Displaced Clavicle and Glenoid Fractures in a Motocross Rider
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
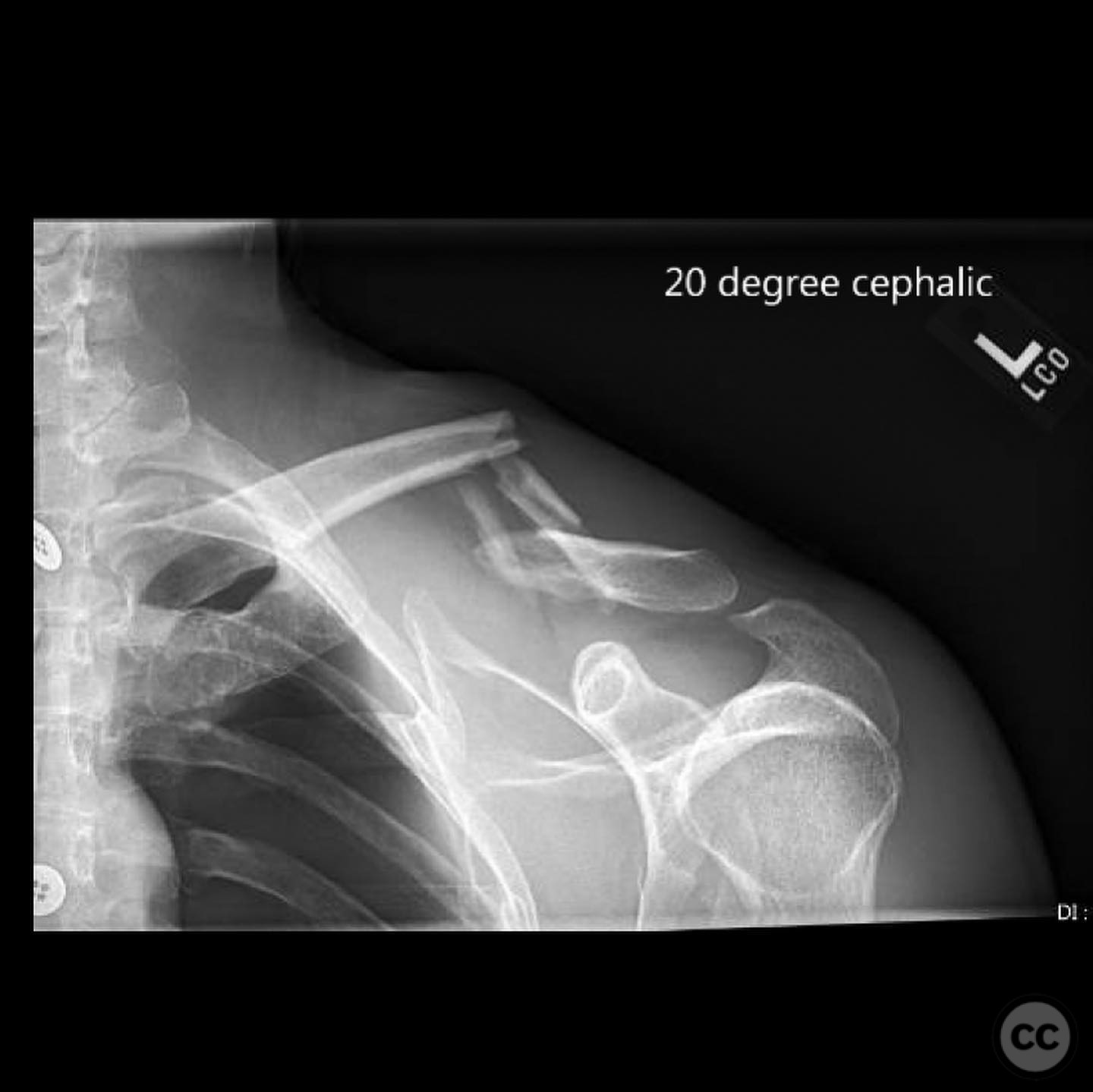
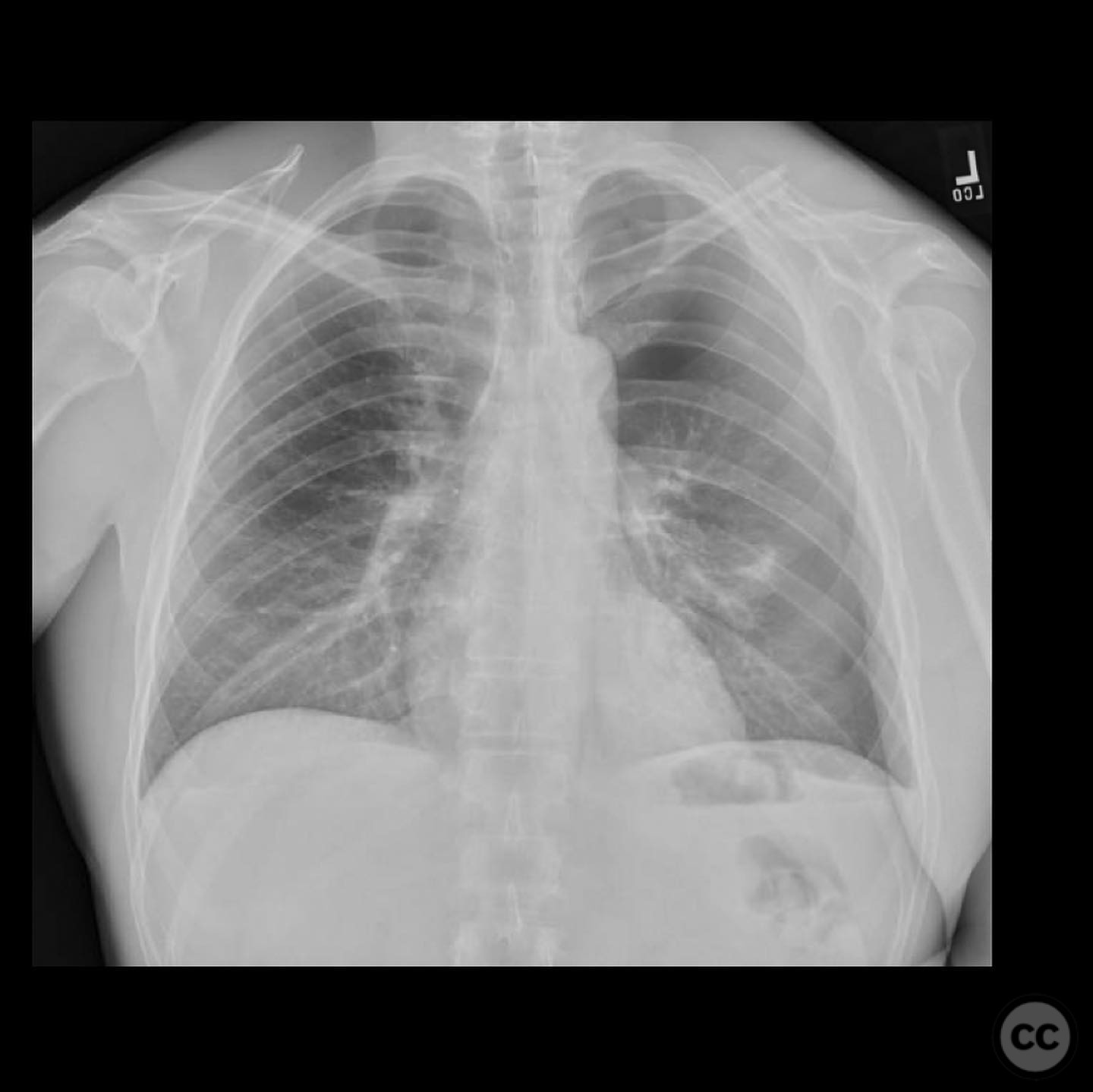
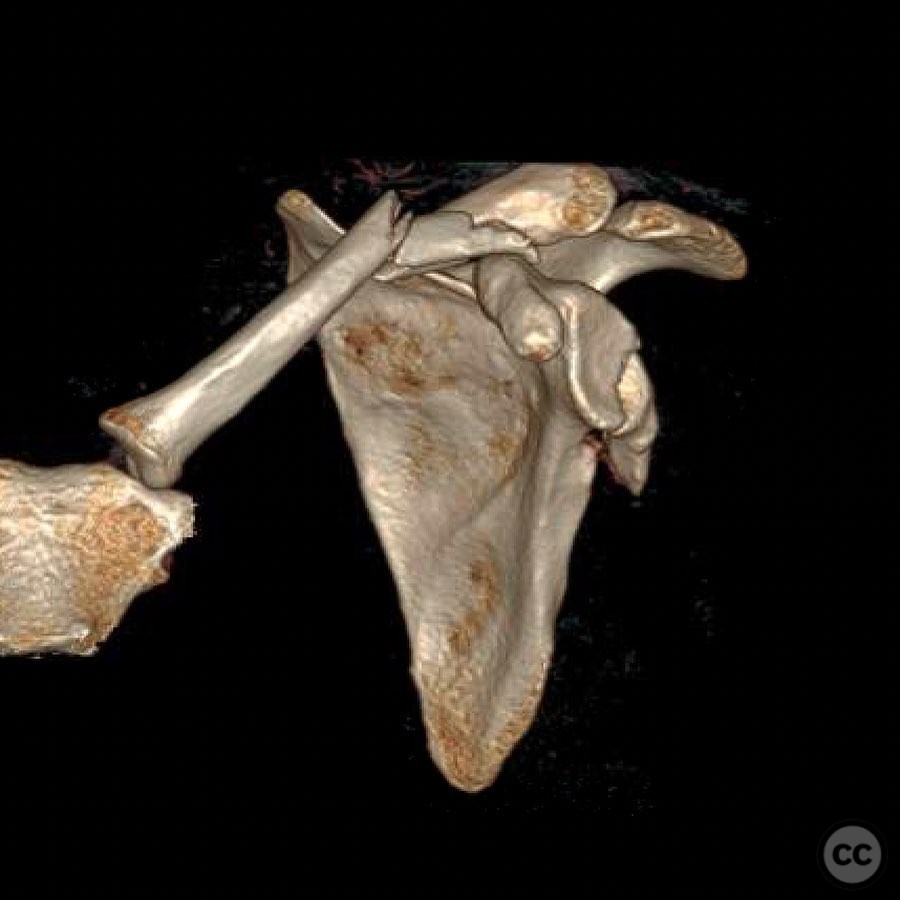
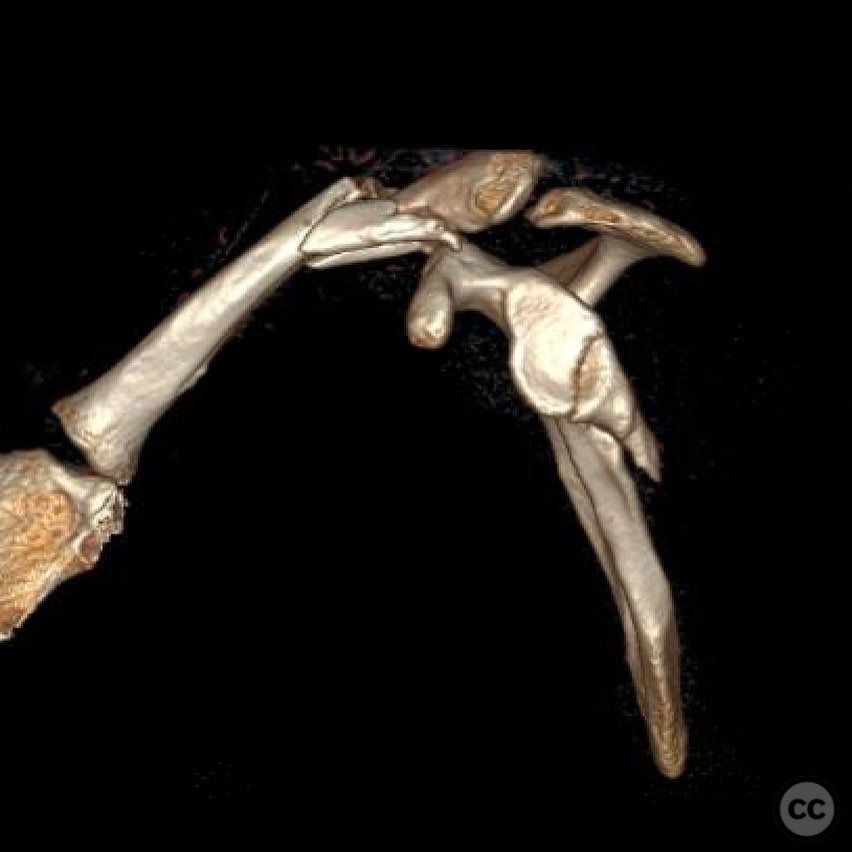
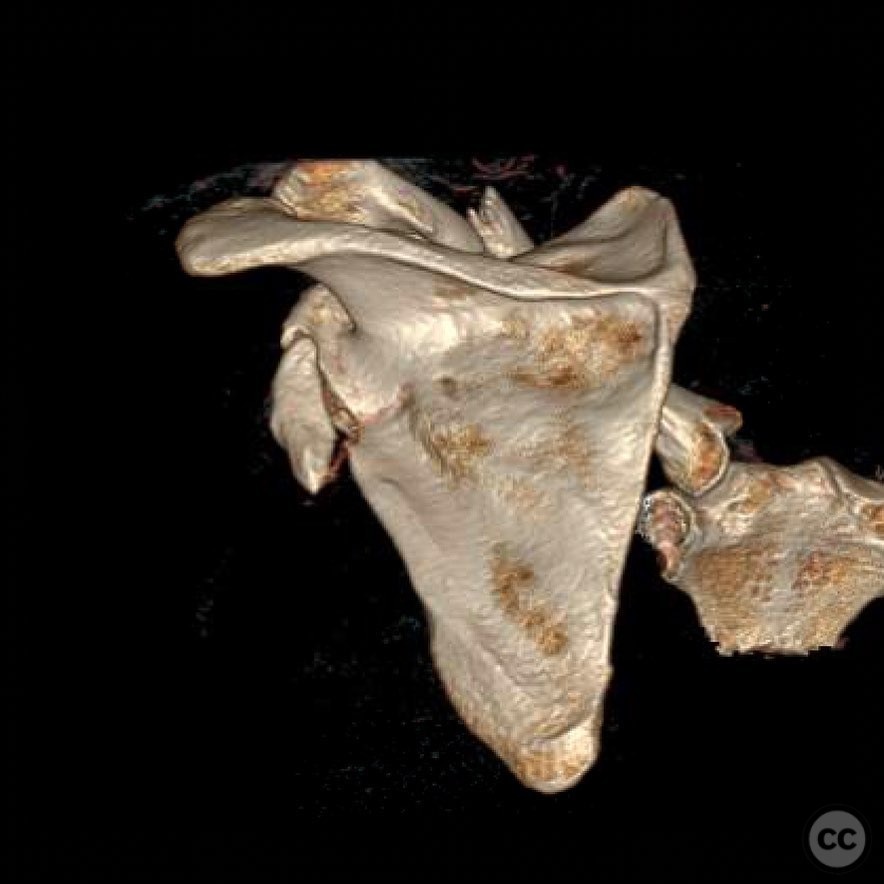
Clinical and radiological findings: A young, active motocross rider presented with displaced fractures of the clavicle and glenoid, accompanied by rib fractures and a pneumothorax. The scapular body, neck, and majority of the glenoid remained in continuity, ruling out a "floating shoulder" diagnosis. Radiological assessment confirmed a displaced clavicle fracture and a B-type glenoid fracture on the same side.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved surgical fixation of both the clavicle and glenoid fractures to optimize upper extremity strength and prevent potential biomechanical dysfunction or malunion-related complications. The clavicle was prioritized for fixation, followed by the glenoid. The modified Judet approach was selected for the glenoid repair.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine for the clavicle fixation procedure. Two days later, the patient was repositioned laterally for the glenoid fixation.
Anatomical surgical approach: For the clavicle fixation, a standard superior approach was utilized. For the glenoid, a modified Judet approach was employed, involving a posterior incision to access the infraglenoid and teres minor interval beneath the posterior deltoid muscle, ensuring careful avoidance of neurovascular structures.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of understanding posterior shoulder girdle anatomy to avoid nerve and artery injury during the modified Judet approach. The decision to use this approach over a limited lateral border/neck approach was based on the surgeon's comfort level and experience with posterior shoulder anatomy.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early mobilization with a focus on maintaining range of motion and gradual strengthening exercises to support recovery and return to motocross activities.
Follow up: Not specified
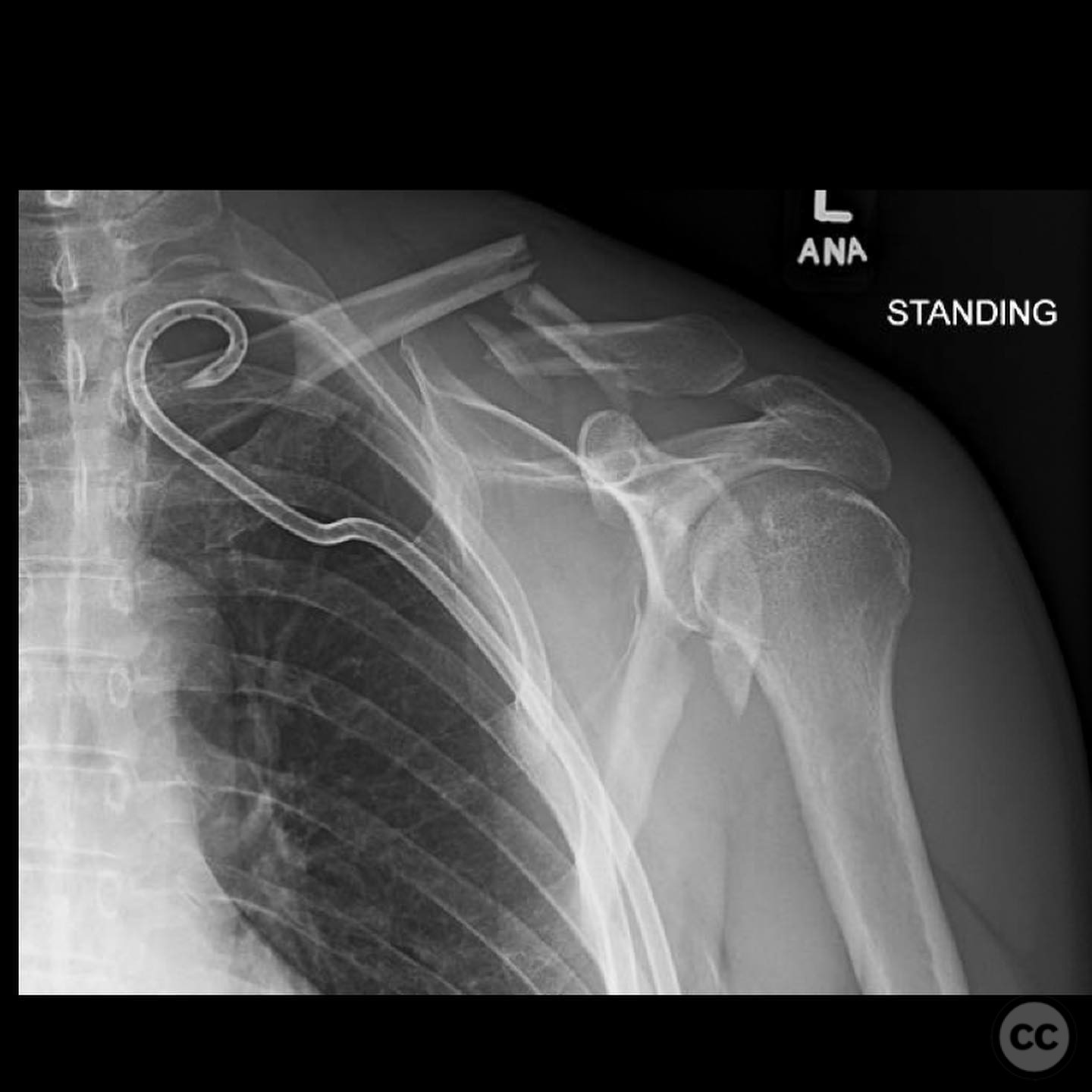
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included a clavicle plate and screws for the clavicle fracture, and a glenoid plate with screws for the glenoid fracture fixation.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. .(.jpg)
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. _1.jpg)
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. _2.jpg)
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. _3.jpg)
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. _4.jpg)
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. _6.jpg)
 with a clavicle_ glenoid and rib fractures- and a pneumothorax. _5.jpg)
Article viewed 161 times
16 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Displaced Clavicle and Glenoid Fractures in a Motocross Rider. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 47375526 Published Online Jul 16 2025.