Open Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fracture in an Adolescent: ORIF Approach
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
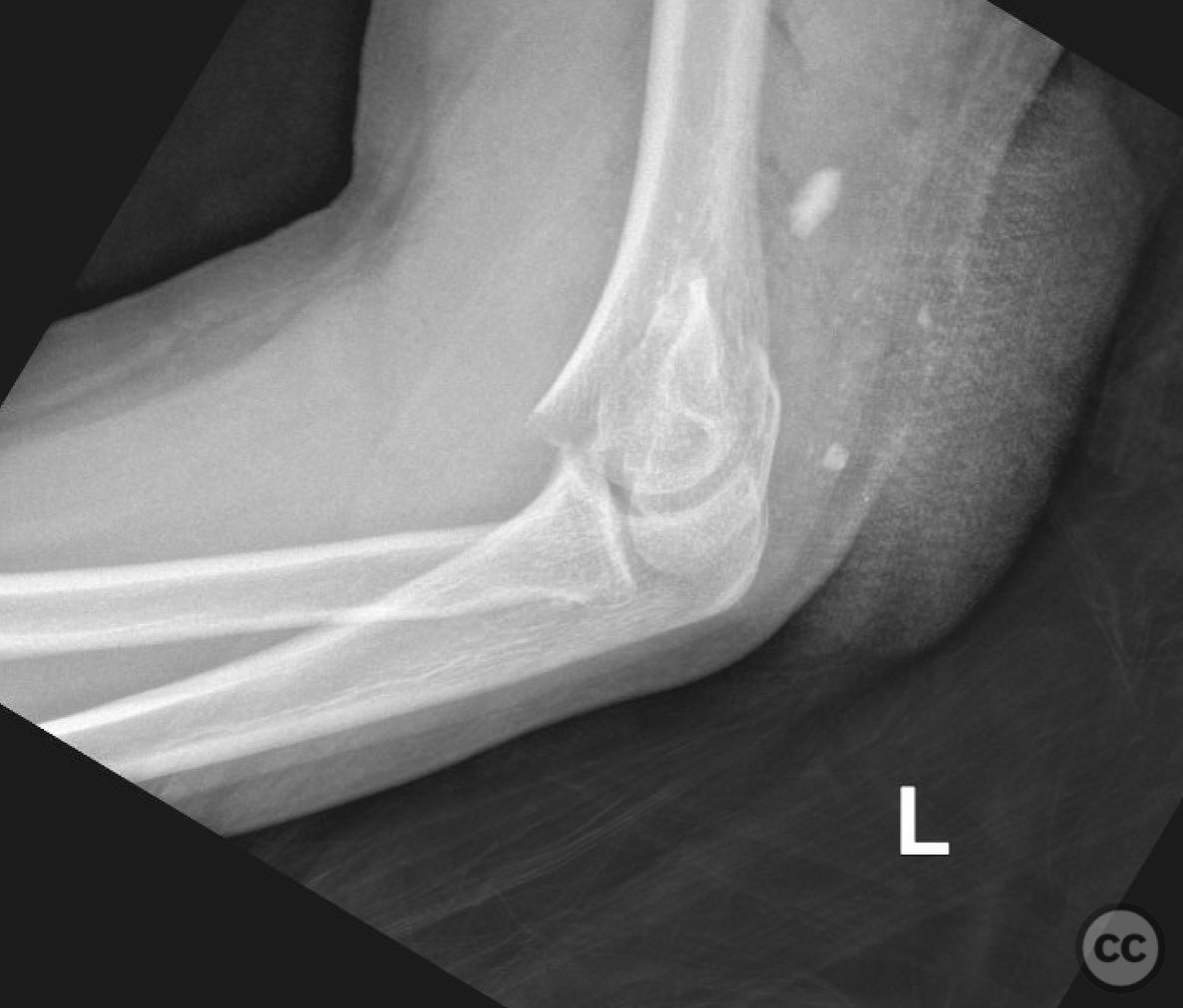
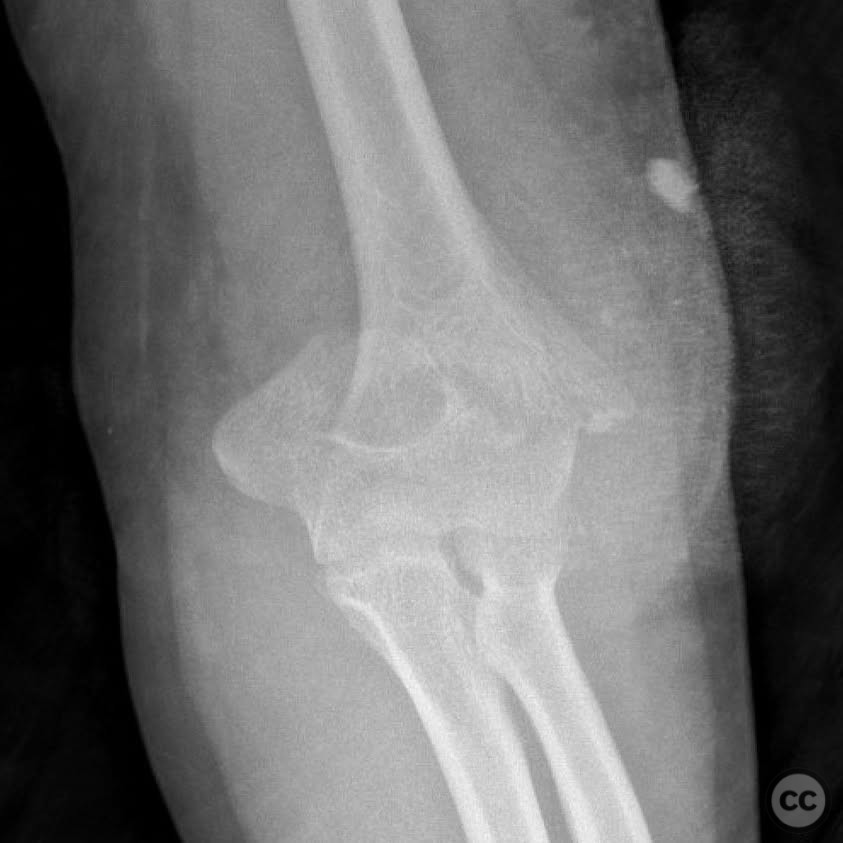
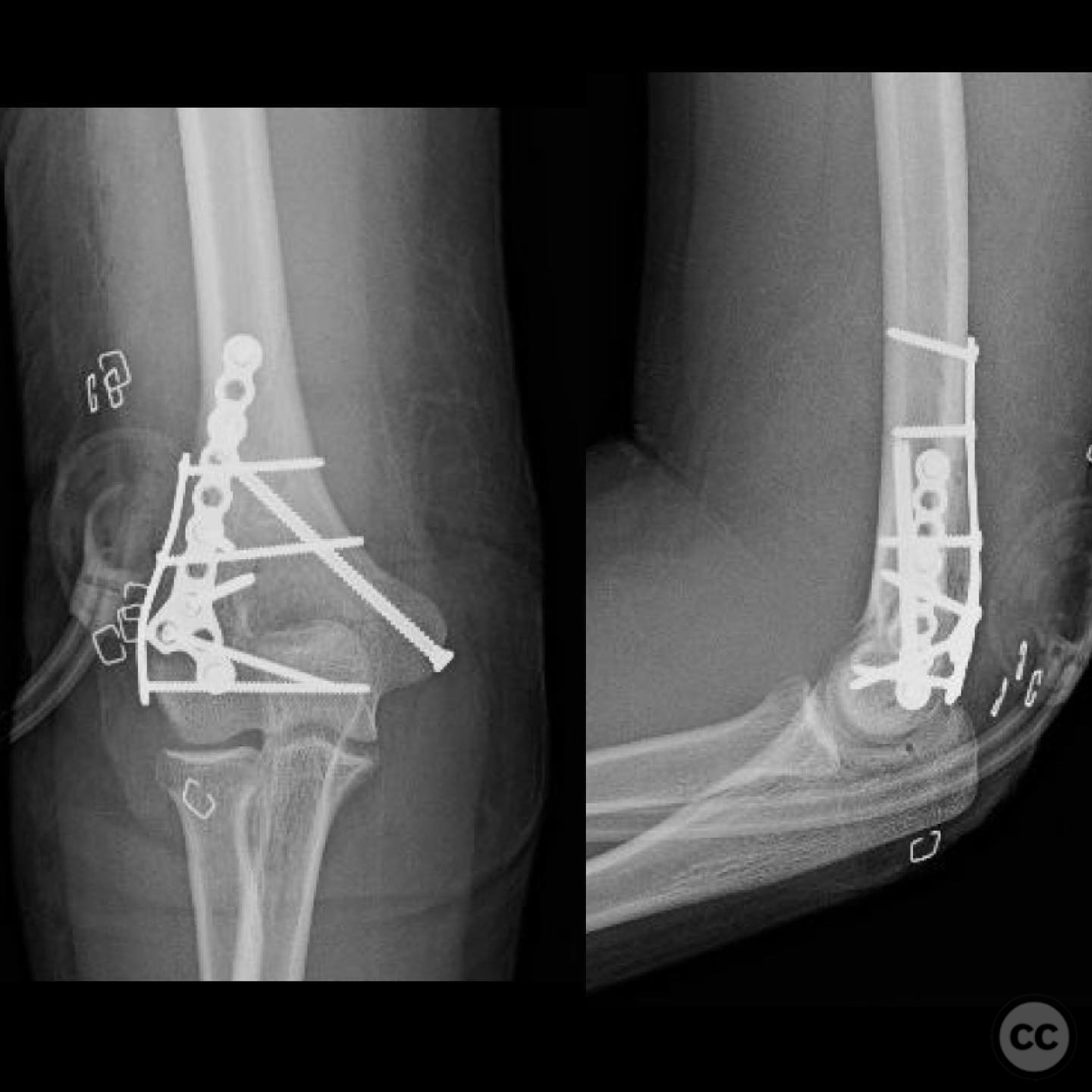
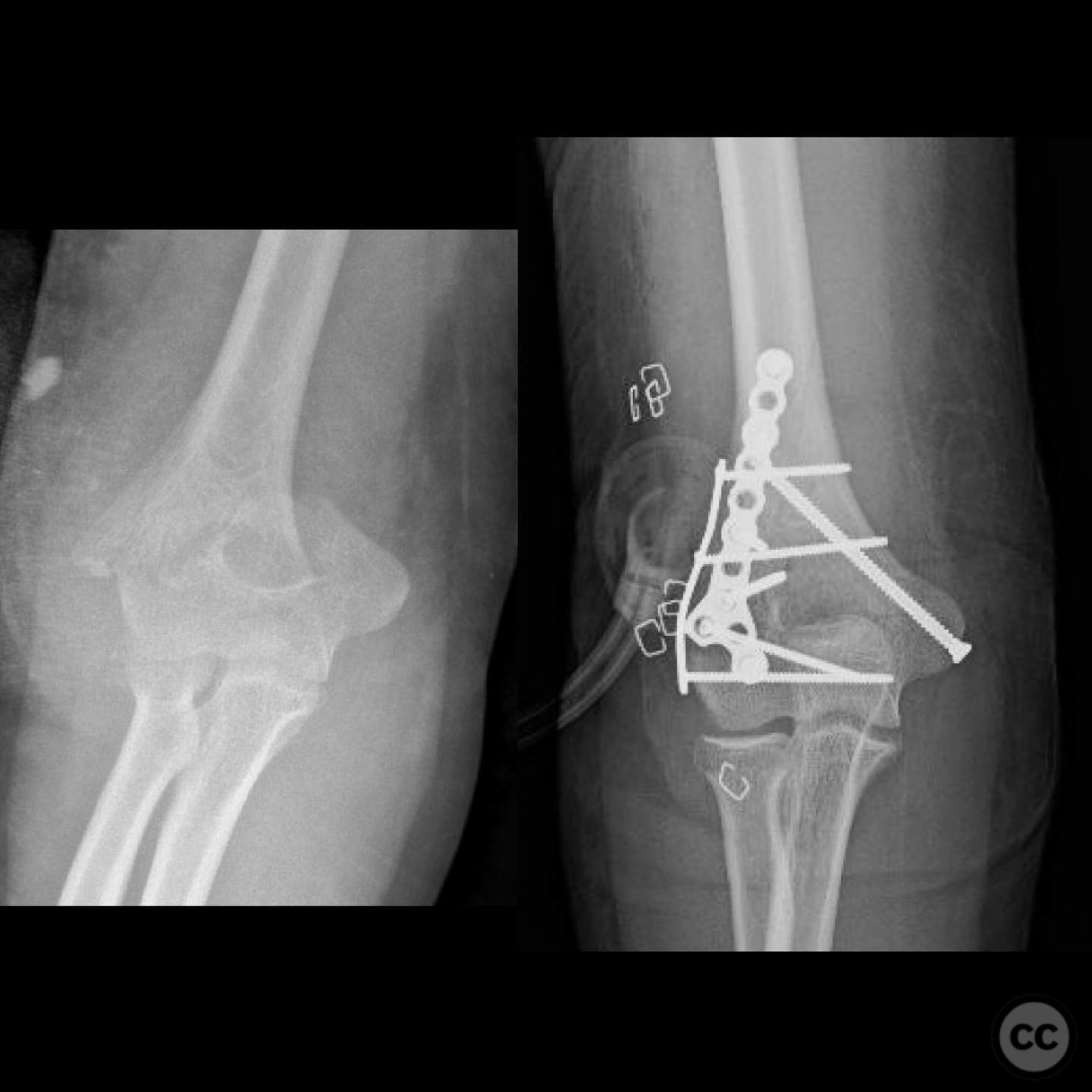
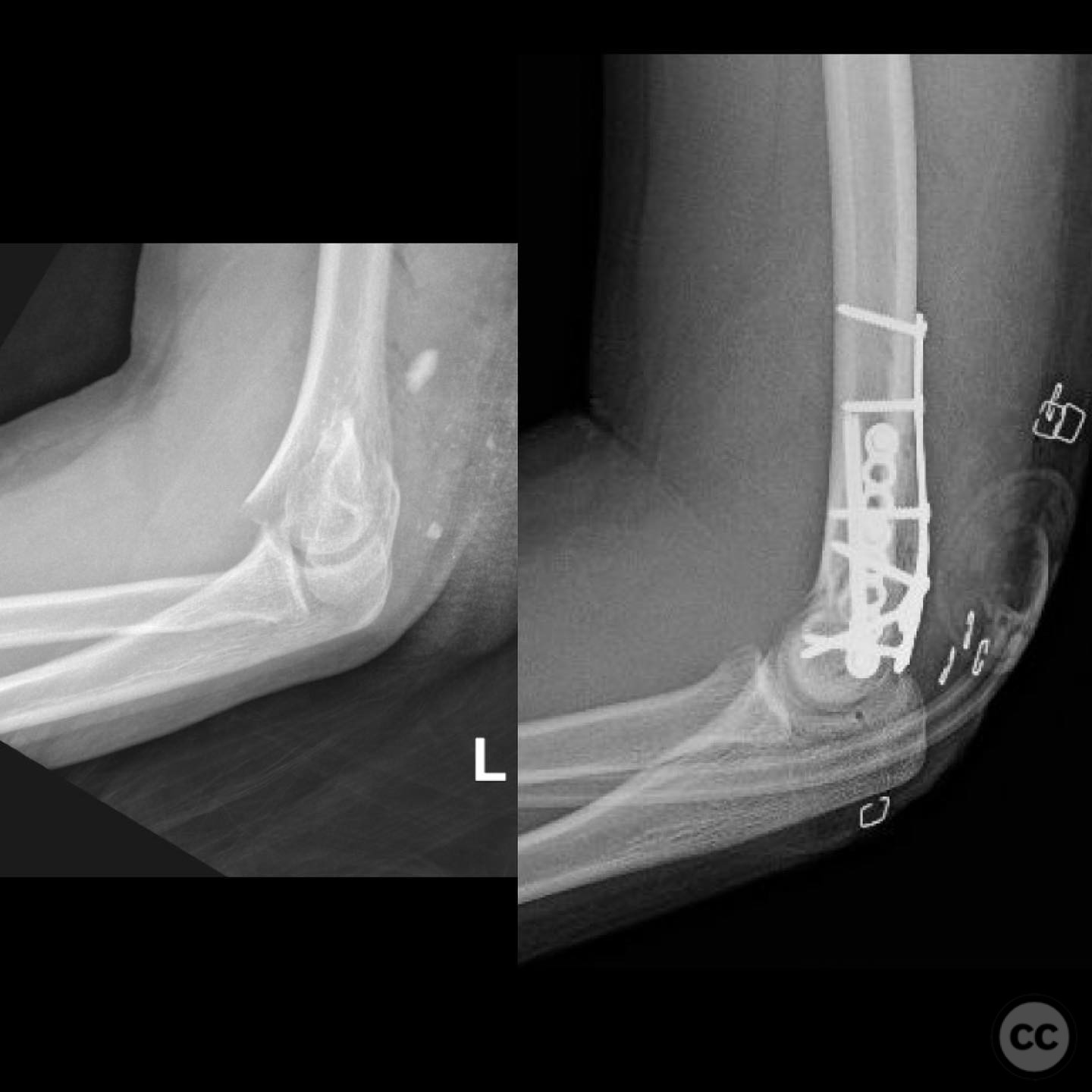
Clinical and radiological findings: A 12-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle collision presented with a type 2 open supracondylar distal humerus fracture. The patient, larger than average for his age, exhibited a direct posterior wound with 3x5 cm skin loss located posterolaterally over the fracture site. Initial clinical examination revealed the necessity for surgical intervention due to the open nature of the fracture and the significant skin loss. Radiological assessment confirmed the diagnosis of a supracondylar distal humerus fracture, classified as AO/OTA 13-M/3.2.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) to achieve high-quality reduction and stable fixation, while also allowing access to the open wound for management. The traumatic wound was utilized for accessing the lateral column, and a mini open approach was planned for the medial epicondyle to facilitate safe placement of medial column screws.
Surgical Discussion
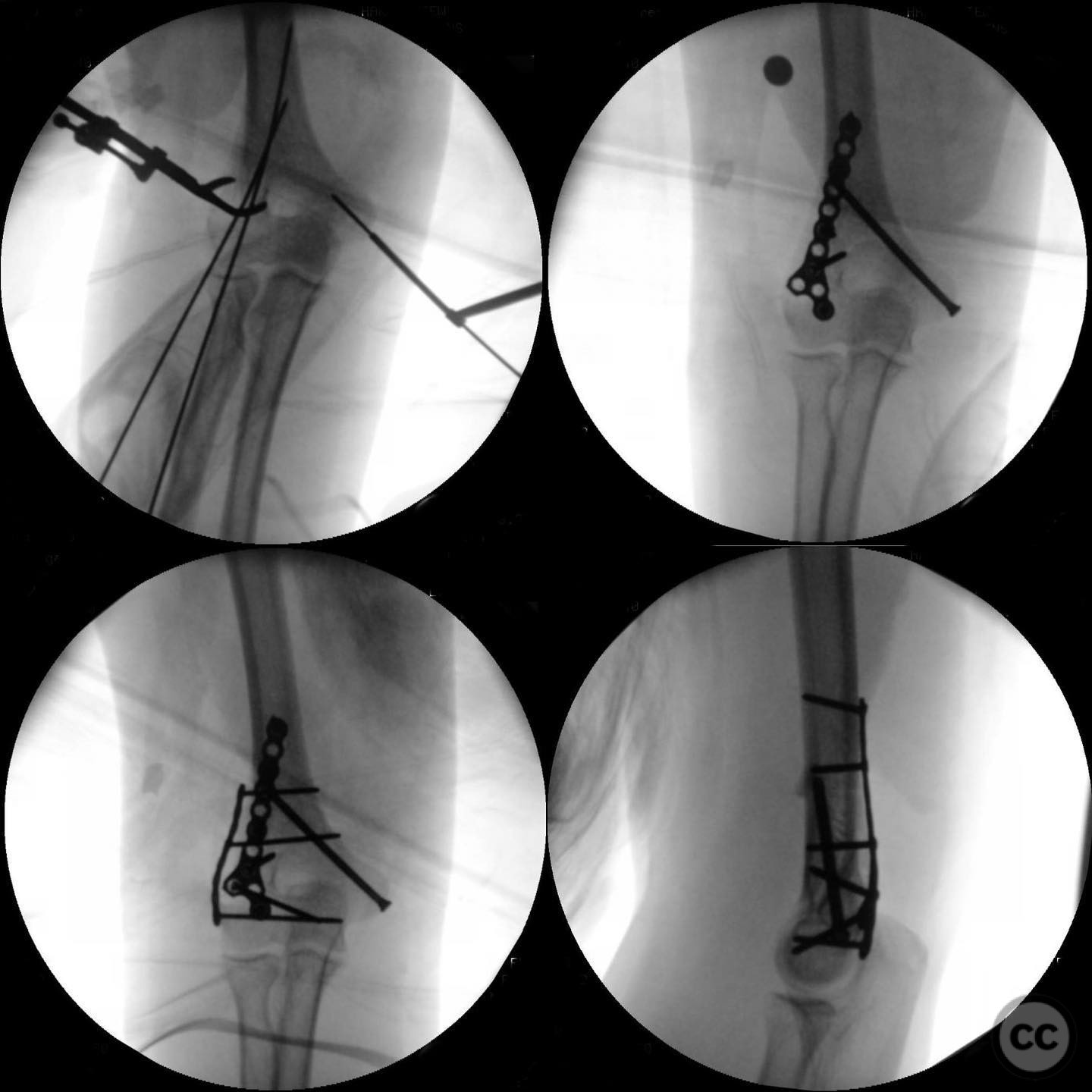
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with the affected arm draped free on a hand table to allow optimal access to the posterior aspect of the distal humerus.
Anatomical surgical approach: The surgical approach involved utilizing the existing traumatic posterolateral wound to access the lateral column of the distal humerus. A mini open approach was performed at the medial epicondyle to enable secure placement of fixation screws in the medial column.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that due to the patient's size and limited remodeling potential, achieving a precise reduction and stable fixation was critical. The decision to proceed with ORIF was influenced by the need for direct access to the fracture site and wound management. In a closed fracture scenario, percutaneous pinning might have been considered; however, given the patient's skeletal maturity and fracture characteristics, ORIF was deemed appropriate.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was advised to maintain immobilization with a posterior splint for initial wound healing and stabilization. Gradual mobilization exercises were introduced after wound healing, with progression to active range of motion exercises as tolerated.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included cannulated screws for medial and lateral column fixation.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 130 times
11 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Open Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fracture in an Adolescent: ORIF Approach. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 47353464 Published Online Jul 11 2025.