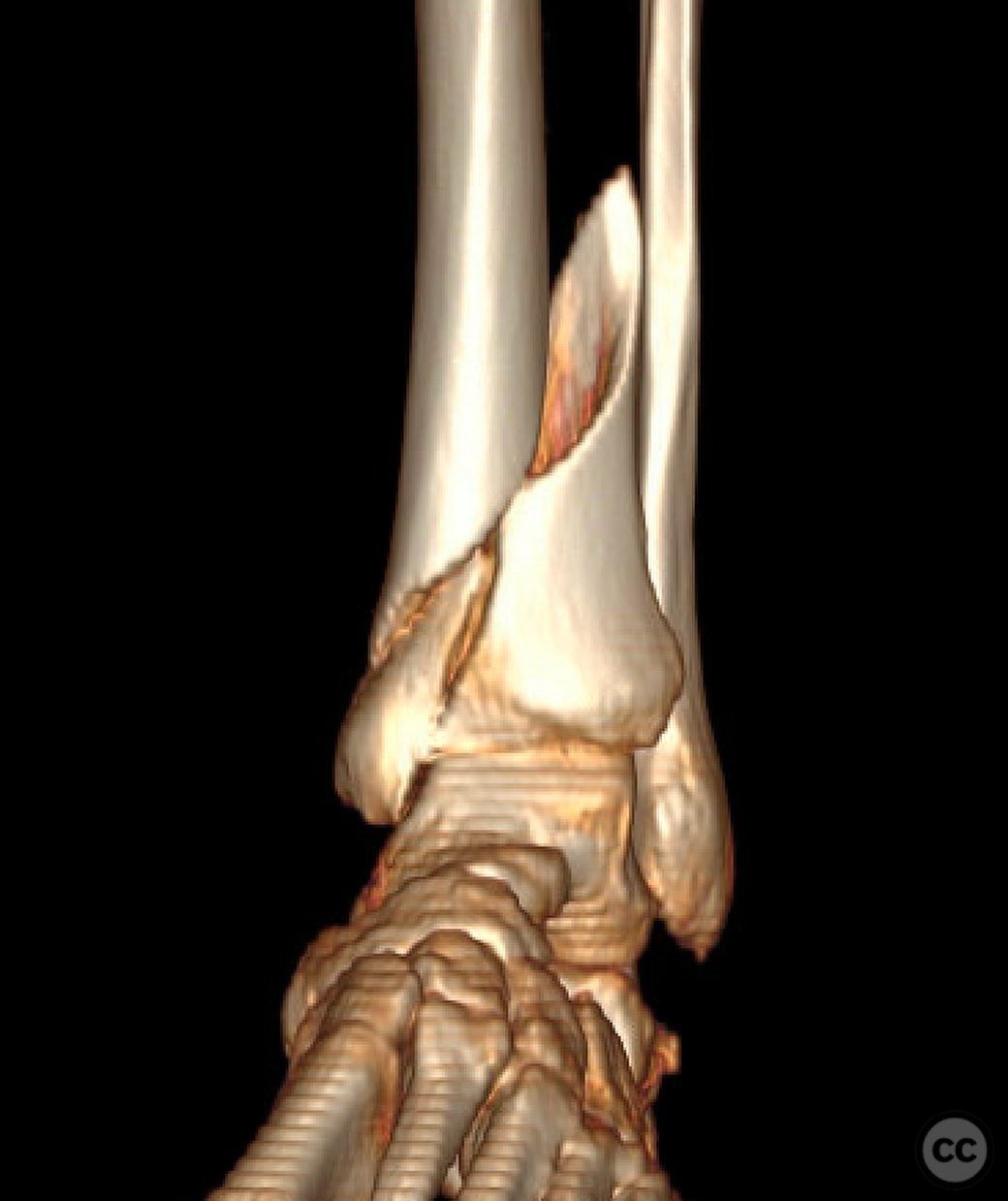
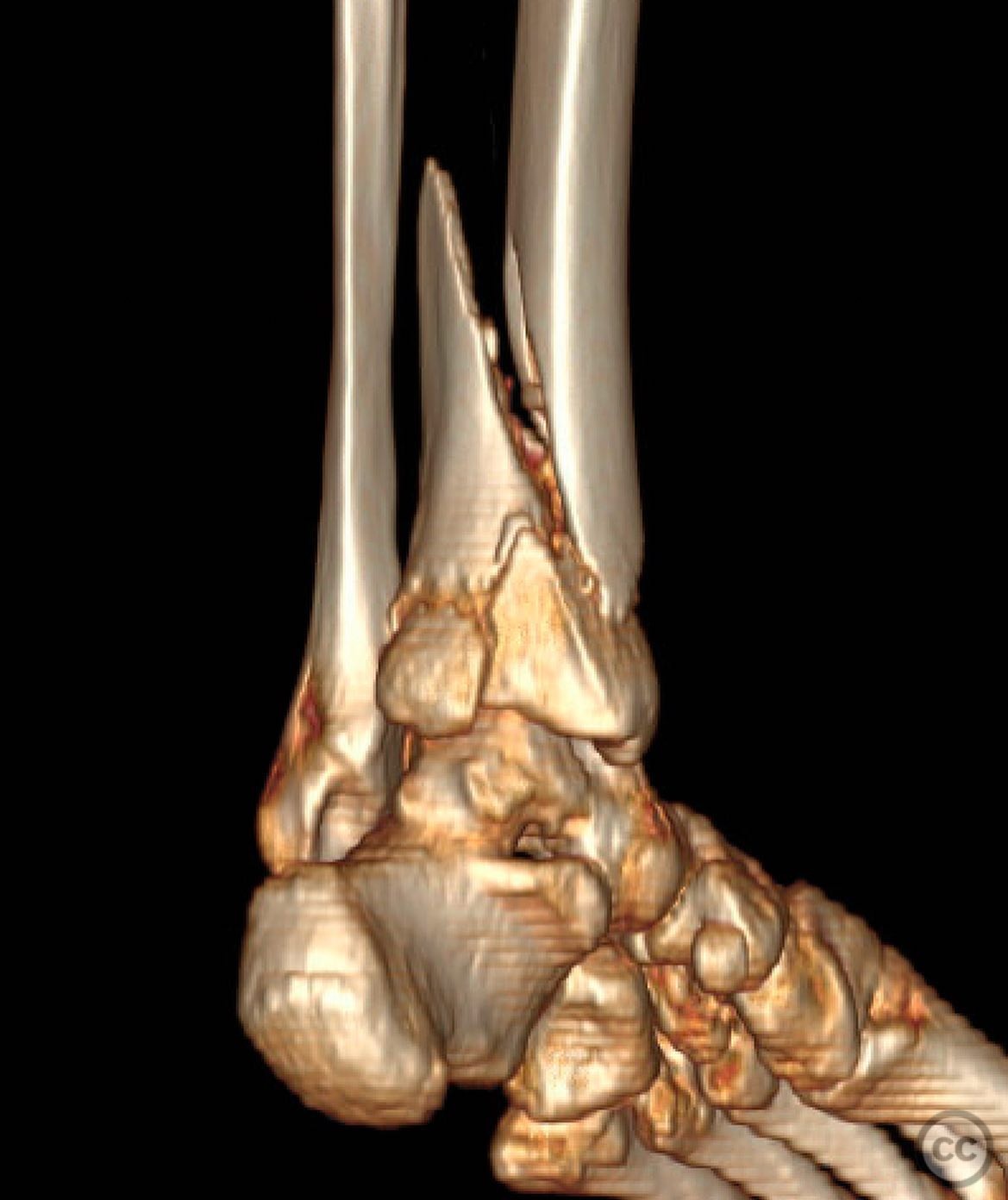
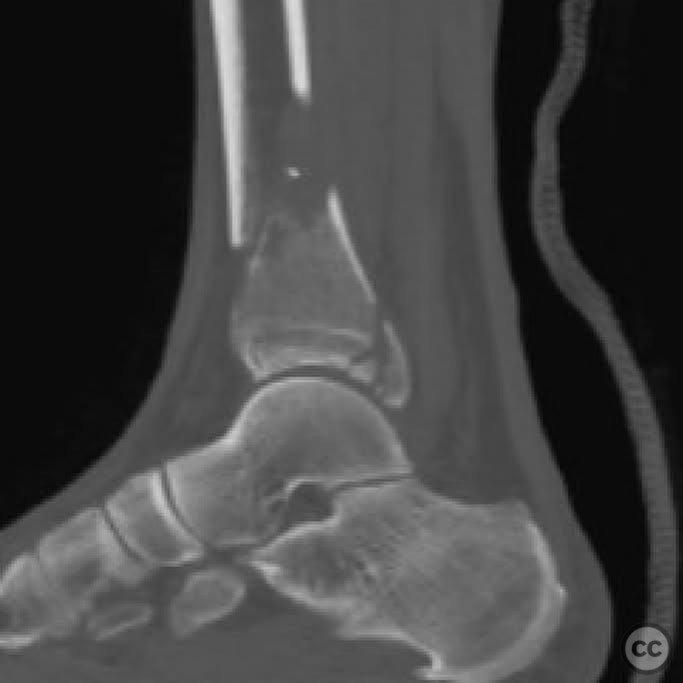
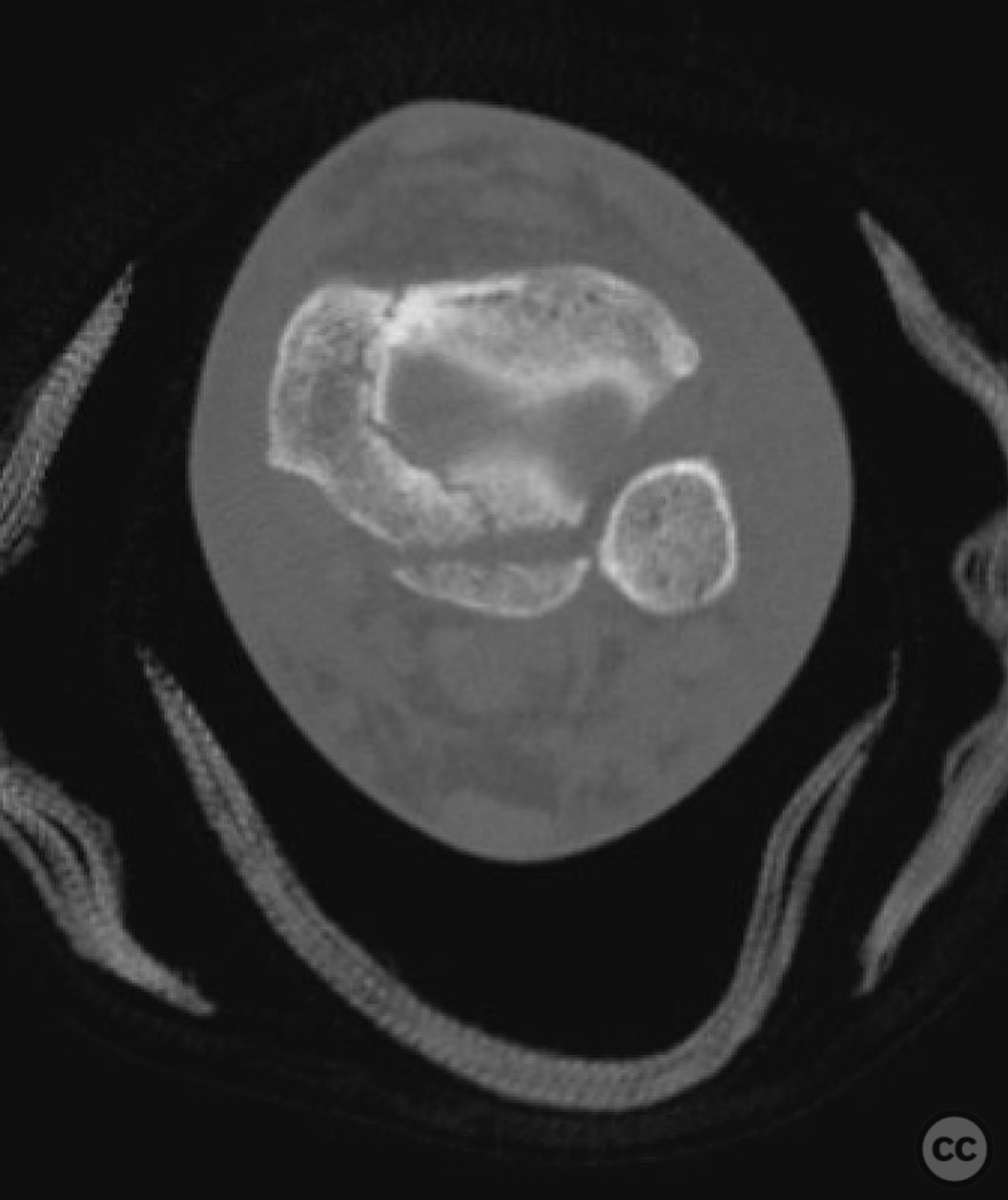
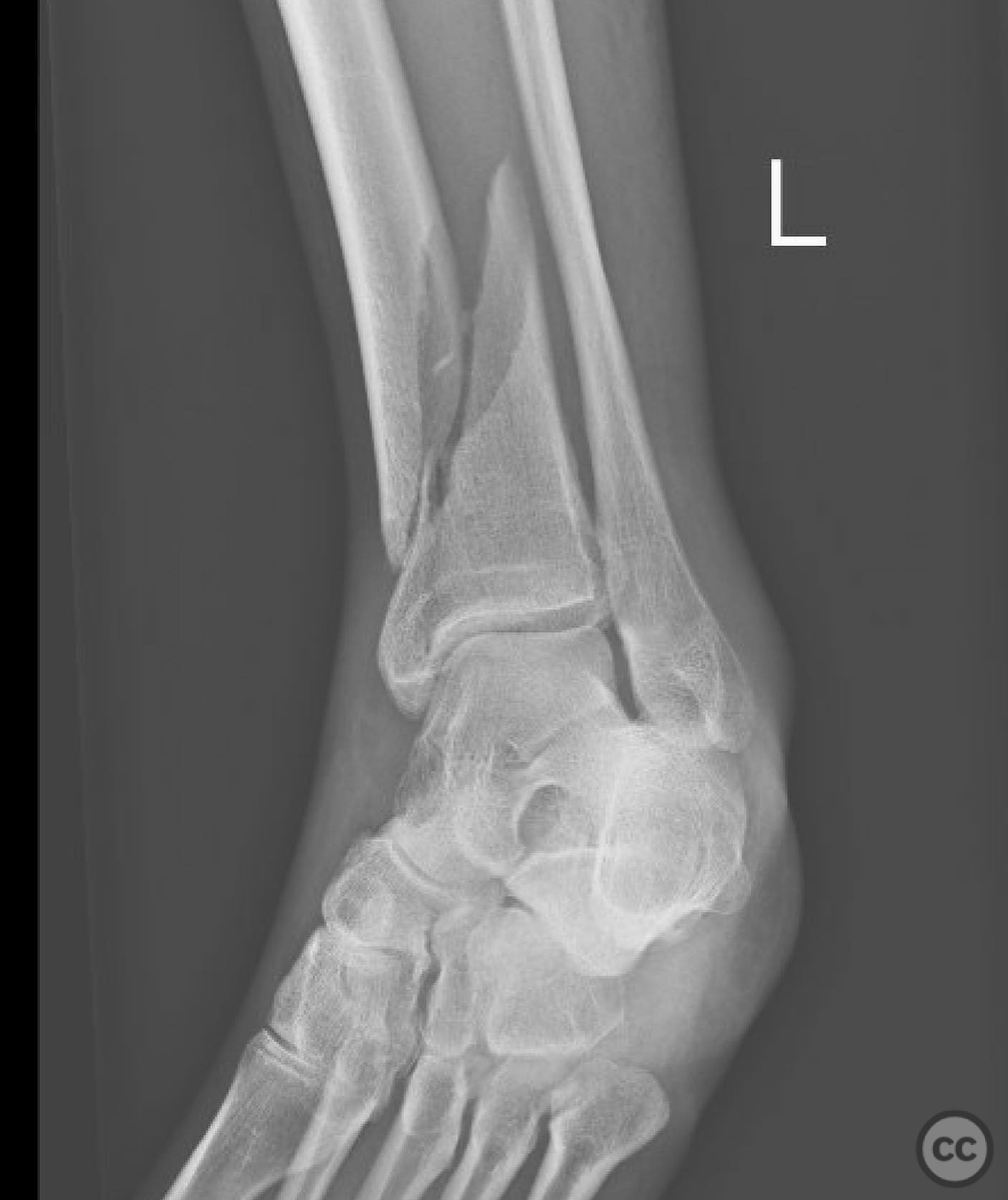
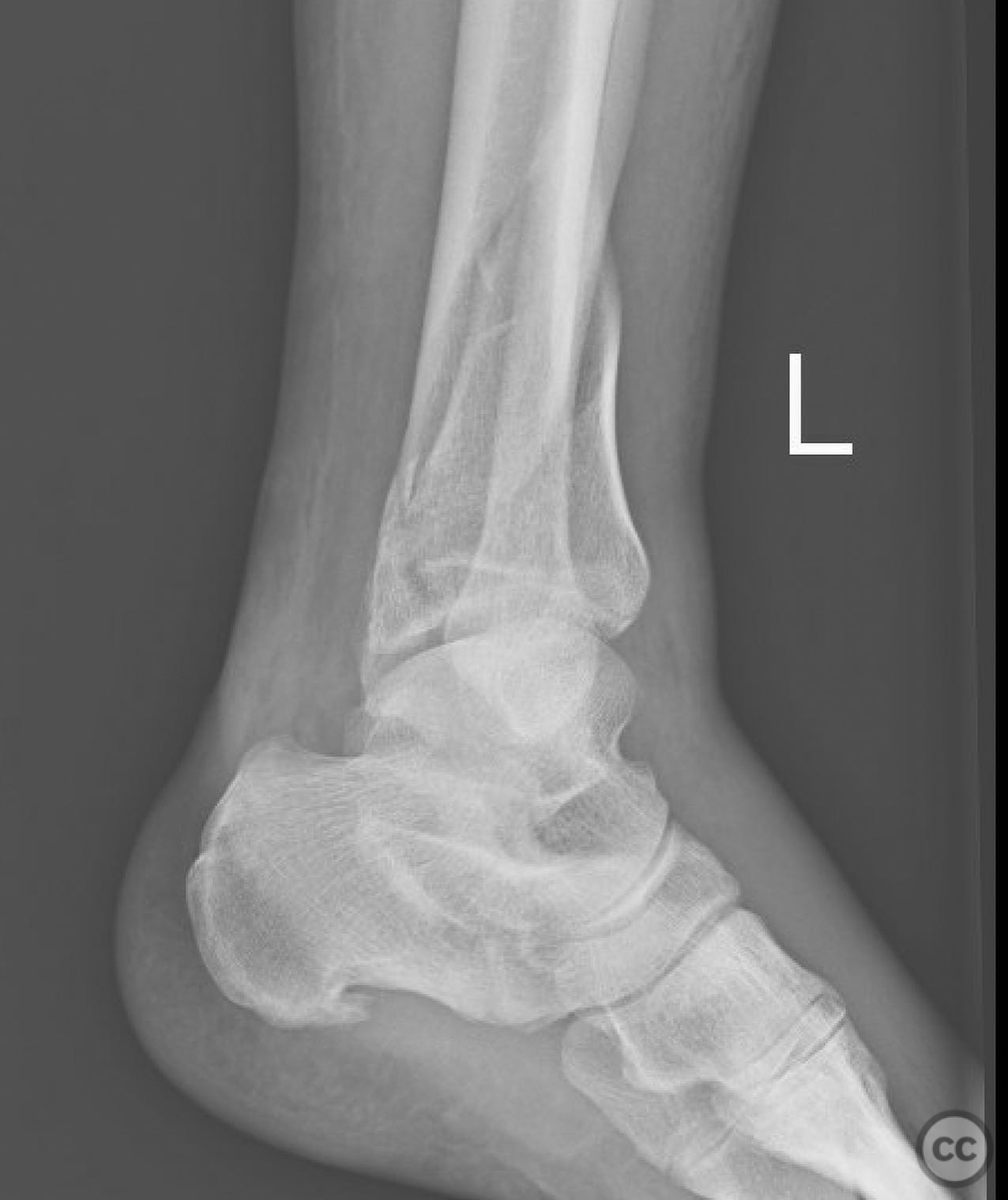
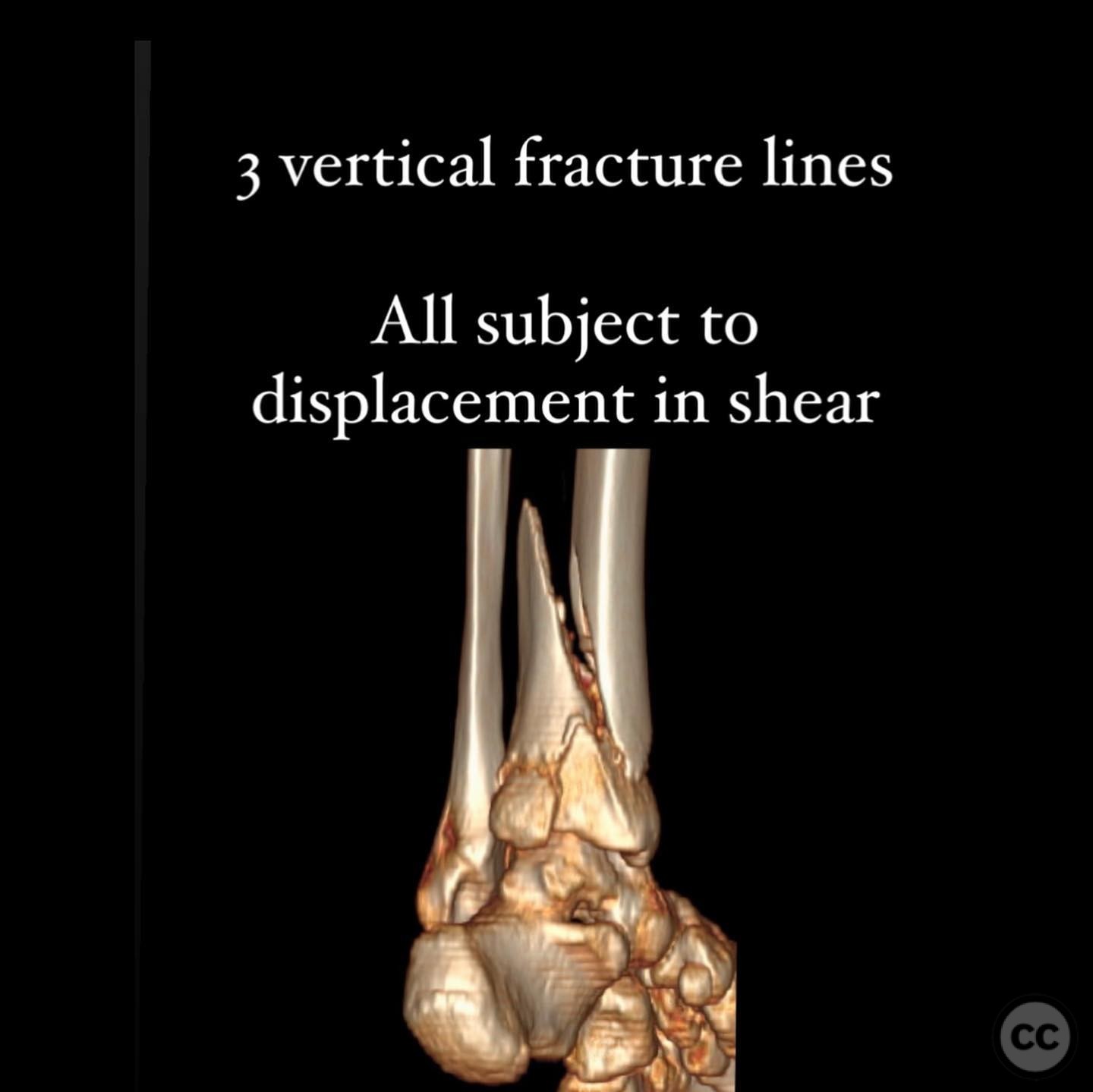
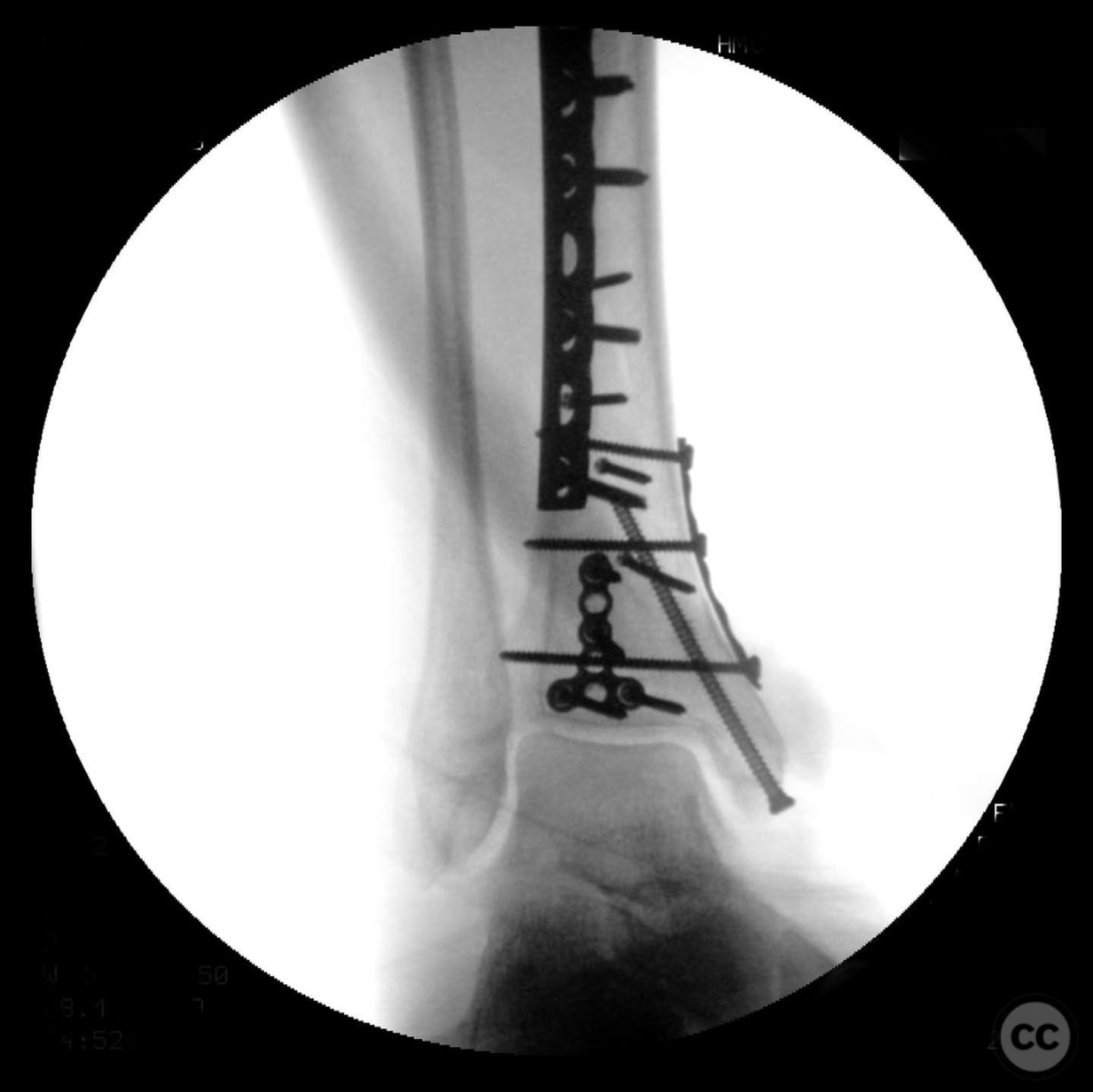
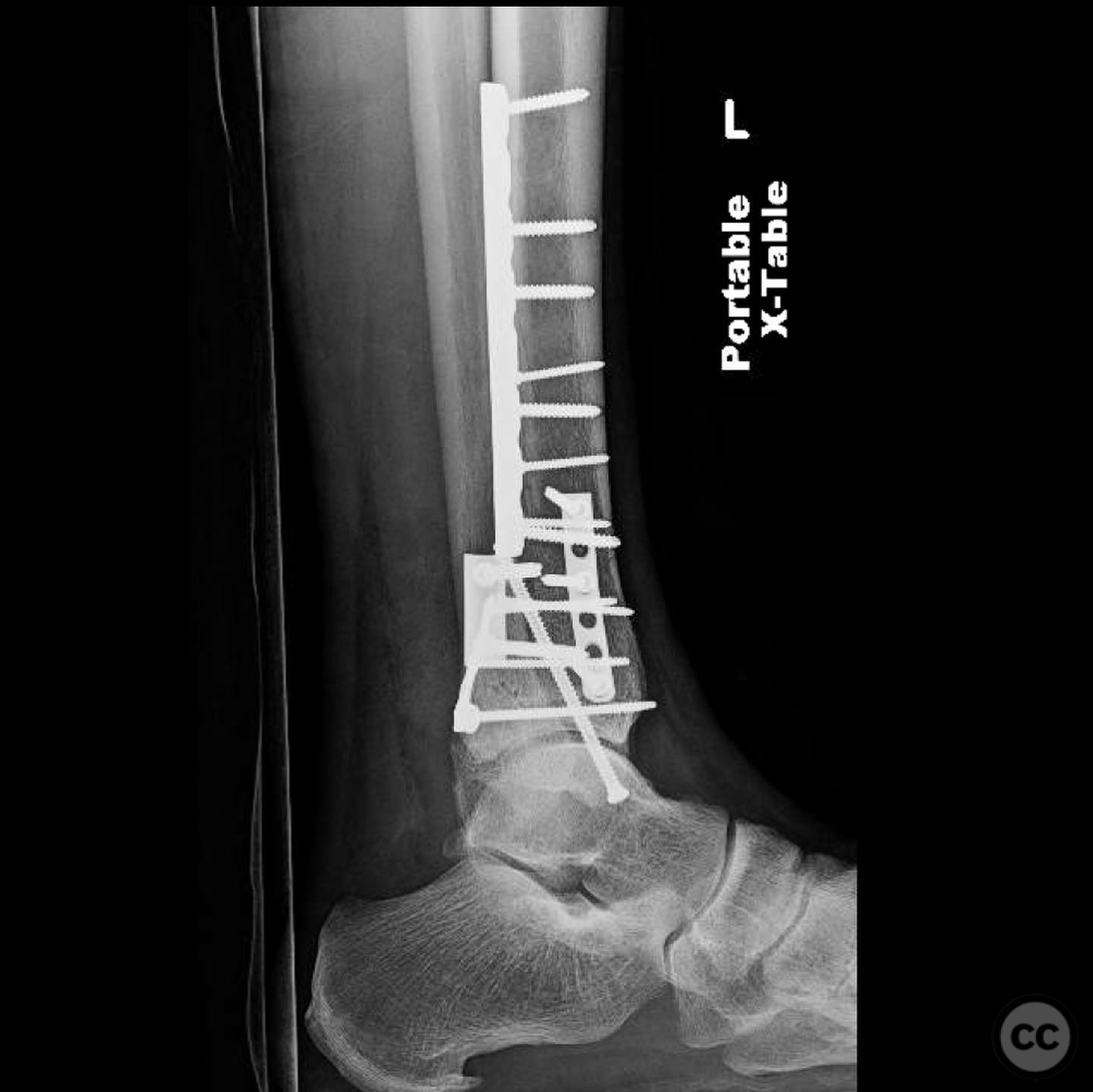
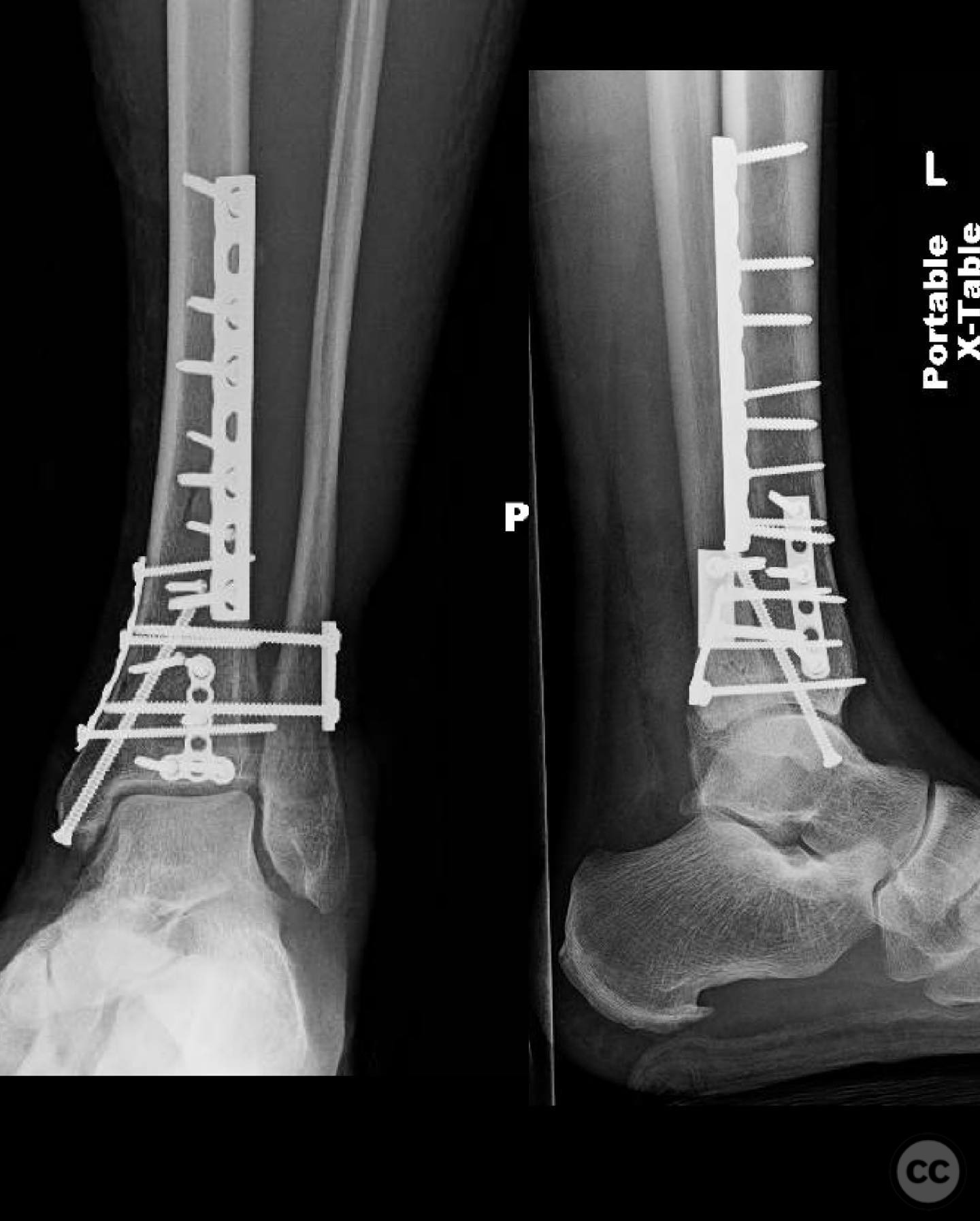
Clinical and radiological findings: A 49-year-old patient sustained a fall from a climbing wall, resulting in a closed distal tibial fracture with minimal soft tissue injury and no blistering. Radiological assessment revealed a low-energy pilon fracture with syndesmotic involvement. The fracture pattern included three distinct vertical fracture lines: two articular shear fractures and an oblique distal tibial fracture with a posterolateral apex. The articular injury morphology closely resembled a Haraguchi II pattern.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved addressing the articular surface and stabilizing the fracture using intramedullary nailing. However, upon intraoperative evaluation through a posteromedial approach, the implant strategy was revised to employ AO Basic principles for fracture fixation.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned prone on the operating table to facilitate access to the posteromedial aspect of the distal tibia.
Anatomical surgical approach: A posteromedial approach was utilized, providing direct access to the distal tibia and articular fragments. The surgical exposure allowed for direct reduction of each fracture component: the distal tibia was addressed first, followed by the medial articular fragment, and finally the Volkmann fragment.
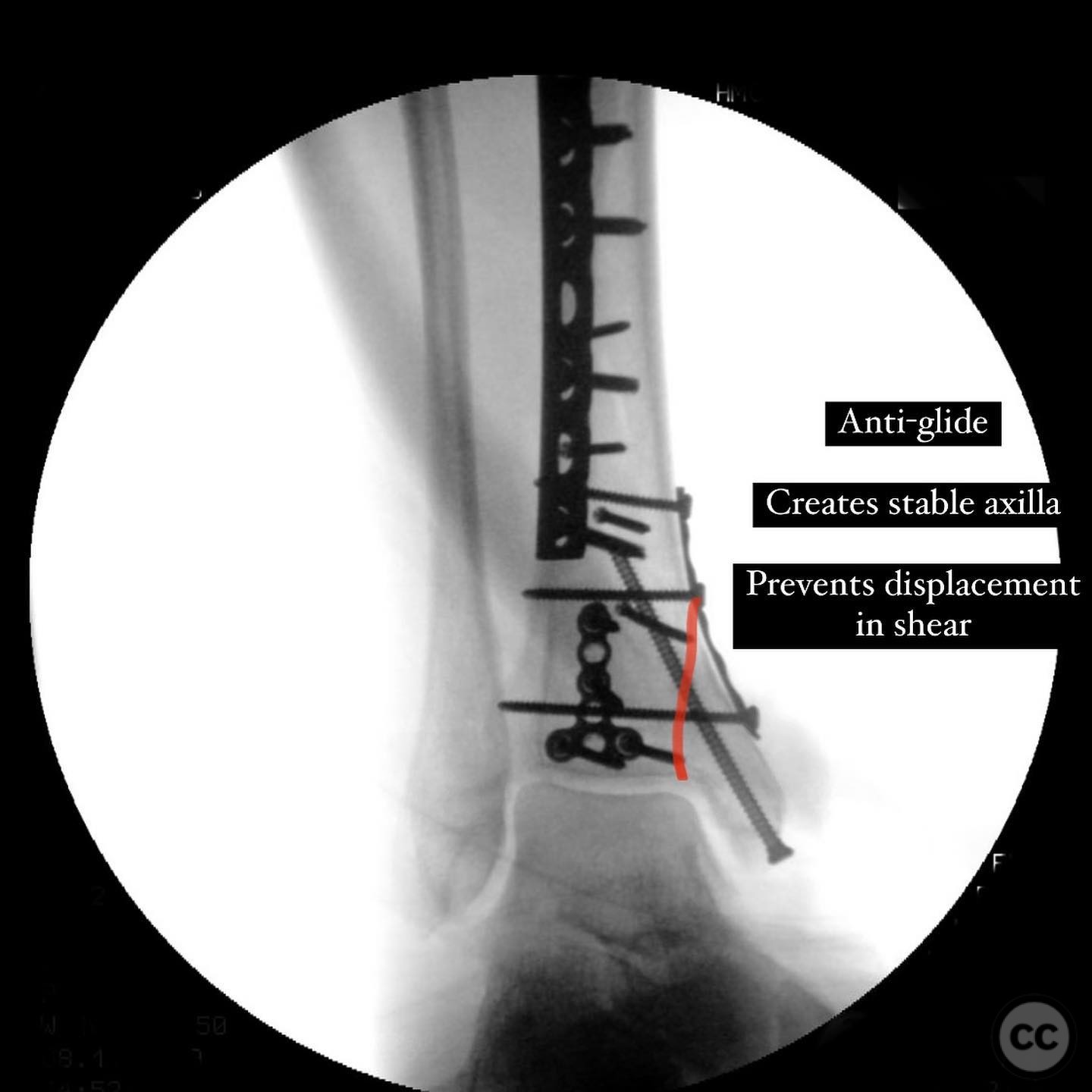
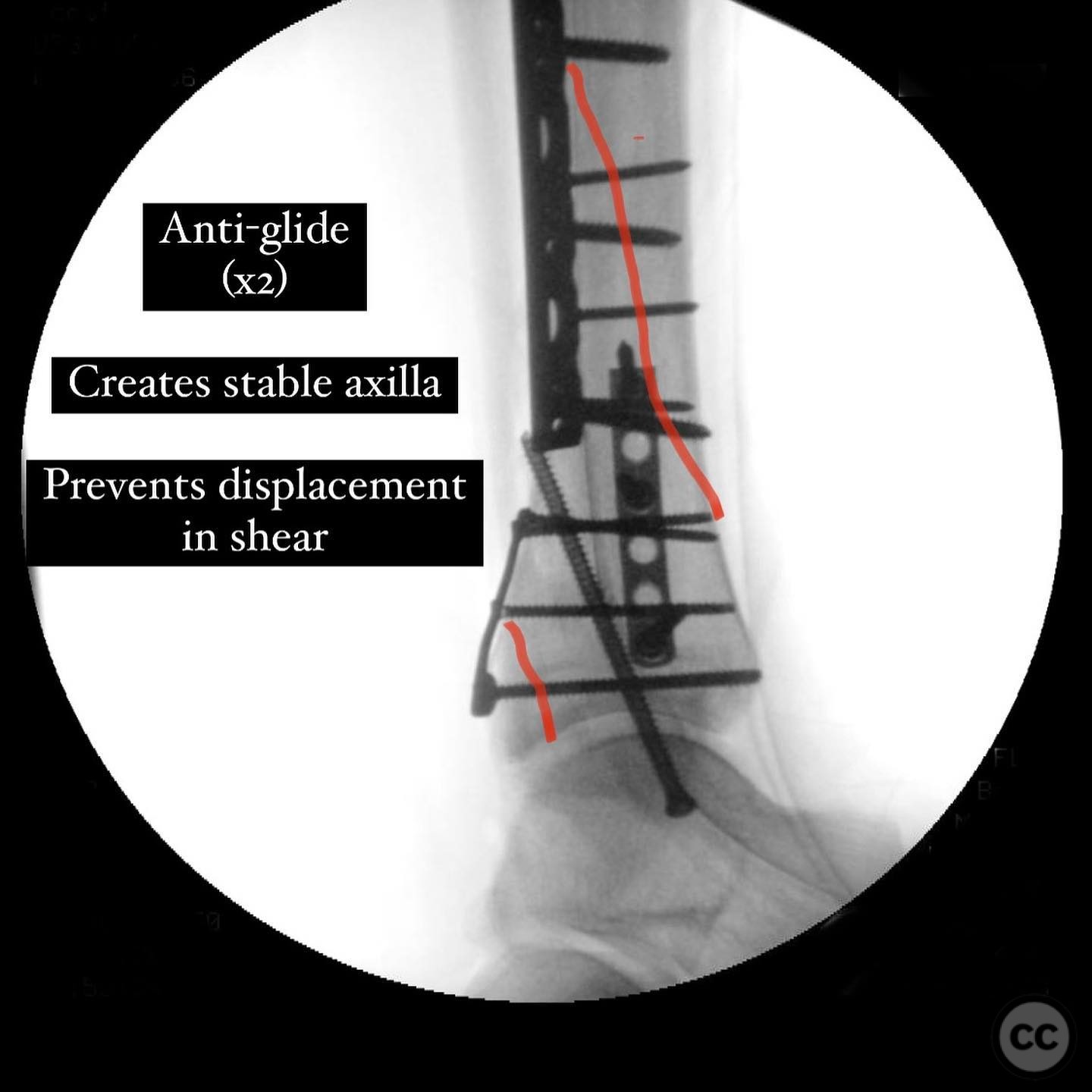
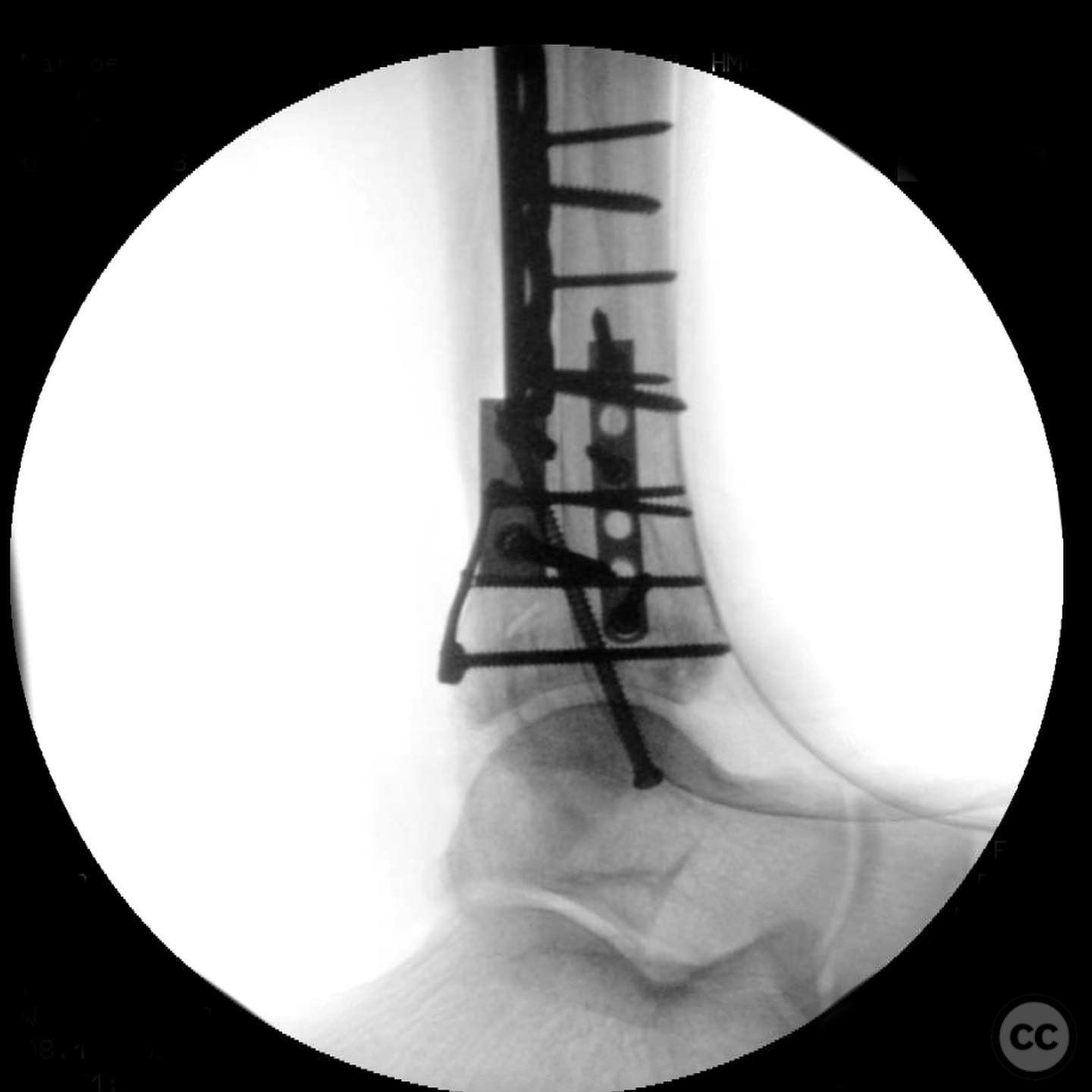
Operative remarks:The surgeon opted for direct reduction of each fracture line, initially using clamps which were subsequently replaced with 2.4 mm interfragmentary screws in the diaphysis. Three separate anti-glide plates were applied, each positioned over the apex of the respective fracture lines to create a stable construct and prevent shear displacement. The approach adhered to AO Basic principles, simplifying the fixation strategy.
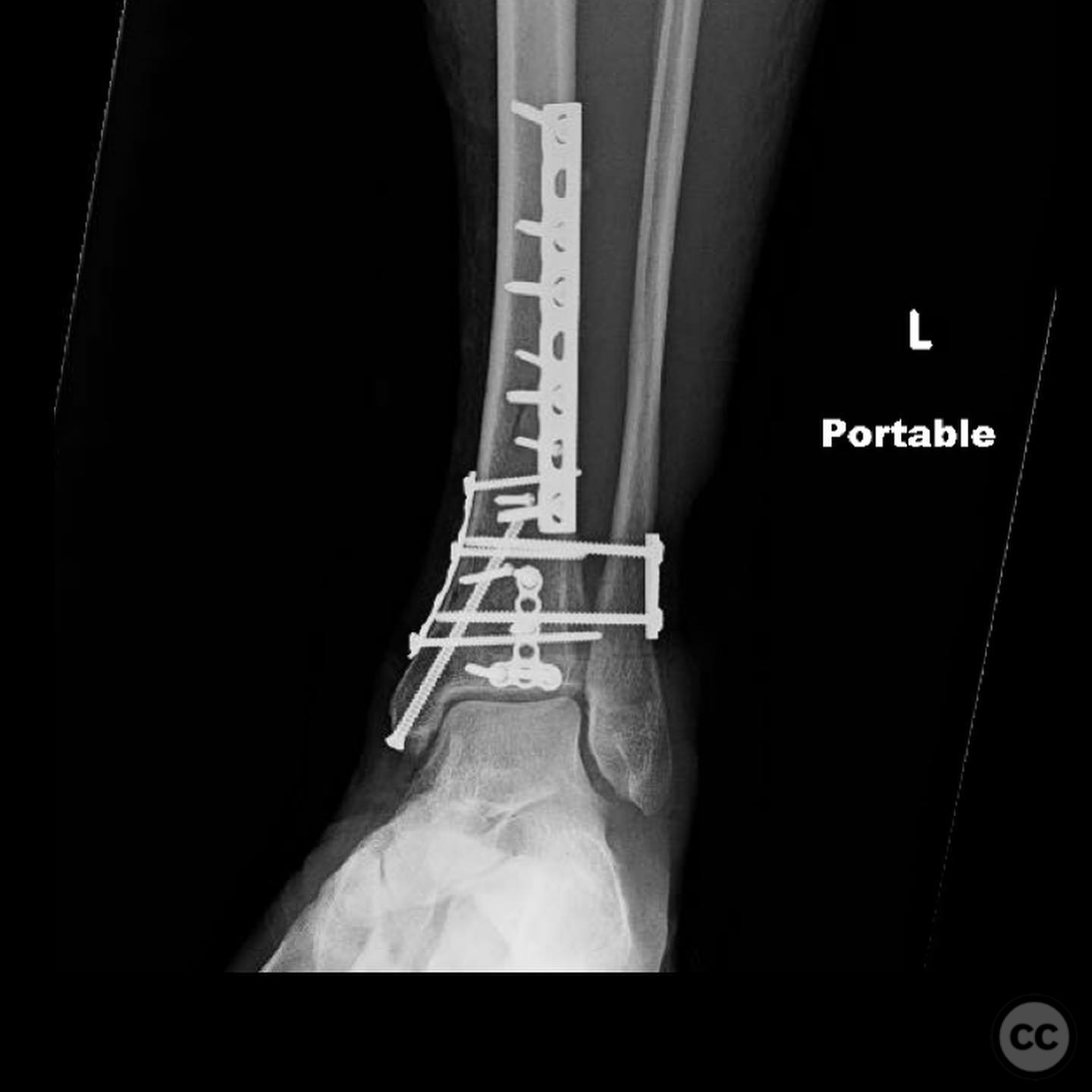
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included non-weight bearing status initially, with gradual progression to partial weight bearing as tolerated. Range of motion exercises were initiated early to maintain joint mobility.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: 2.4 mm interfragmentary screws, anti-glide plates.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 196 times
11 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Complex Pilon Fracture with Haraguchi II Pattern and Syndesmotic Injury. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 8464399 Published Online Jul 11 2025.