Neglected Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia Fracture with Osteomyelitis: Mechanical Knee Arthrodesis
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
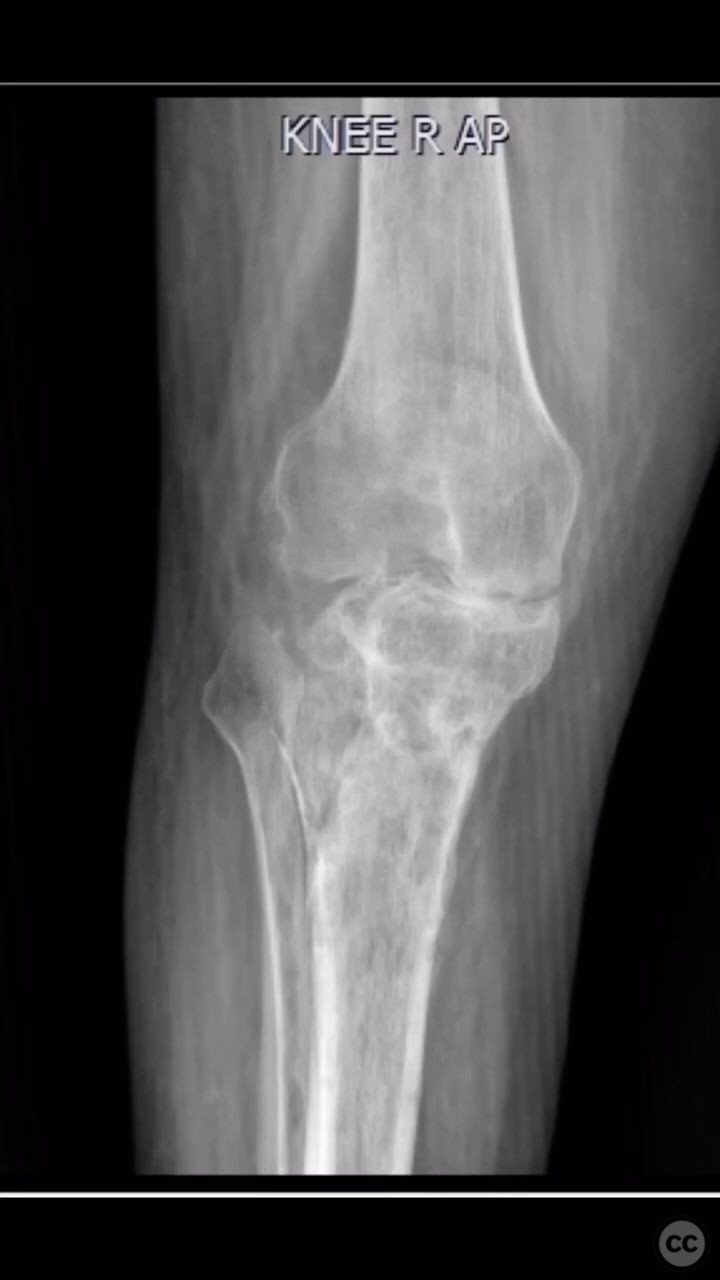
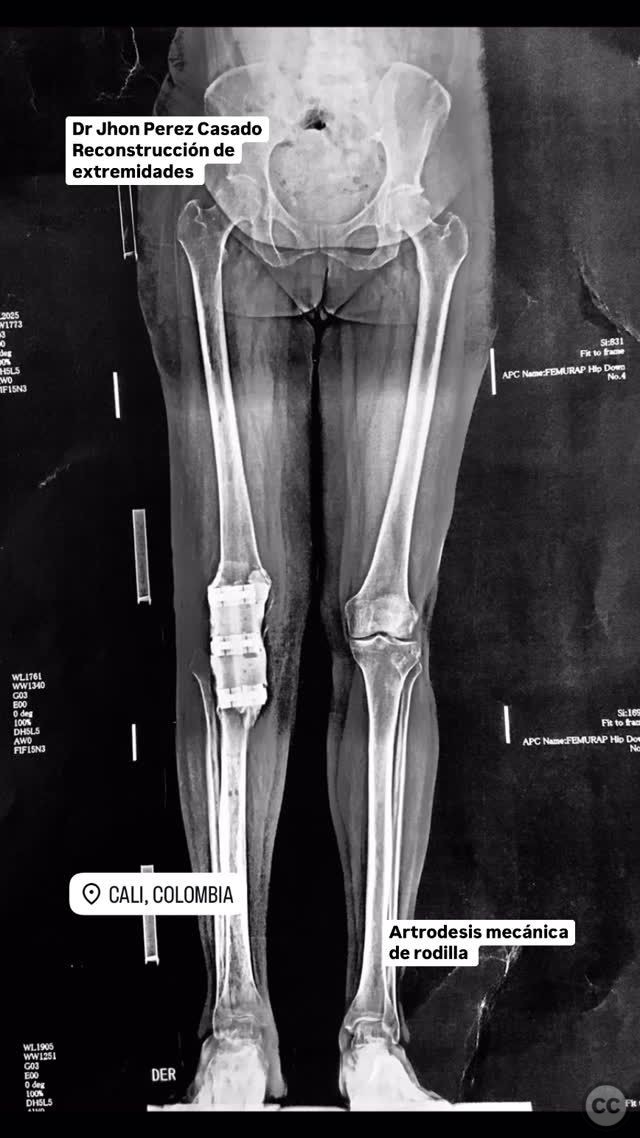
Clinical and radiological findings: The patient presented with a neglected fracture of the distal femur and proximal tibia, complicated by bone loss, post-traumatic osteoarthritis, and osteomyelitis. Radiological assessment revealed significant bone destruction and joint space obliteration. The fracture classification according to AO/OTA is indeterminate due to the chronicity and bone loss.
Preoperative Plan
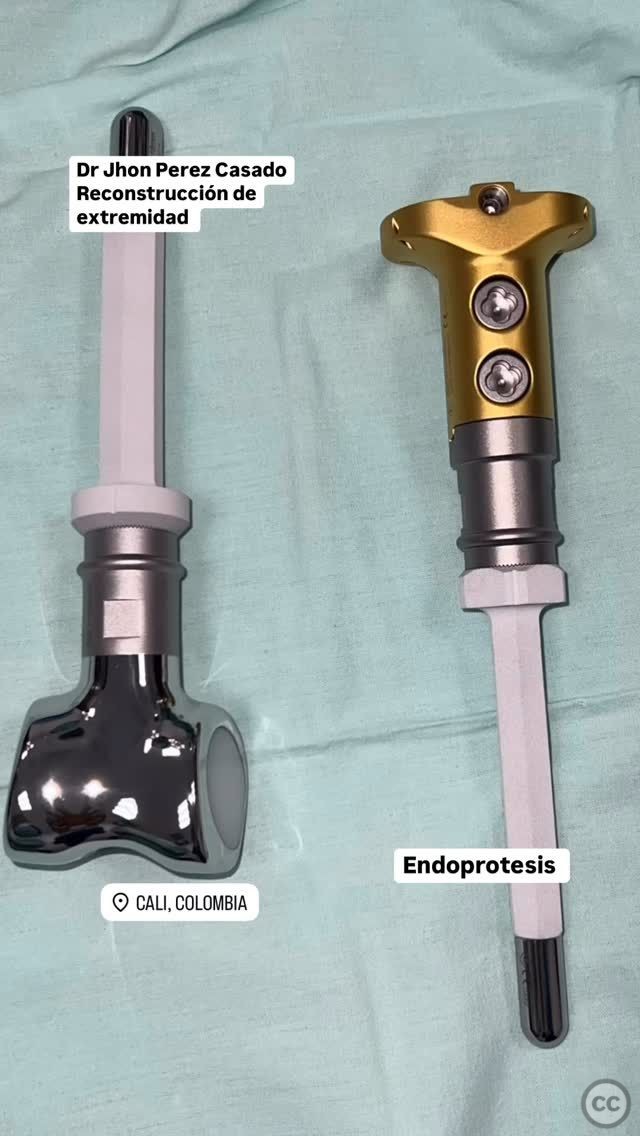
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved radical debridement of infected and necrotic bone tissue from the distal femur and proximal tibia. The surgical strategy included mechanical knee arthrodesis using carbon rods and bone cement to stabilize the joint and address the infection.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table, with the affected limb prepared for extensive exposure from the distal femur to the proximal tibia.
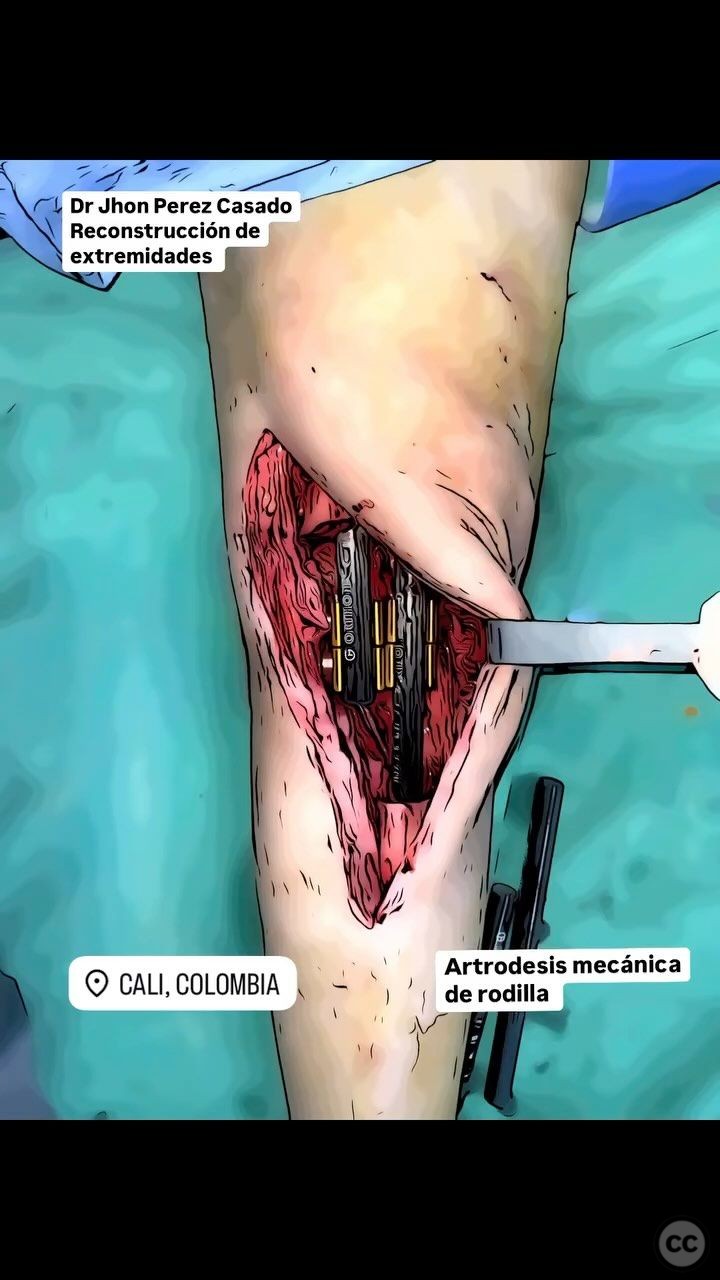
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal midline incision was made over the knee joint, extending from the distal femur to the proximal tibia. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the distal femur and proximal tibia. Radical debridement of infected and necrotic bone was carried out, followed by stabilization with carbon rods and bone cement to achieve mechanical arthrodesis.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted significant bone loss and extensive osteomyelitic changes necessitating aggressive debridement. Mechanical arthrodesis was achieved with carbon rods and bone cement, providing immediate stability. The plan included removal of the mechanical construct at 12 weeks, followed by consideration for endoprosthetic replacement.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early mobilization with walking and muscle strength training to maintain overall limb function and prepare for potential future reconstructive procedures.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Carbon rods, bone cement.
Search for Related Literature

Jhon Perez Casado
- Colombia , Cali - Valle del Cauca
- Area of Specialty - Lower Limb
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 133 times
23 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Perez Casado, J.J.. (2025). Neglected Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia Fracture with Osteomyelitis: Mechanical Knee Arthrodesis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 6427329 Published Online Jul 23 2025.