Isolated Closed Proximal Tibia Fracture with Tibial Tubercle Involvement
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
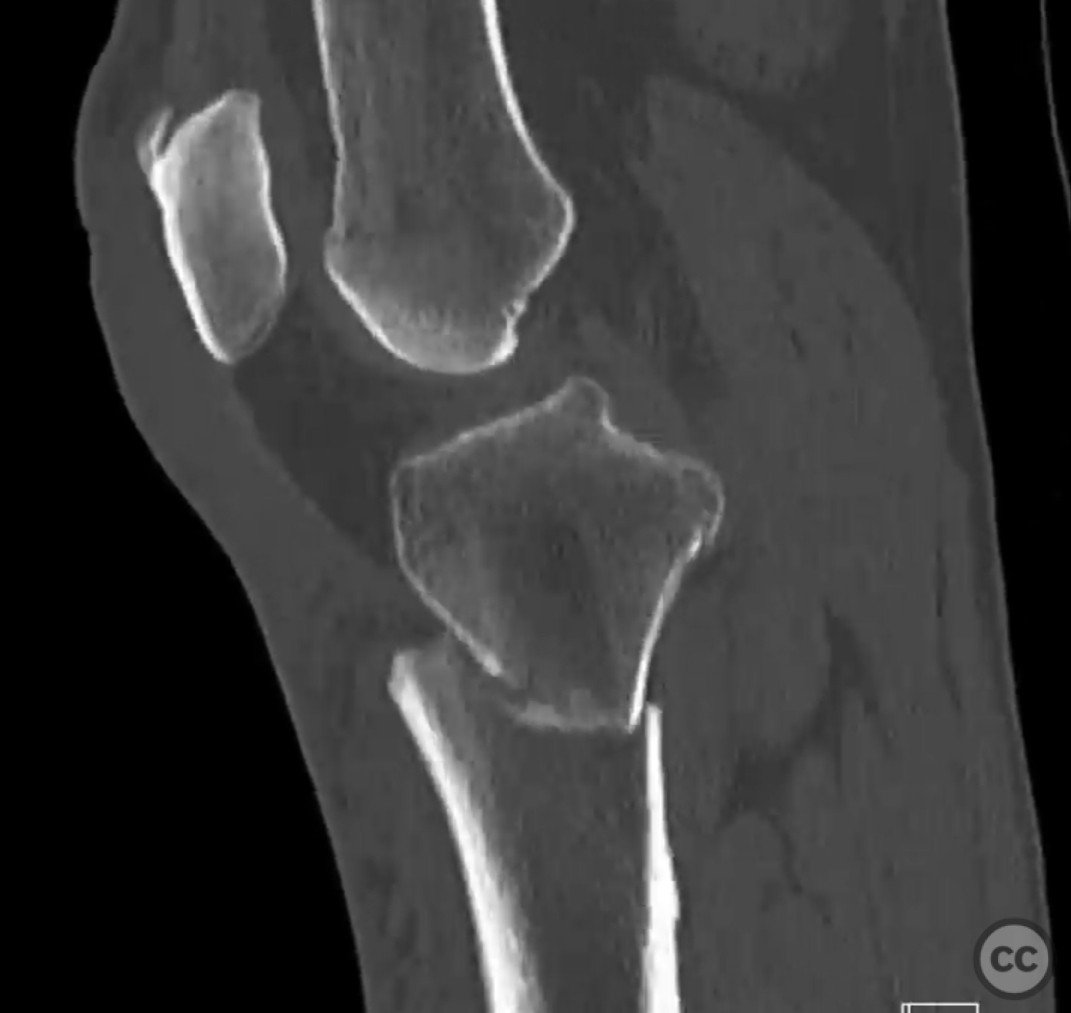
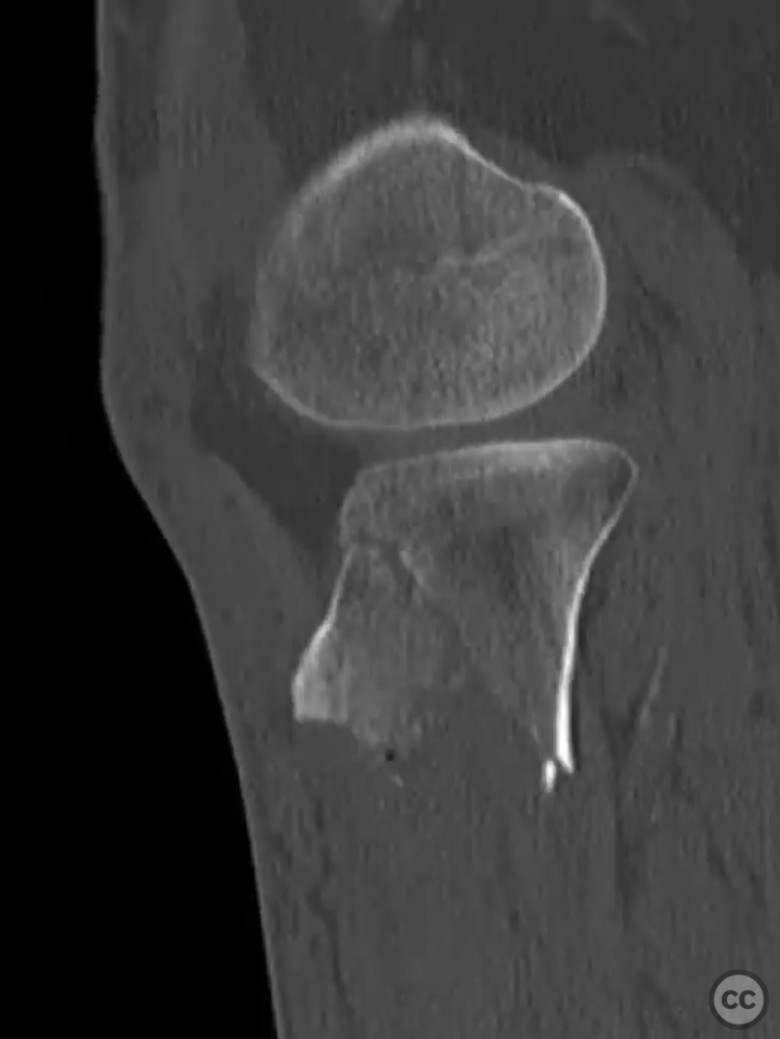
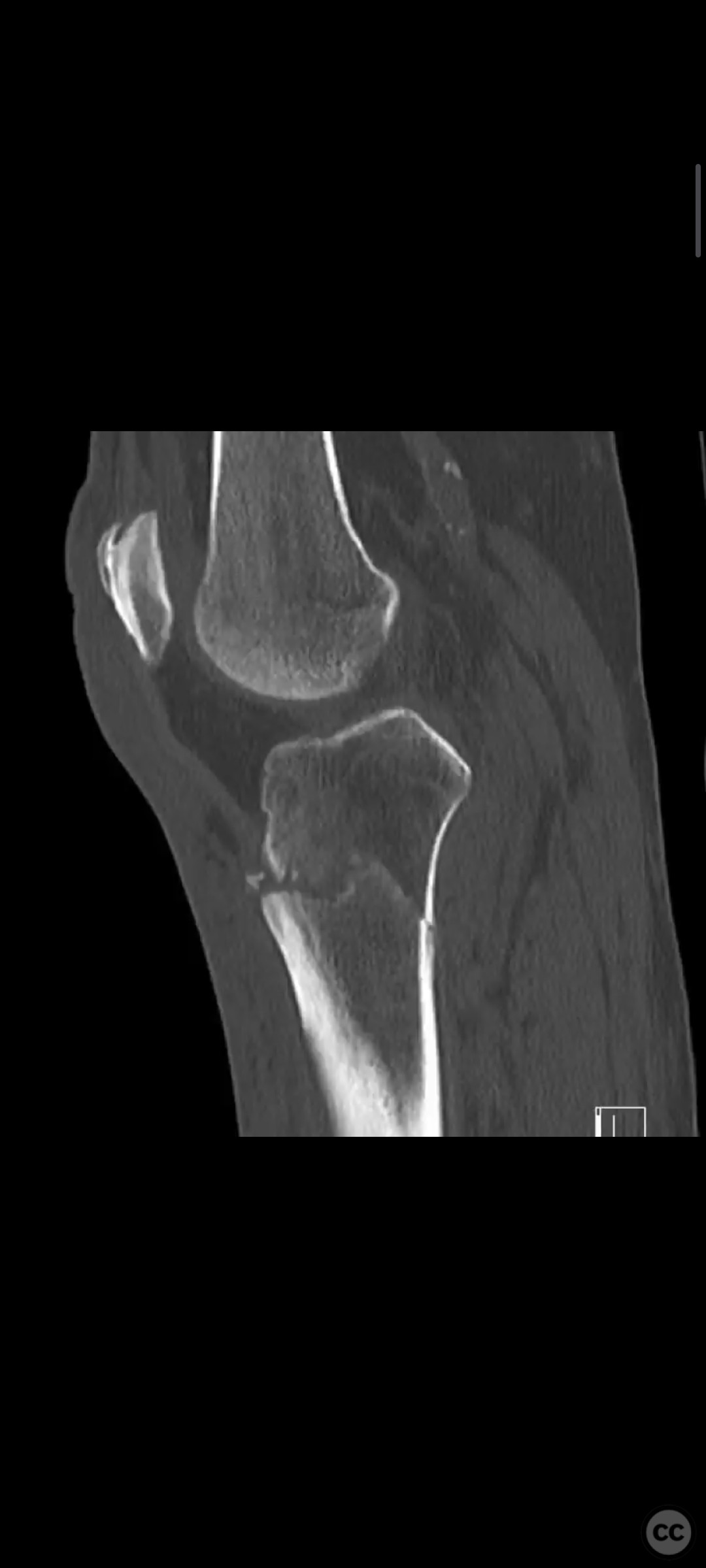
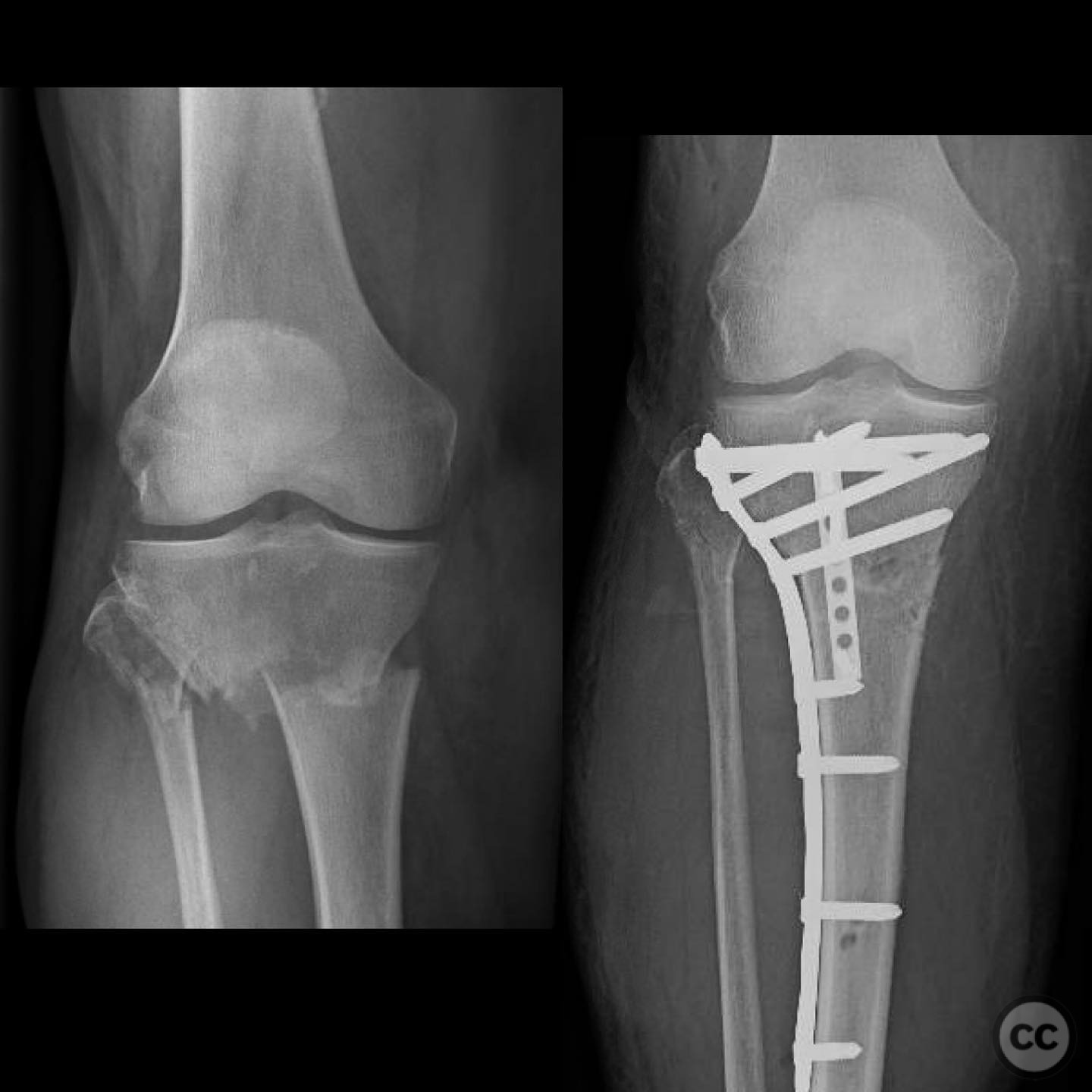
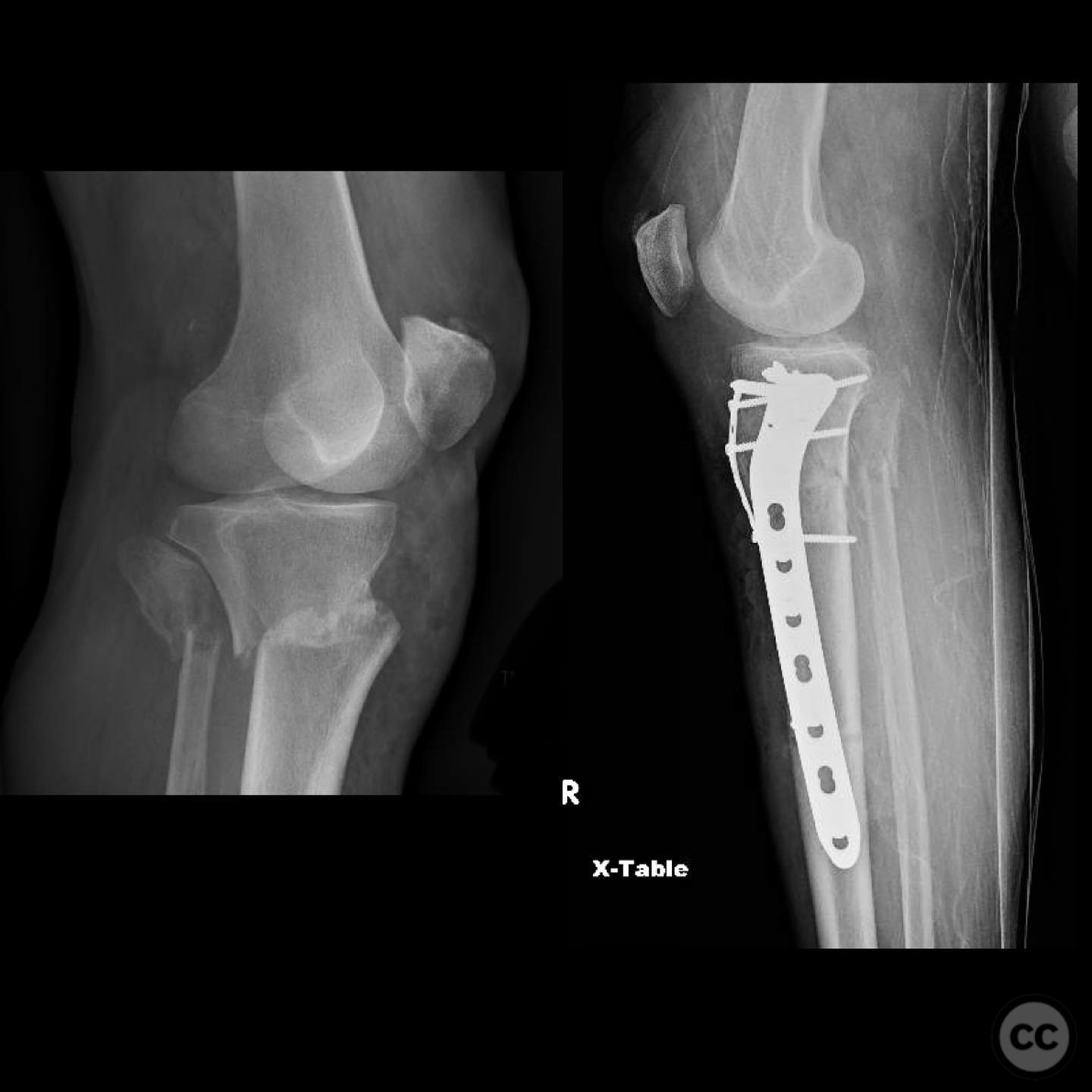
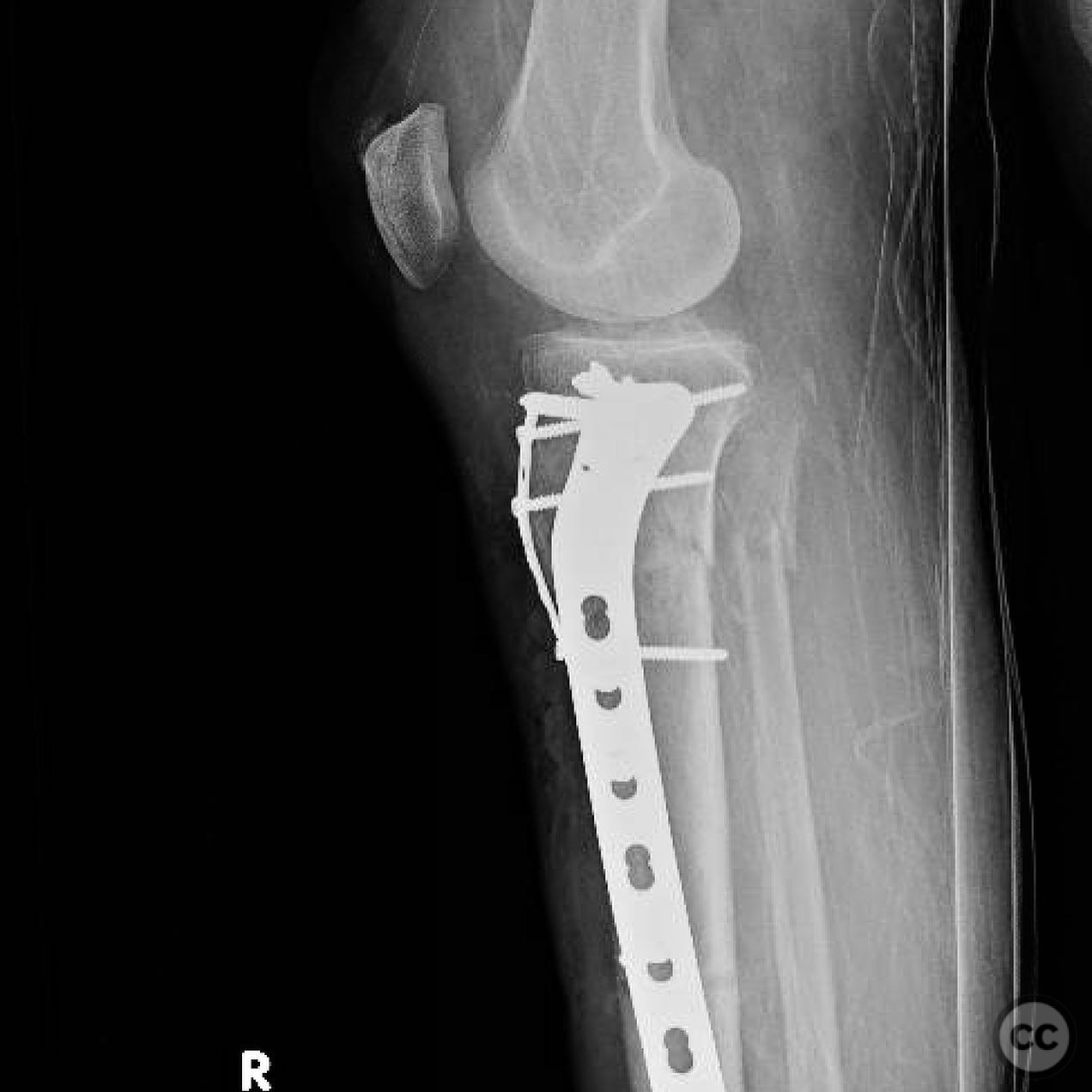
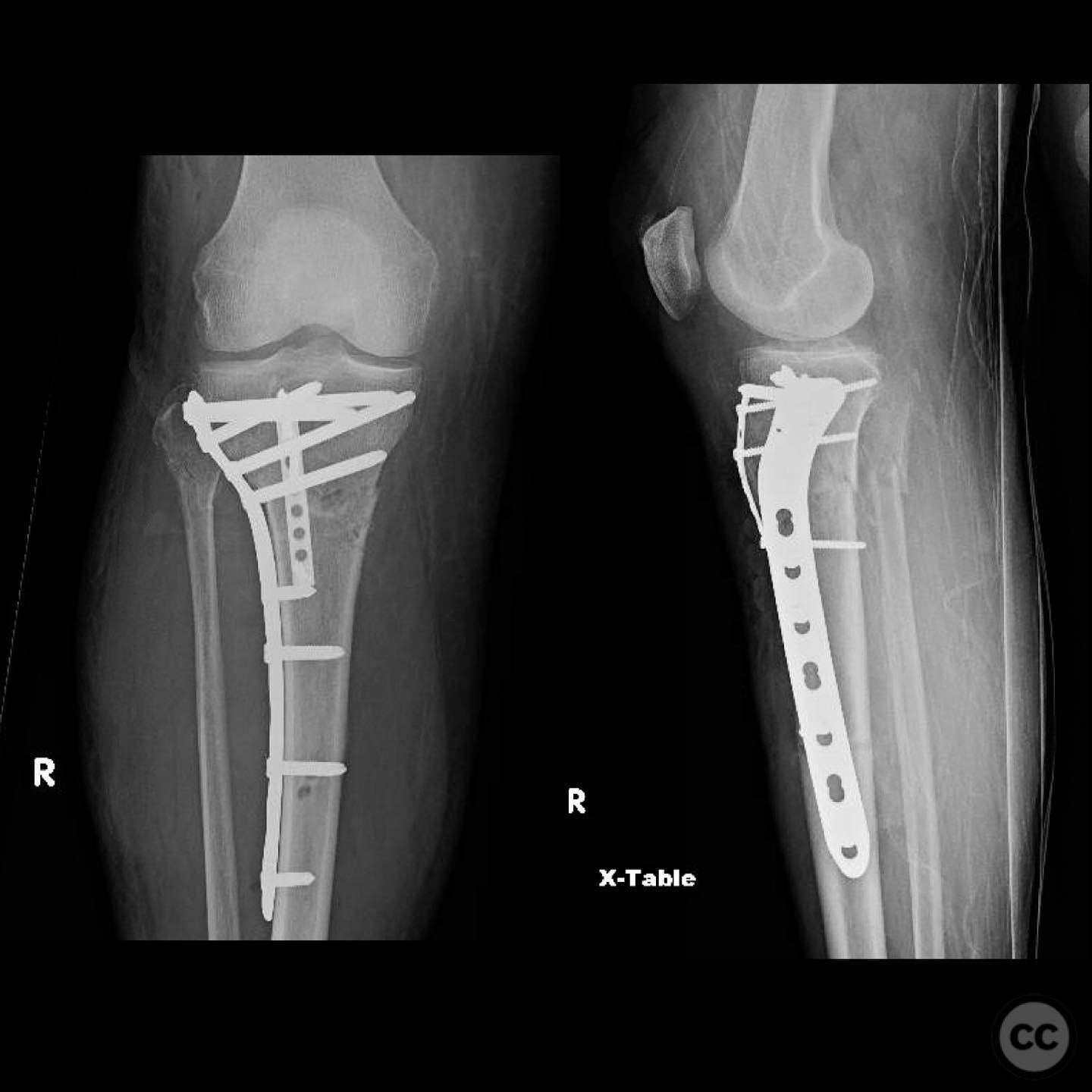
Clinical and radiological findings: A 56-year-old healthy female sustained an isolated closed proximal tibia fracture with an associated tibial tubercle fracture after being struck at low speed by a vehicle while riding a bicycle. The injury presented with mild bruising, minimal swelling, and intact skin condition. The neurovascular examination was unremarkable, and there were no signs of compartment syndrome. Radiographs confirmed the fracture pattern without articular extension.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of the proximal tibia fracture with specific attention to the tibial tubercle to facilitate early knee motion. A CT scan was obtained to aid in surgical planning. The decision was made to proceed with plating due to the simplicity of reduction and fixation in this fracture pattern.
Surgical Discussion
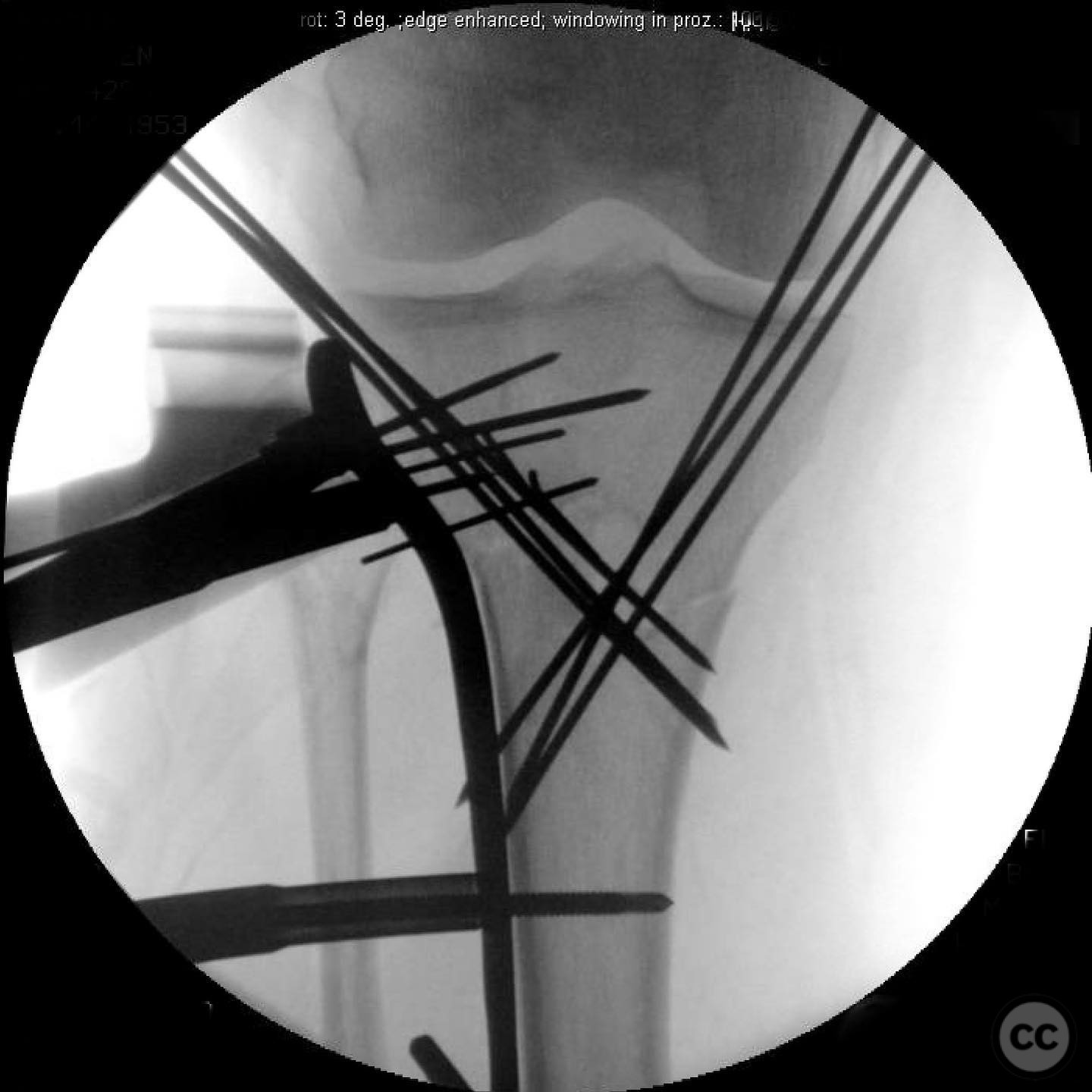
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table. A tourniquet was applied to the proximal thigh, and a radiolucent table was used to allow intraoperative imaging.
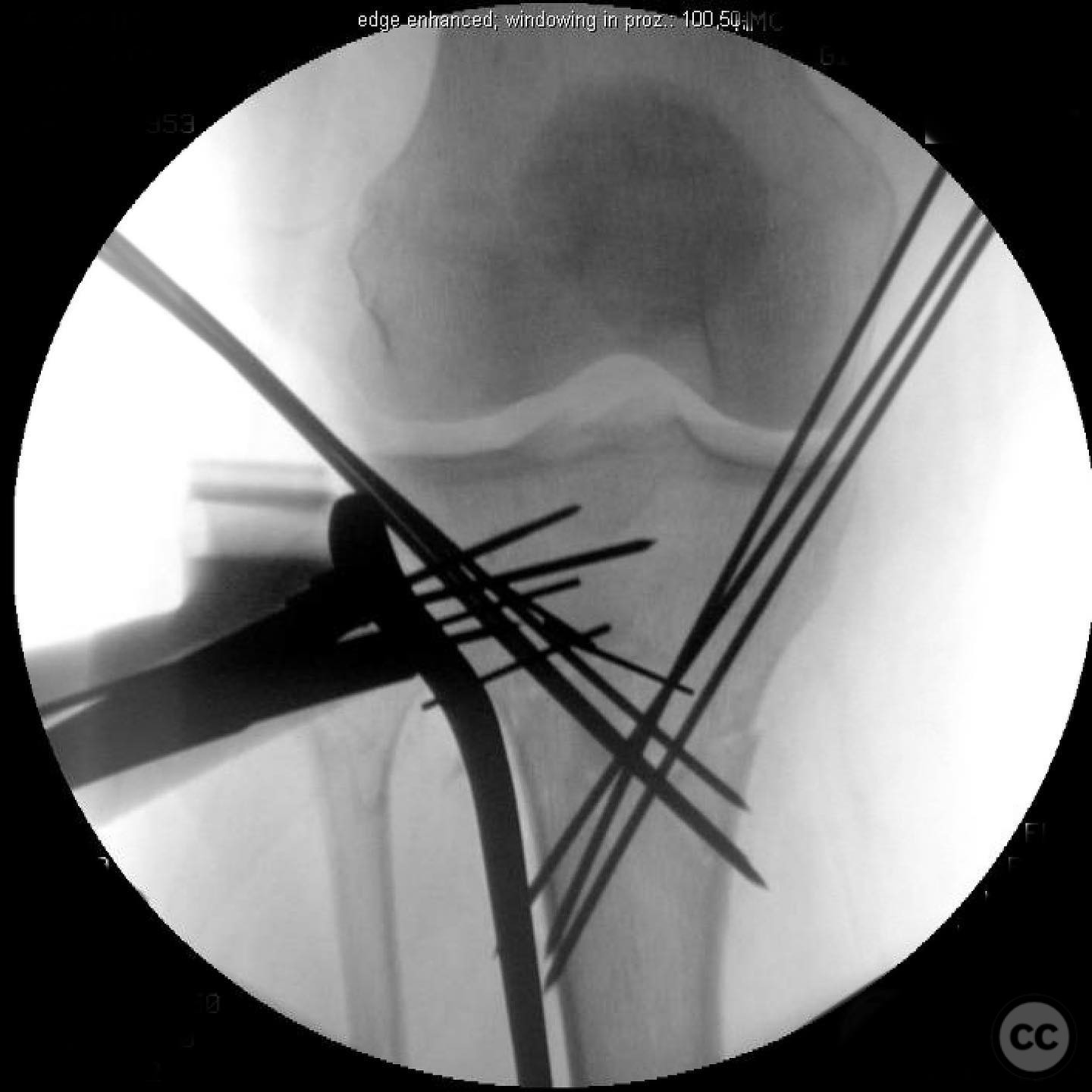
Anatomical surgical approach: A direct anterior approach to the proximal tibia was utilized. An incision was made over the anterior aspect of the tibia, extending from the level of the tibial tubercle distally. The patellar tendon was retracted laterally to expose the fracture site. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to visualize the fracture fragments, particularly focusing on the tibial tubercle.
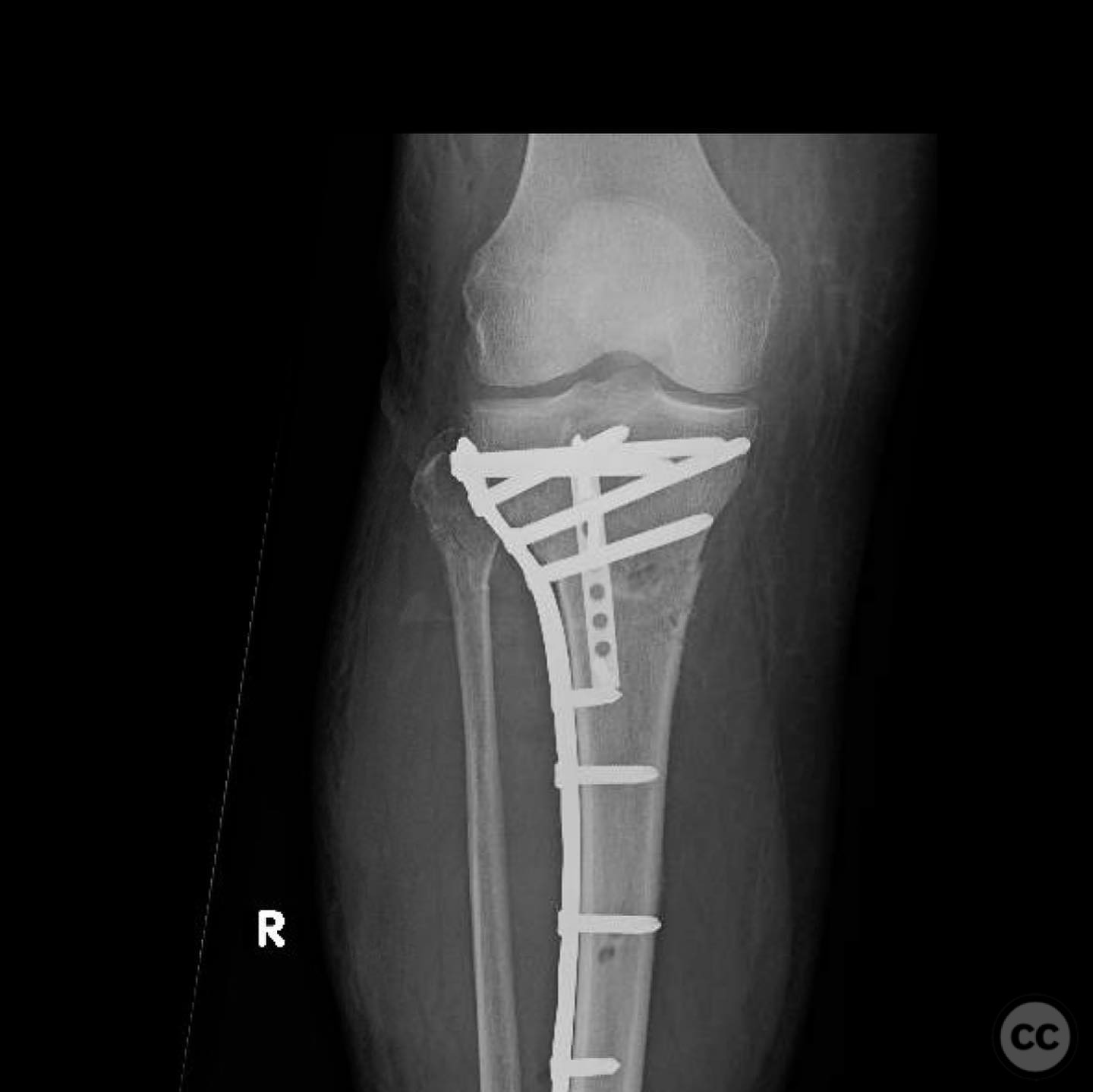
Operative remarks:The tibial tubercle was addressed first to ensure stability for early motion postoperatively. Reduction was achieved using direct manipulation and temporarily held with K-wires. Definitive fixation was accomplished using a plate, which also facilitated fine-tuning of the overall reduction of the proximal tibia fracture. Care was taken to avoid malreduction, which can occur with intramedullary nailing in this fracture pattern.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early range of motion exercises to prevent knee arthrofibrosis. Weight-bearing as tolerated was initiated immediately post-surgery, with progression based on clinical and radiographic healing.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used: Plate fixation system for proximal tibia, K-wires for temporary stabilization.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities



Article viewed 146 times
14 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Isolated Closed Proximal Tibia Fracture with Tibial Tubercle Involvement. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 7482899 Published Online Jul 14 2025.