Bilateral Distal Tibia Fractures with Comminution and Fibular Involvement in a Young Male
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
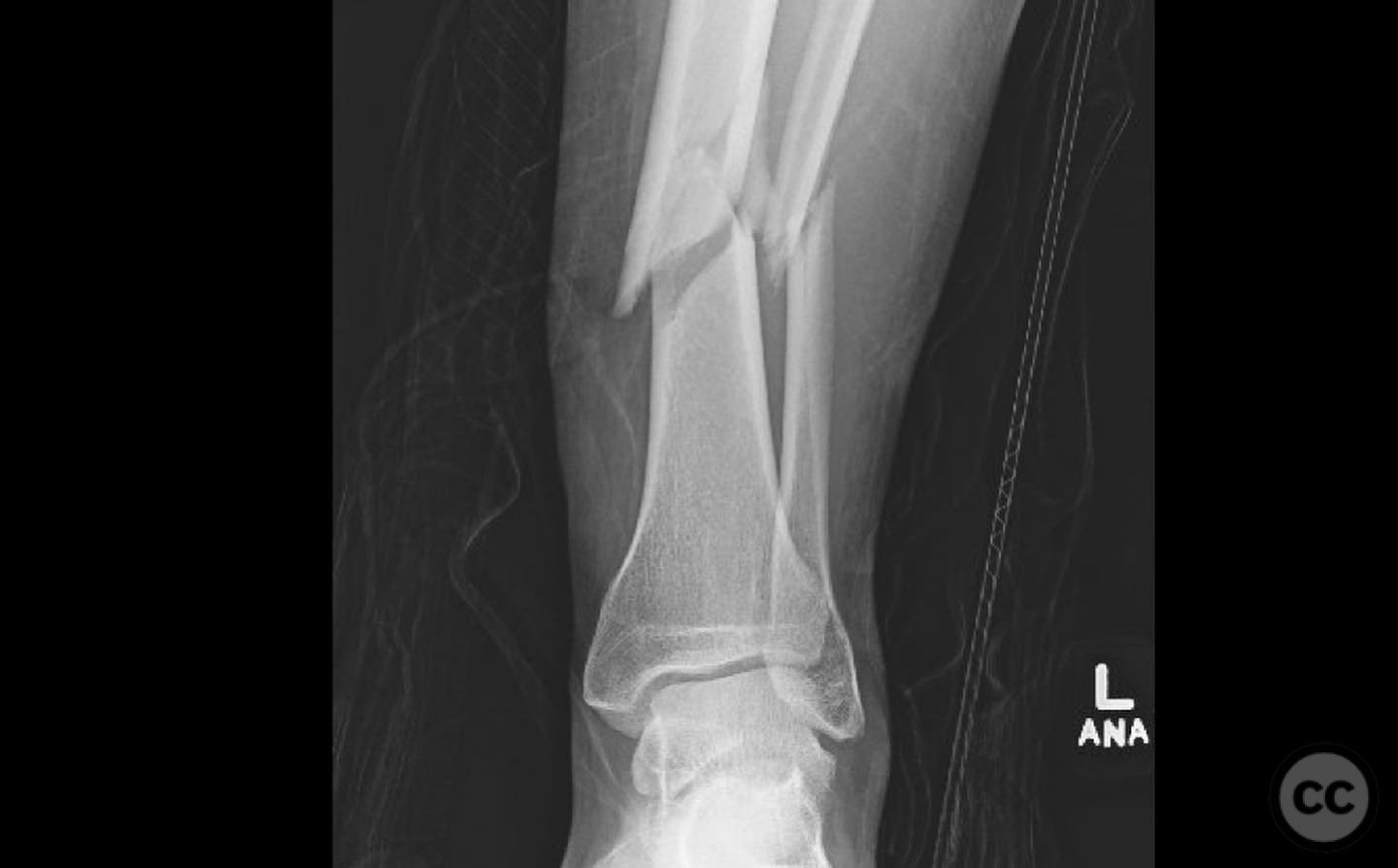
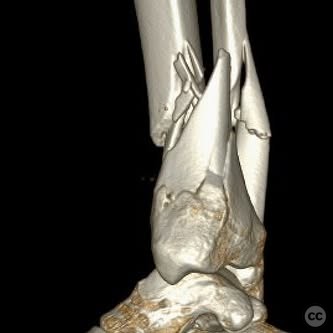
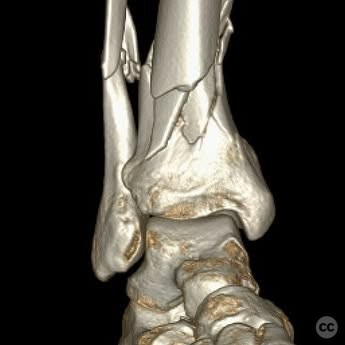
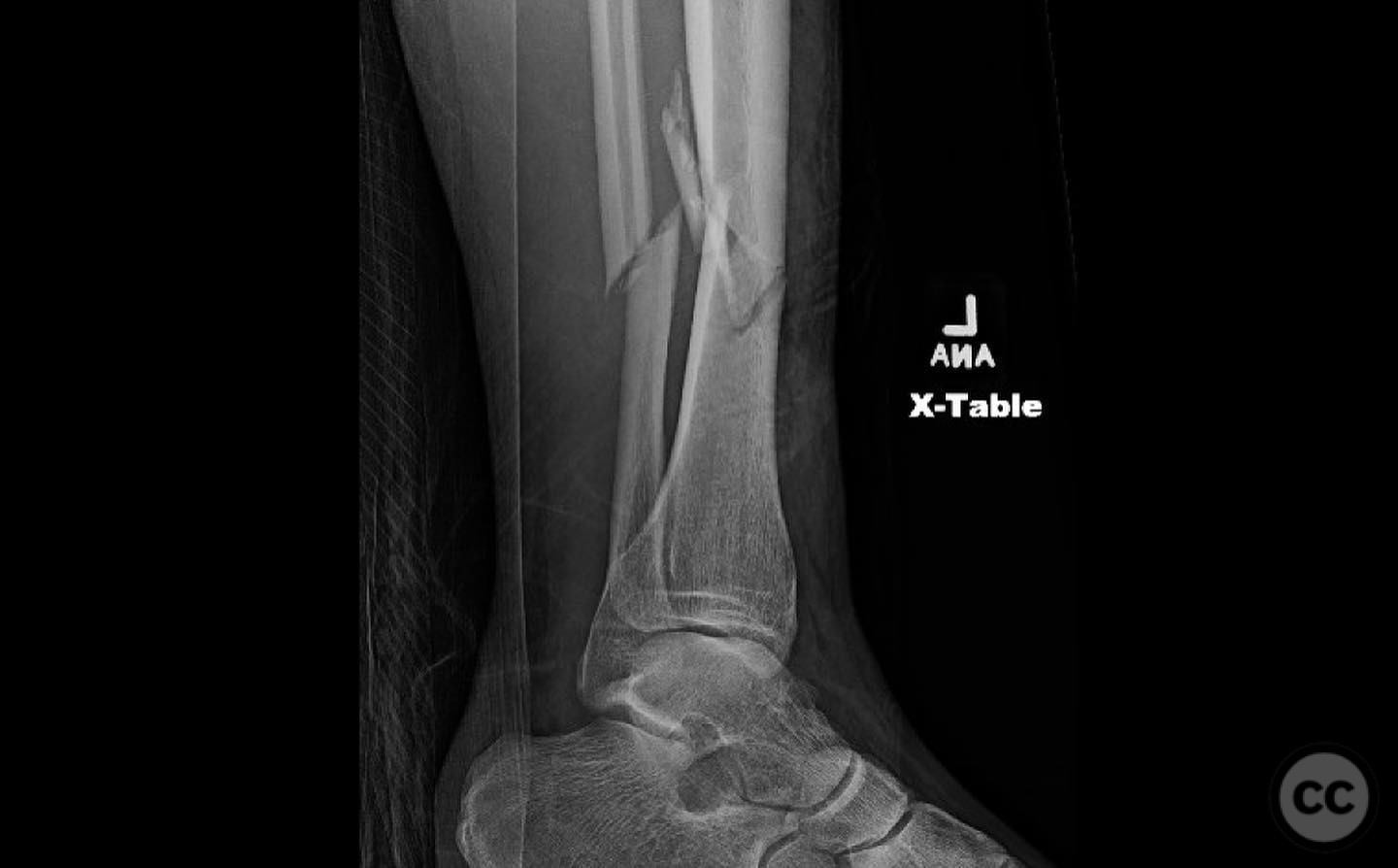
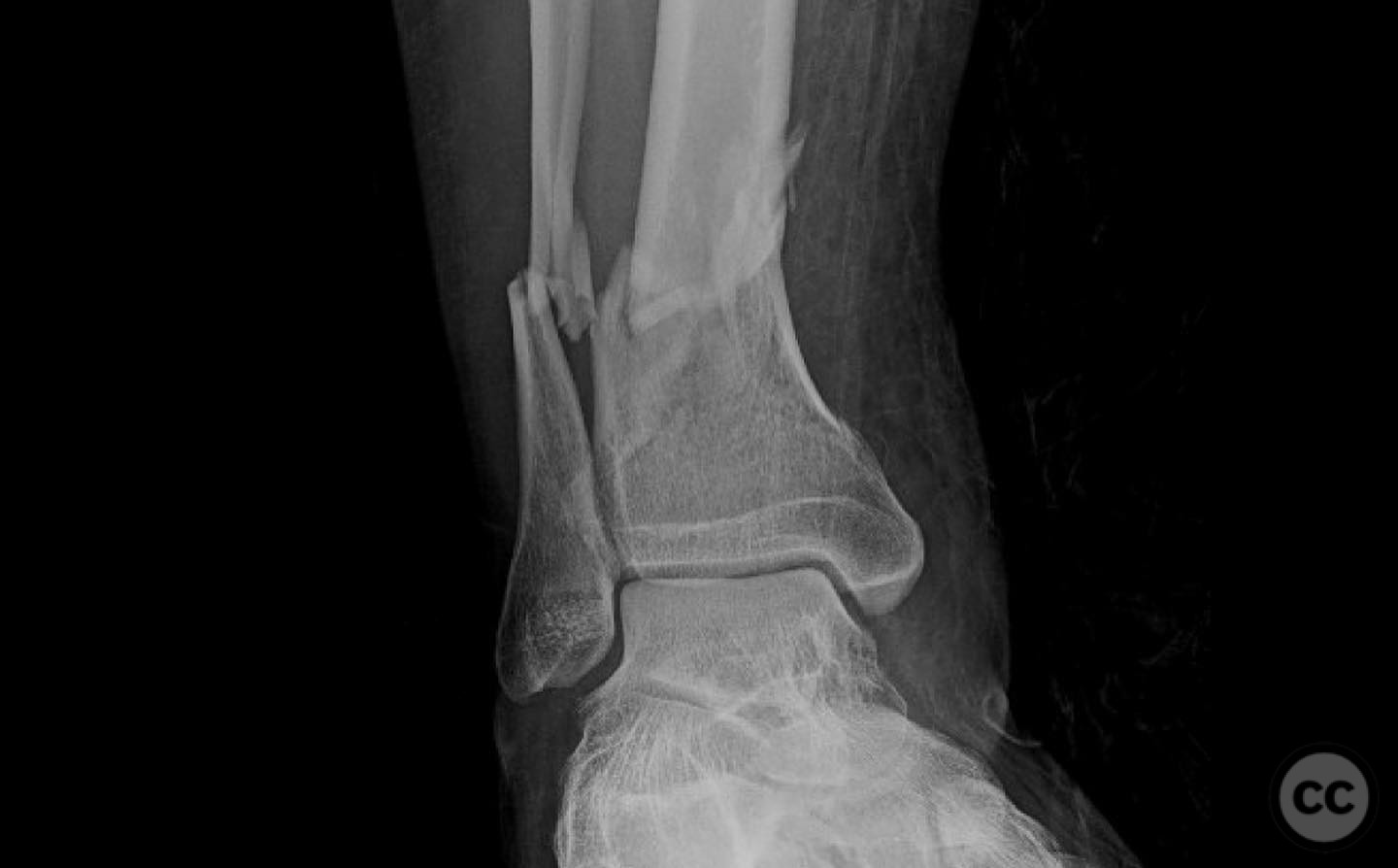
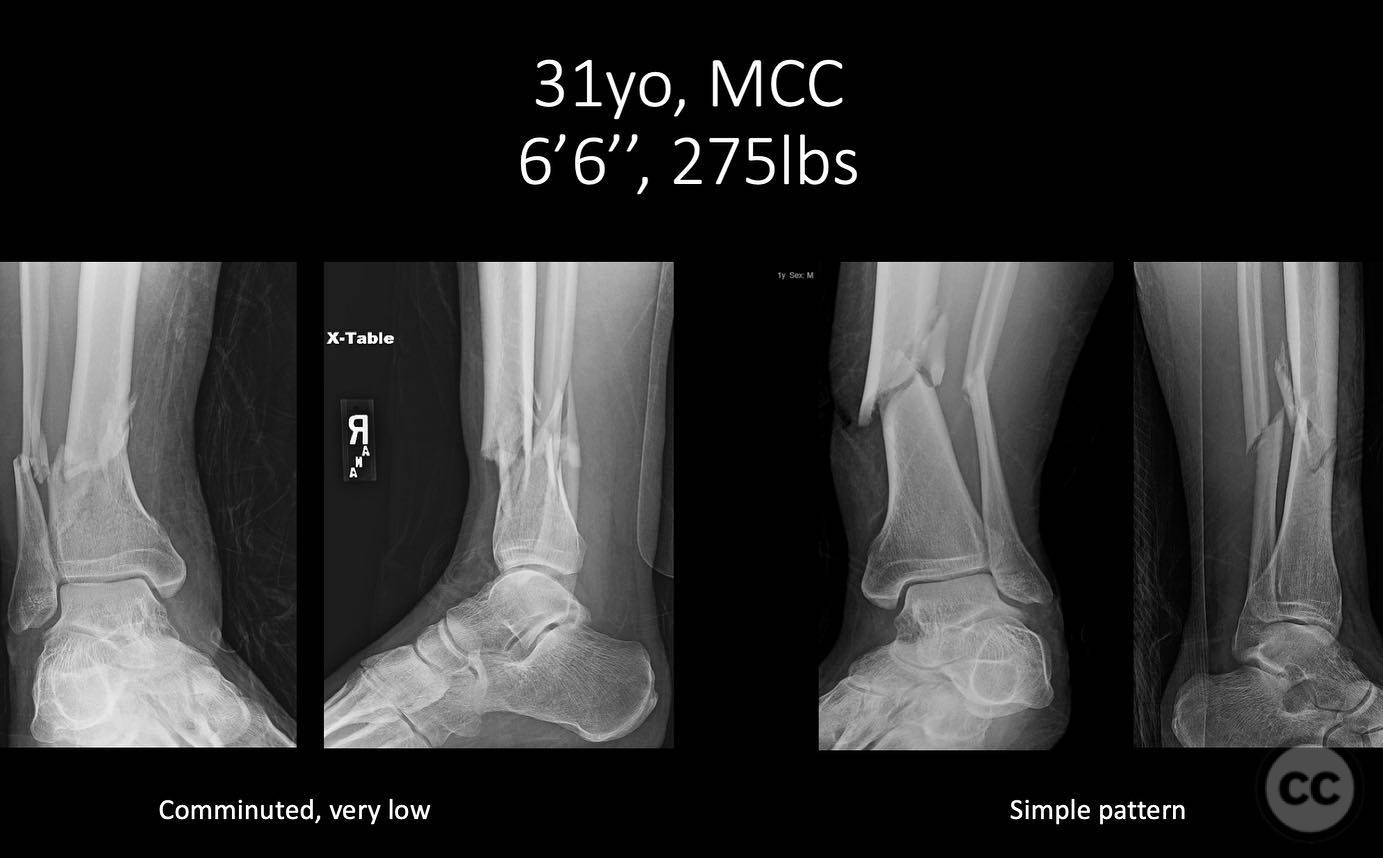
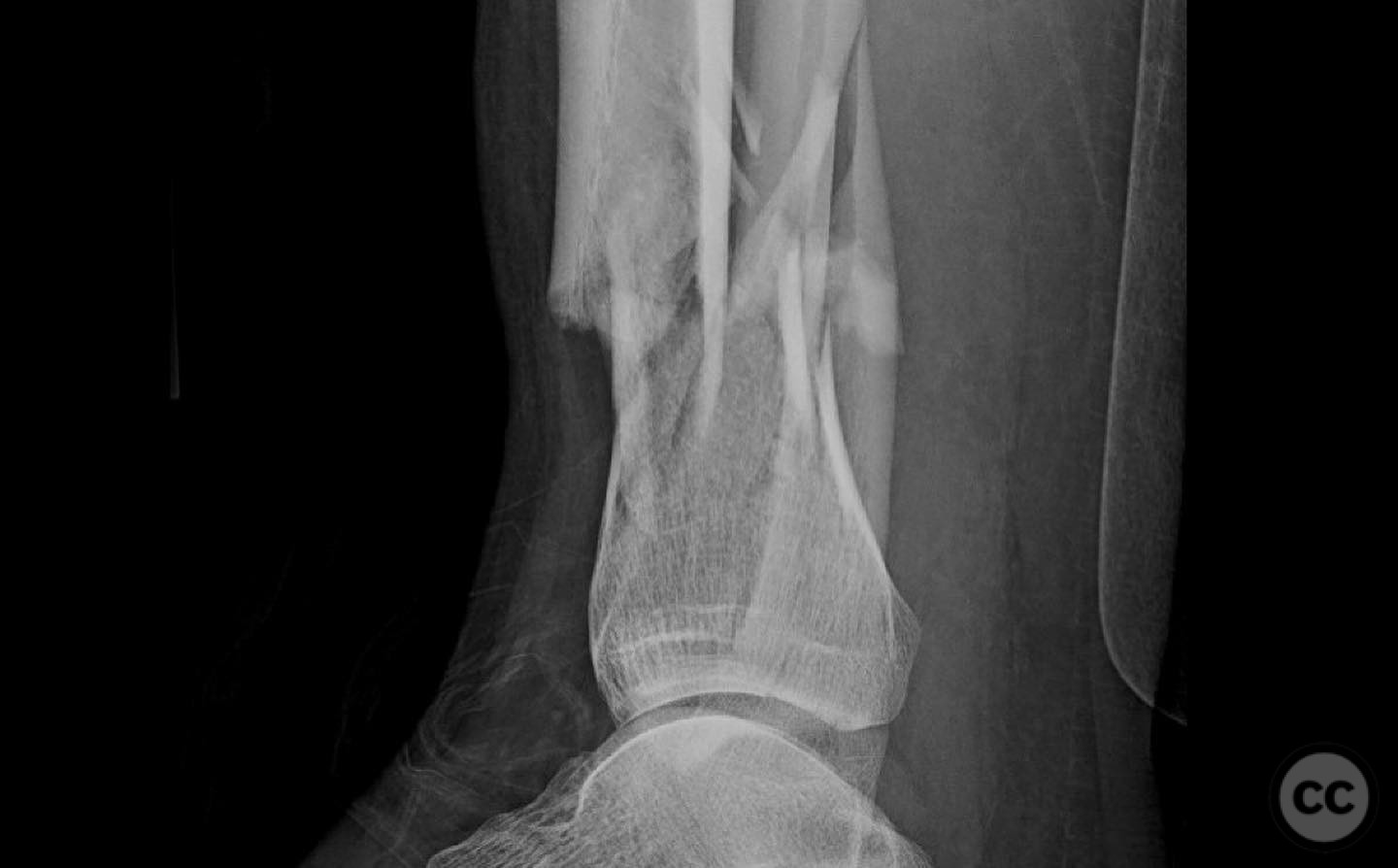
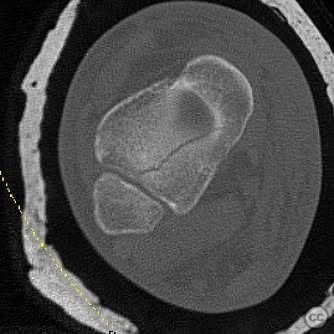
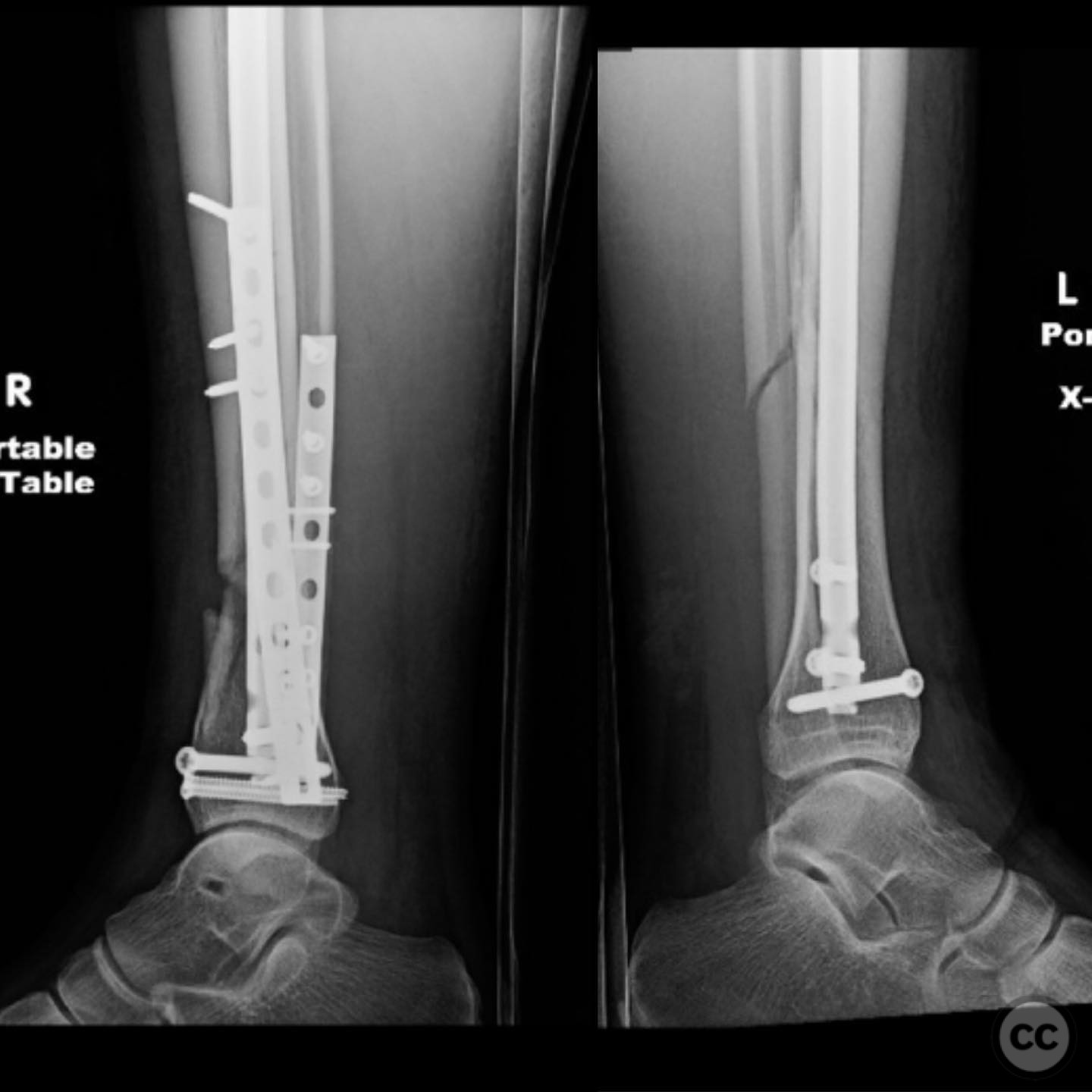
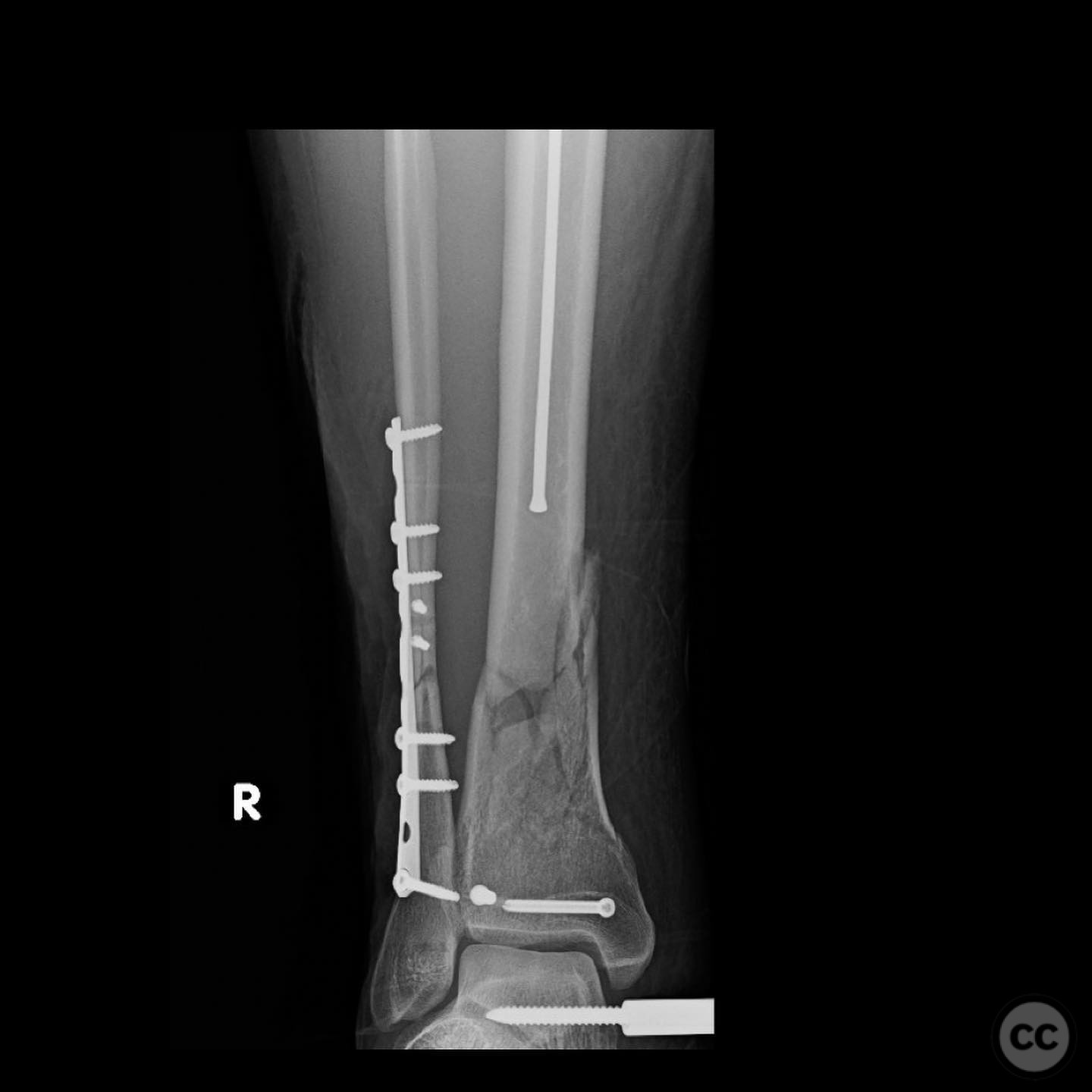
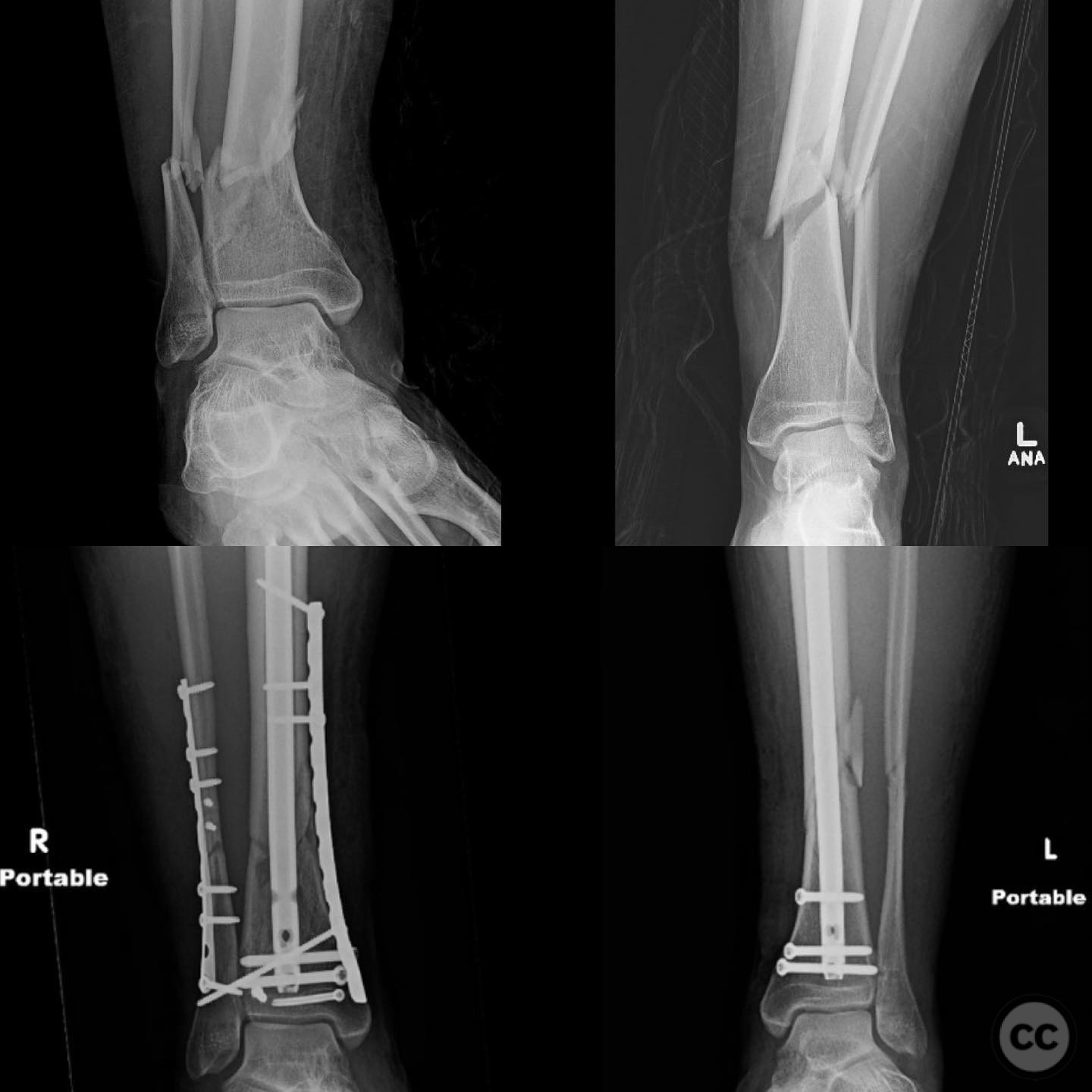
Clinical and radiological findings: A young, healthy, large, and muscular male presented with bilateral distal tibia fractures. The injuries were characterized by comminution, particularly on the right side, and involved the fibula. The patient was cleared for operative intervention.
Preoperative Plan
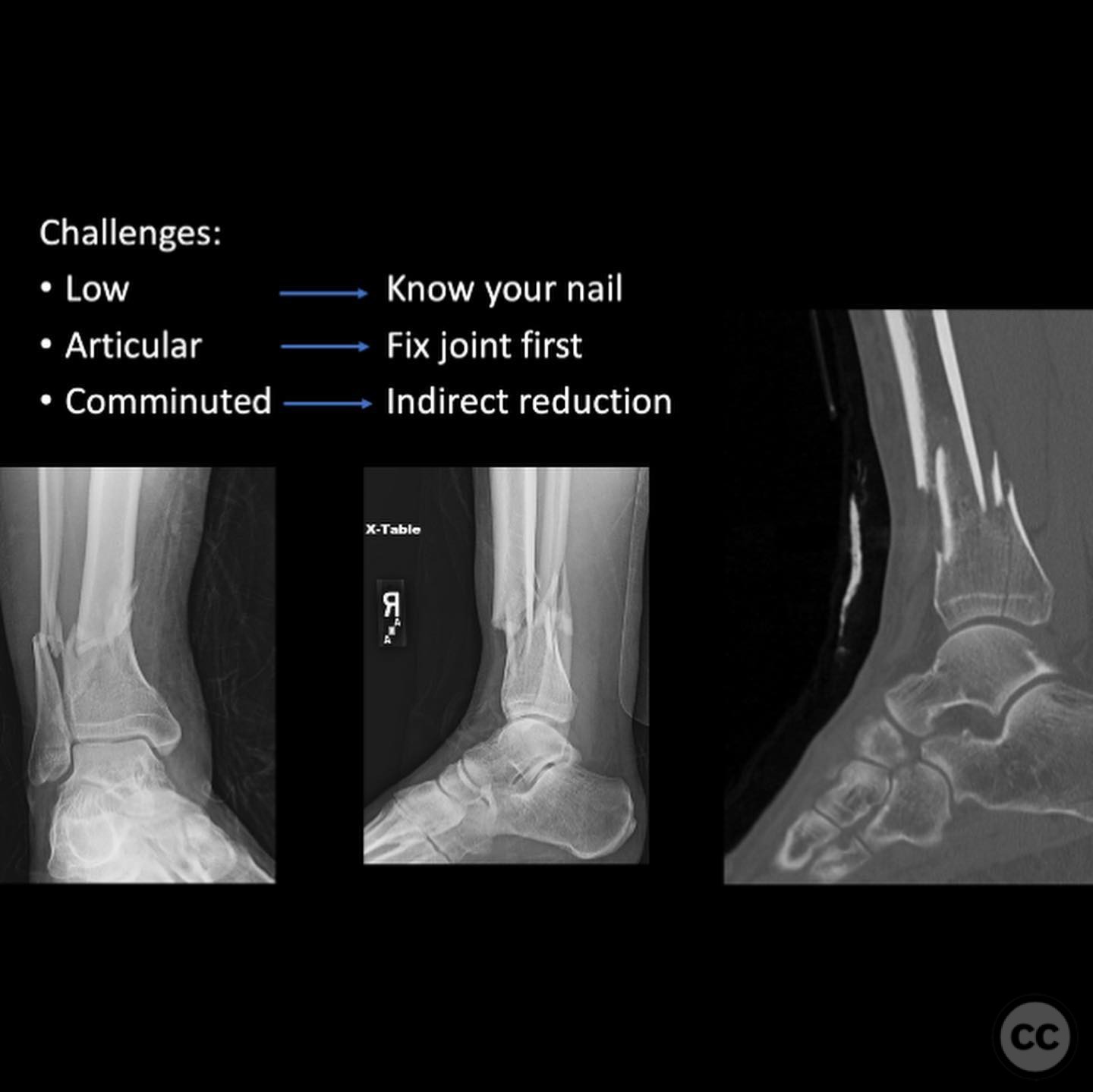
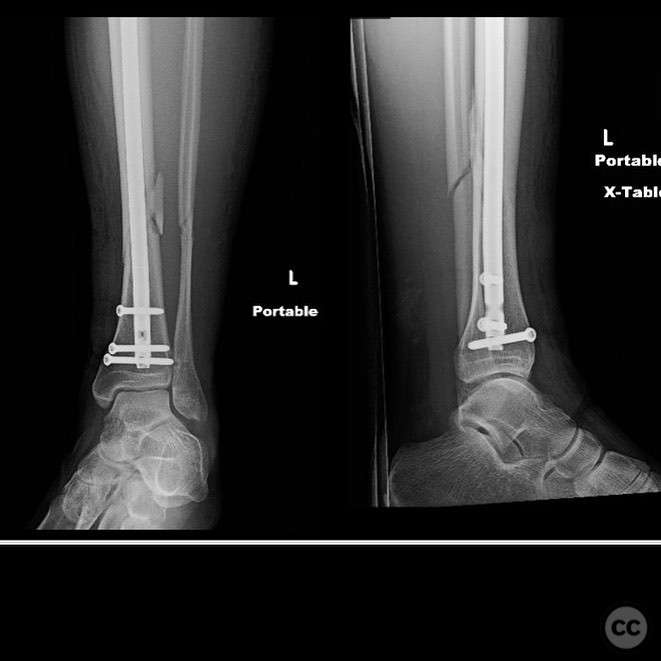
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan for the right side involved using the fibula as a guide to restore tibial alignment due to the complexity of the distal tibia fracture. A distractor was planned for indirect reduction techniques. Consideration was given to the use of an intramedullary nail versus plating, with a decision to use a percutaneous medial plate for additional stability. On the left side, percutaneous clamping was planned to maintain fracture alignment during nail deployment, with attention to preventing valgus displacement by ensuring lateral column integrity.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine positioning on a radiolucent table, allowing for bilateral access and imaging.
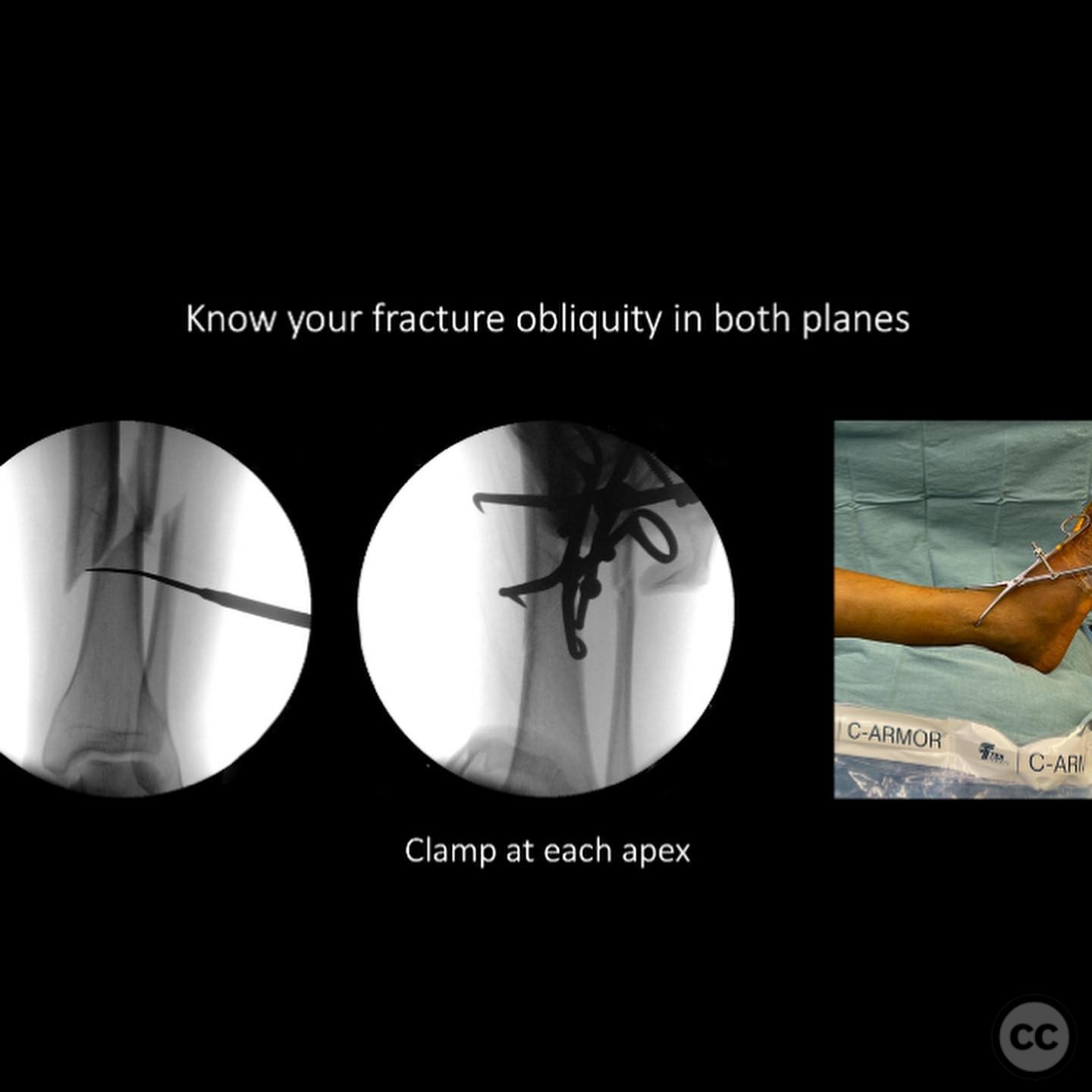
Anatomical surgical approach: Right Side: A percutaneous approach was utilized for the medial plating, with indirect reduction achieved through distraction techniques. Left Side: Percutaneous clamping was employed to stabilize the fracture during intramedullary nailing.
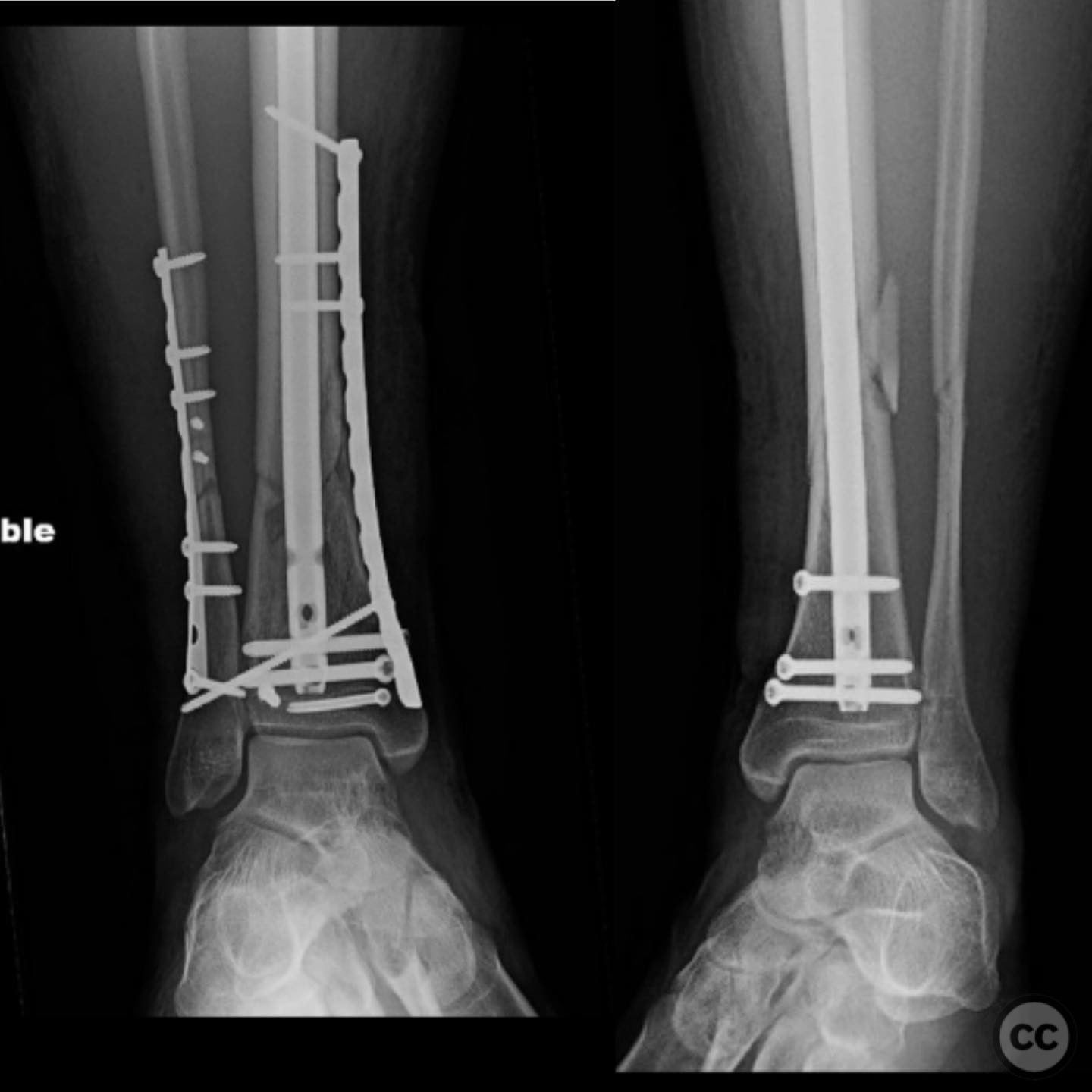
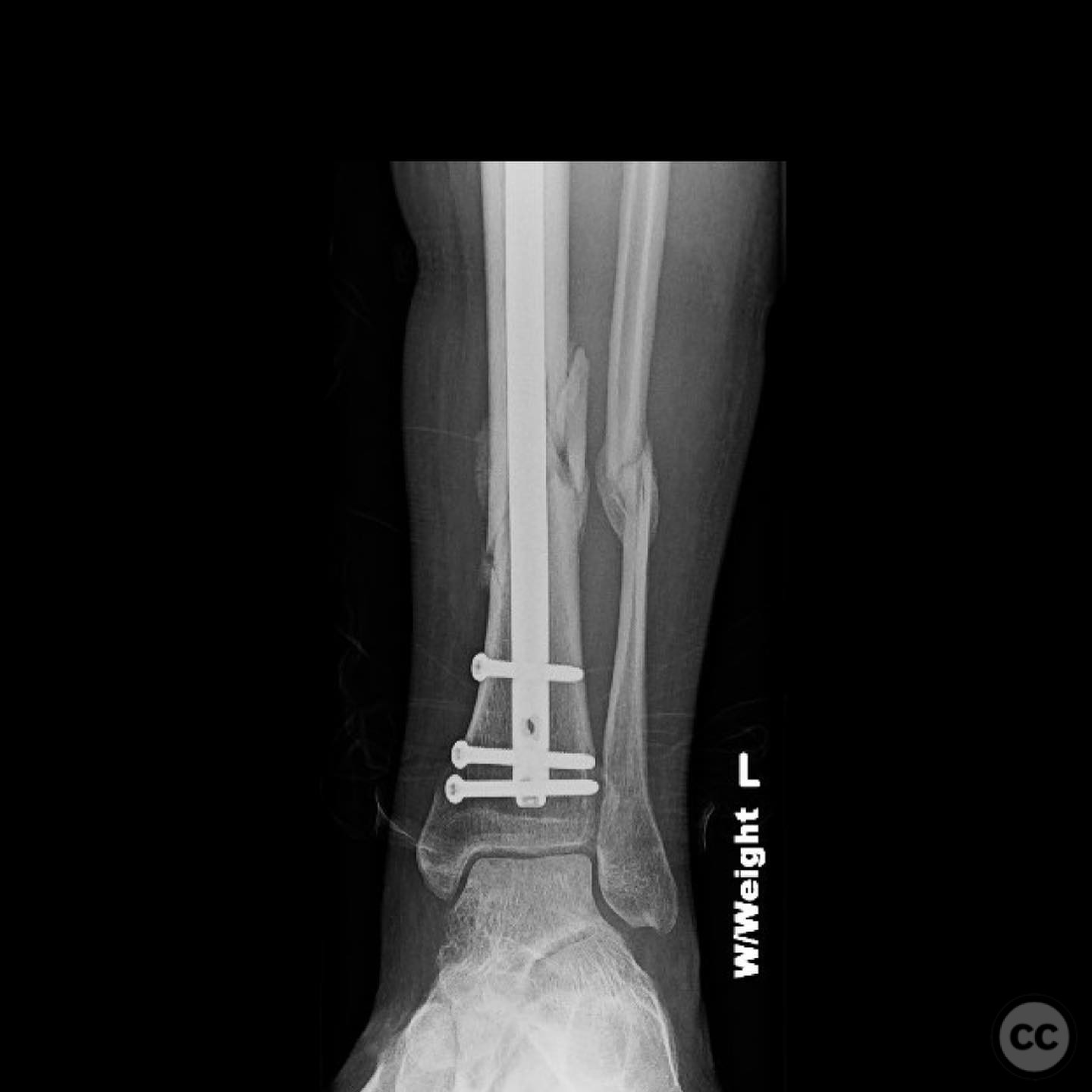
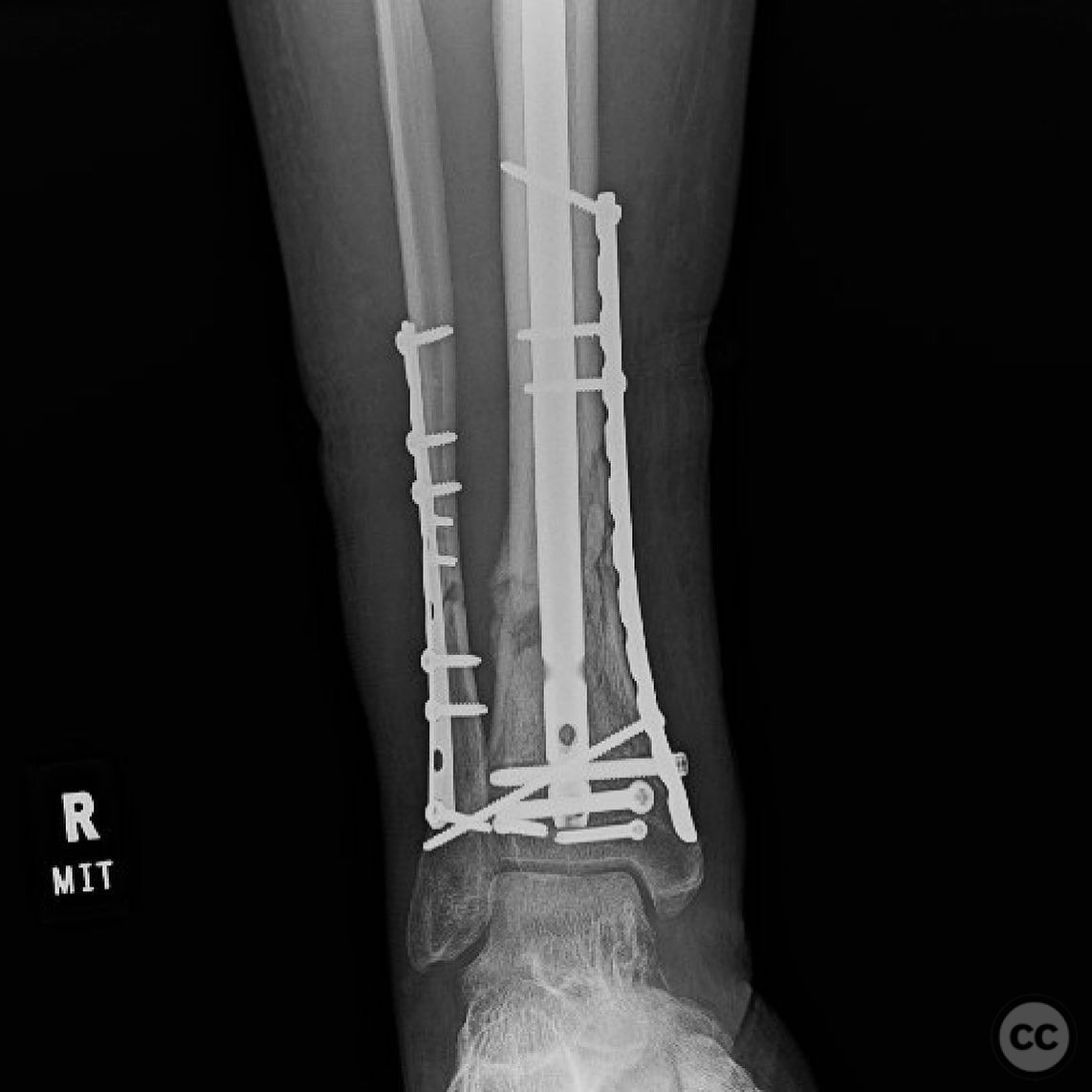
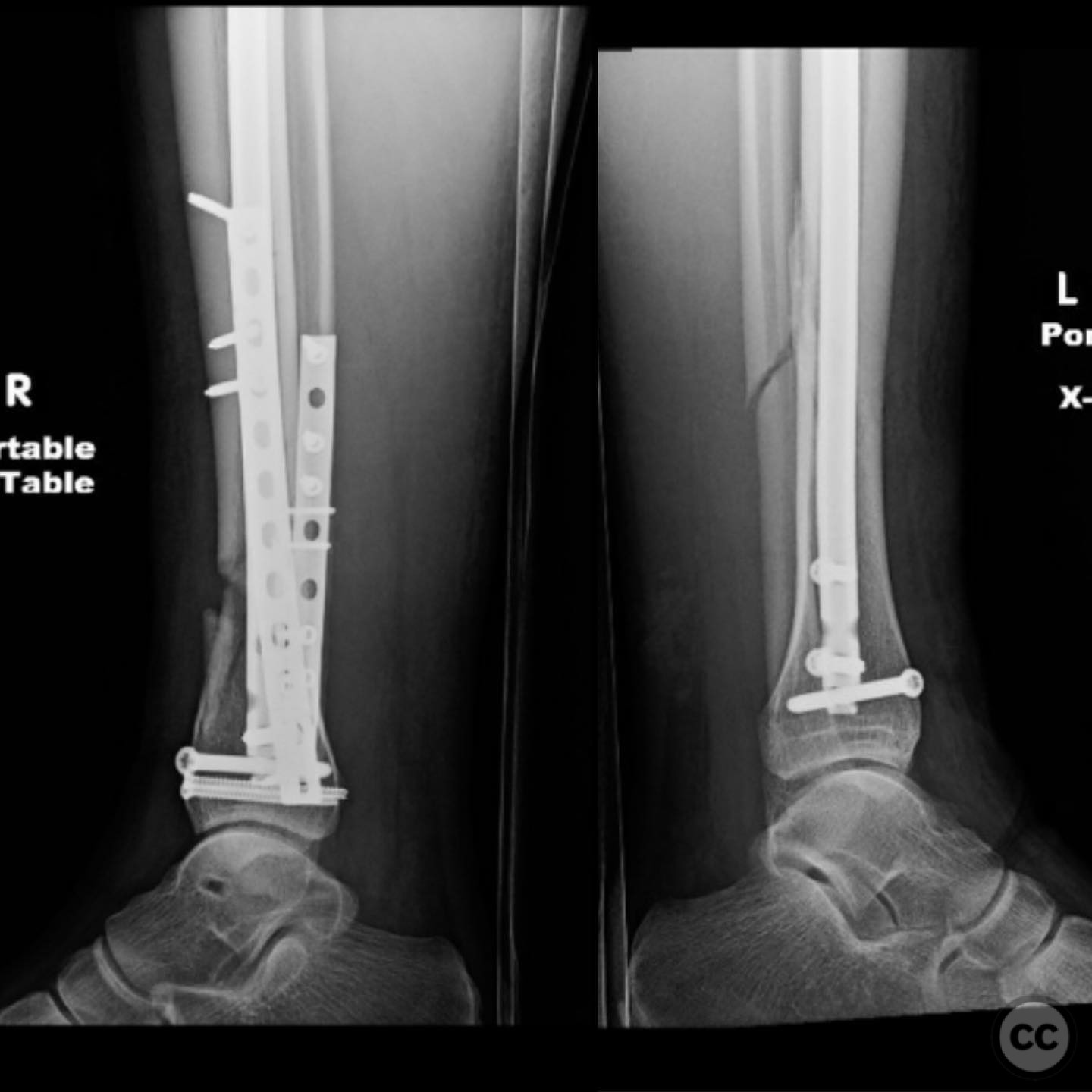
Operative remarks:The right tibia presented a challenge due to its comminuted nature, necessitating reliance on indirect reduction techniques with a distractor. The fibula served as a crucial guide for alignment. The surgeon emphasized the importance of understanding nail characteristics, such as bolt distance and location relative to the fracture, when choosing intramedullary fixation. A percutaneous medial plate was added for additional stability due to the patient's size. On the left side, successful percutaneous clamping prevented displacement during nail deployment. The surgeon noted that maintaining an intact lateral column by addressing the fibula can prevent valgus displacement, although it was not required in this case.
Postoperative protocol: Early mobilization with weight-bearing as tolerated was encouraged, with progression based on clinical and radiological healing.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail, percutaneous medial plate, distractor device.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 216 times
10 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Bilateral Distal Tibia Fractures with Comminution and Fibular Involvement in a Young Male. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 4503277 Published Online Jul 10 2025.