AO/OTA 41-B3 Lateral Tibial Plateau Fracture with Ipsilateral Tibial Shaft Fracture
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
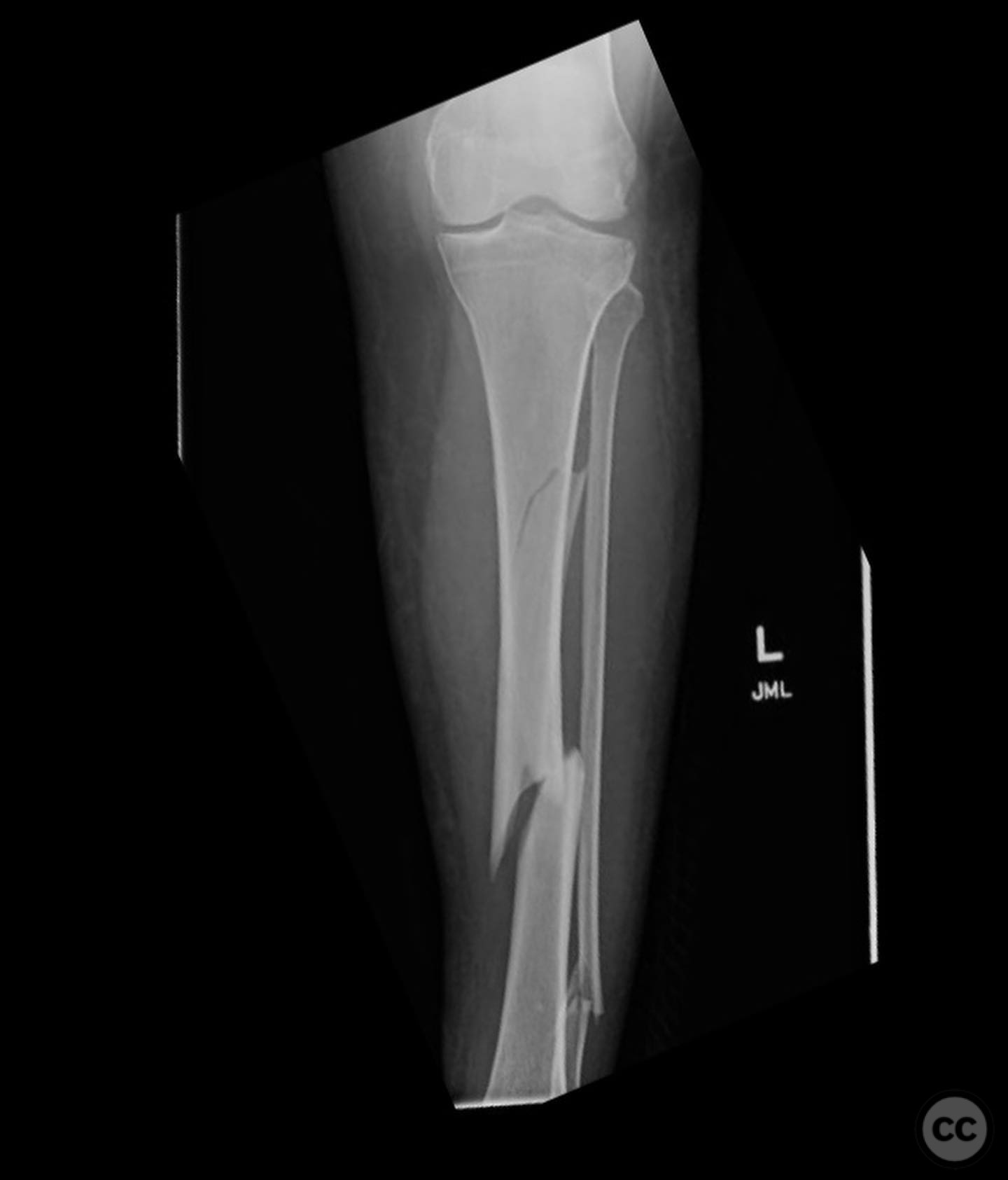
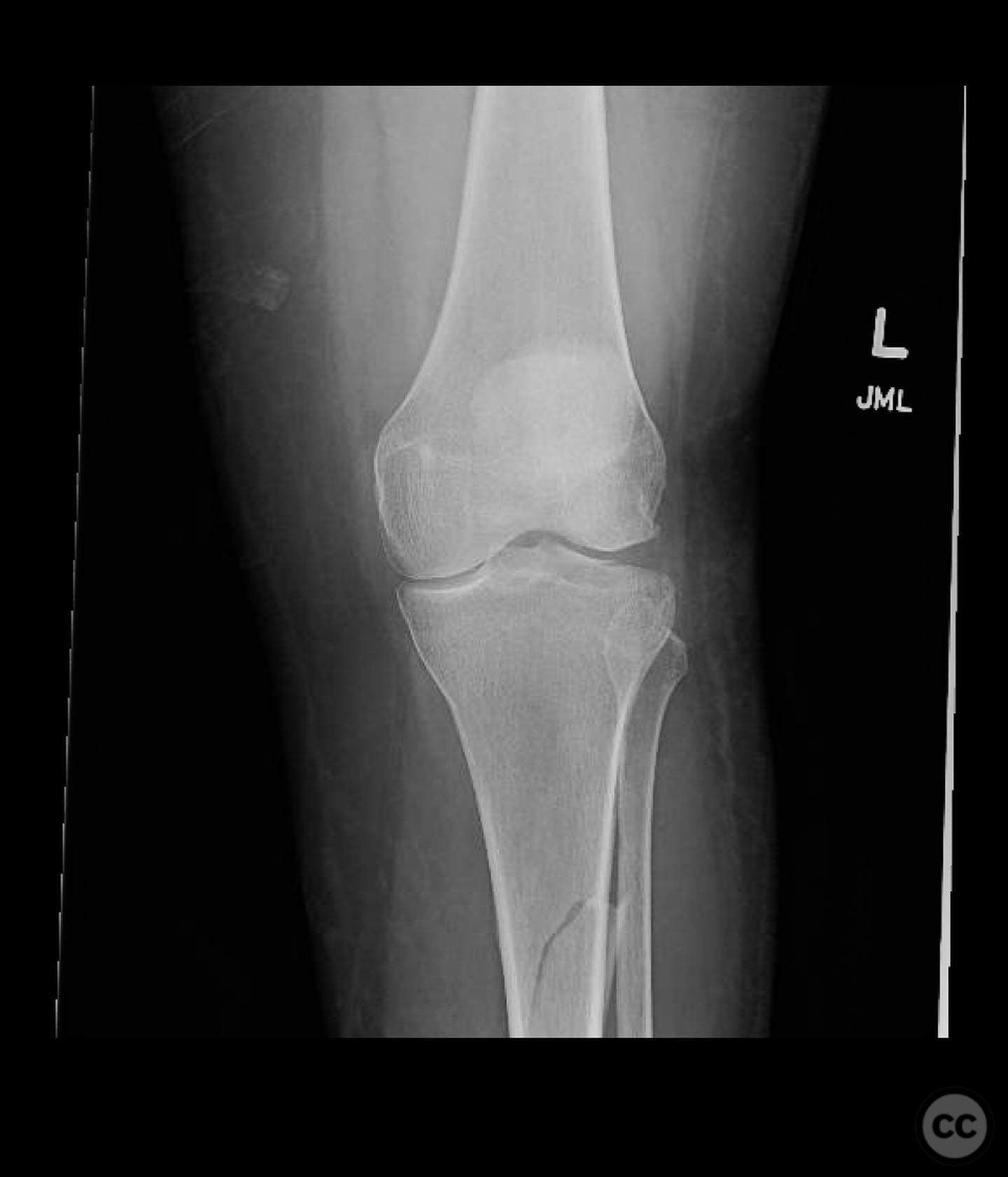
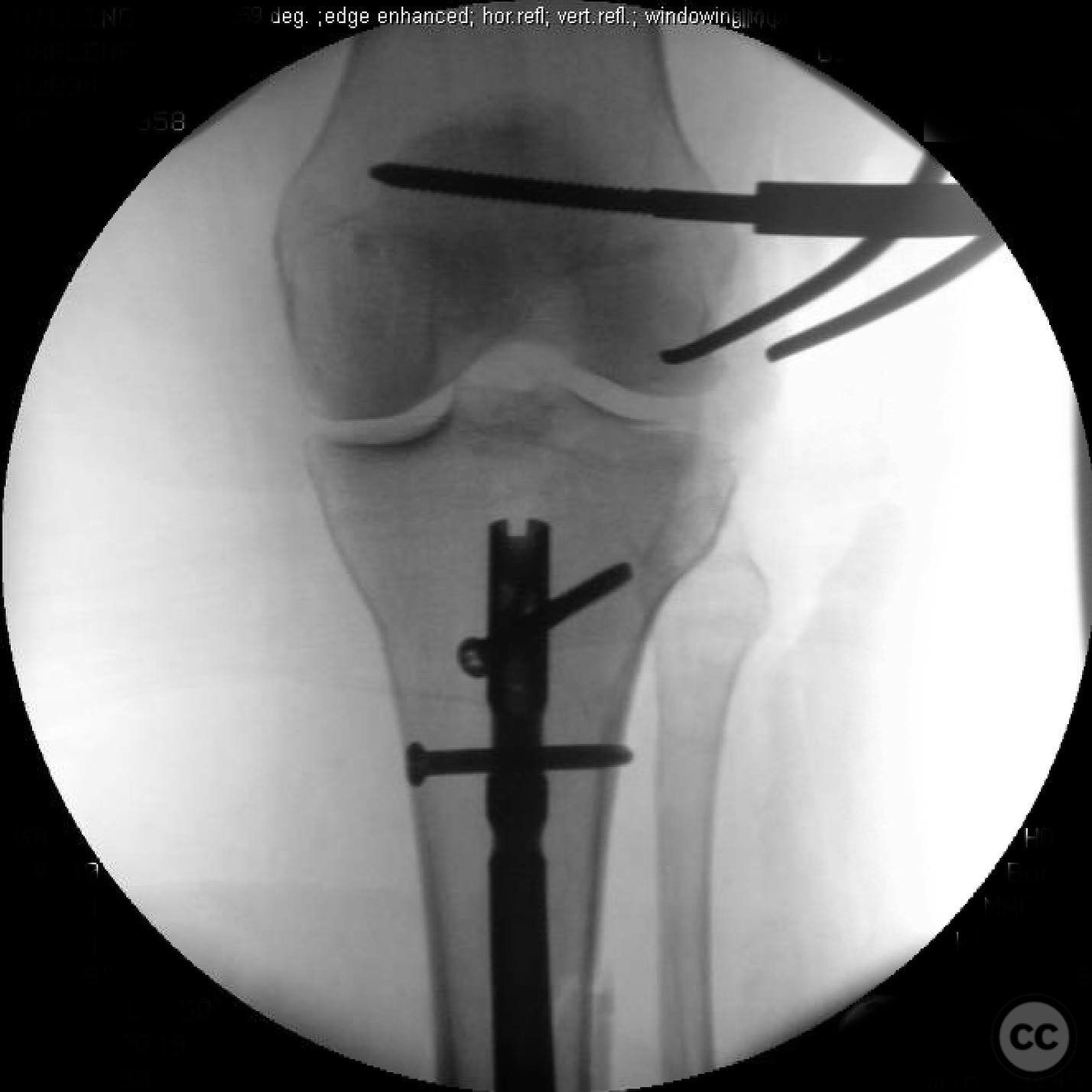
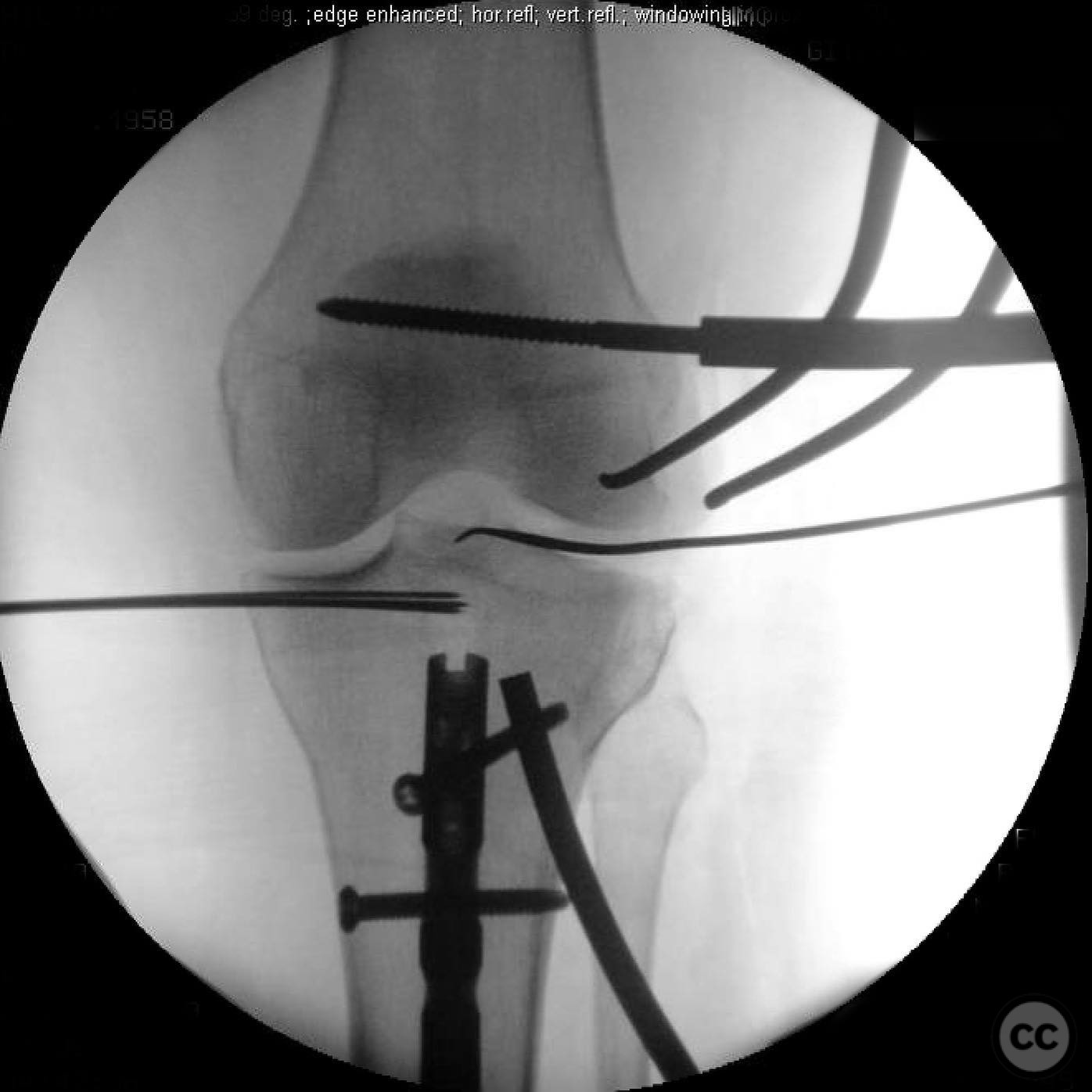
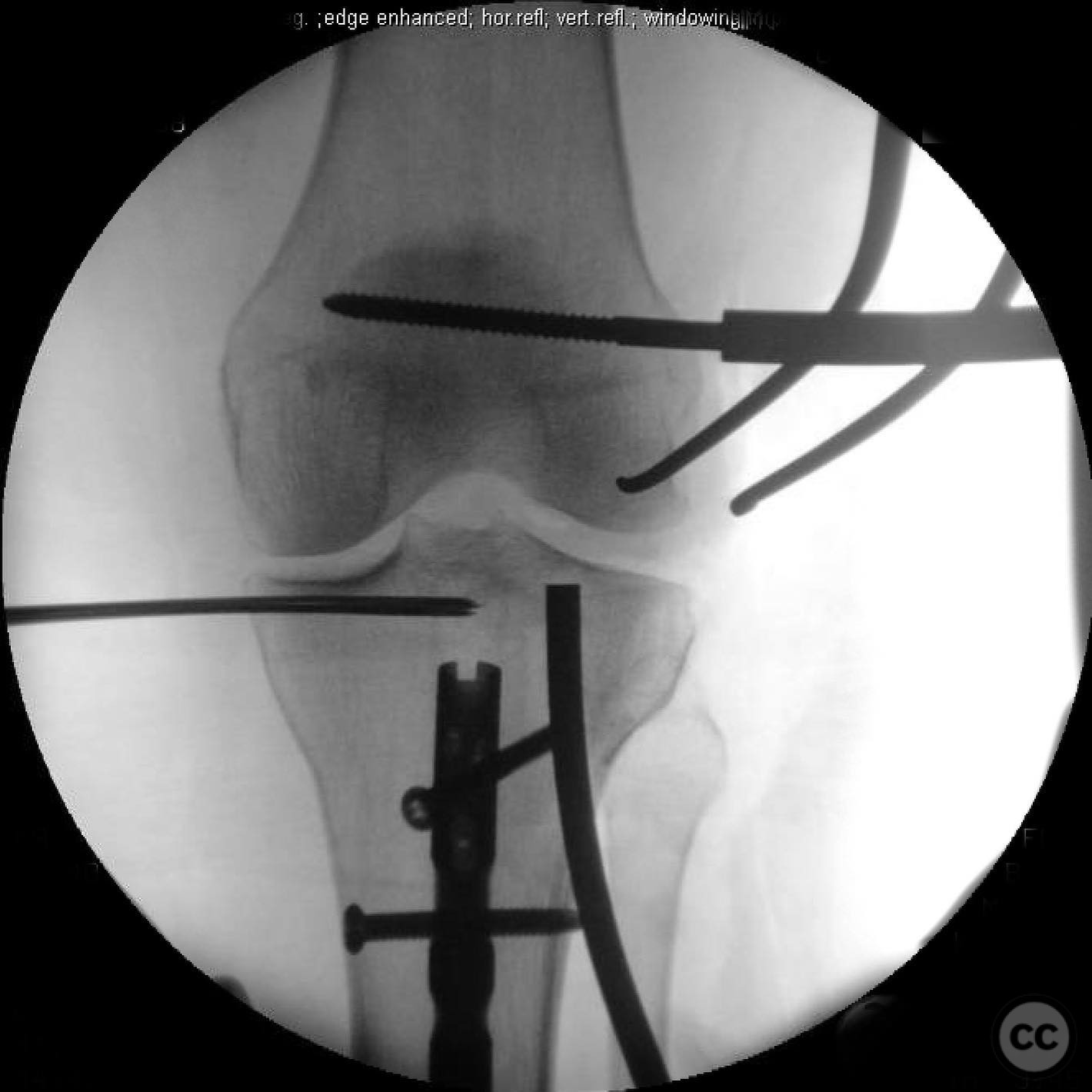
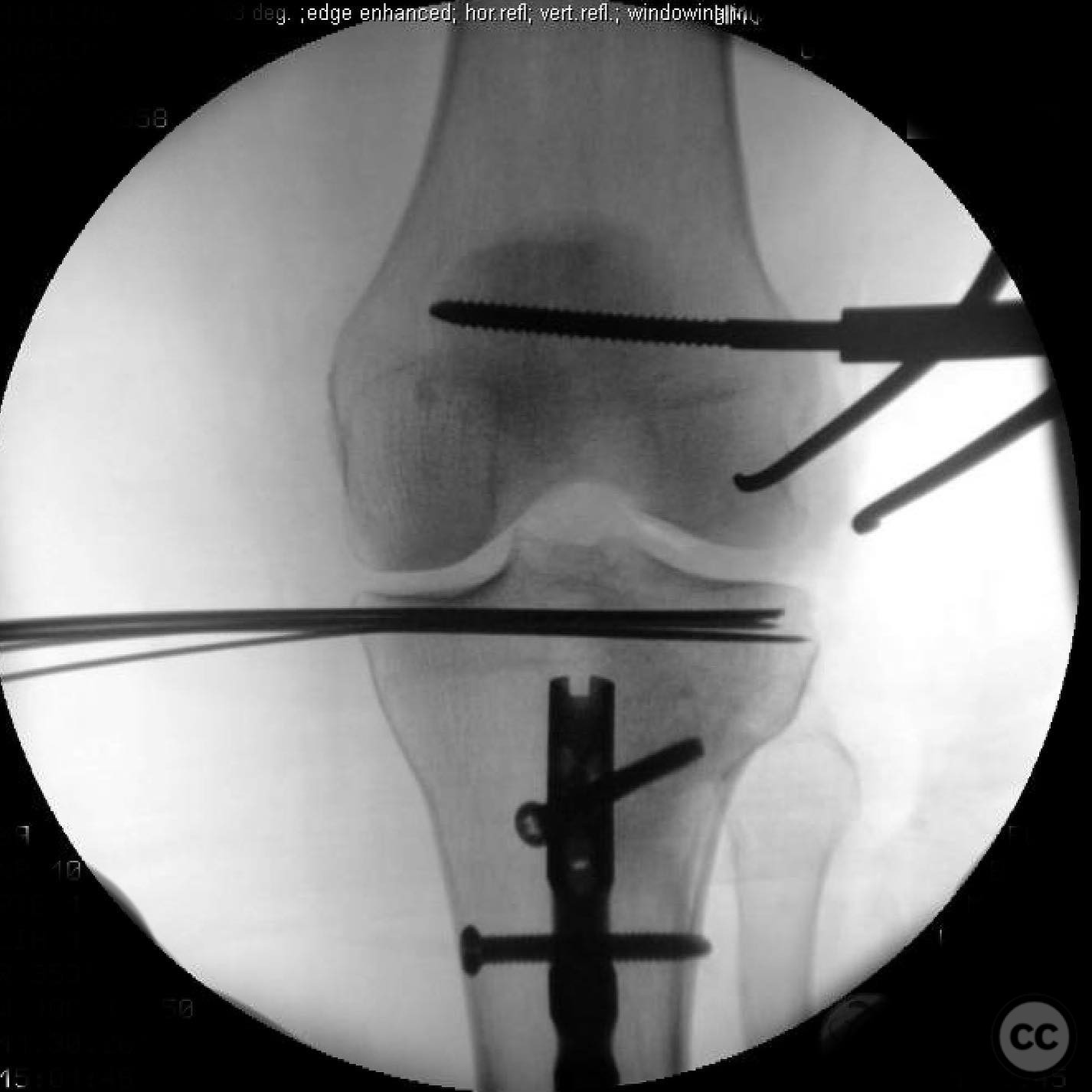
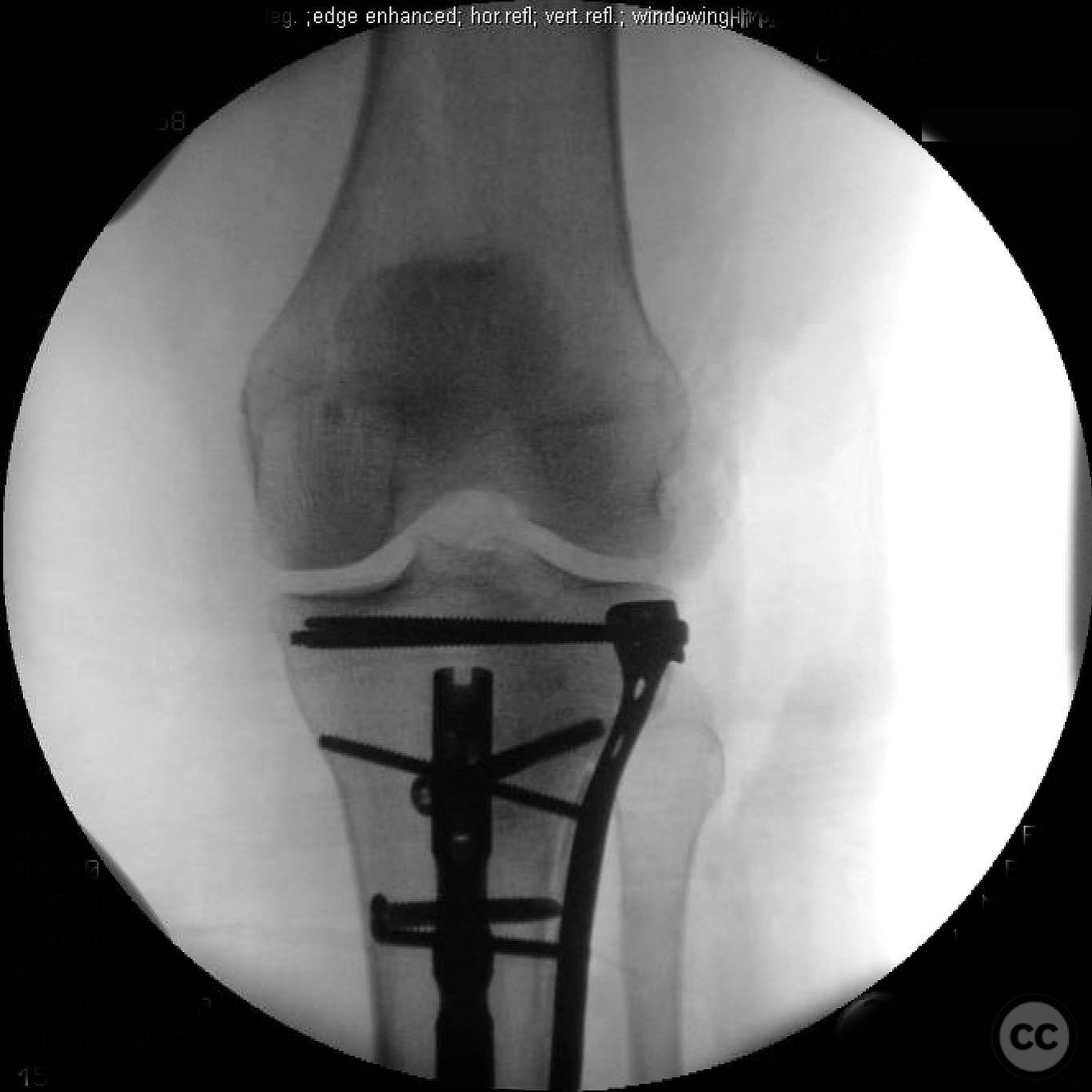
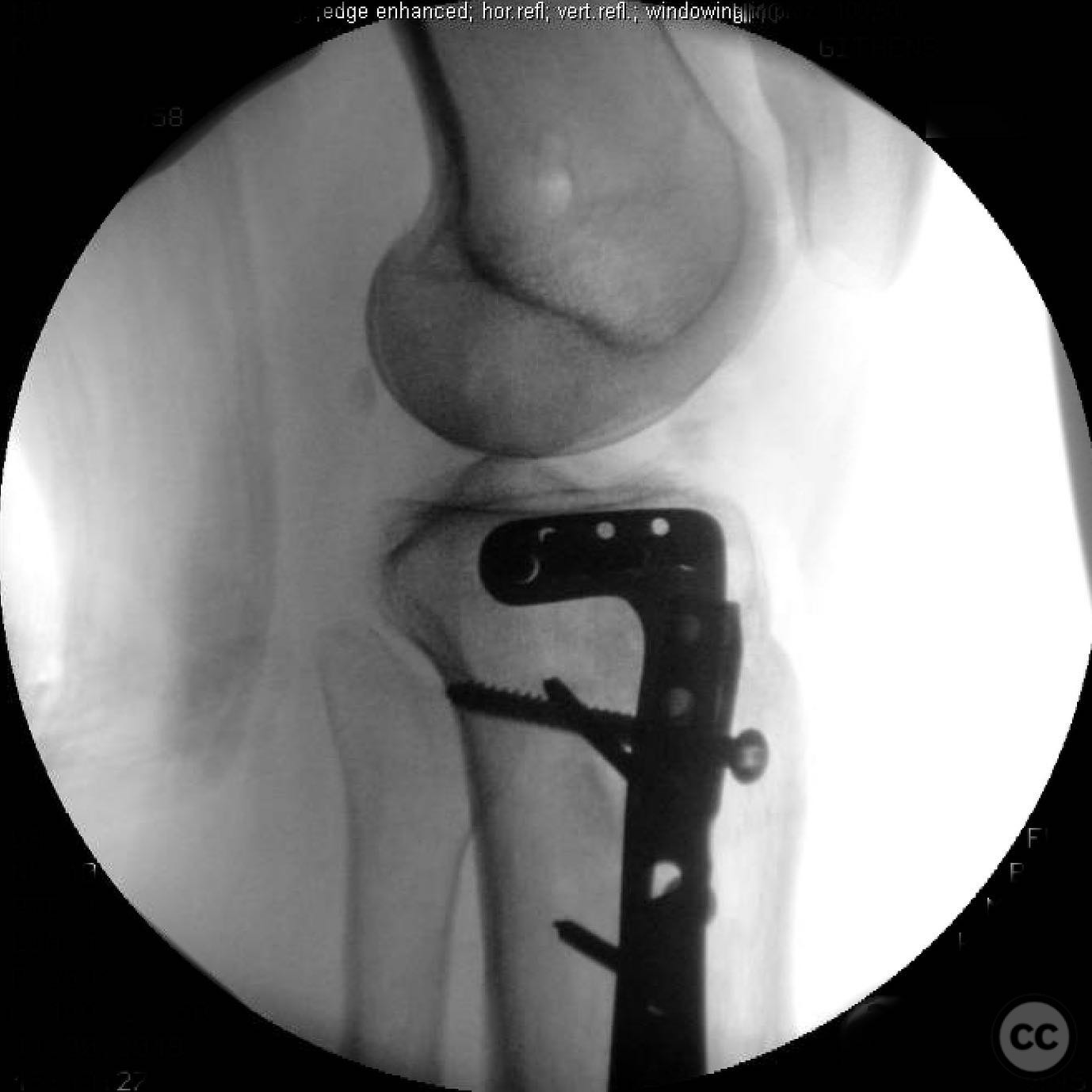
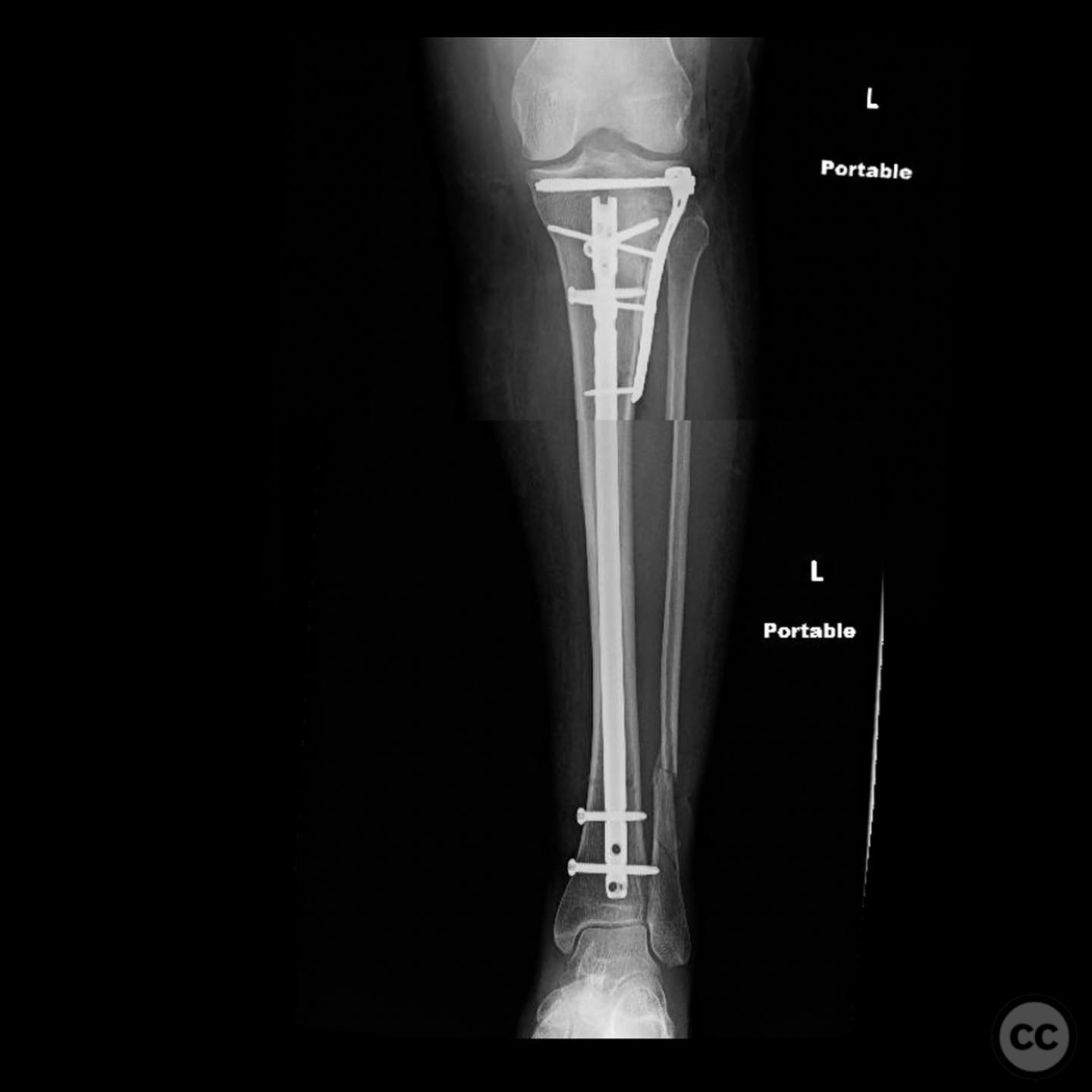
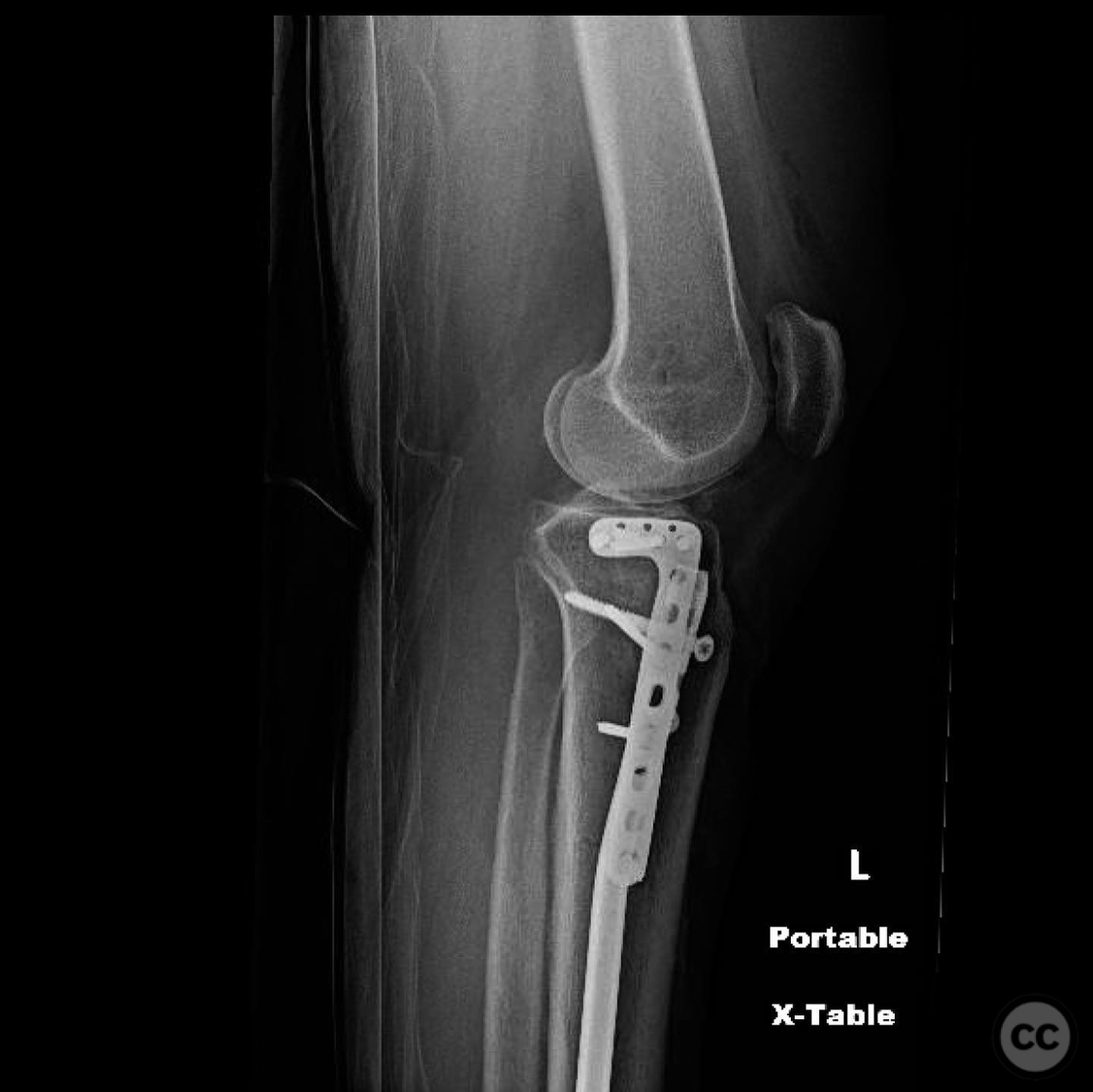
Clinical and radiological findings: A 45-year-old patient involved in a pedestrian versus automobile accident sustained an isolated, closed injury. The initial clinical examination revealed no neurovascular compromise. Radiological assessment identified a non-contiguous fracture pattern involving the lateral tibial plateau and ipsilateral tibial shaft. The lateral tibial plateau fracture was subtle and required careful evaluation to avoid oversight.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved addressing the tibial shaft fracture first with intramedullary nailing, followed by open reduction and internal fixation of the lateral tibial plateau fracture. This sequence was chosen to prevent interference with the reduction and plating of the plateau.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine position on a radiolucent table, with the injured leg prepared for both intramedullary nailing and subsequent lateral approach for plateau fixation.
Anatomical surgical approach: A direct lateral approach to the proximal tibia was utilized. The incision was made along the lateral aspect of the knee, extending distally to expose the lateral tibial plateau. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to elevate soft tissues and provide access to the fracture site for reduction and fixation.
Operative remarks:The decision to reverse the usual sequence of fixation was based on the specific fracture pattern, allowing for unimpeded access to the lateral plateau after nailing the shaft. This approach facilitated optimal reduction and stabilization of both fracture components.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included immediate partial weight-bearing with crutches, progressing to full weight-bearing as tolerated over 6-8 weeks. Range of motion exercises were initiated early to prevent joint stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified.
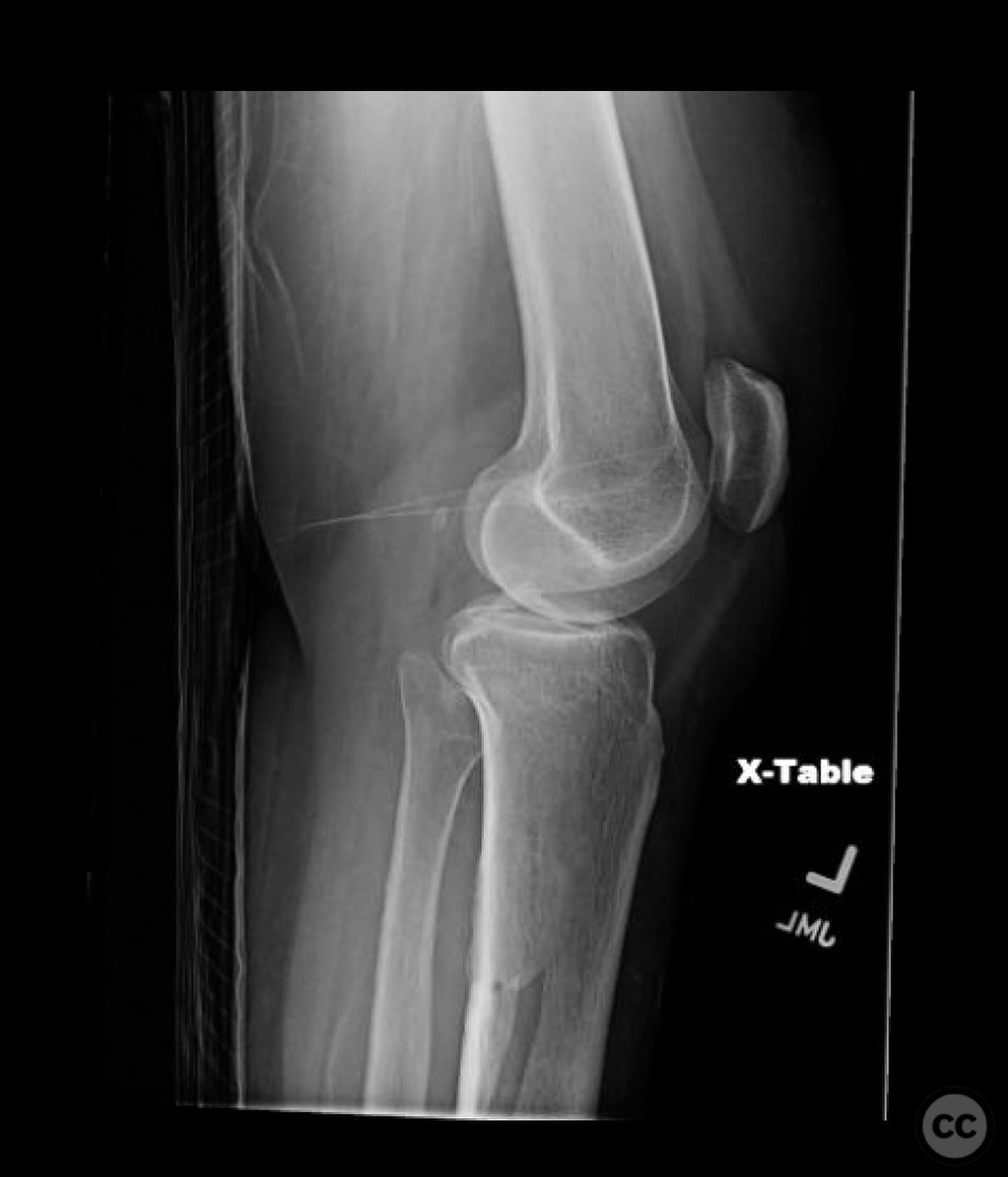
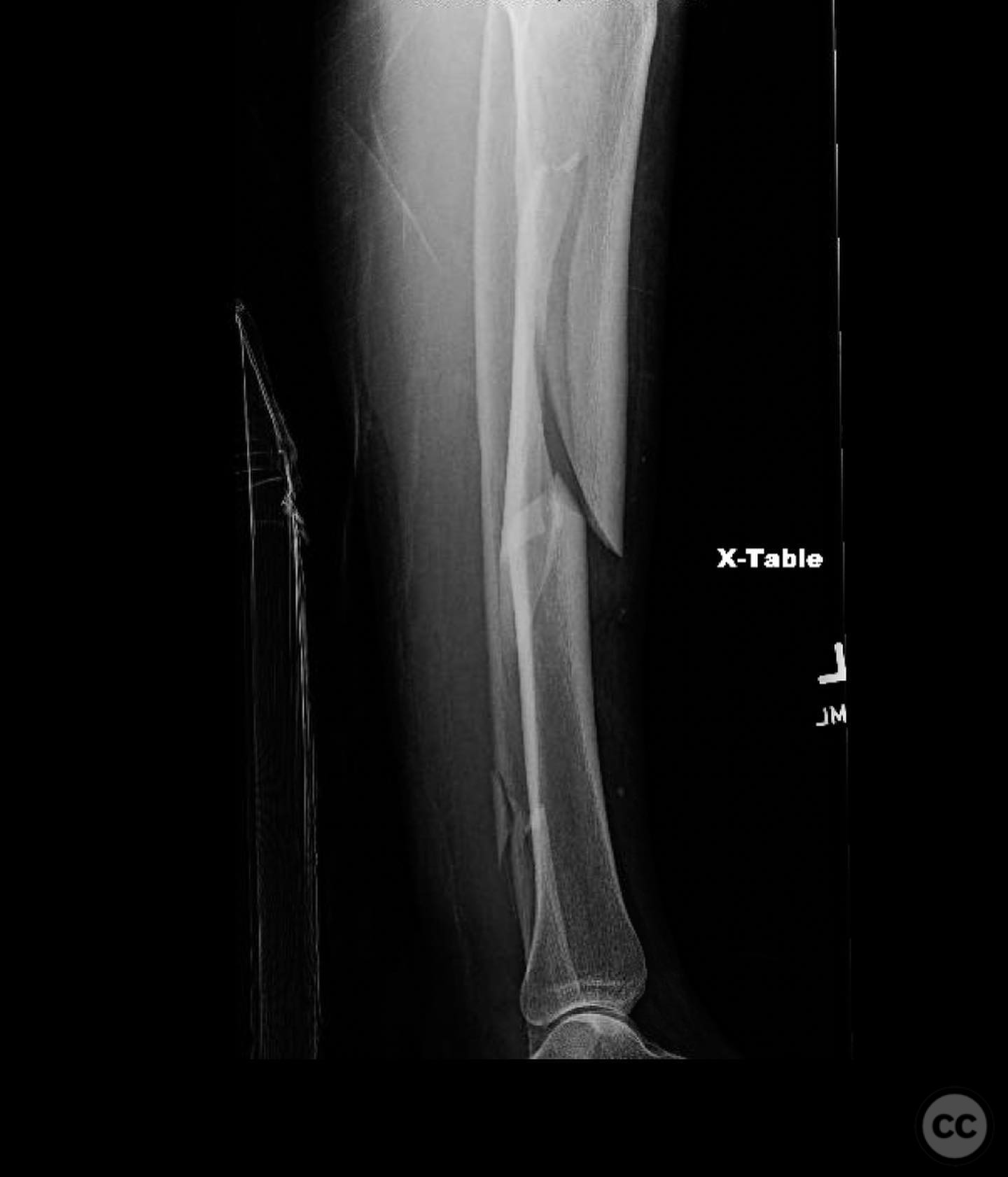
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail for tibial shaft fracture, lateral locking plate for tibial plateau fracture.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 160 times
17 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). AO/OTA 41-B3 Lateral Tibial Plateau Fracture with Ipsilateral Tibial Shaft Fracture. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 48867205 Published Online Jul 17 2025.