APC II Pelvic Ring Injury with Sagittal and External Rotation Deformity.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
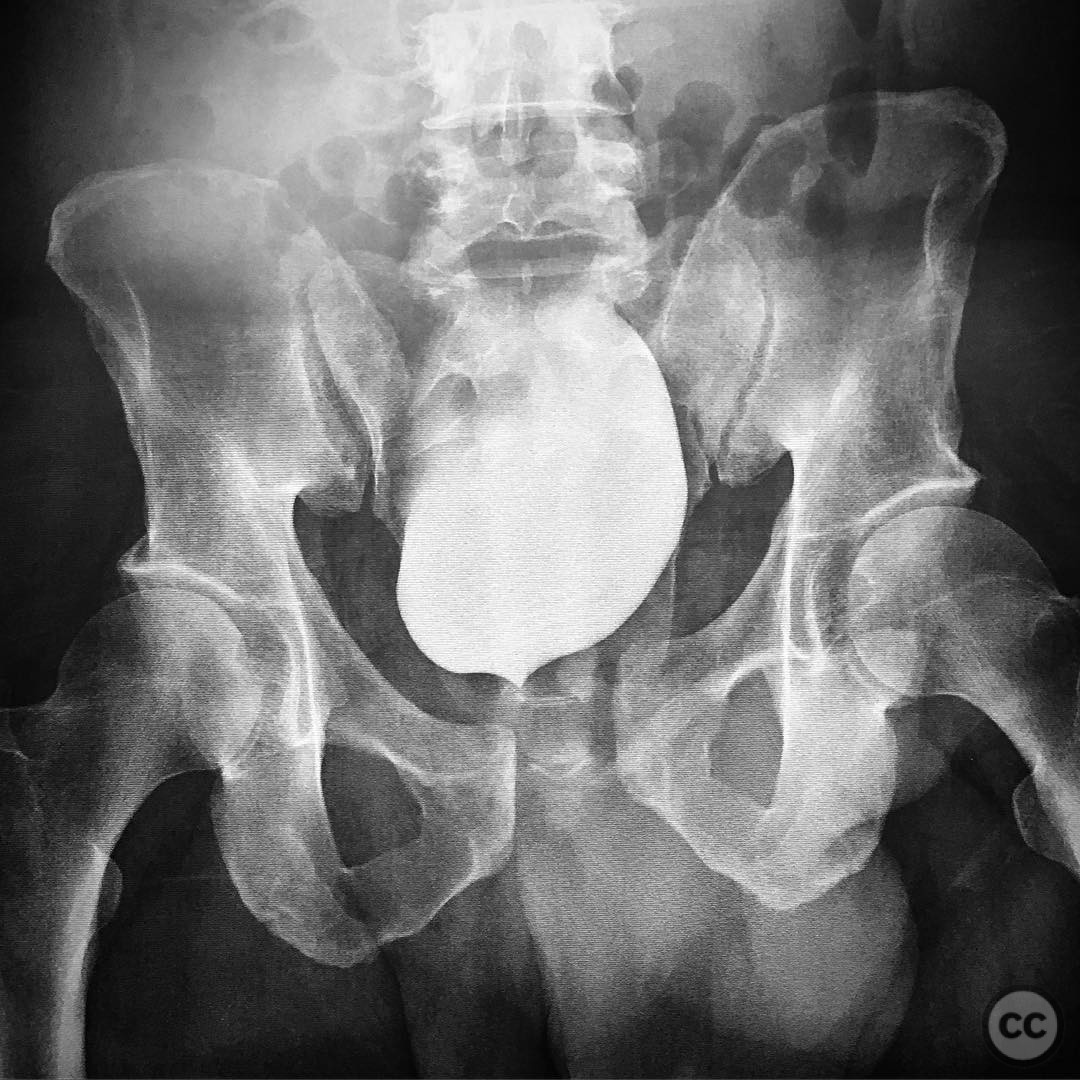
Clinical and radiological findings: A 44-year-old male presented to the emergency department following a snowmobile accident involving a 6-foot drop. Initial radiographs revealed an anterior-posterior compression (APC) type II pelvic ring injury, characterized by instability in two planes: sagittal plane rotational deformity with extension of the right hemipelvis, and external rotation deformity. The sacroiliac (SI) joint was noted to be displaced.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved closed reduction of the symphysis pubis with careful attention to the alignment of the SI joint. If the SI joint remained displaced after symphyseal reduction, an open reduction through a lateral window approach was considered prior to final fixation of the symphysis.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine position on a radiolucent table to facilitate intraoperative imaging and manipulation of the pelvic ring.
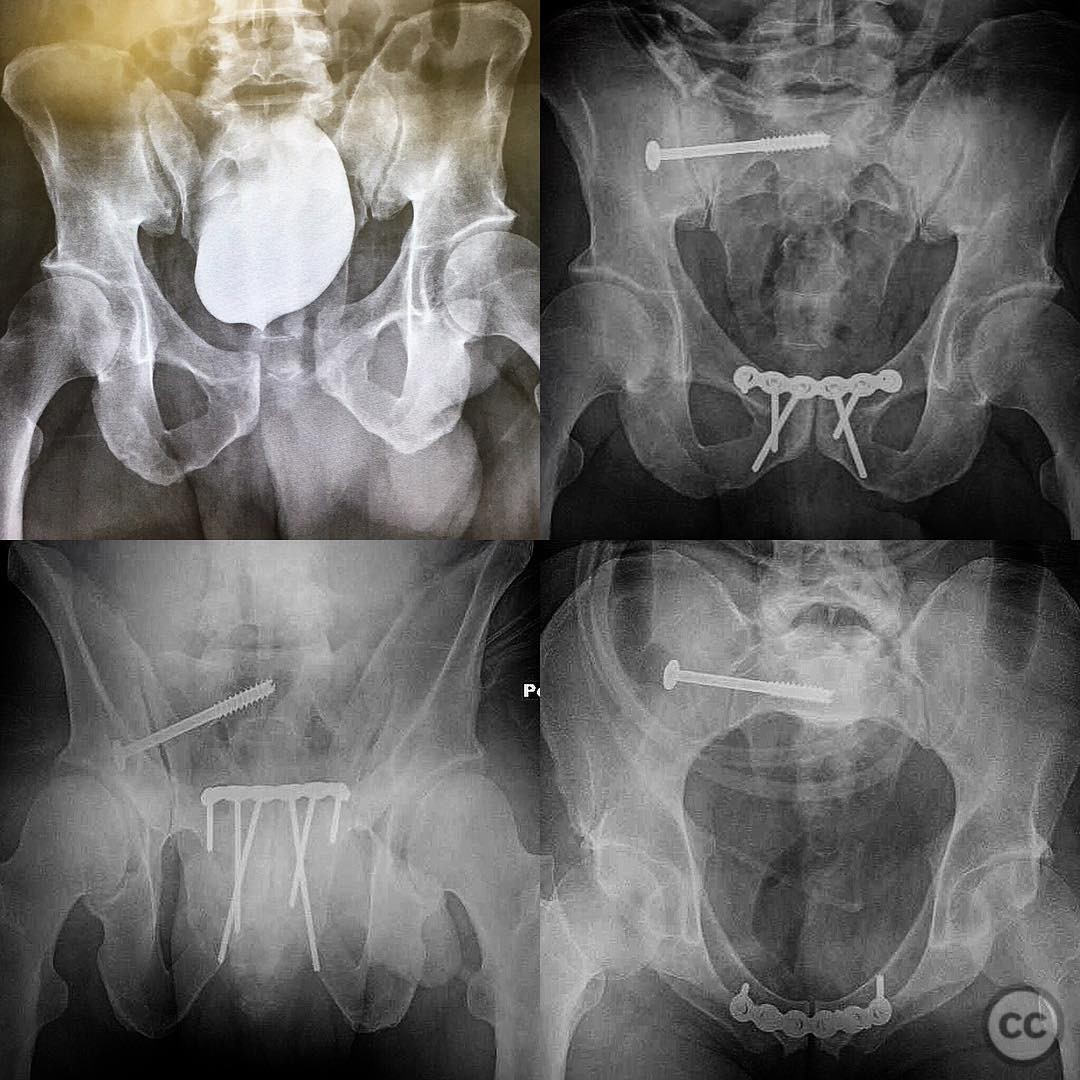
Anatomical surgical approach: A Pfannenstiel incision was utilized for access to the symphysis pubis. In cases requiring SI joint intervention, a lateral window approach to the SI joint was prepared, involving dissection through the gluteal musculature to expose the joint for potential open reduction.
Operative remarks:The symphyseal reduction achieved accurate realignment of the SI joint, negating the need for additional open reduction through the lateral window. The importance of recognizing and addressing both sagittal and external rotation deformities was emphasized to ensure stable fixation and optimal postoperative outcomes.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included protected weight-bearing with crutches for 6 weeks, followed by gradual progression to full weight-bearing as tolerated. Emphasis was placed on early mobilization and strengthening exercises to restore function.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Symphyseal plate fixation system.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 181 times
05 Aug 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). APC II Pelvic Ring Injury with Sagittal and External Rotation Deformity.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 45819186 Published Online Aug 05 2025.