Comminuted Coronoid Fracture with Anterior Displacement due to Gunshot Wound
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
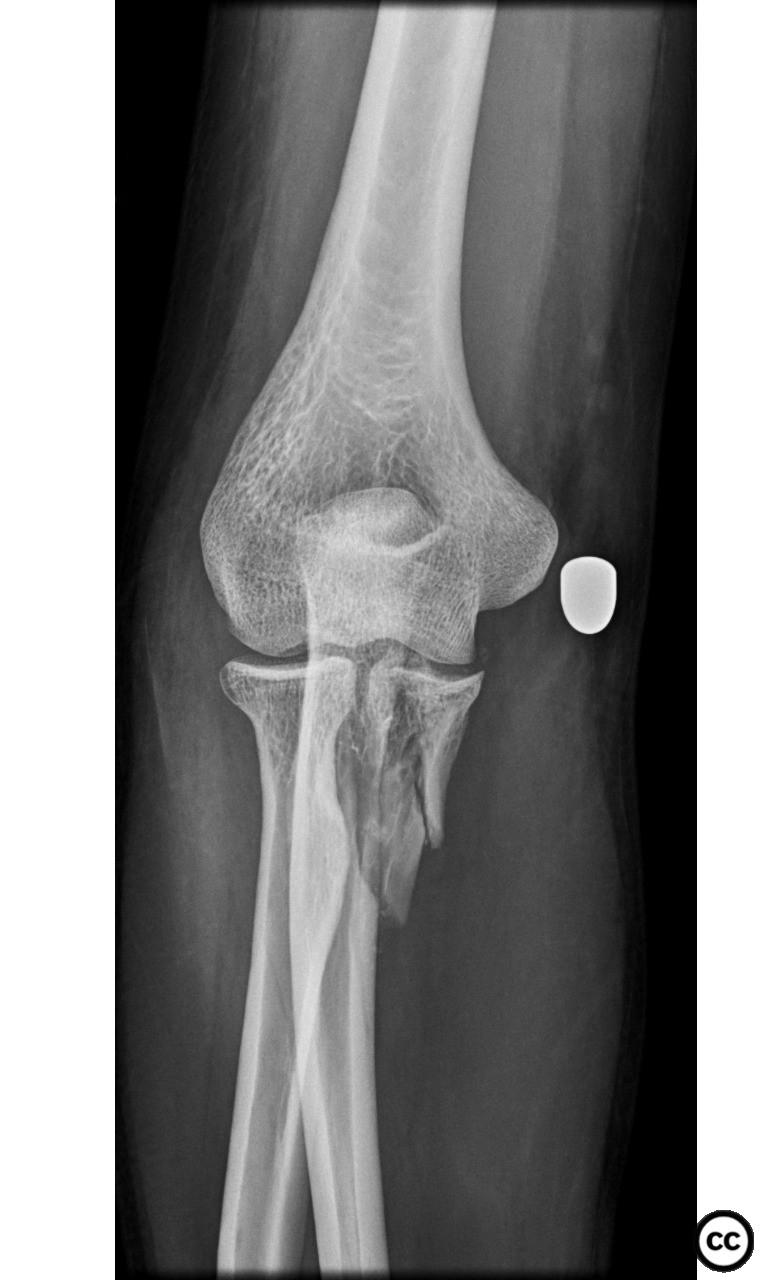
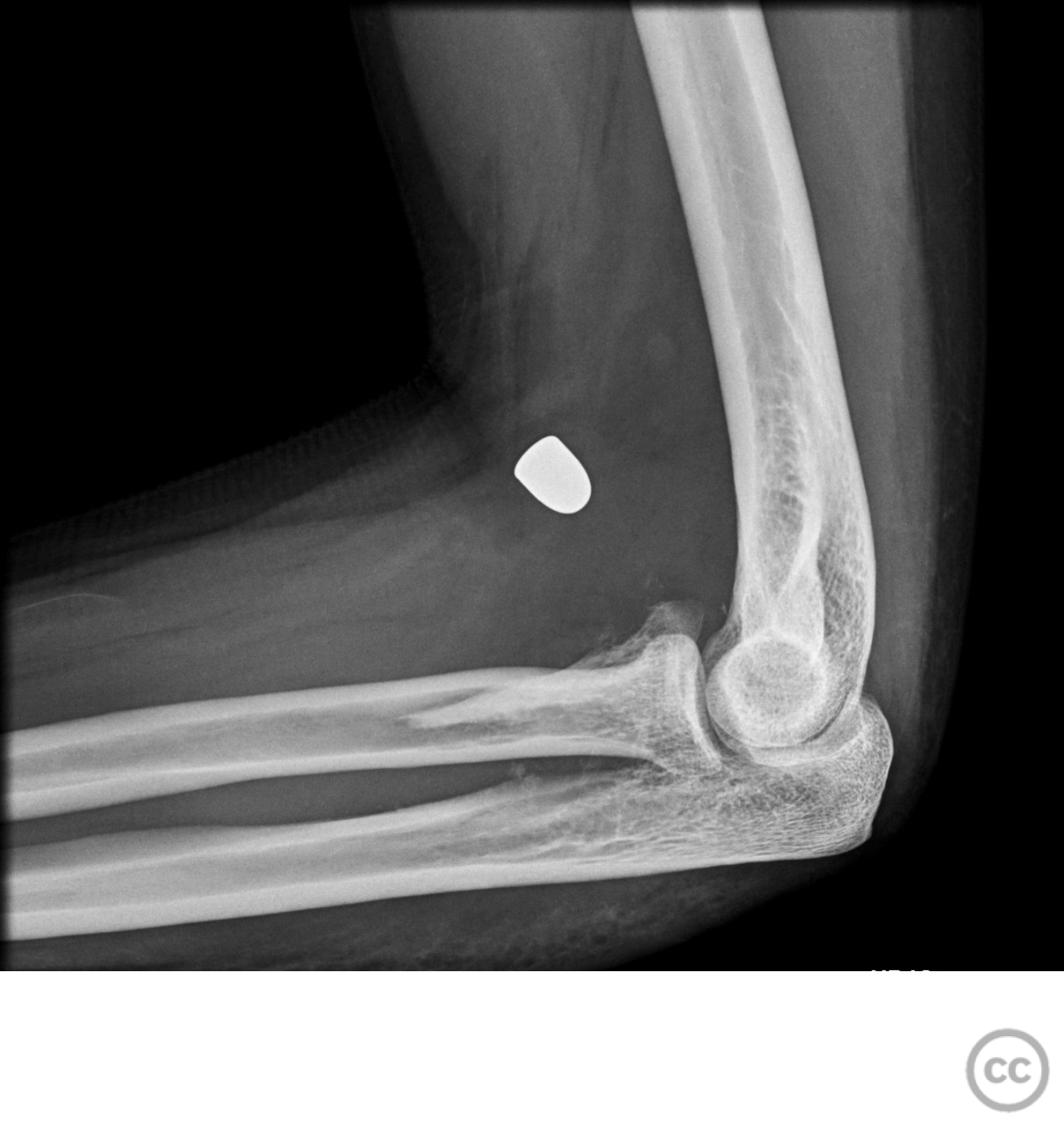
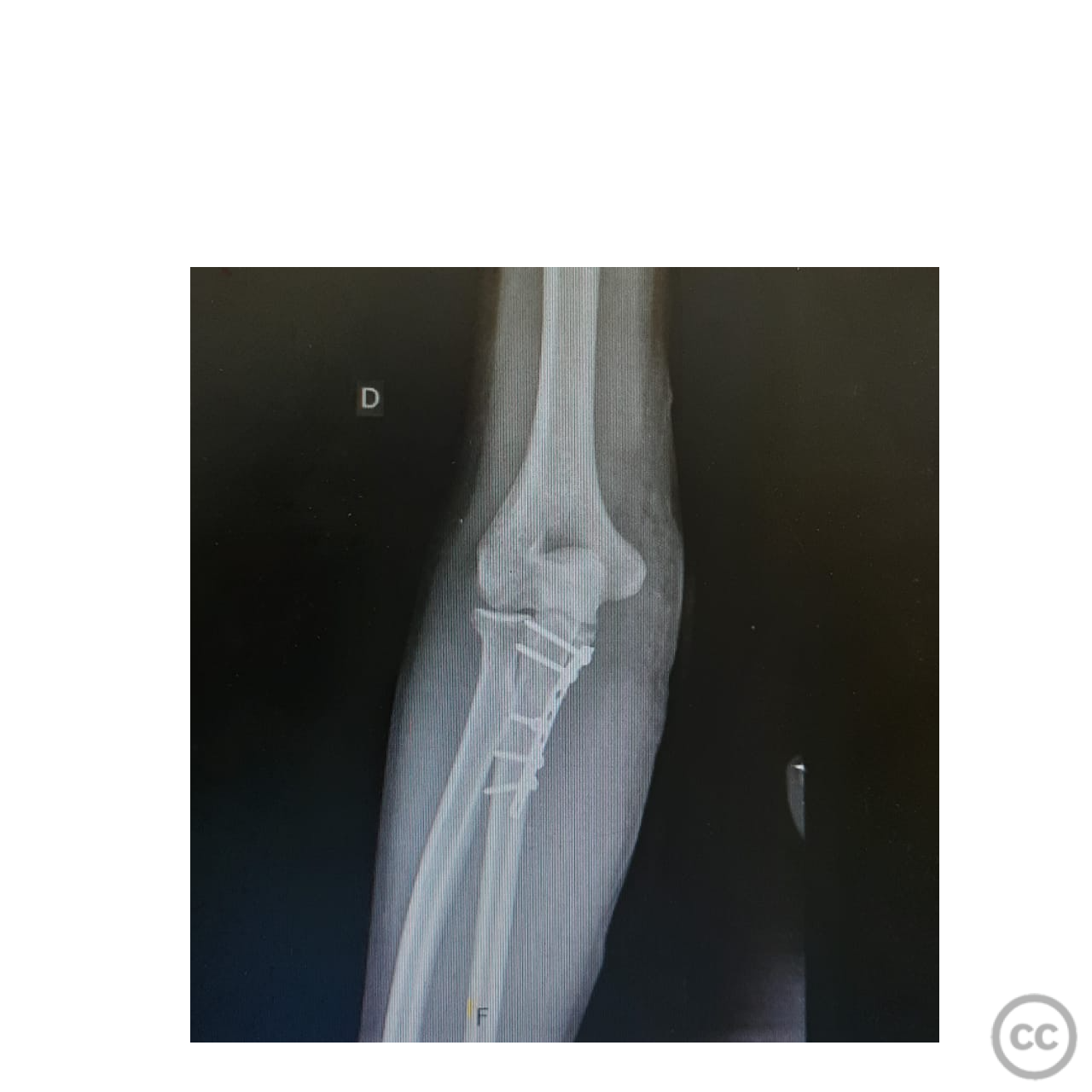
Clinical and radiological findings: A male patient sustained a gunshot wound to the forearm. Radiographic evaluation revealed a displaced comminuted fracture of the coronoid process with marked anterior displacement. There was no neurovascular injury noted.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan included a trans-flexor carpi ulnaris approach to access the coronoid process. The ulnar nerve would be released, and reduction would be achieved using forceps. An interfragmentary screw would be used to reduce the largest fragment, followed by the application of a 1/4 tubular plate with screws for support. Additionally, a second percutaneous volar approach would be used for projectile removal.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table.
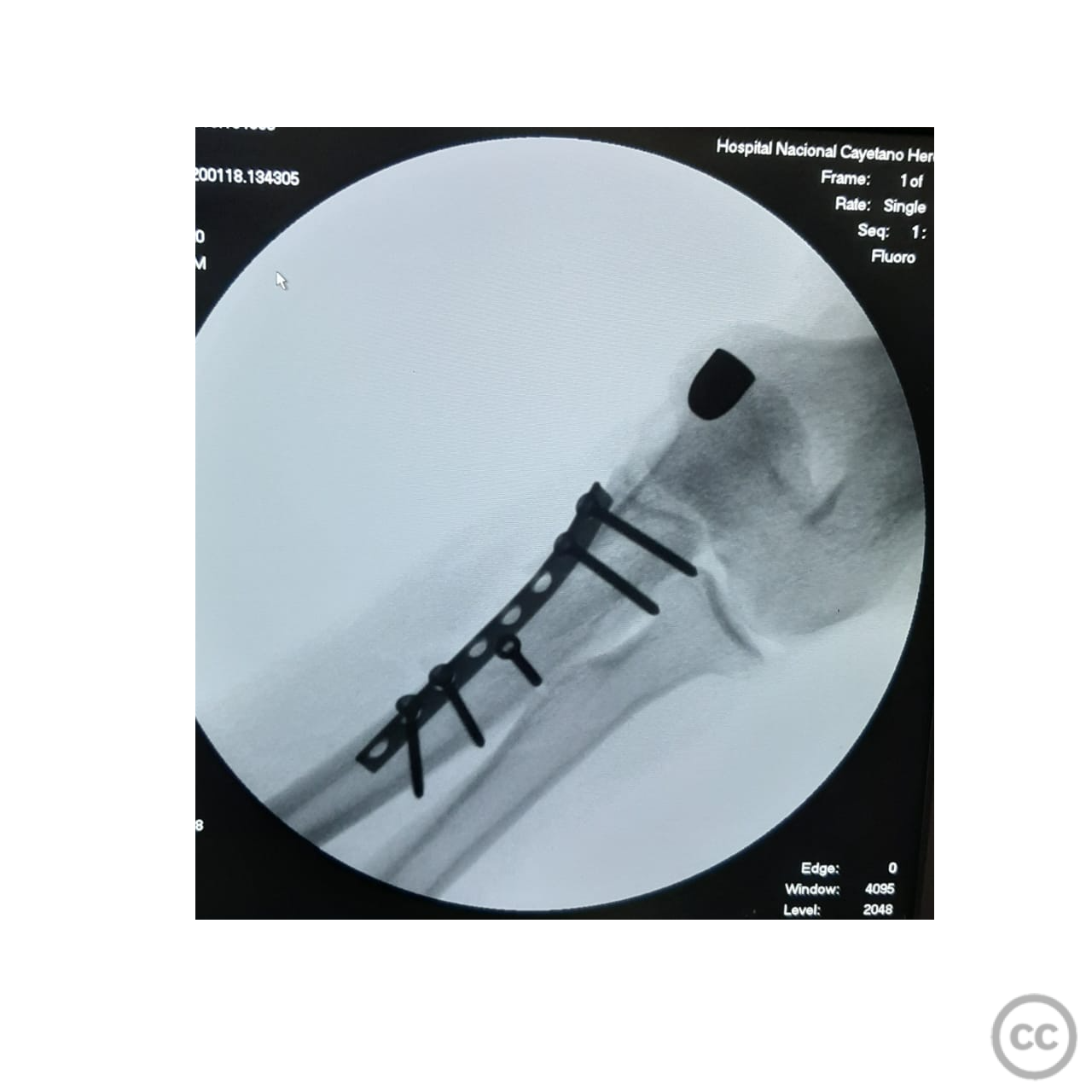
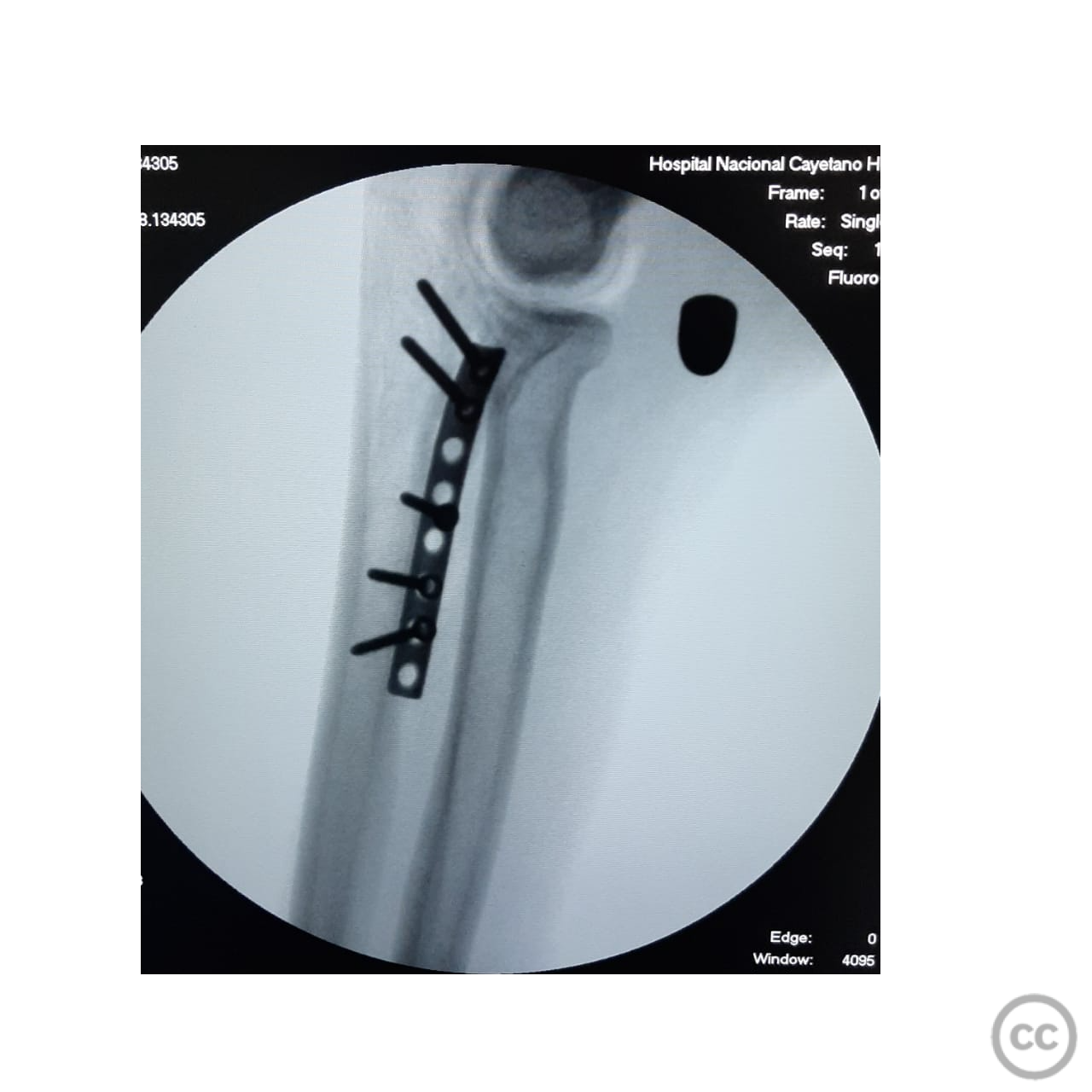
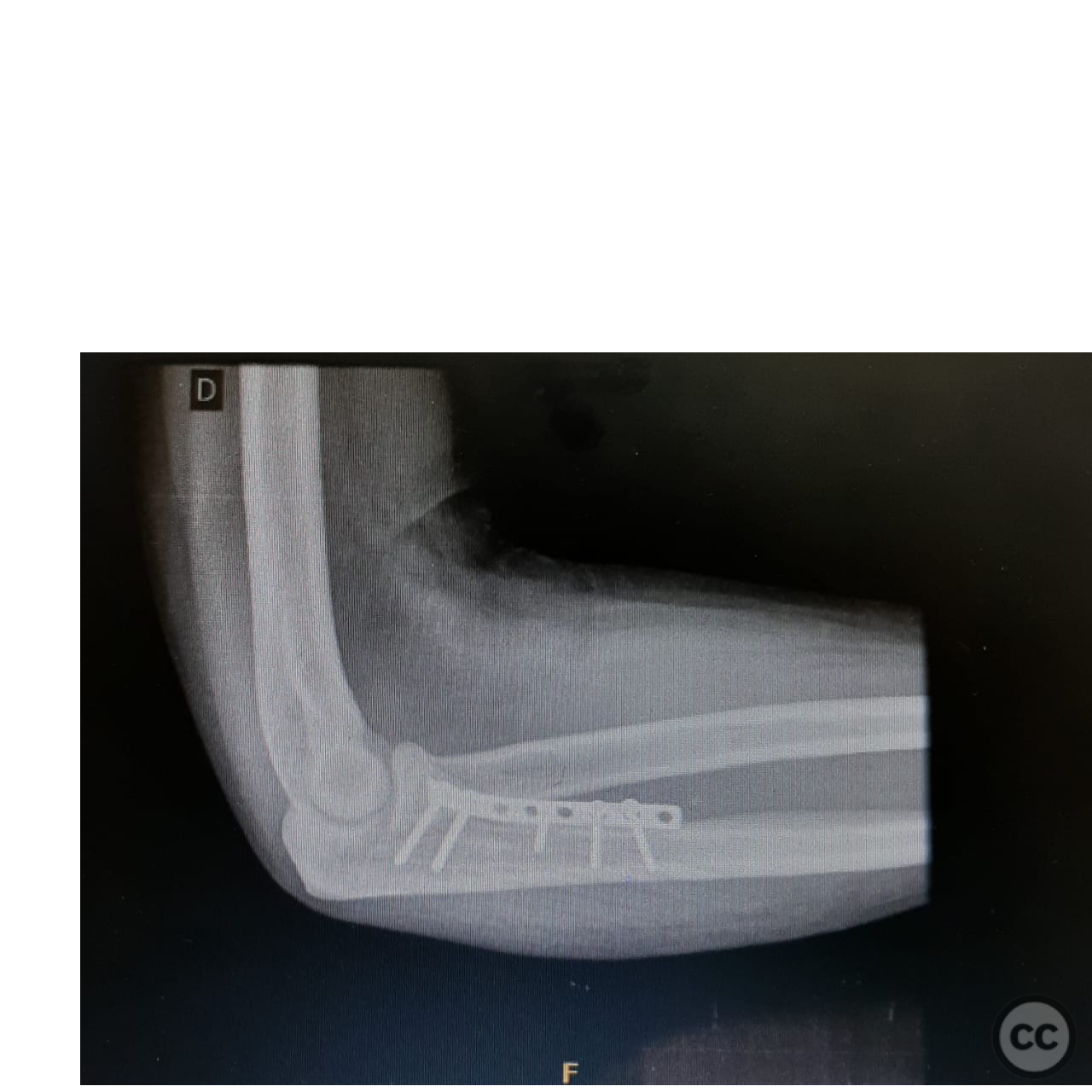
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal incision was made along the flexor carpi ulnaris. The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle was split, and the ulnar nerve was identified and carefully released. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the coronoid process. Reduction of the fracture was achieved using forceps, and an interfragmentary screw was placed to secure the largest fragment. A 1/4 tubular plate was then applied with screws to provide additional support. Finally, a second percutaneous volar approach was utilized to remove the projectile.
Operative remarks:The fracture was highly comminuted with significant anterior displacement, necessitating careful handling of multiple small fragments. The use of an interfragmentary screw provided initial stability to the largest fragment, while the 1/4 tubular plate offered additional support to maintain reduction. The ulnar nerve was meticulously protected throughout the procedure to prevent iatrogenic injury.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was advised to avoid weight-bearing activities involving the affected arm for 6 weeks. Passive range of motion exercises were initiated immediately, progressing to active-assisted and active range of motion exercises by week 4. Strengthening exercises were introduced at week 8.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: - Interfragmentary screw - 1/4 tubular plate with screws
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities


Article viewed 686 times
29 Jul 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
LUIS LEONCIO TEMOCHE DIAZ. (2024). Comminuted Coronoid Fracture with Anterior Displacement due to Gunshot Wound. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 45752471 Published Online Jul 29 2024.