Revision of Distal Femur Nonunion with Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing and Medial Column Support
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
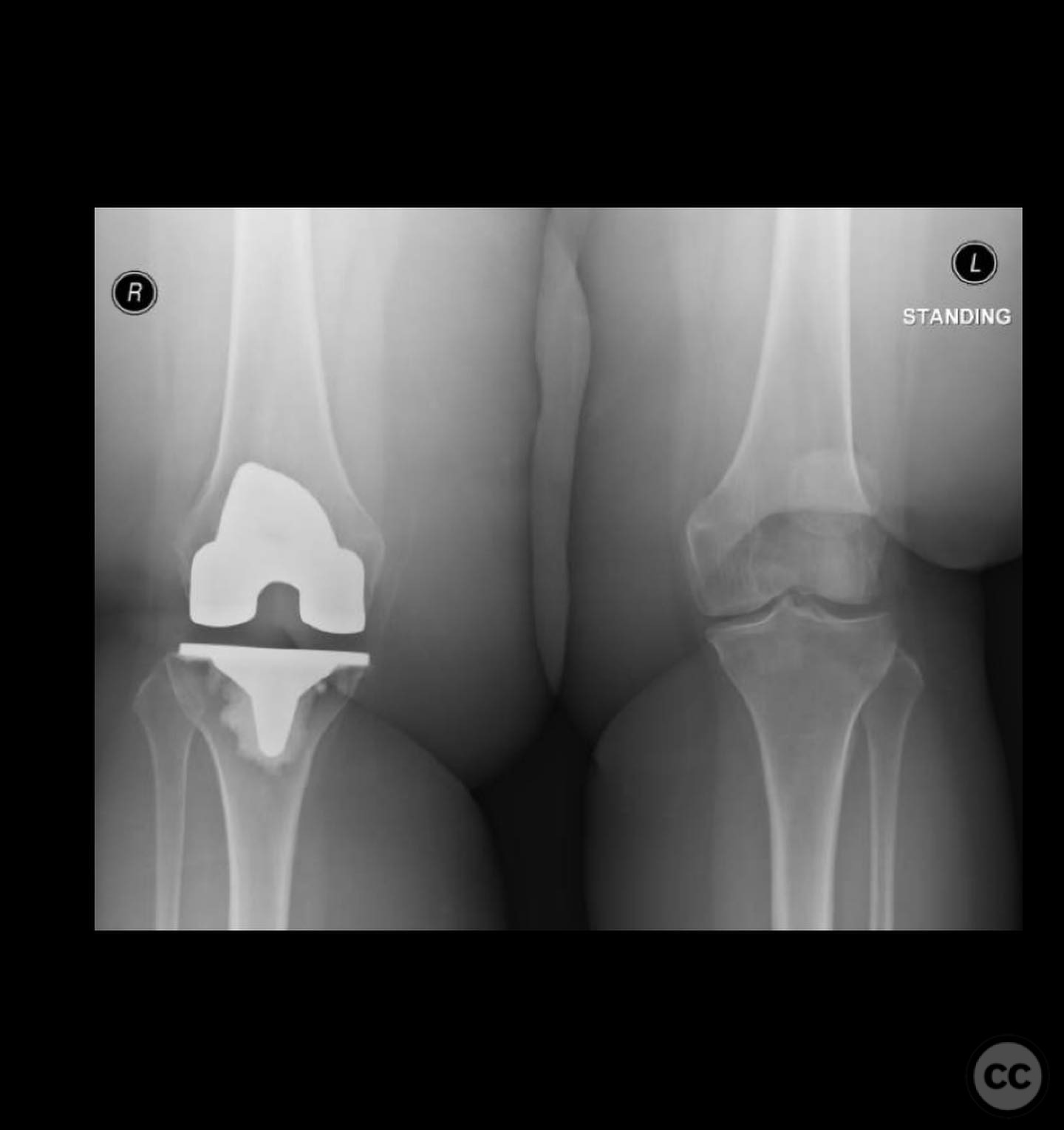
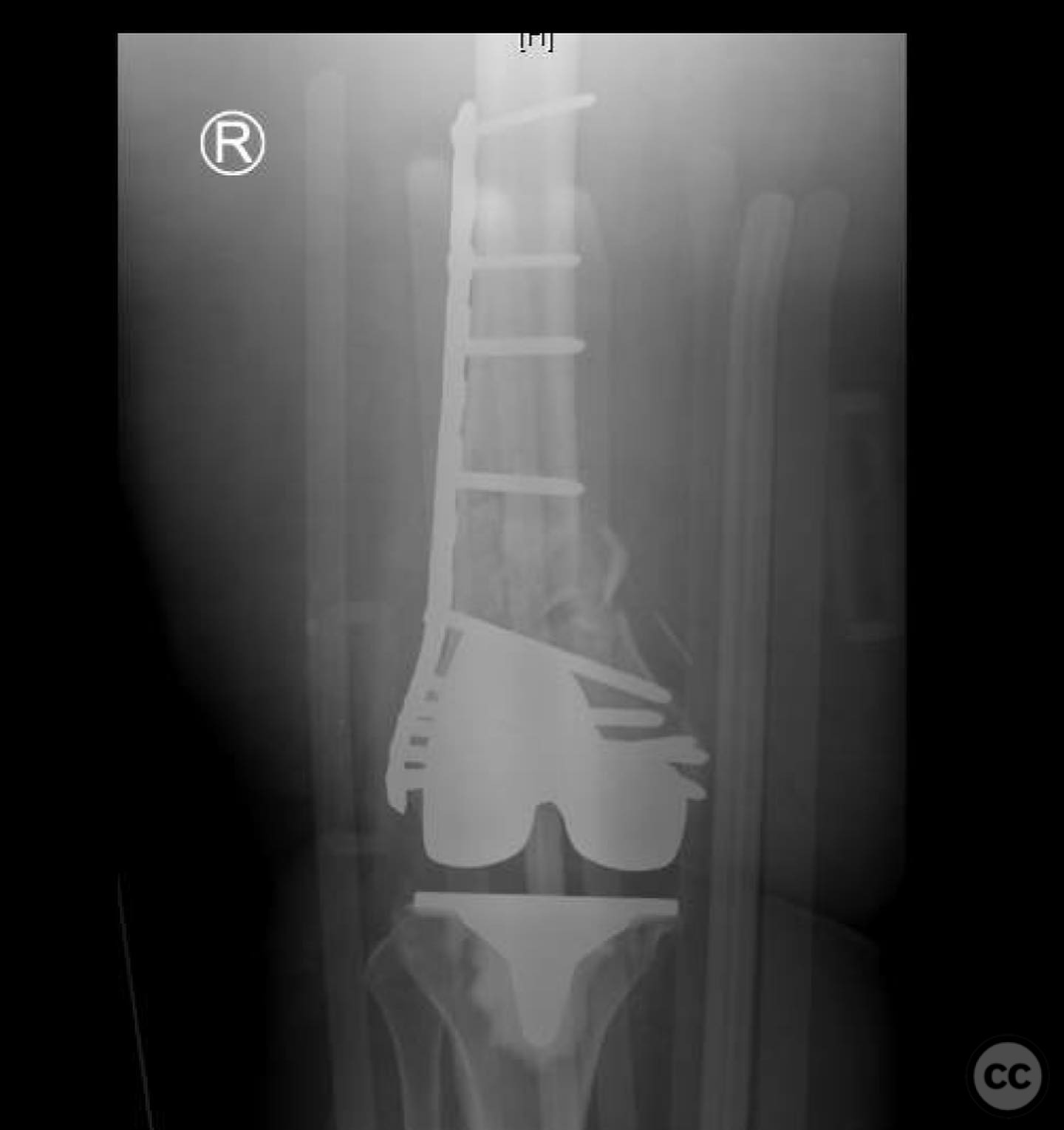
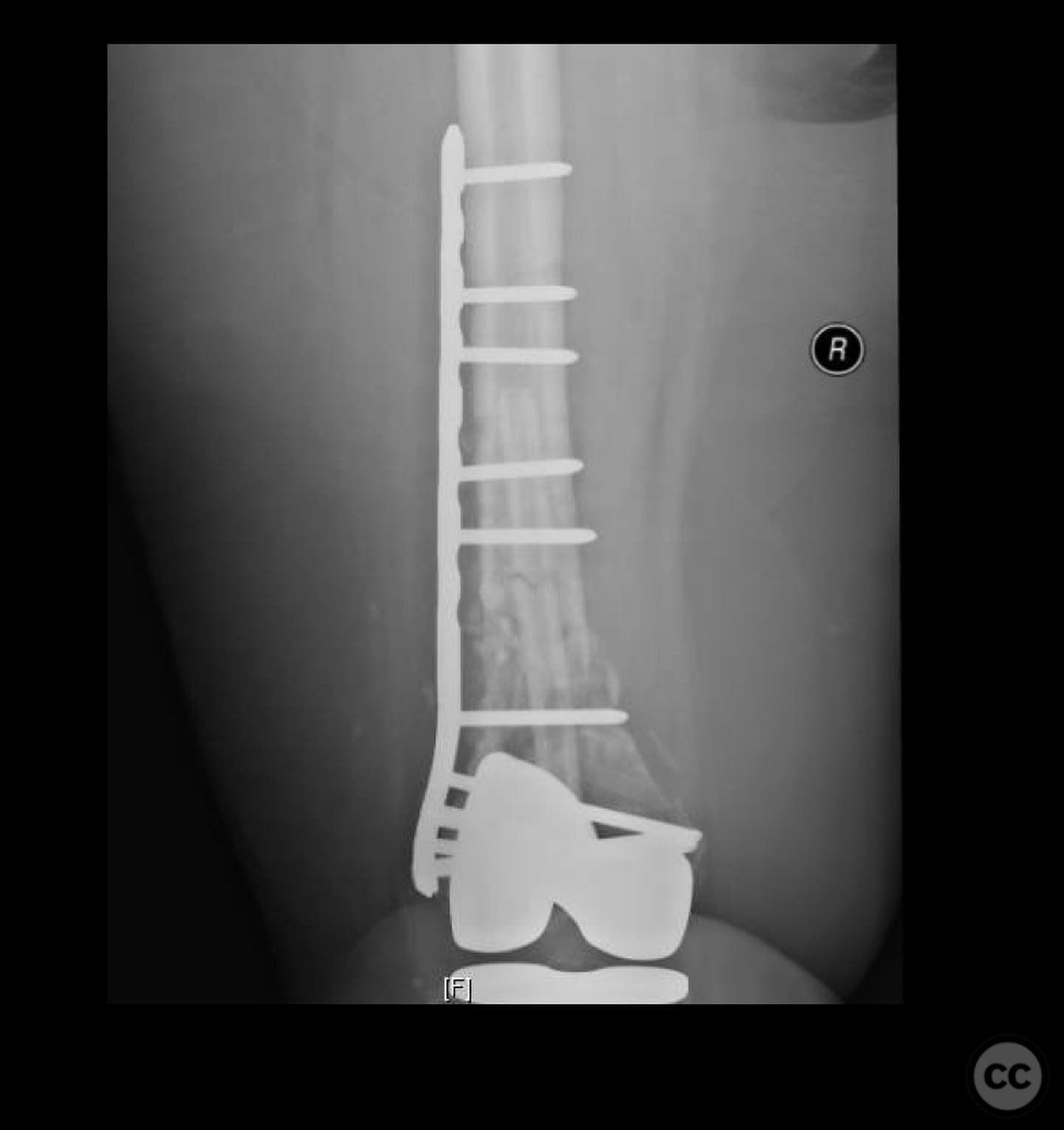
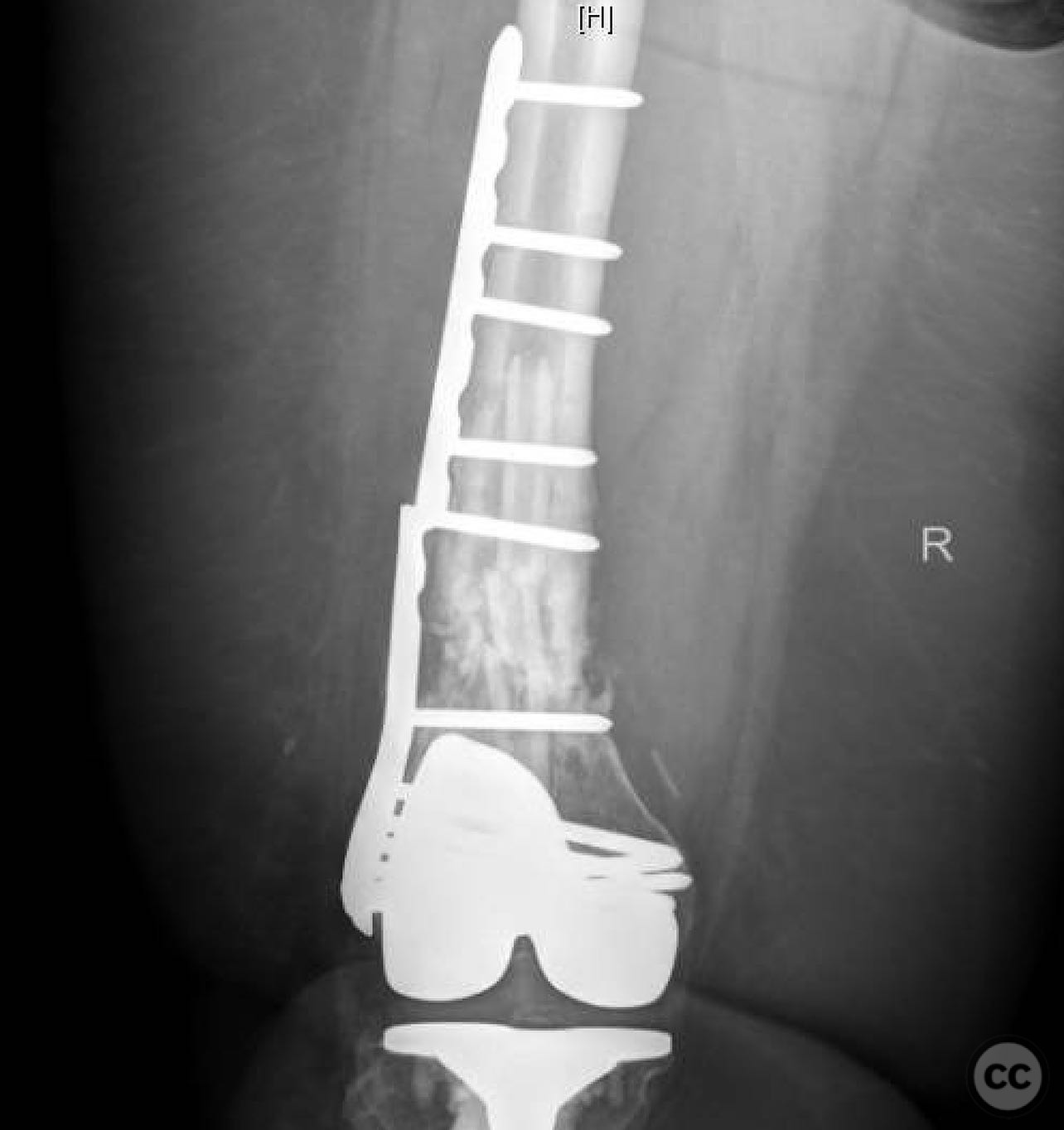
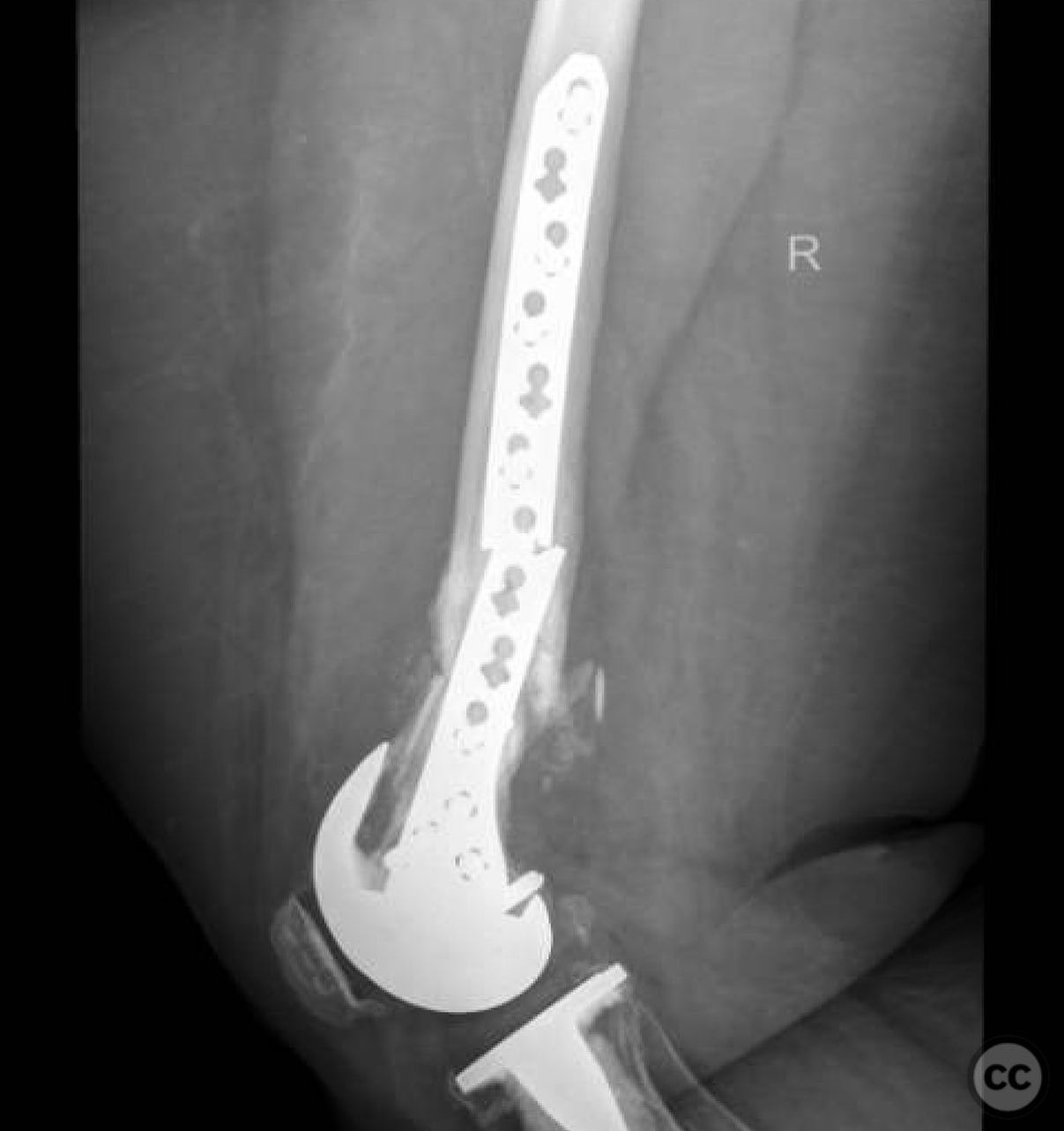
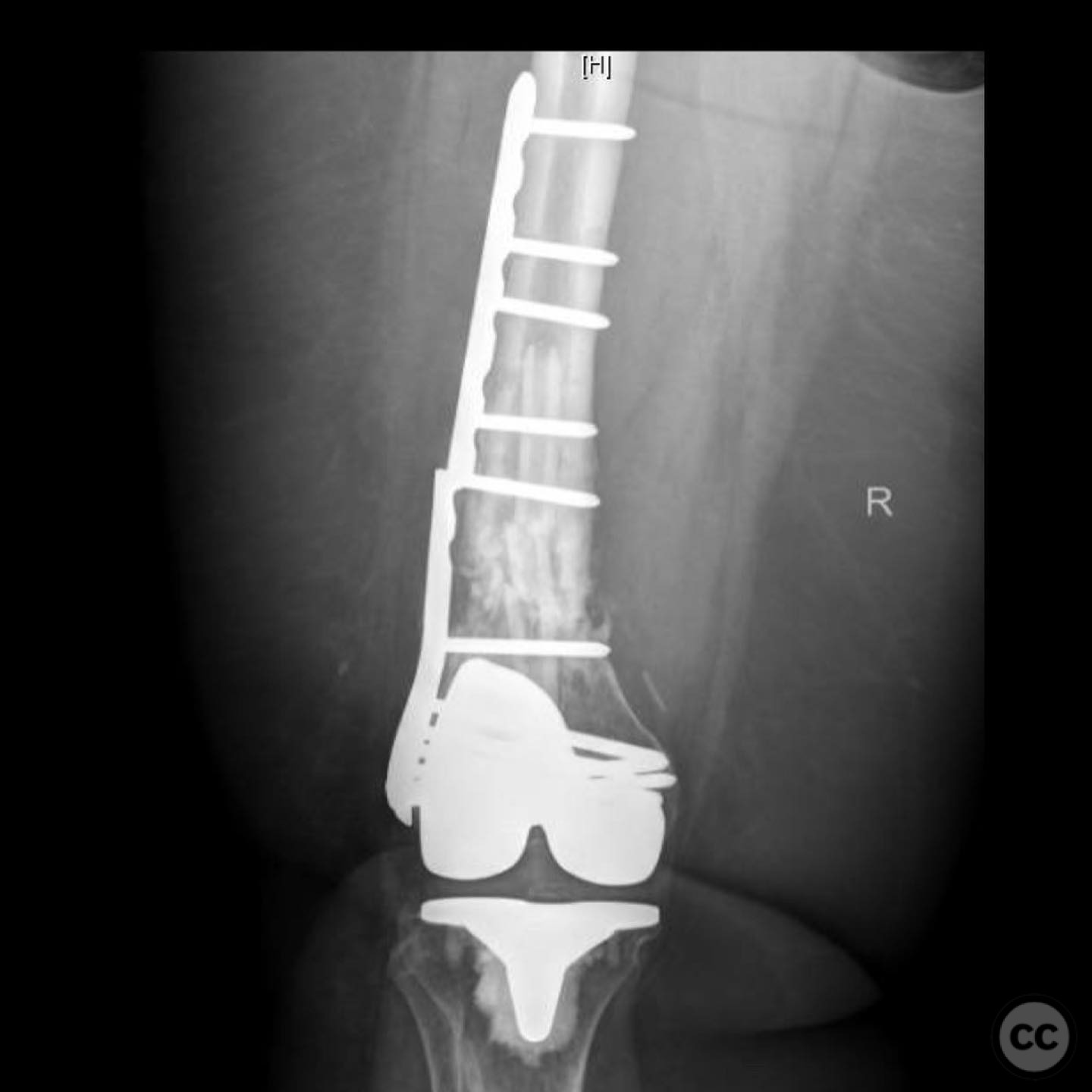
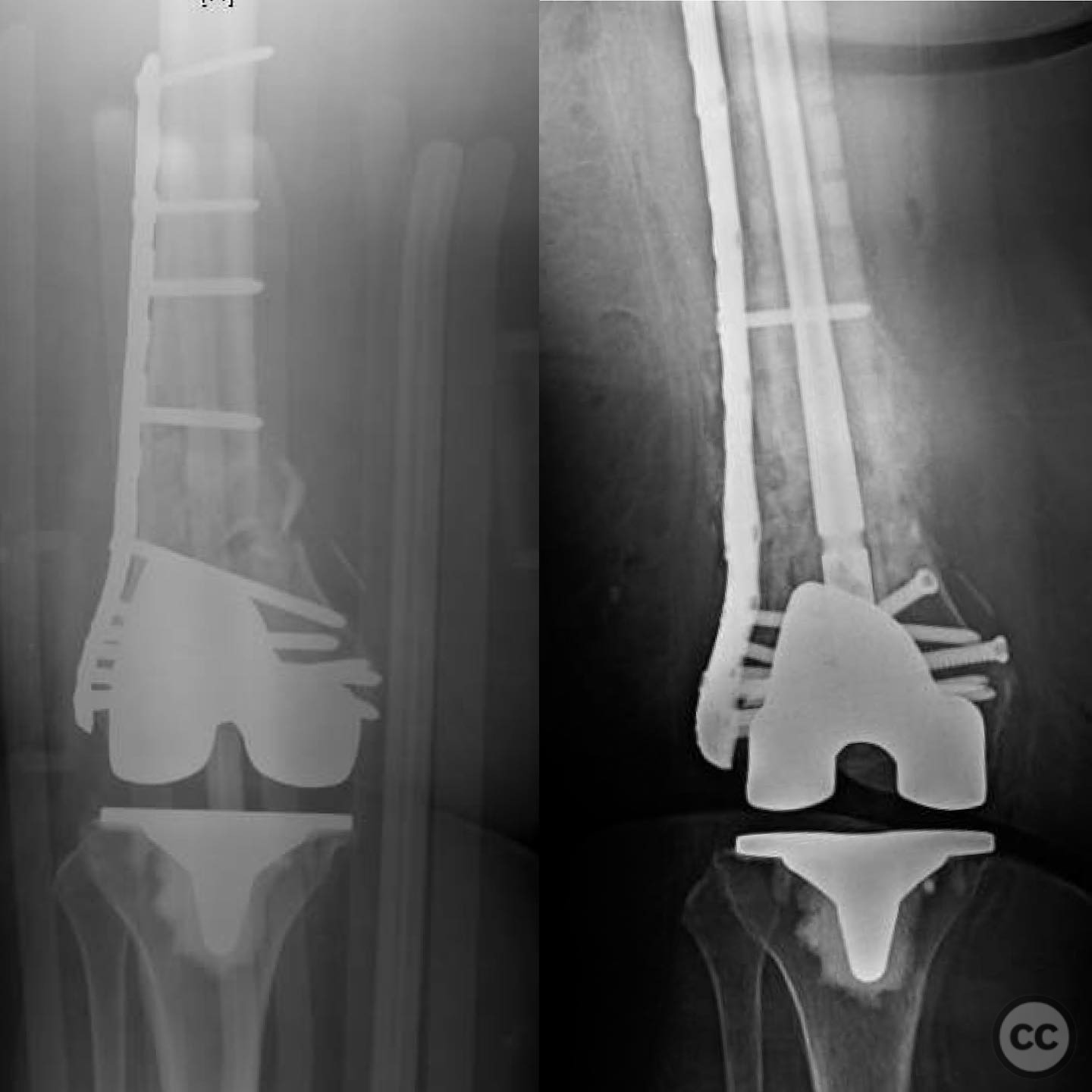
Clinical and radiological findings: A 62-year-old obese female with a history of a successful total knee arthroplasty (TKA) presented with a distal femur fracture following a fall. Initial open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) by a non-trauma trained orthopaedic surgeon resulted in nonunion and implant failure. A subsequent revision ORIF with endomedullary fibular strut also failed, leading to persistent pain and inability to ambulate. Radiological evaluation revealed a comminuted distal femur fracture with nonunion and mechanical insufficiency.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved addressing both mechanical and biological deficiencies of the nonunion. A retrograde intramedullary nail was selected for mechanical stabilization, with emphasis on medial column support due to the patient's obesity and previous fixation failures. The plan included realignment, re-establishment of the medullary canal, and bone grafting using the Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator (RIA) technique.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on a radiolucent table to facilitate fluoroscopic imaging during the procedure.
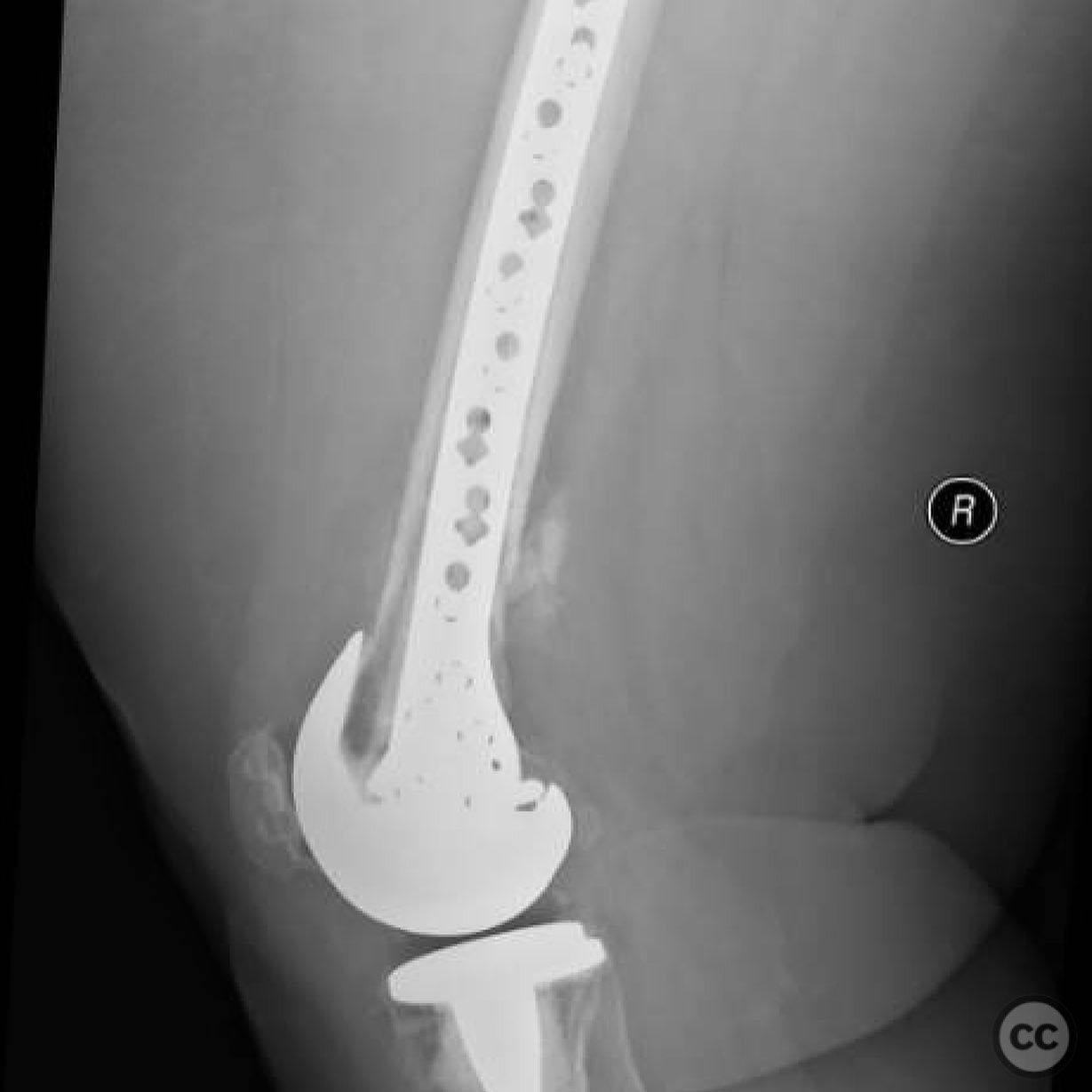
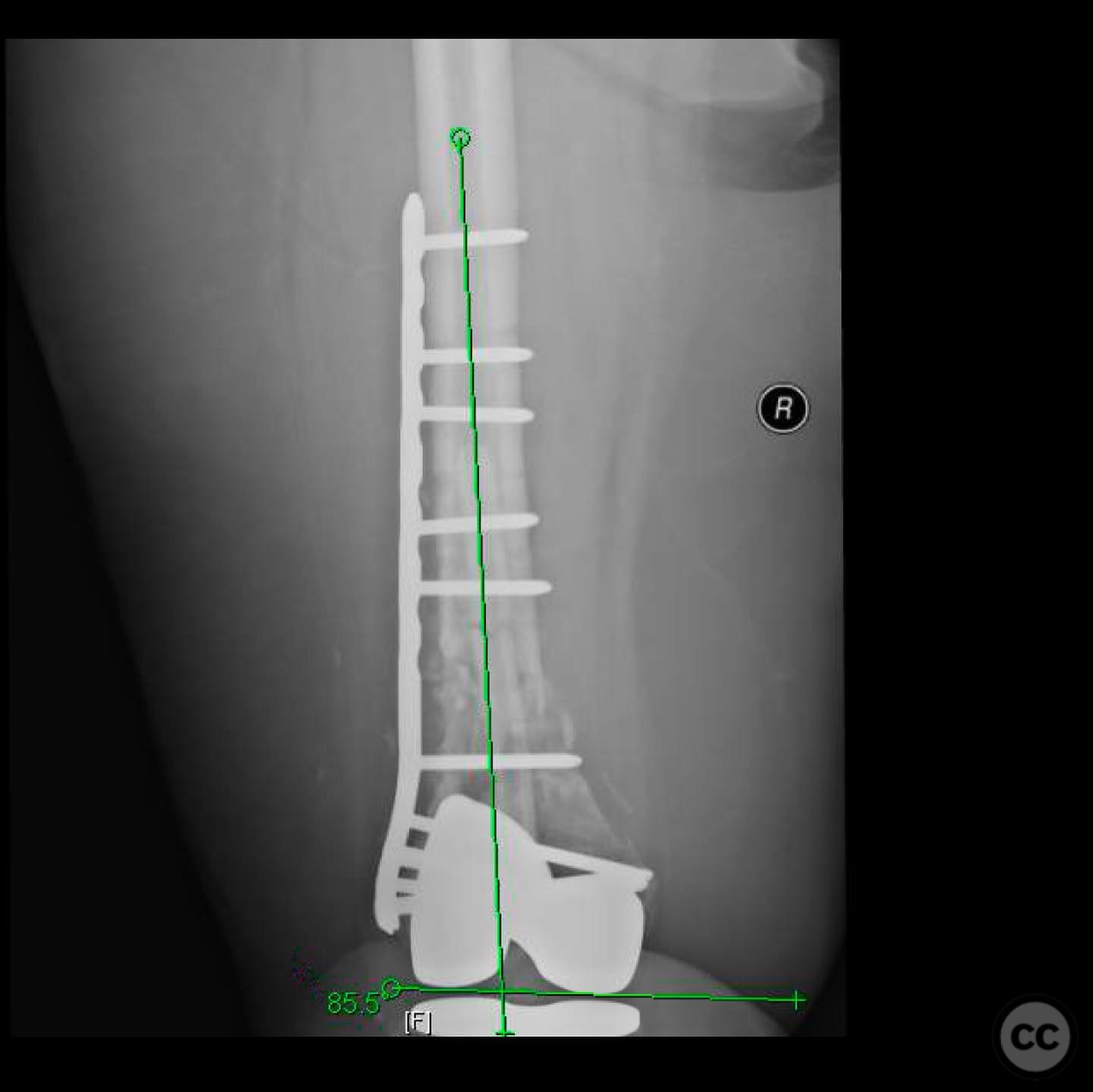
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal midline incision was made over the distal femur. The nonunion site was approached with careful dissection using a scalpel to preserve soft tissue and vascularity. The fibular strut was removed with difficulty due to healing above and below the fracture site, requiring long solid reamers for extraction. The medullary canal was re-established, and the fracture was realigned under fluoroscopic guidance.
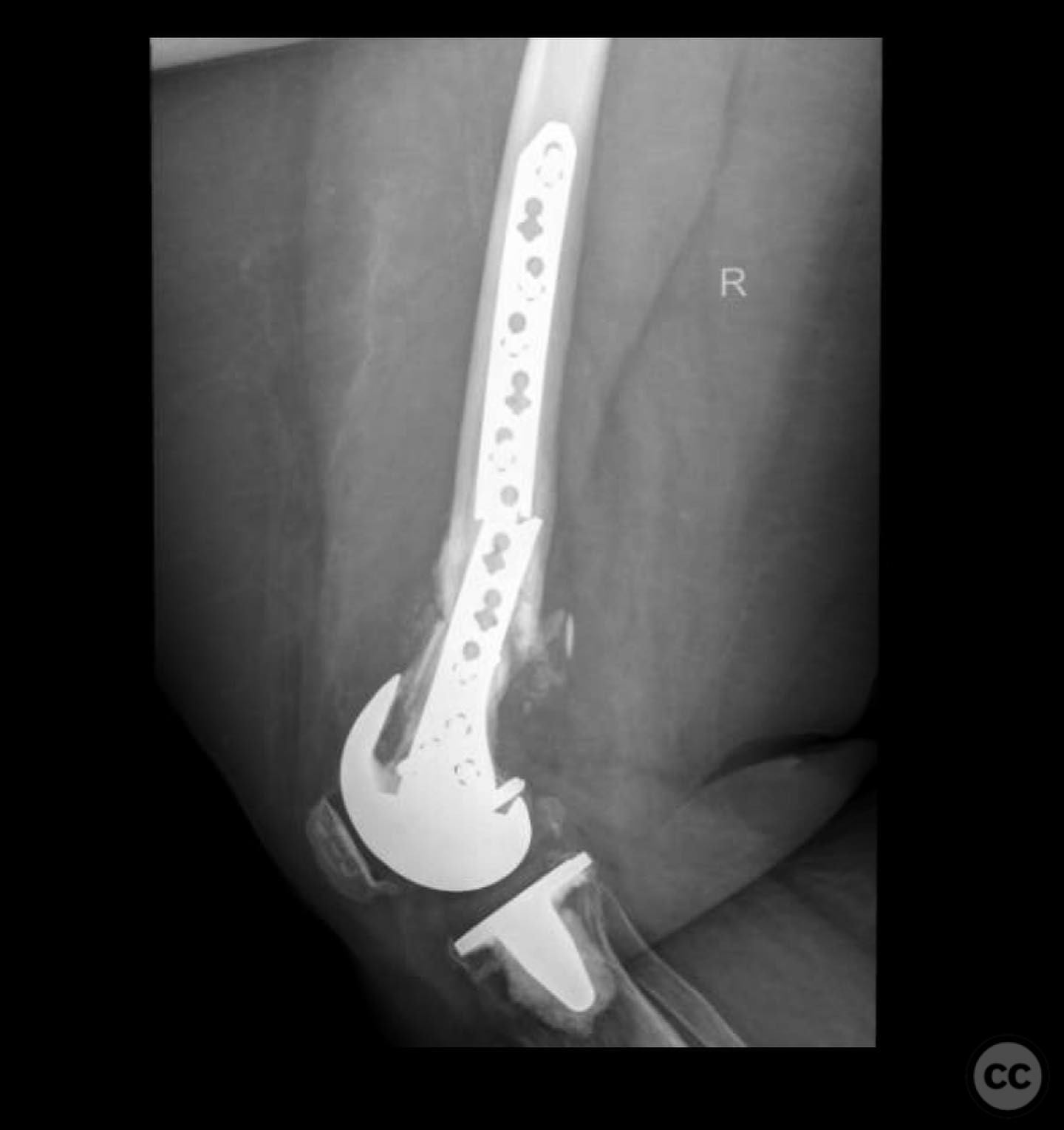
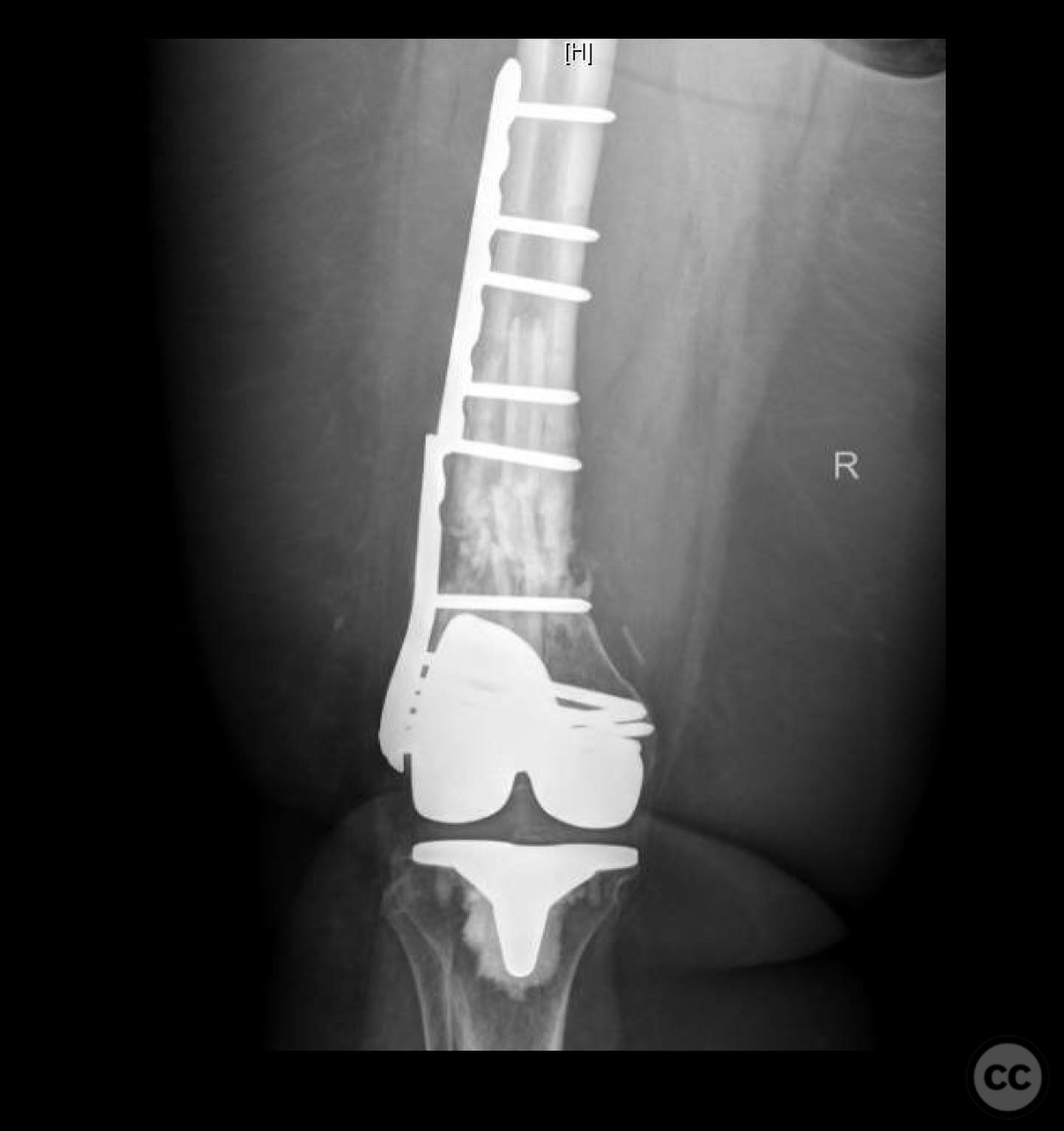
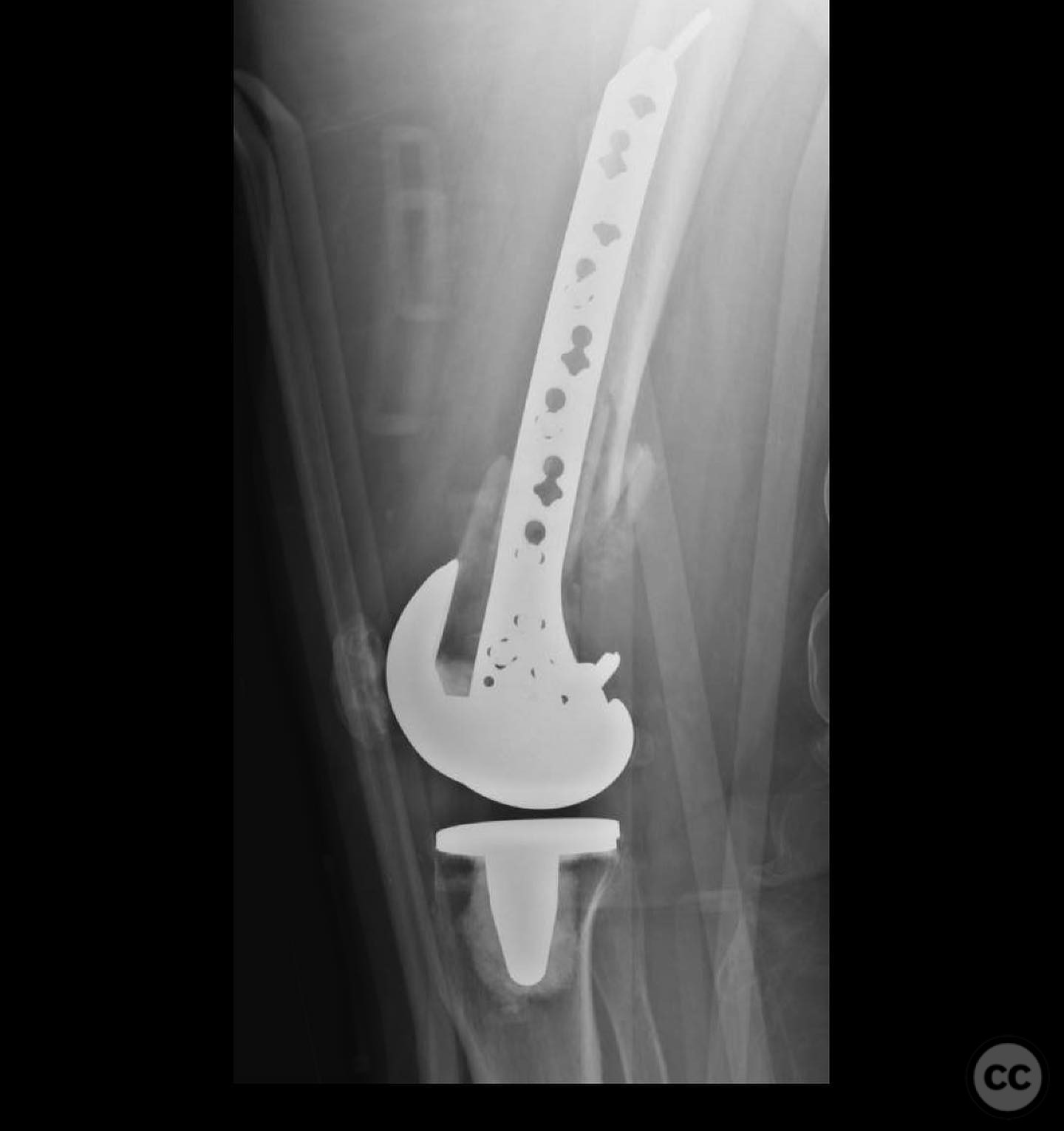
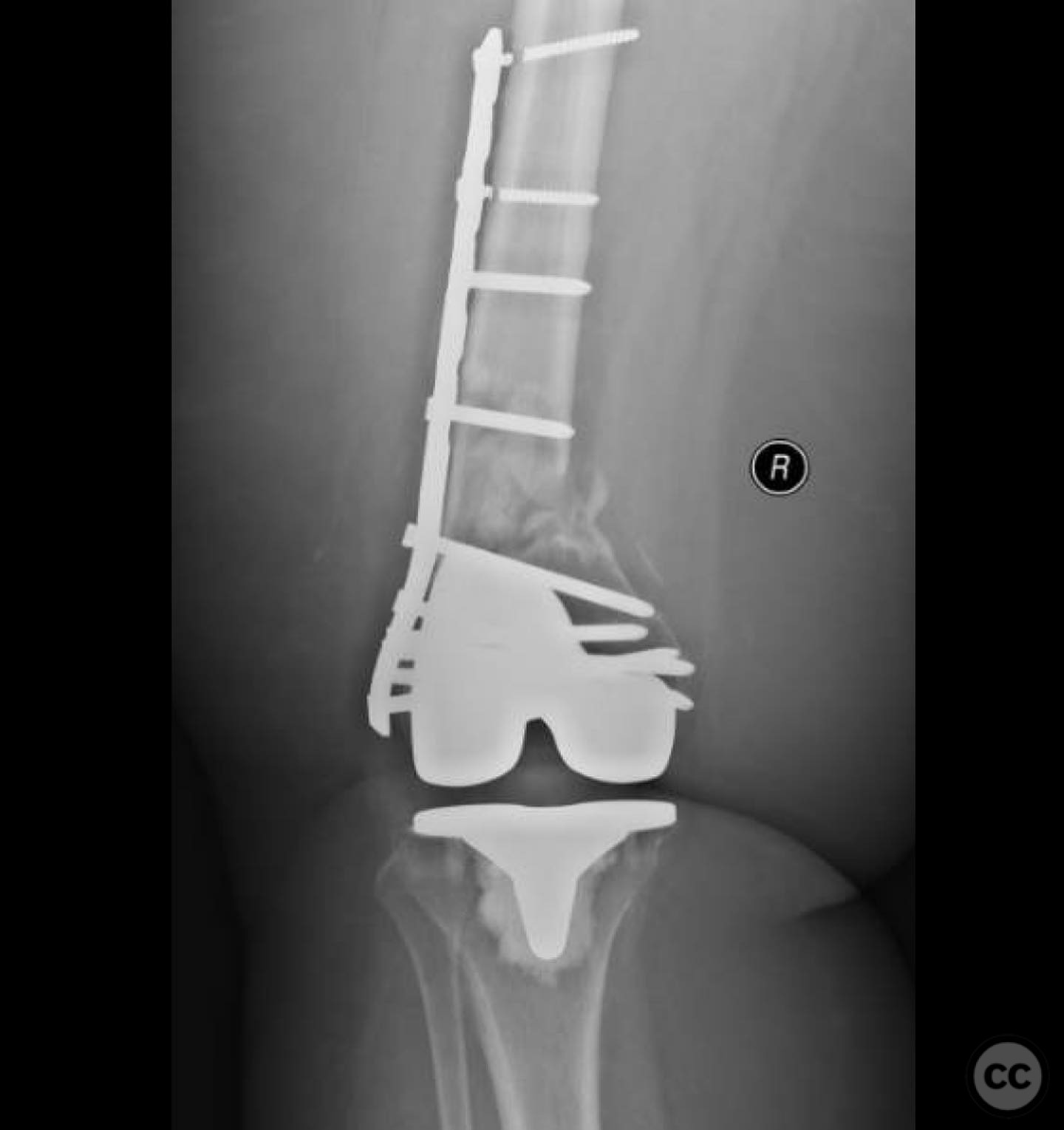
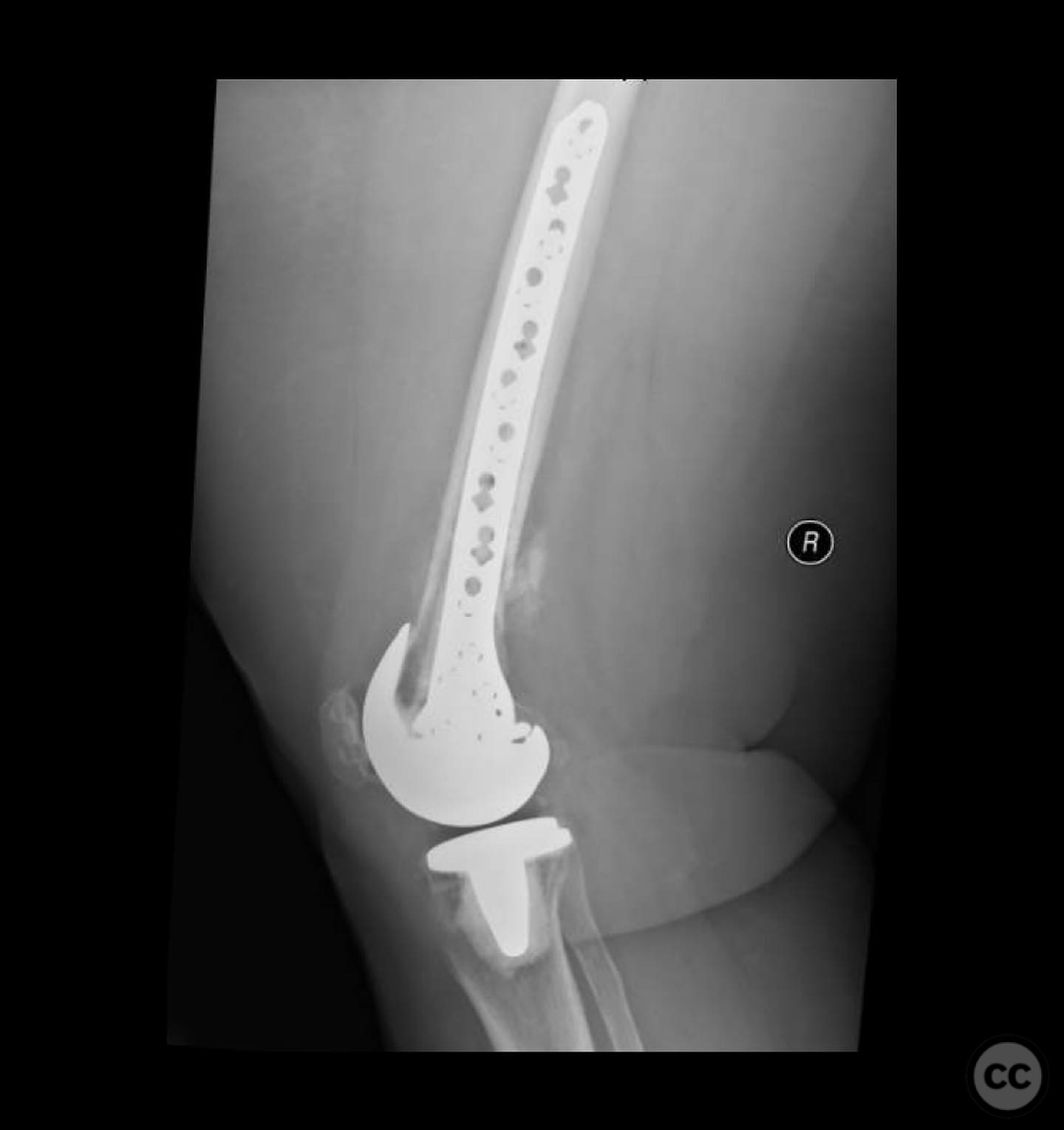
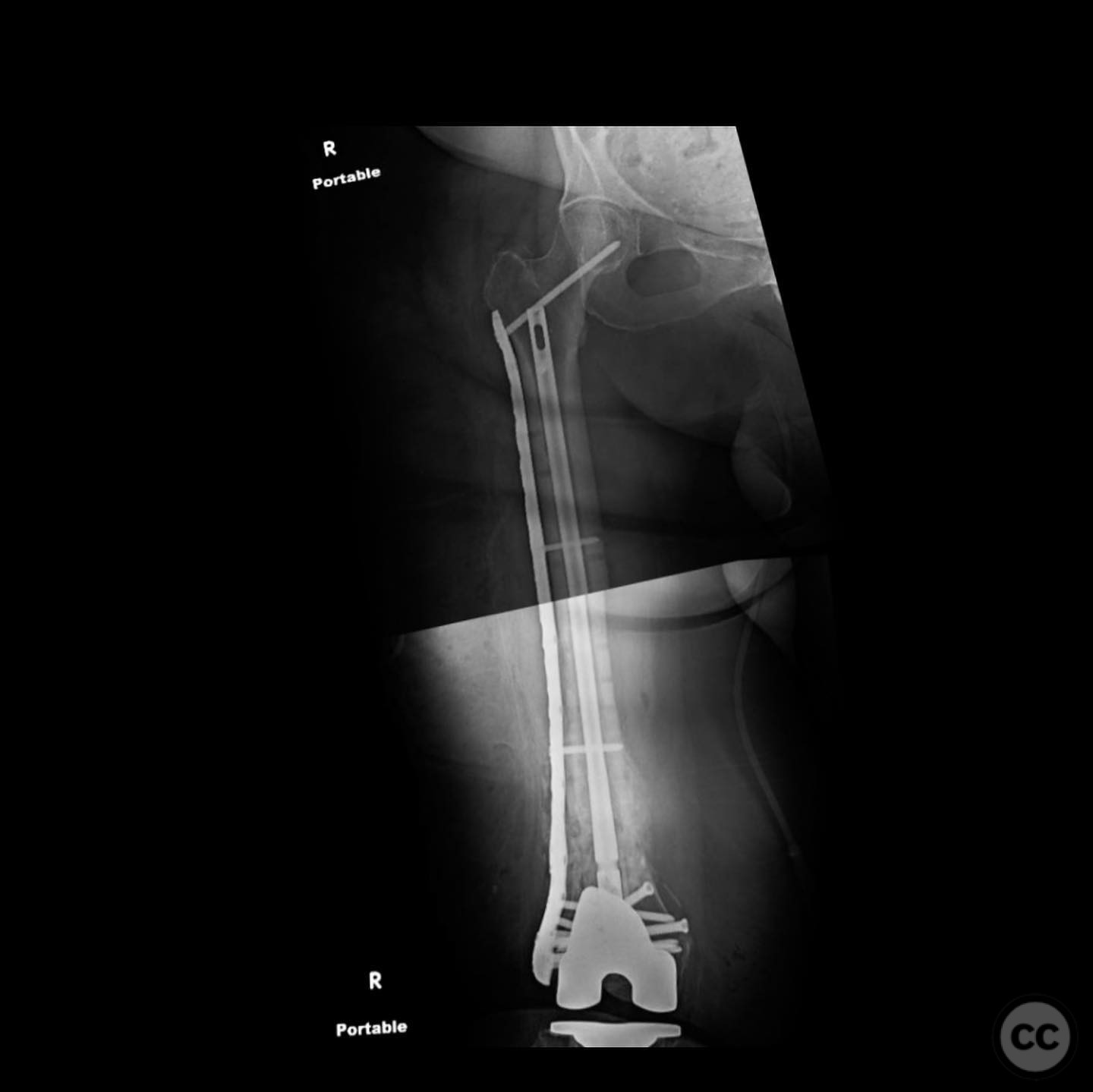
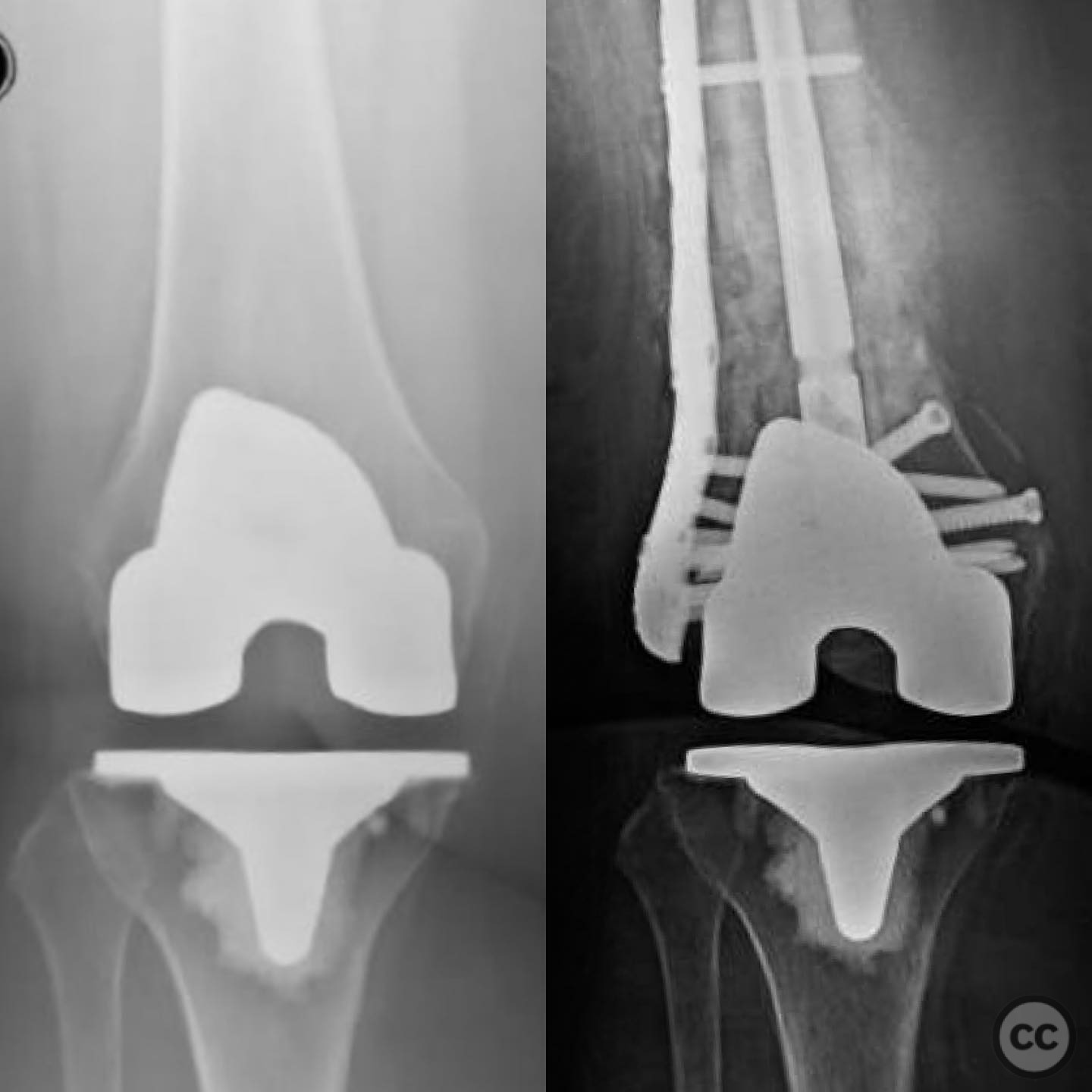
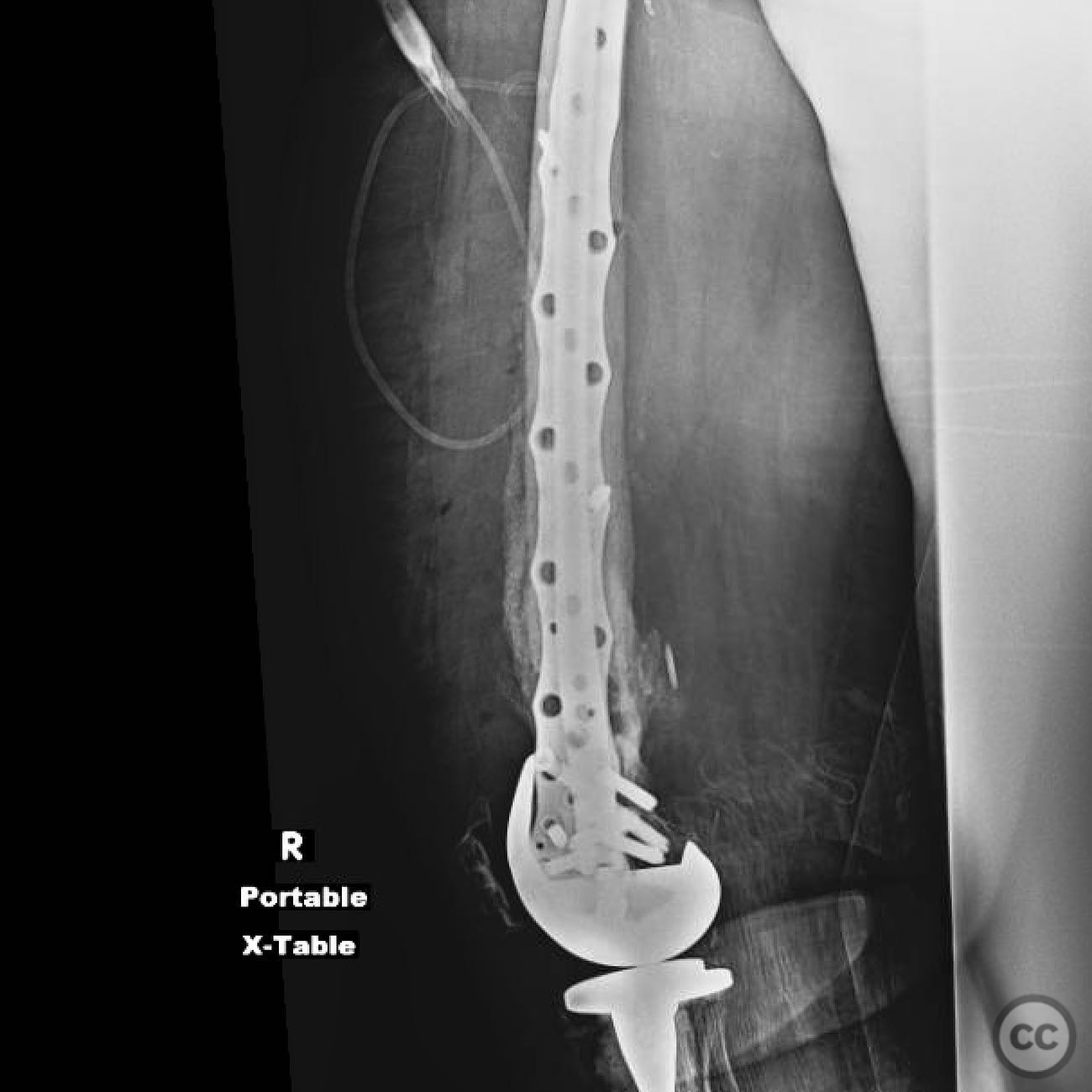
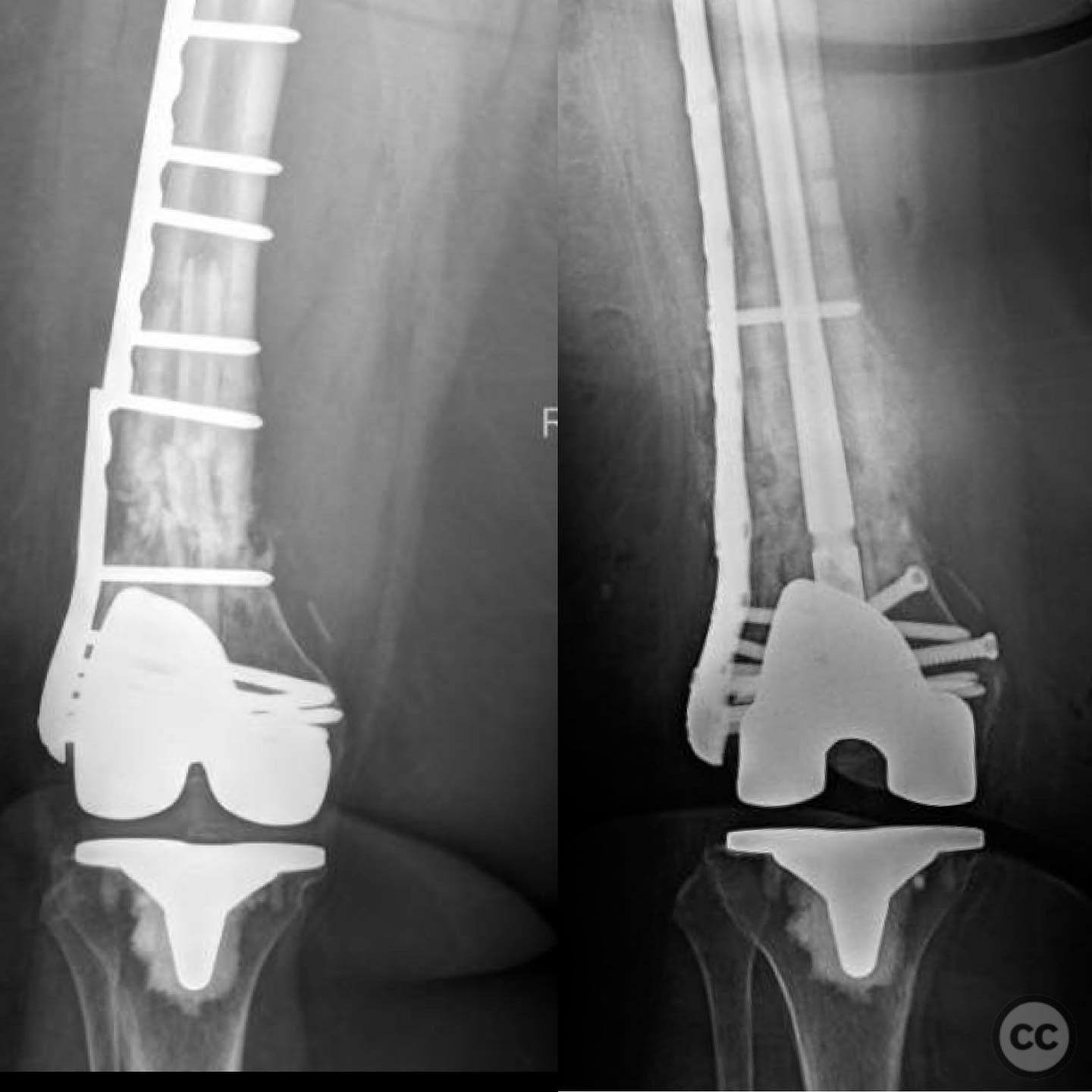
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted the challenge of extracting the fibular strut due to its healed state. Intraoperative alignment was verified with flat plate imaging to ensure proper positioning before fixation. The retrograde intramedullary nail was inserted through the open box of the DePuy Attune component, providing medial column support. Bone grafting was performed using RIA to enhance biological healing potential.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included protected weight-bearing with gradual progression based on radiological evidence of healing. Emphasis was placed on maintaining alignment and stability during the early postoperative period.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Retrograde intramedullary nail, Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator (RIA) system, bone graft material.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 266 times
15 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Revision of Distal Femur Nonunion with Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing and Medial Column Support. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 47773343 Published Online Jul 15 2025.