Severely Contaminated OTA C3 Open Pilon Fracture from Rope Swing Fall: Challenges in Debridement, Staged Fixation, and Entrapment of Neurovascular Structures
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
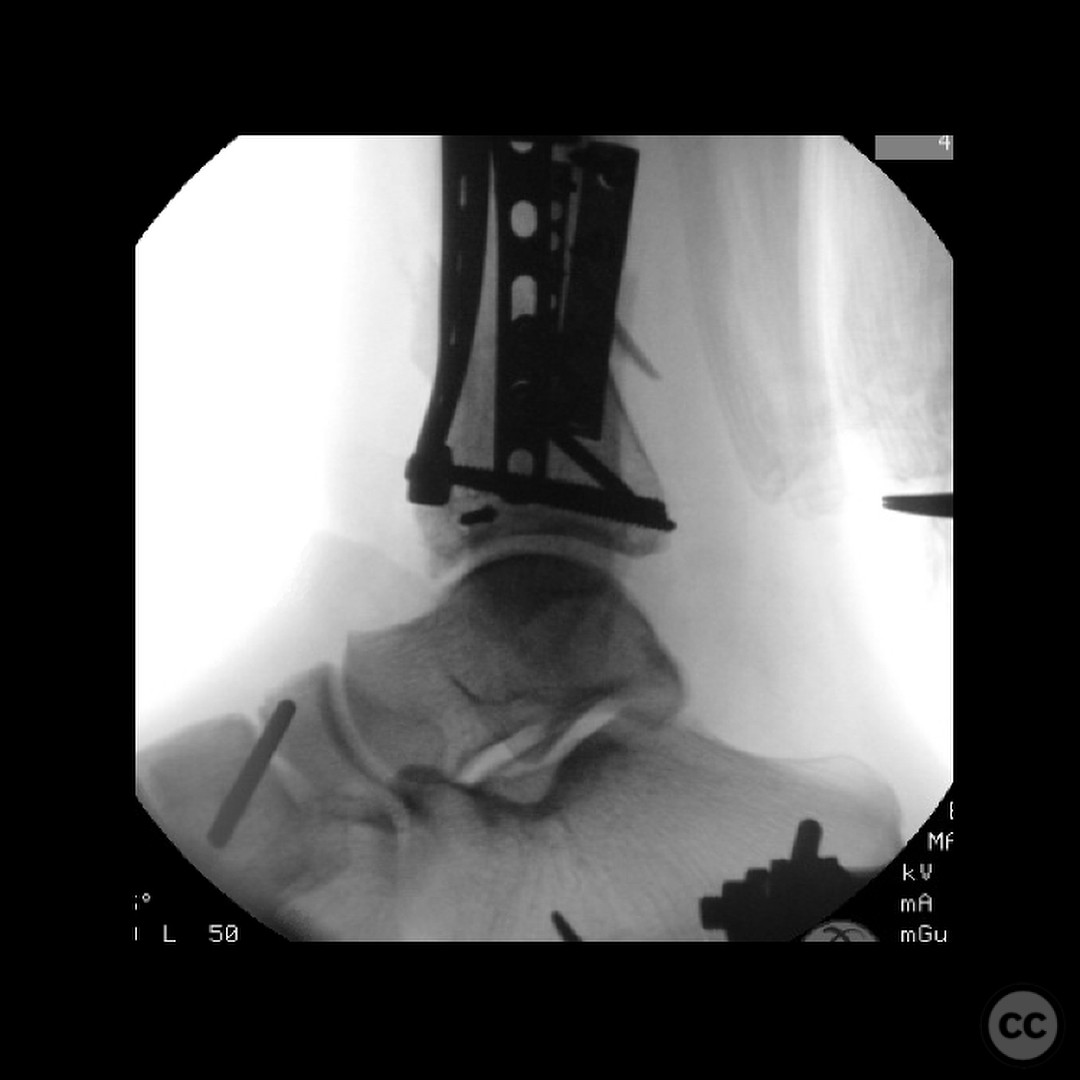
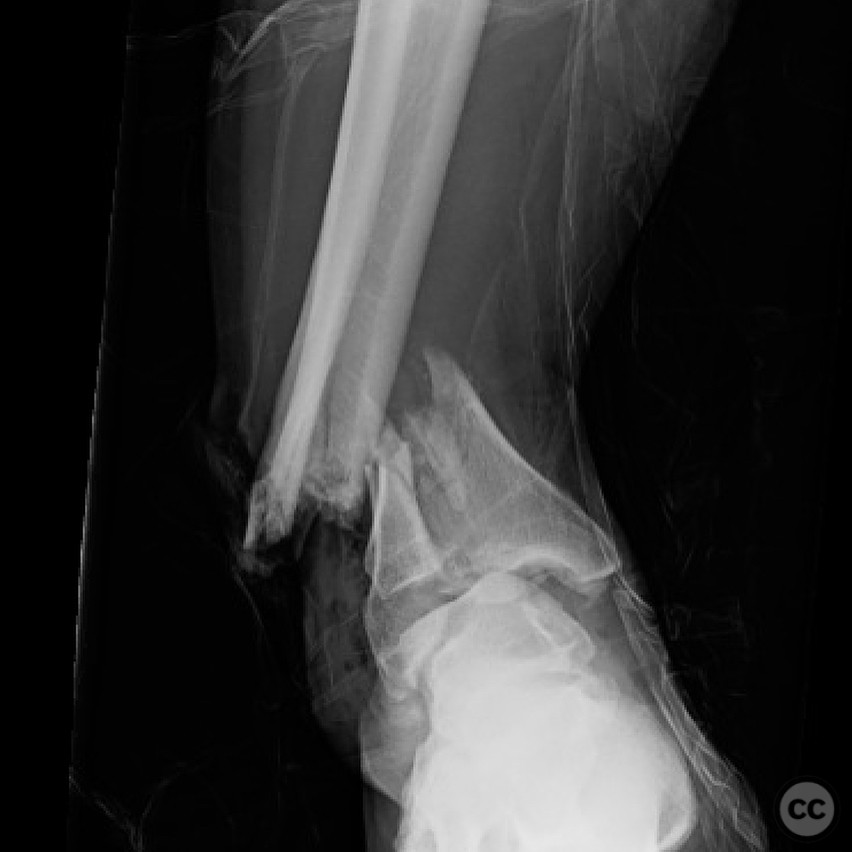
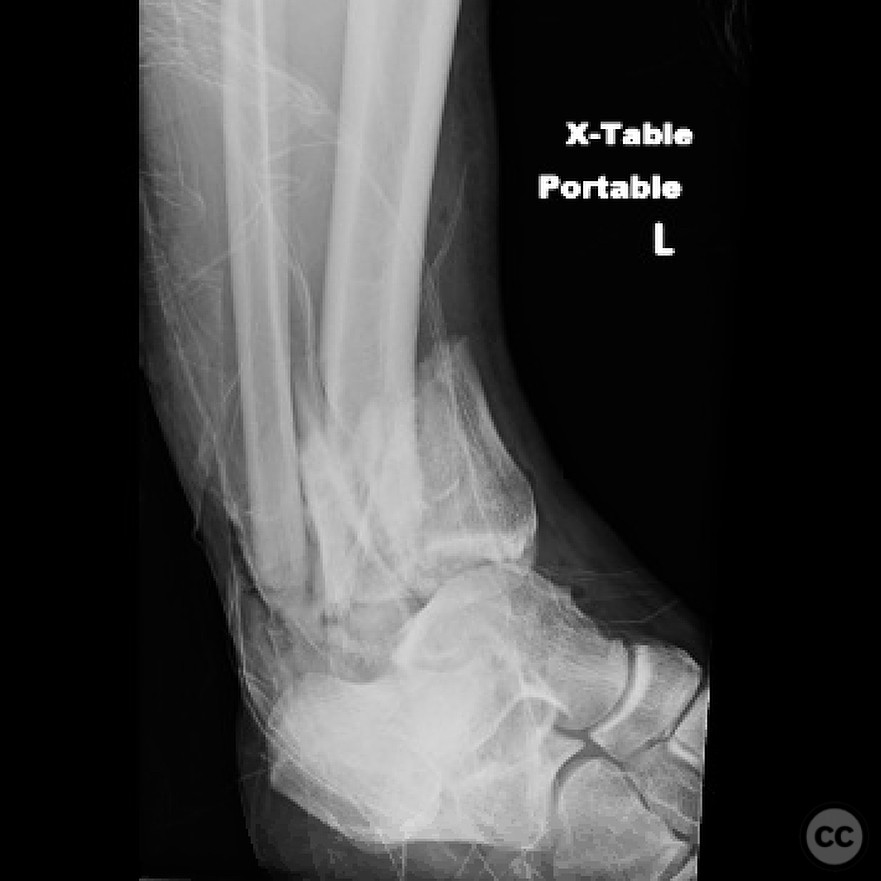
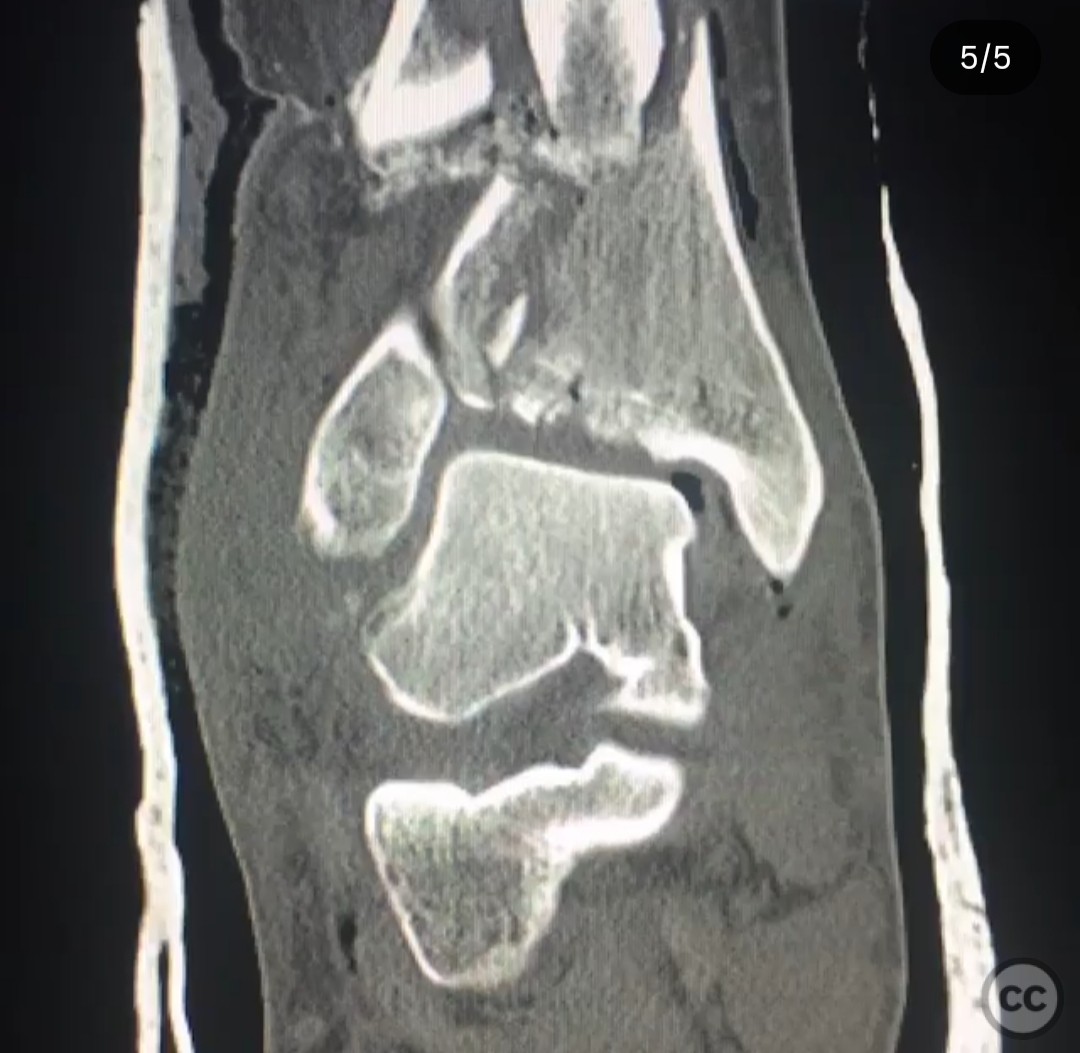
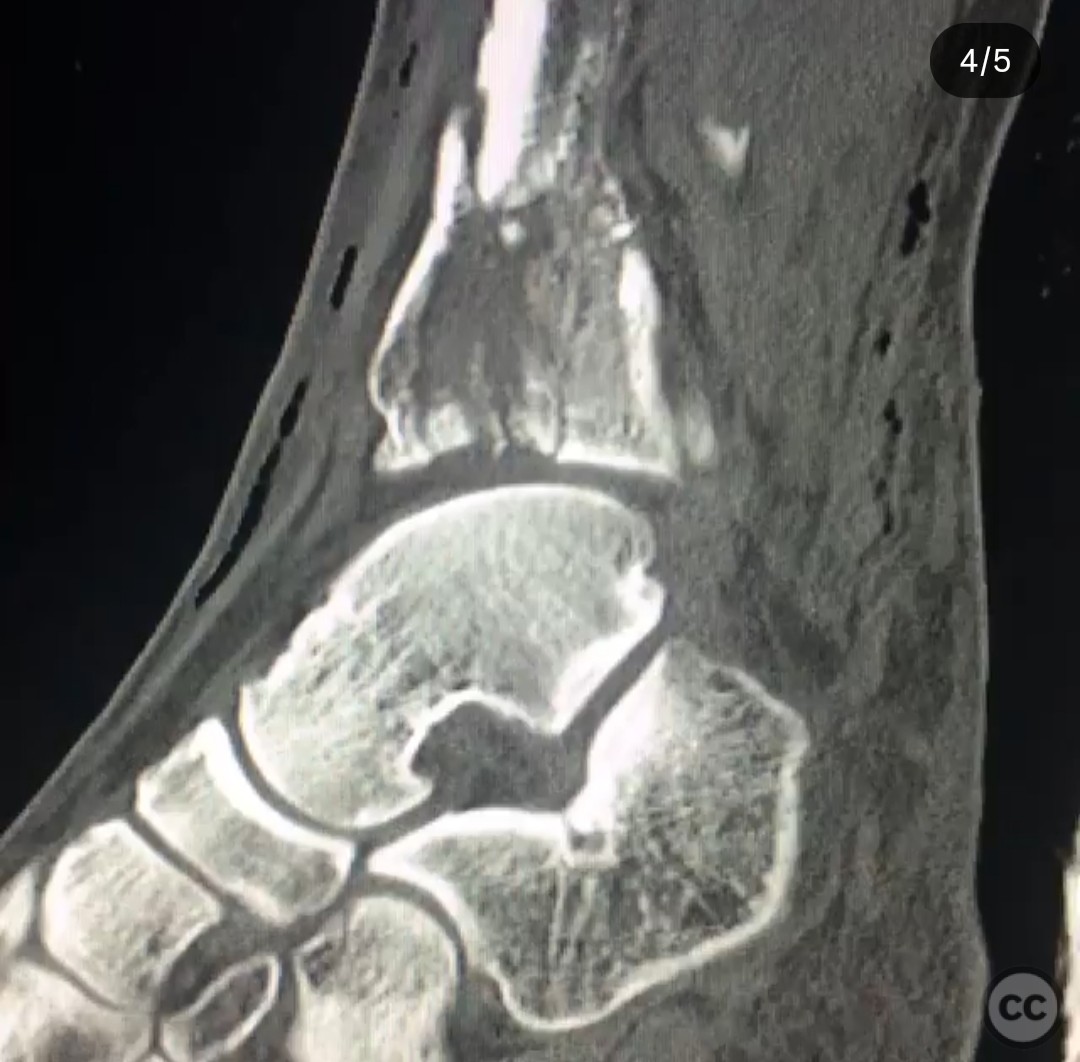
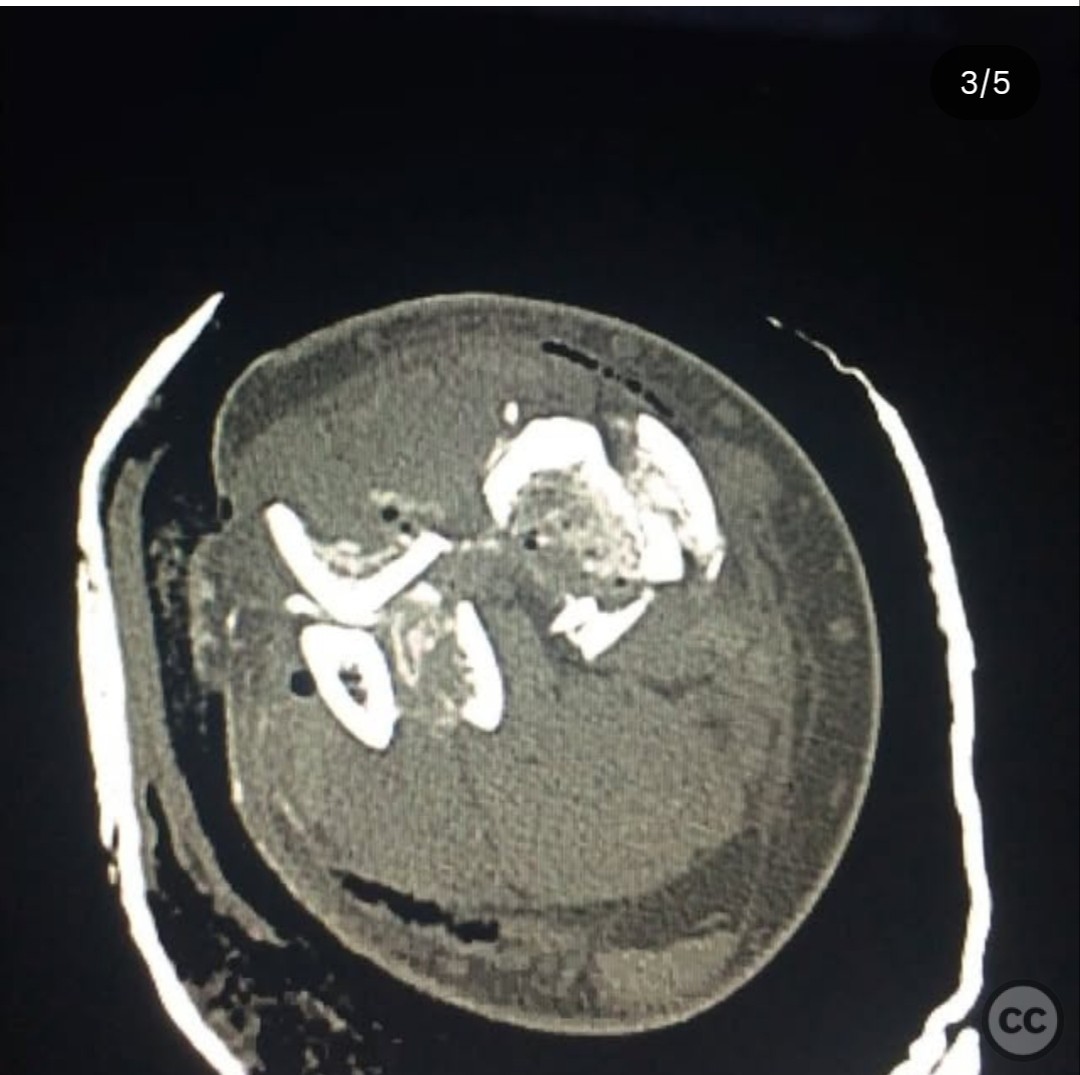
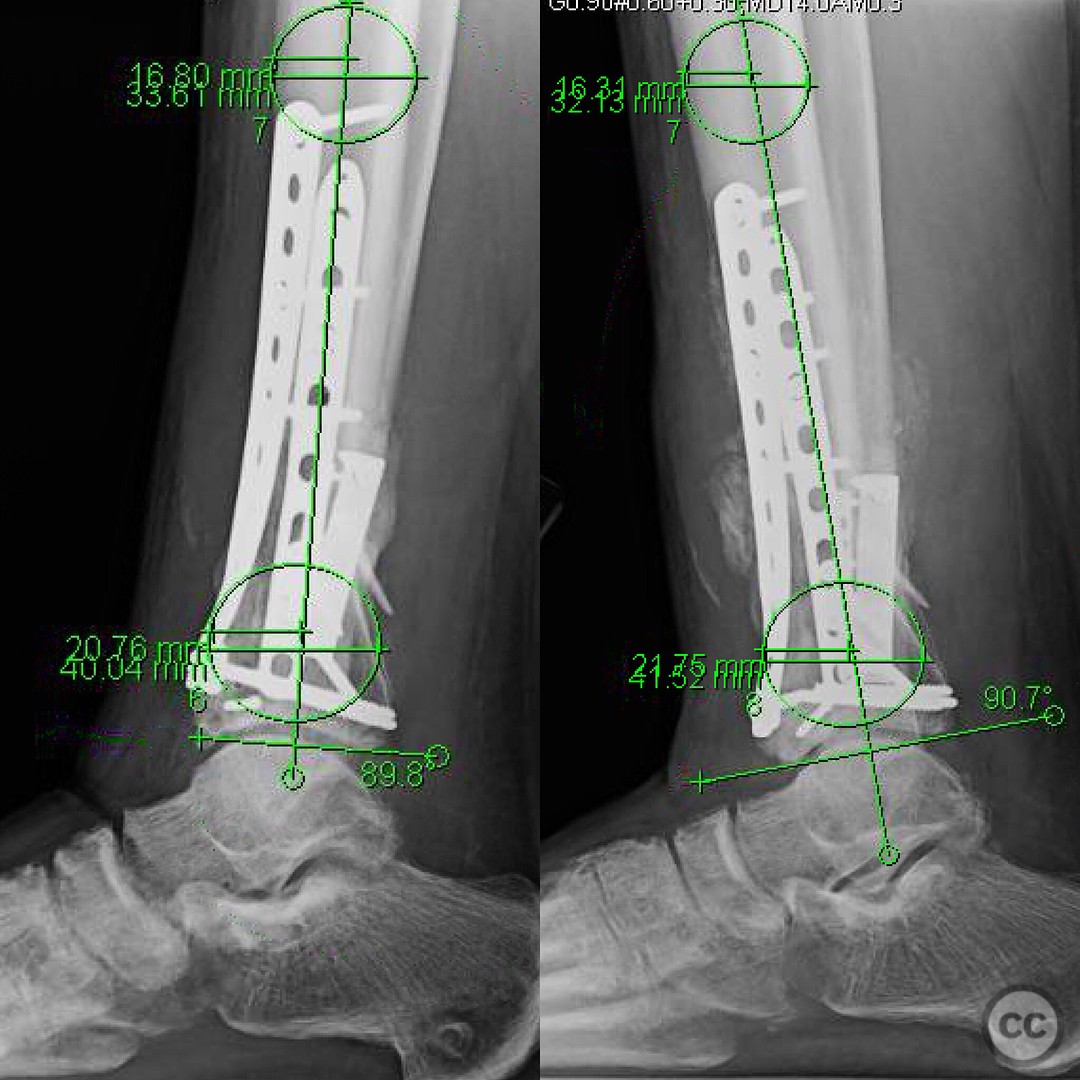
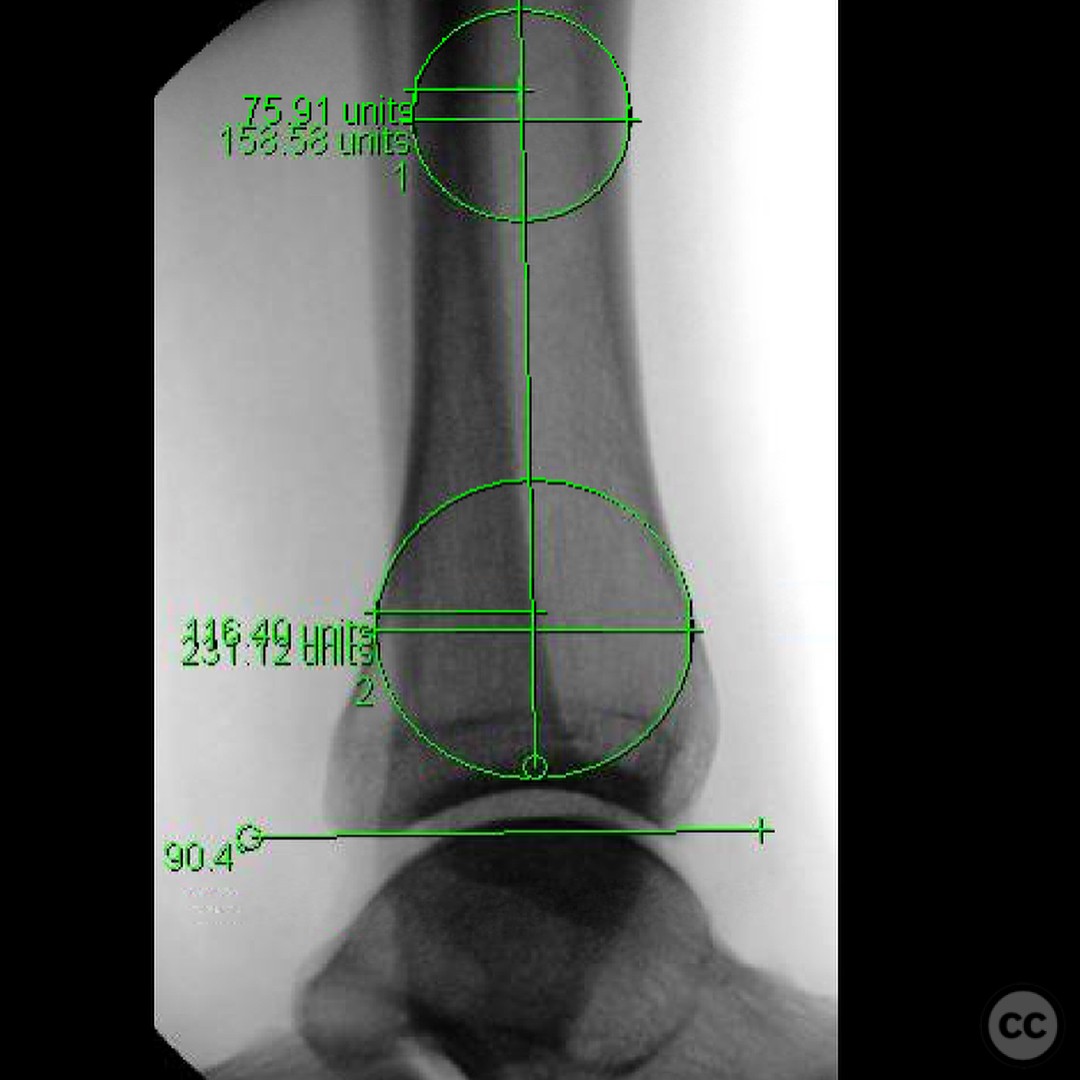
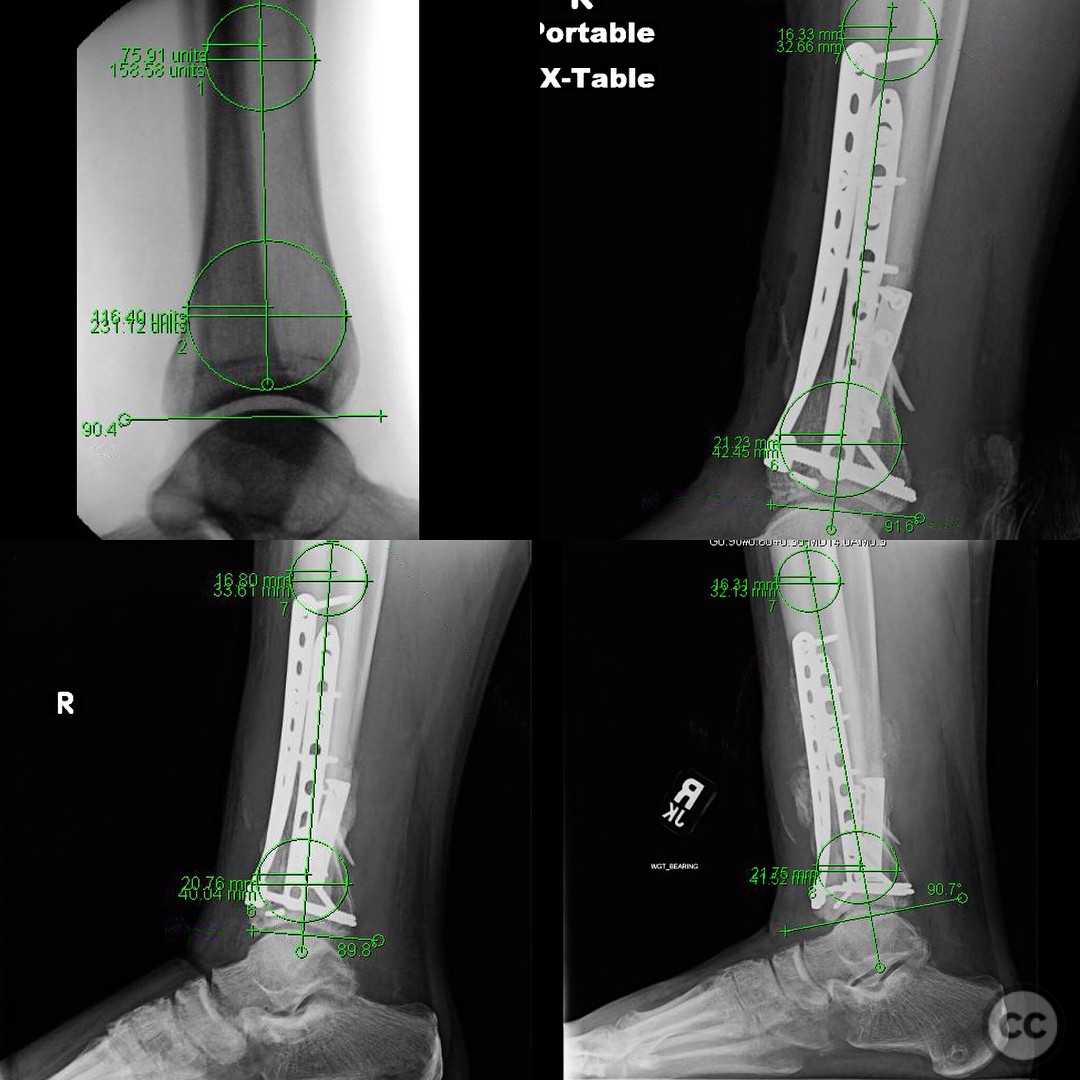
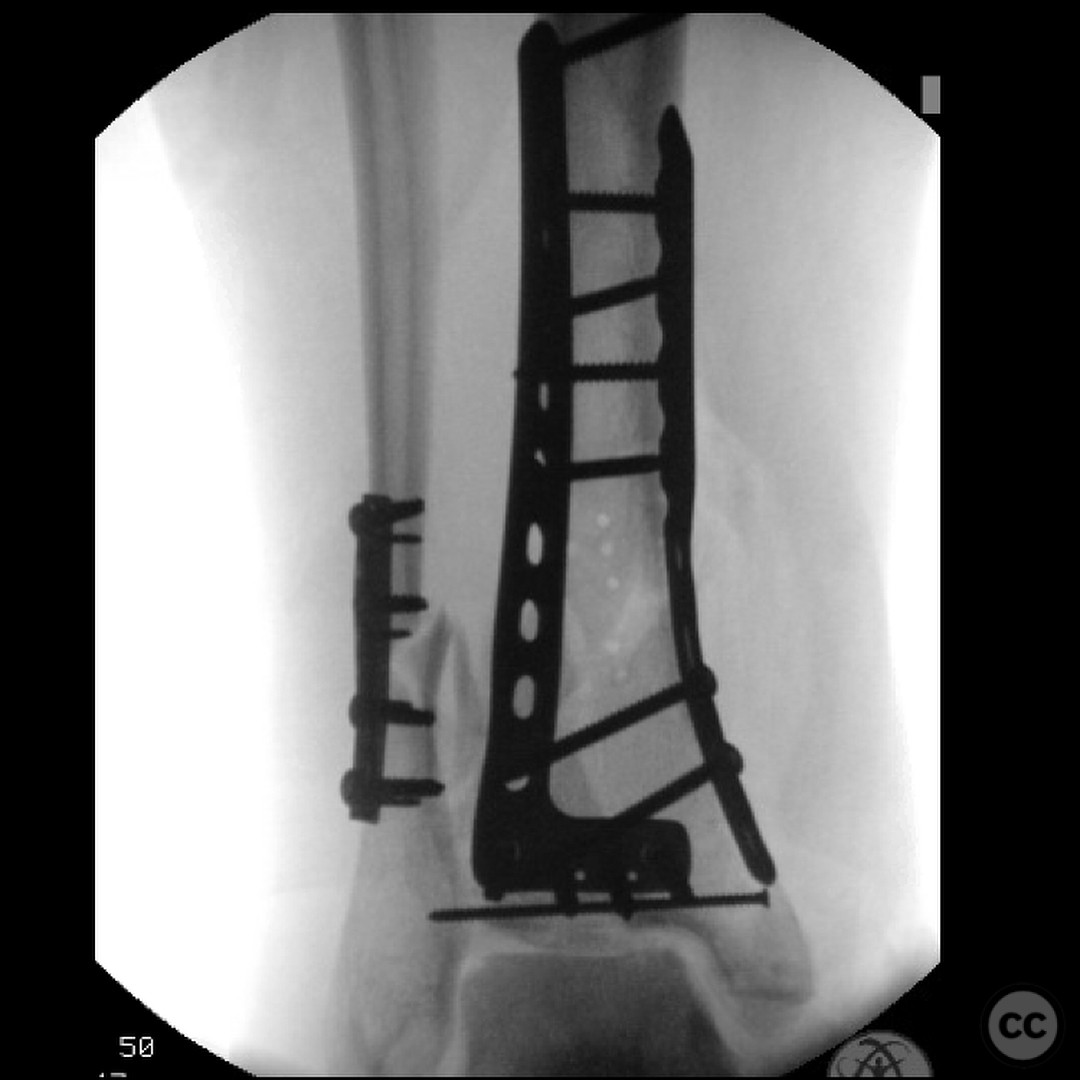
Clinical and radiological findings: A 29-year-old male sustained an open 3A OTA C3 pilon fracture from a rope swing accident, resulting in a heavily contaminated freshwater injury with river sediment. Initial clinical evaluation revealed significant contamination, necessitating urgent surgical intervention. Radiological assessment, including CT imaging, demonstrated a classic pilon fracture with significant articular impaction and displacement. Anterior tibial artery and deep peroneal nerve were noted to be in proximity to the fracture site.
Preoperative Plan
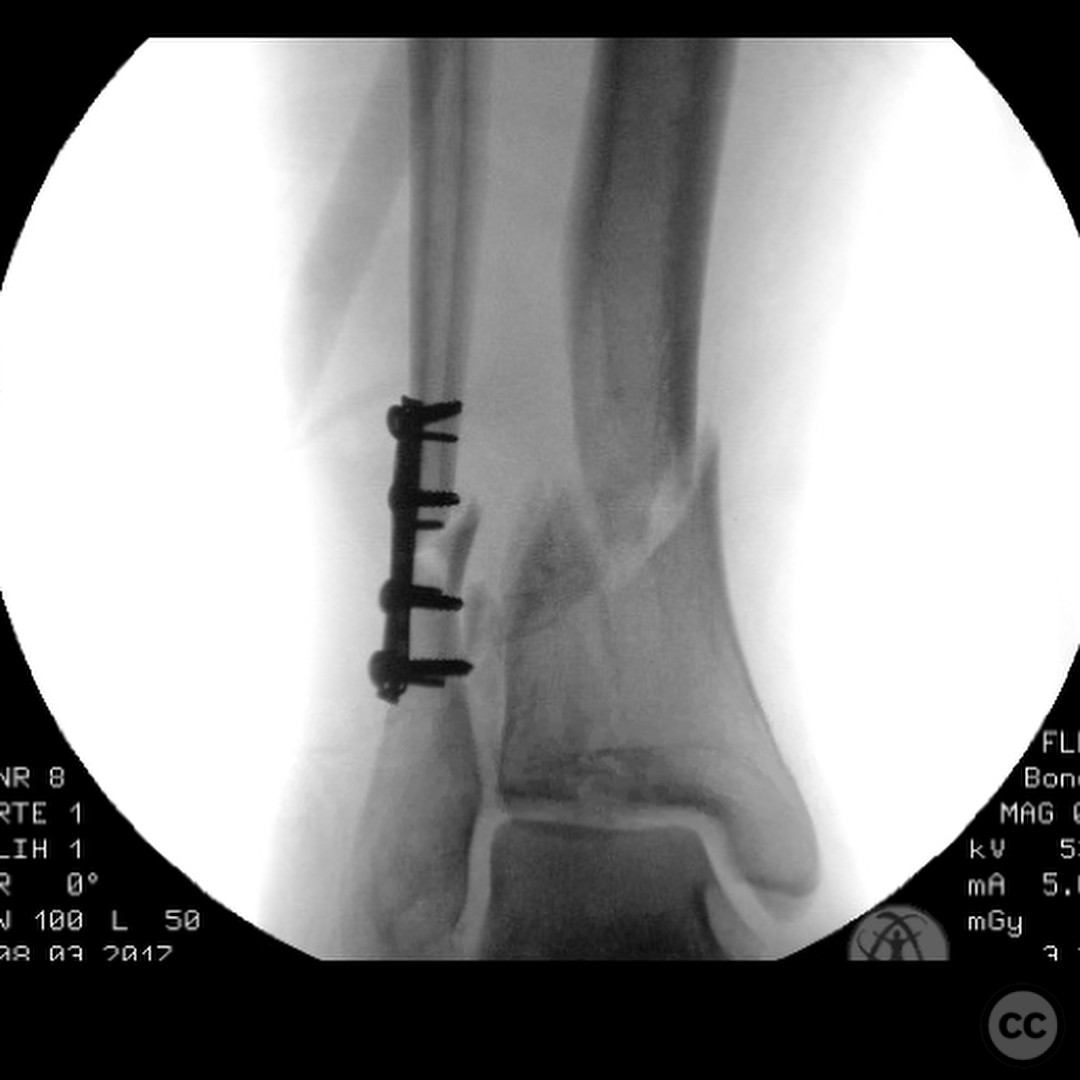
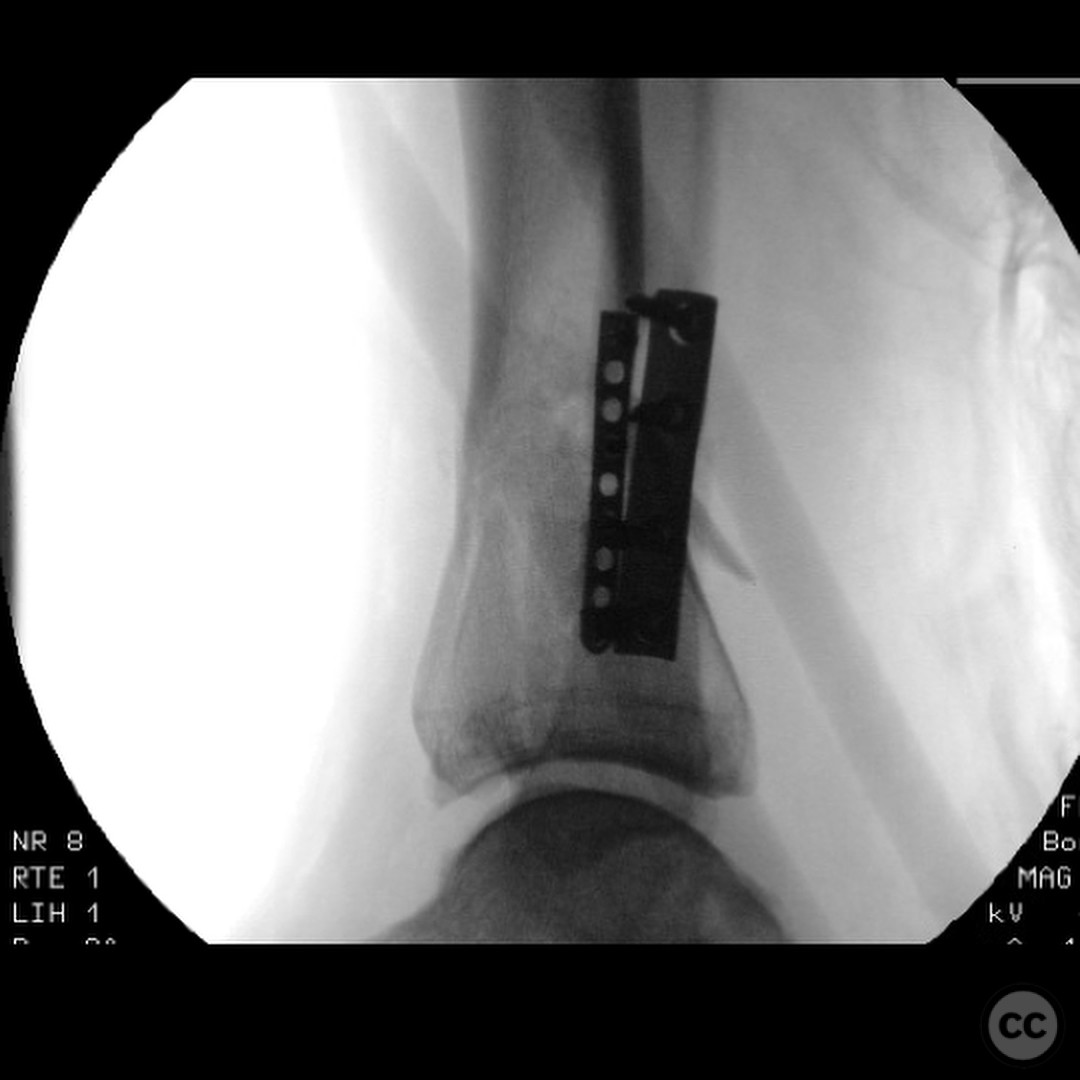
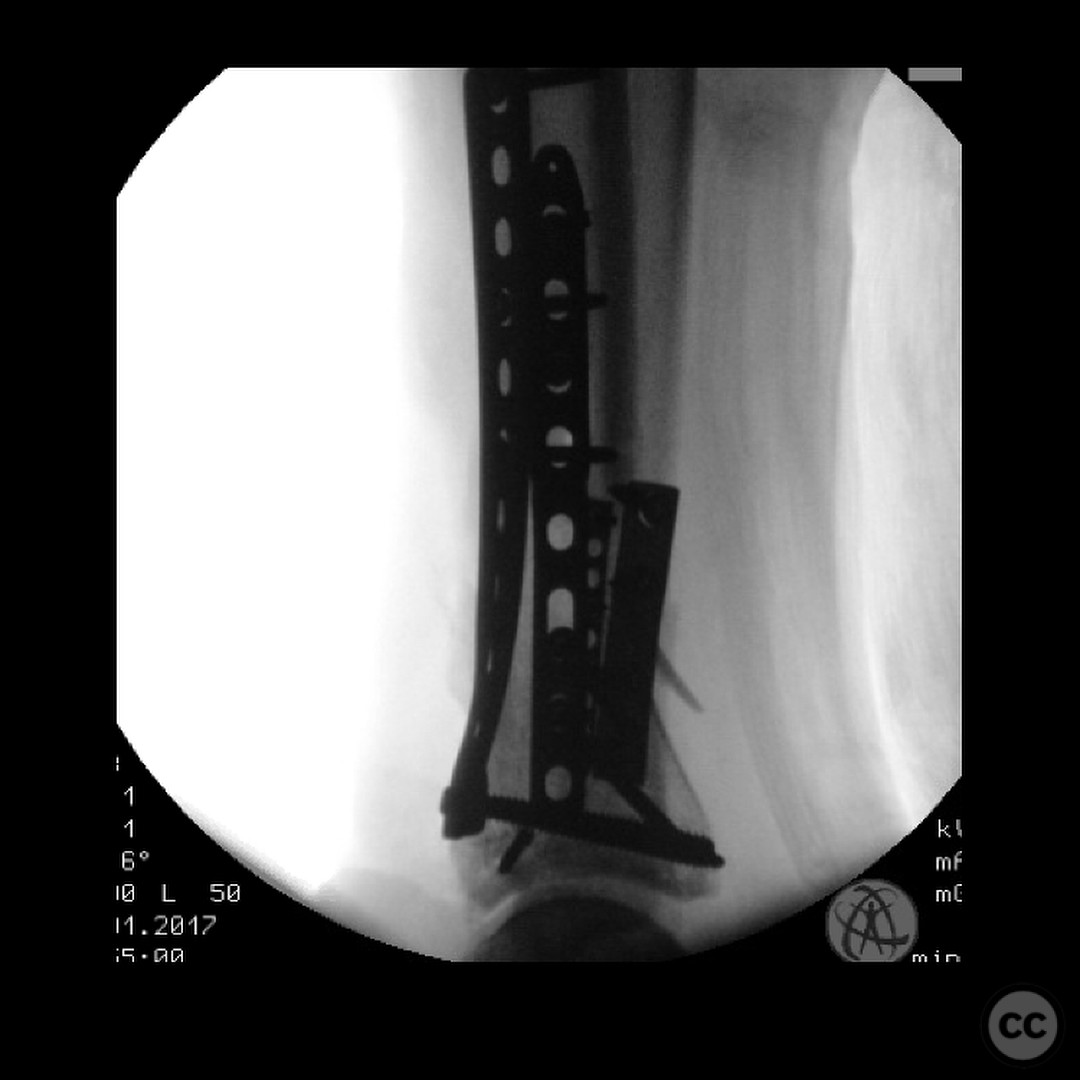
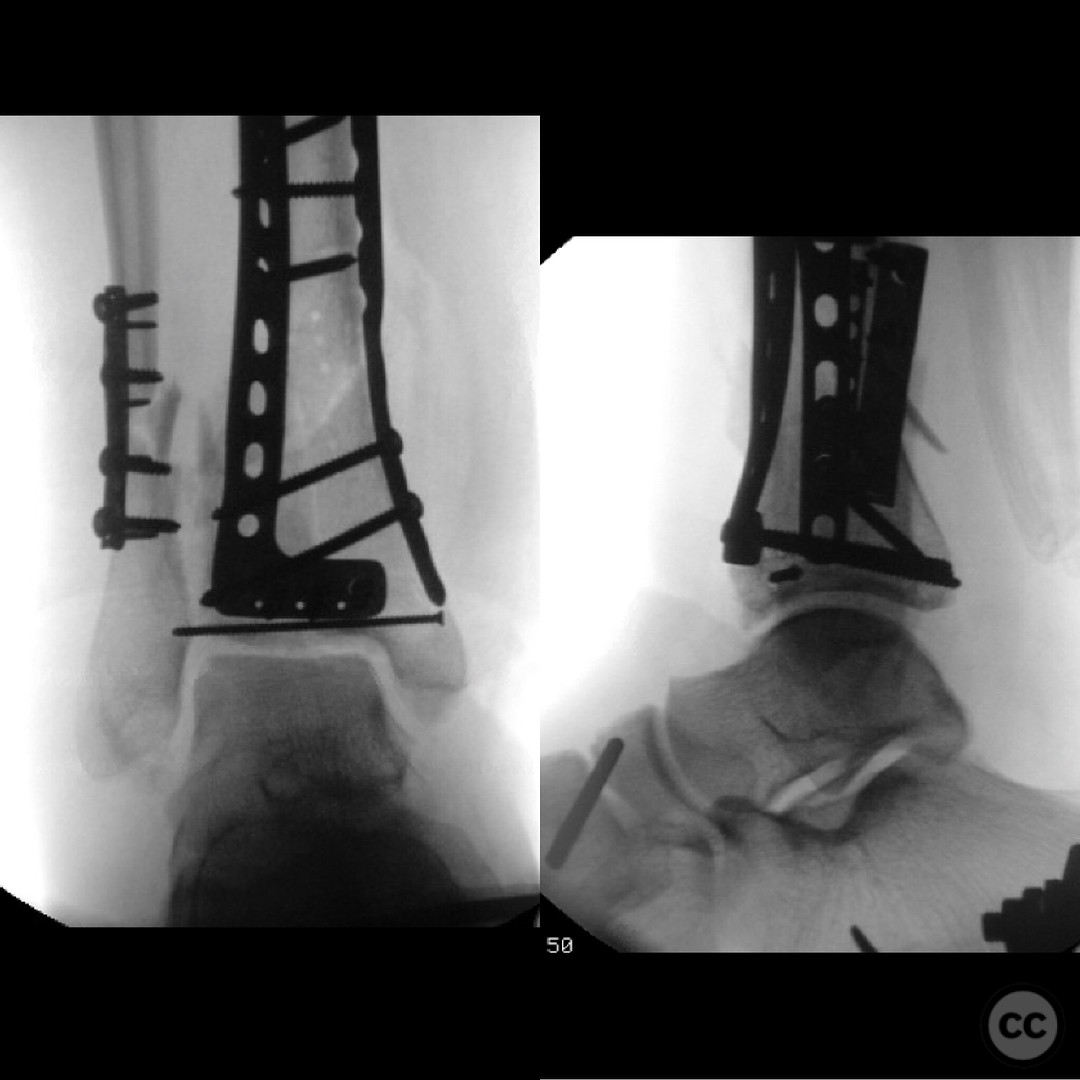
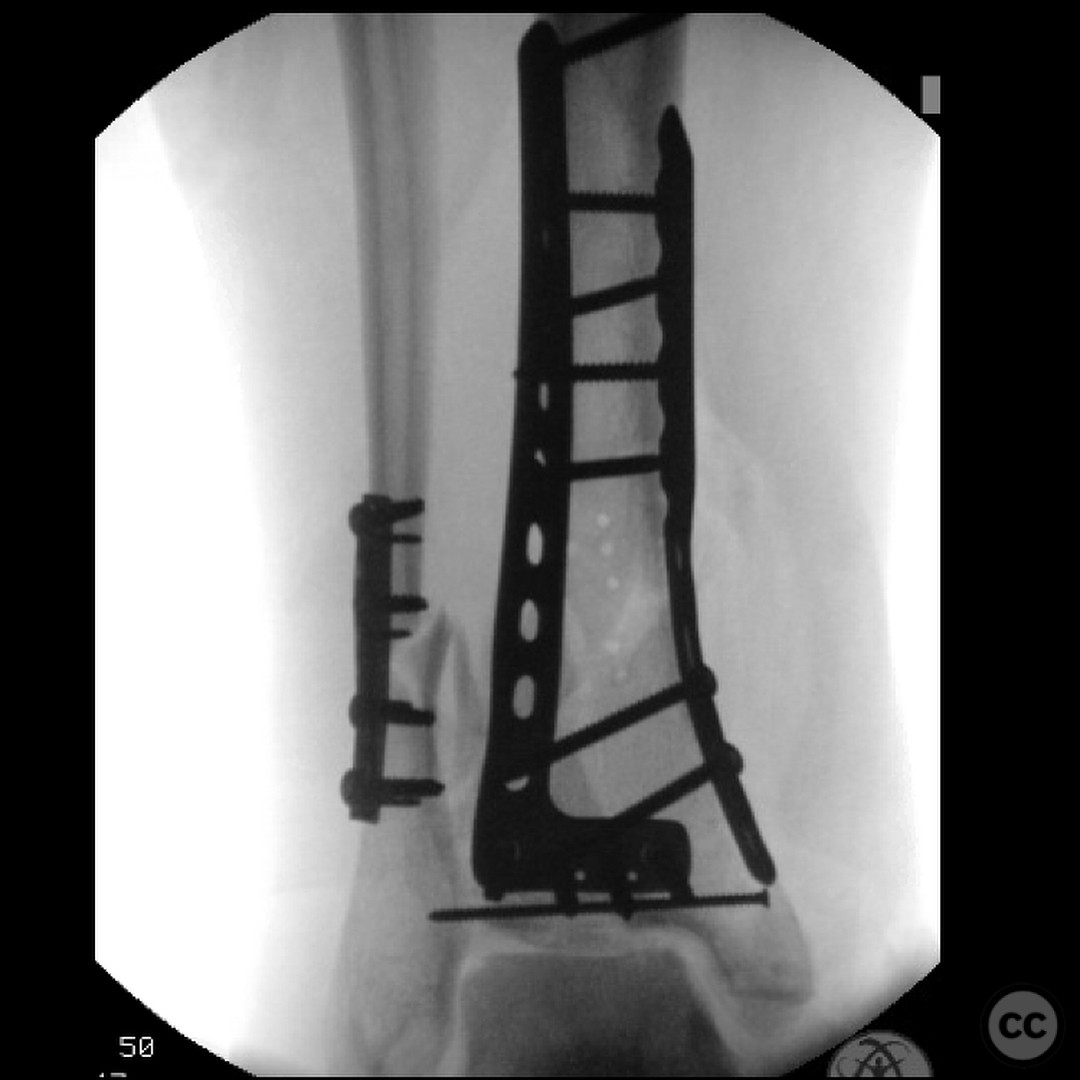
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved an initial stage of meticulous debridement and irrigation to address the open wound contamination. This was followed by fibular fixation to restore lateral column length and facilitate subsequent pilon reduction. An external fixator was applied to maintain length, alignment, and provide joint distraction. The definitive ORIF of the pilon was planned through an anteromedial approach due to the location of traumatic wounds and the need for optimal fracture fragment access.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table to allow access for both debridement and subsequent fixation procedures.
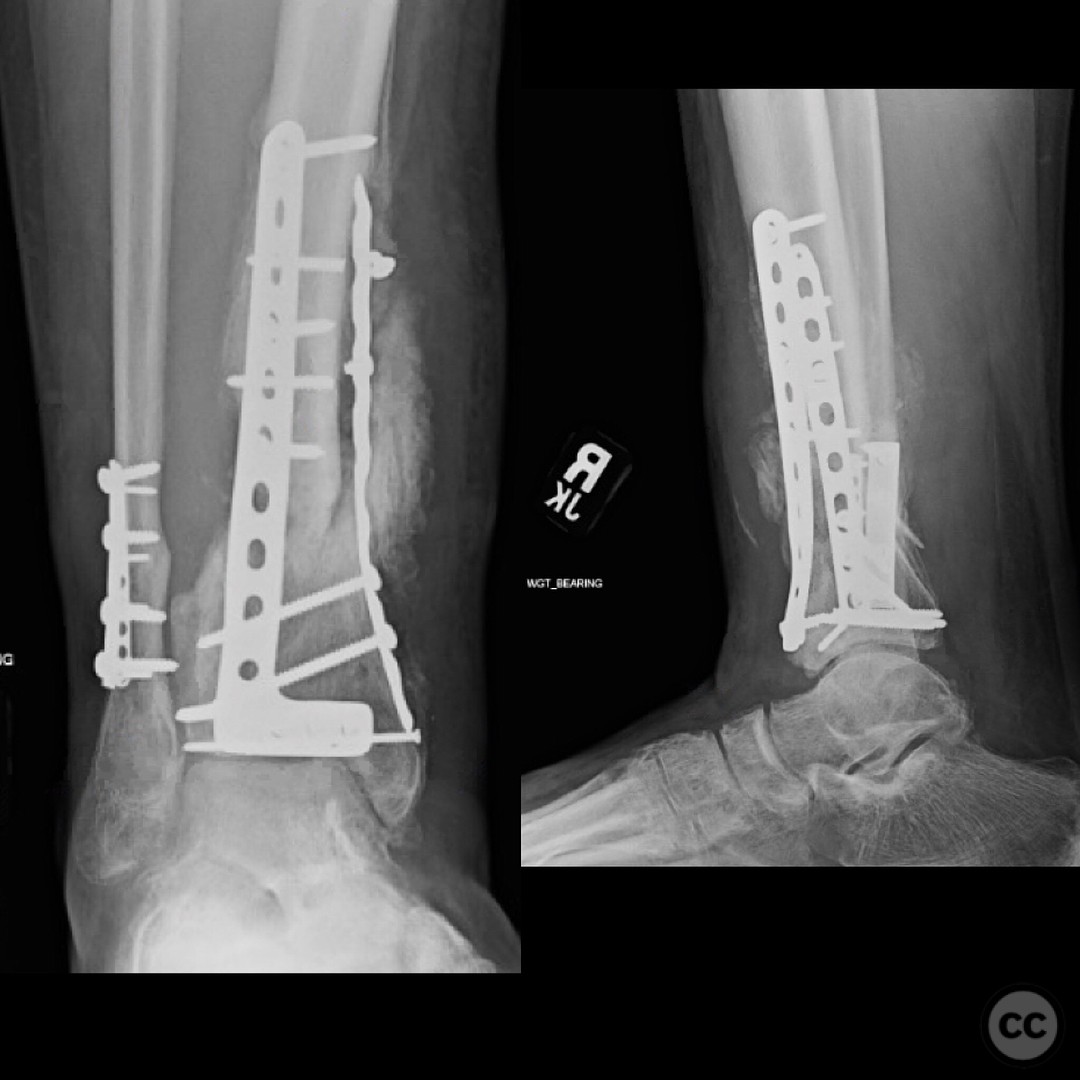
Anatomical surgical approach: The surgical approach for the ORIF of the pilon fracture was an anteromedial incision. Careful dissection was performed to avoid injury to the anterior tibial artery and deep peroneal nerve, which were noted to be in close proximity to the fracture site. The approach allowed for direct visualization and reduction of the fracture fragments, with particular attention to the impacted articular surface.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the critical importance of a thorough and systematic debridement in the initial stage, as the outcome is heavily dependent on the quality of this procedure. The fibular fixation was performed to ensure proper alignment and facilitate later pilon reconstruction. During the ORIF, careful handling of neurovascular structures was paramount due to their proximity to the fracture. The surgeon noted the challenges posed by the articular impaction and emphasized the need for innovative solutions in such cases.
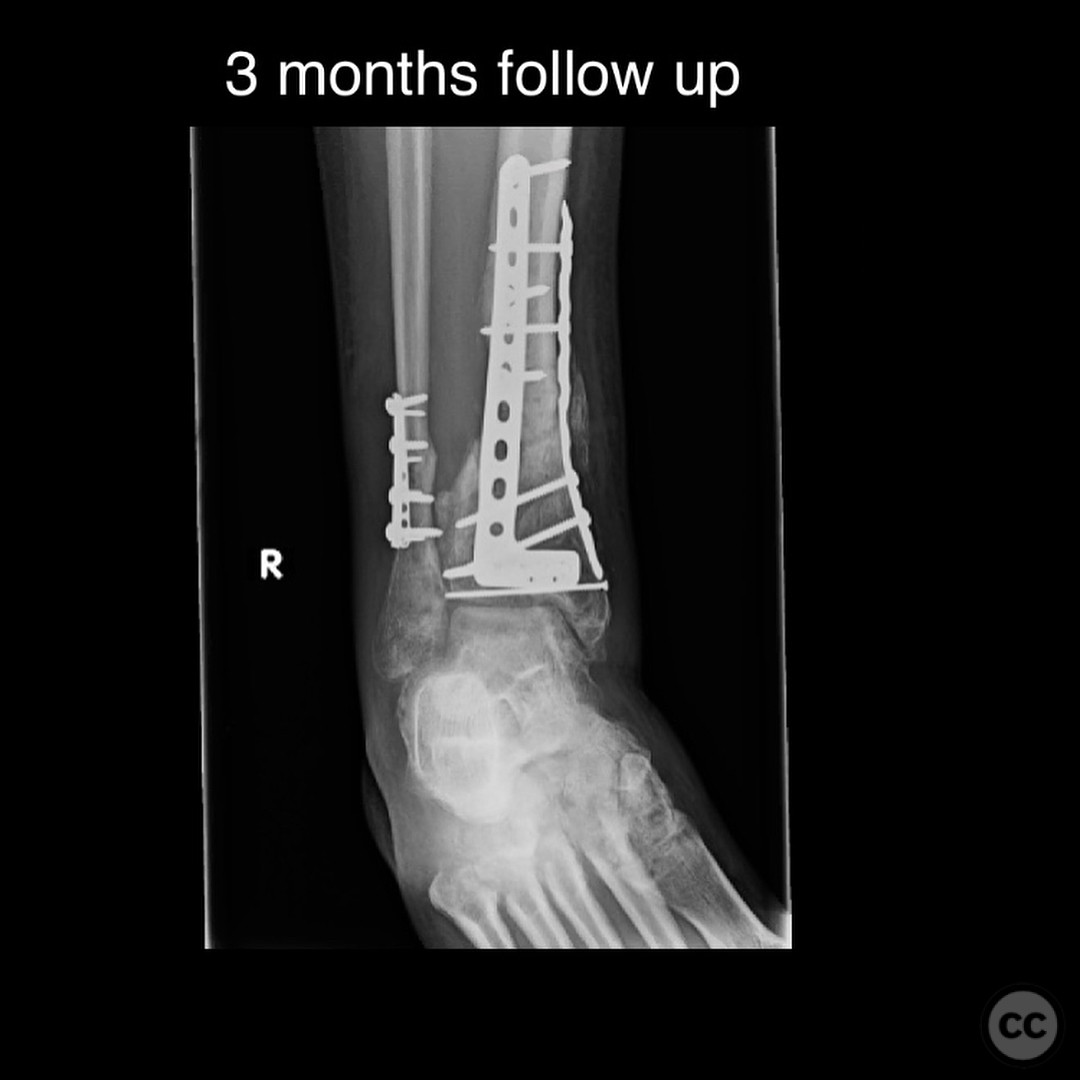
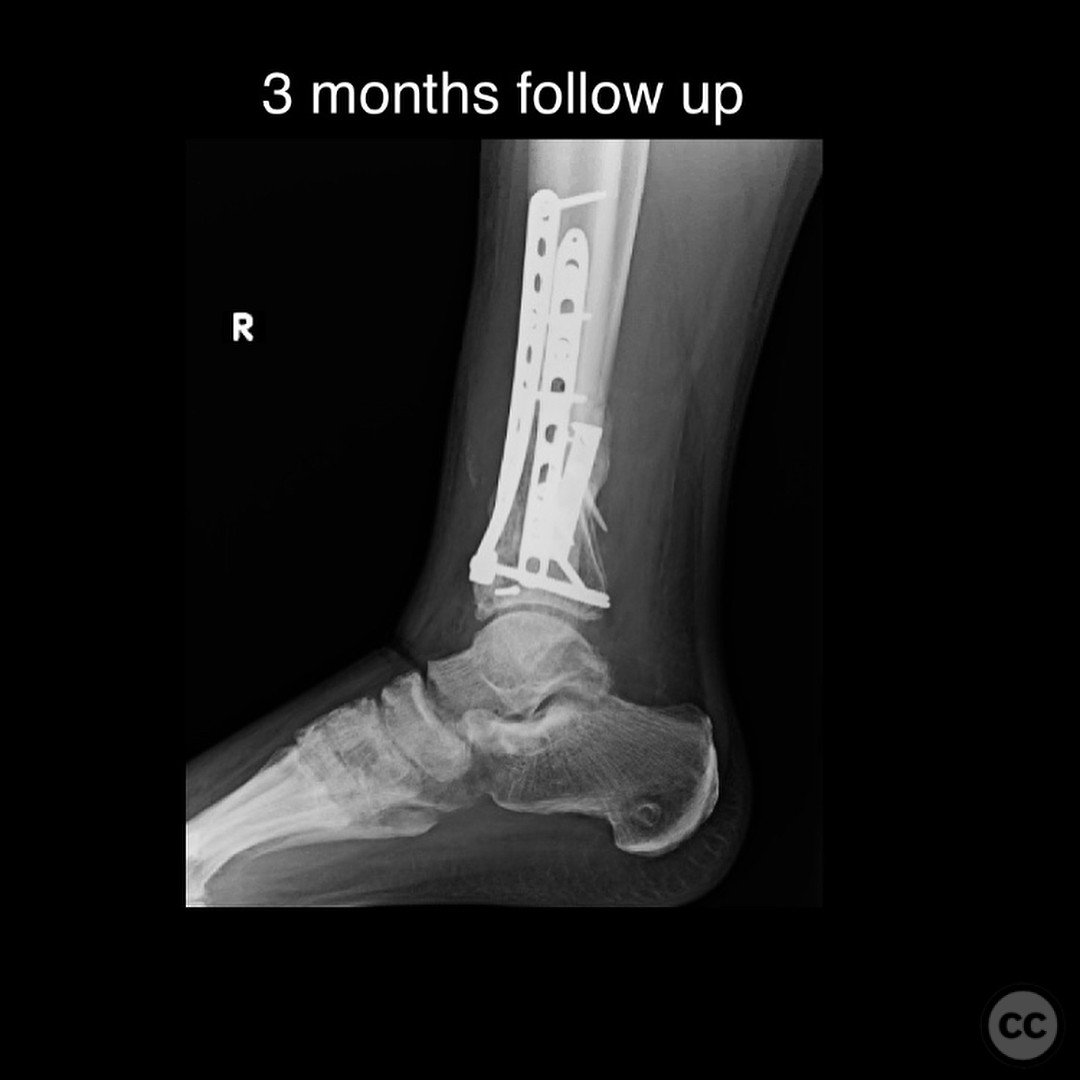
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was allowed progressive weight bearing as tolerated in a CAM boot starting at 3 months post-surgery. The rehabilitation protocol included gradual increase in weight bearing, with transition out of the boot as tolerated by 6 months.
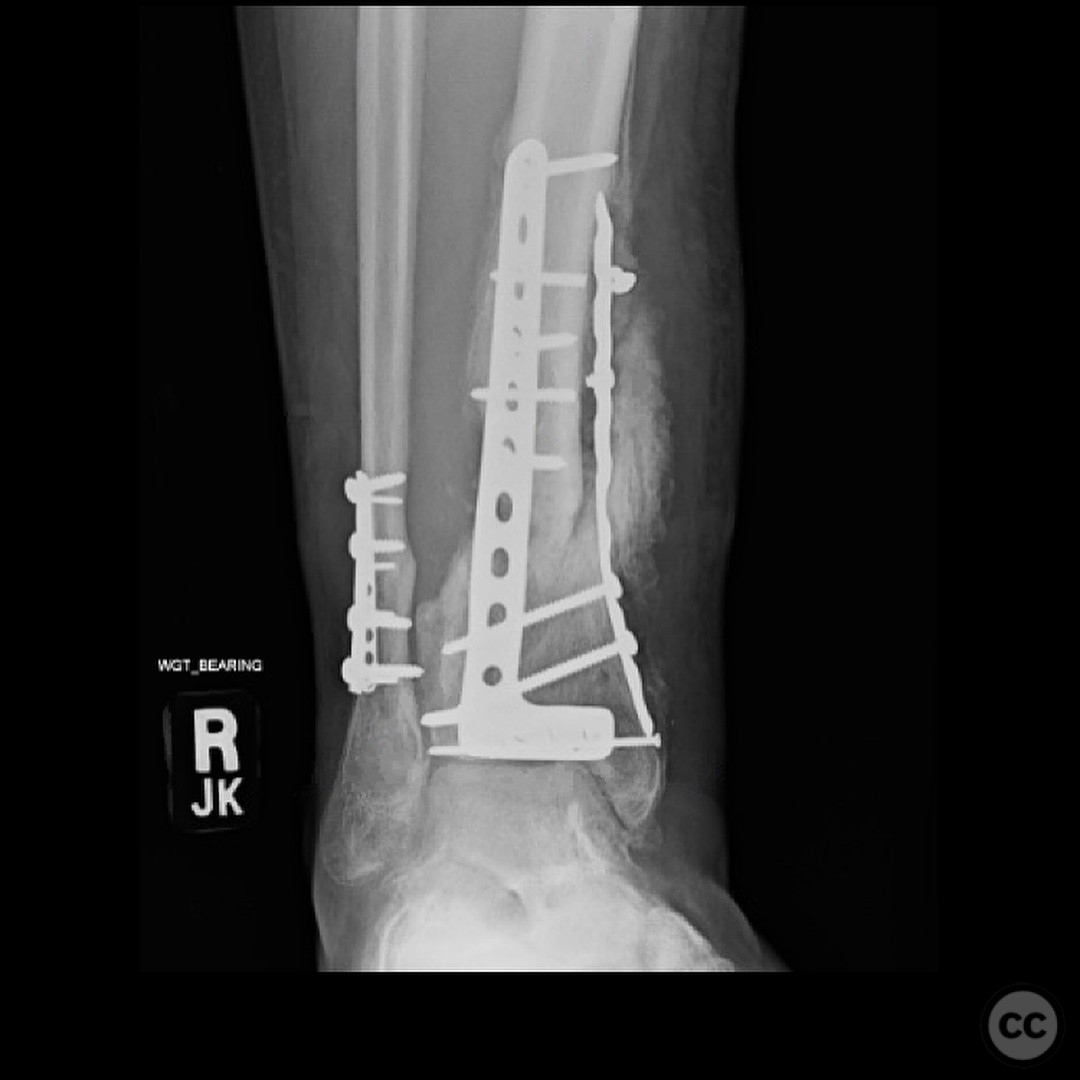
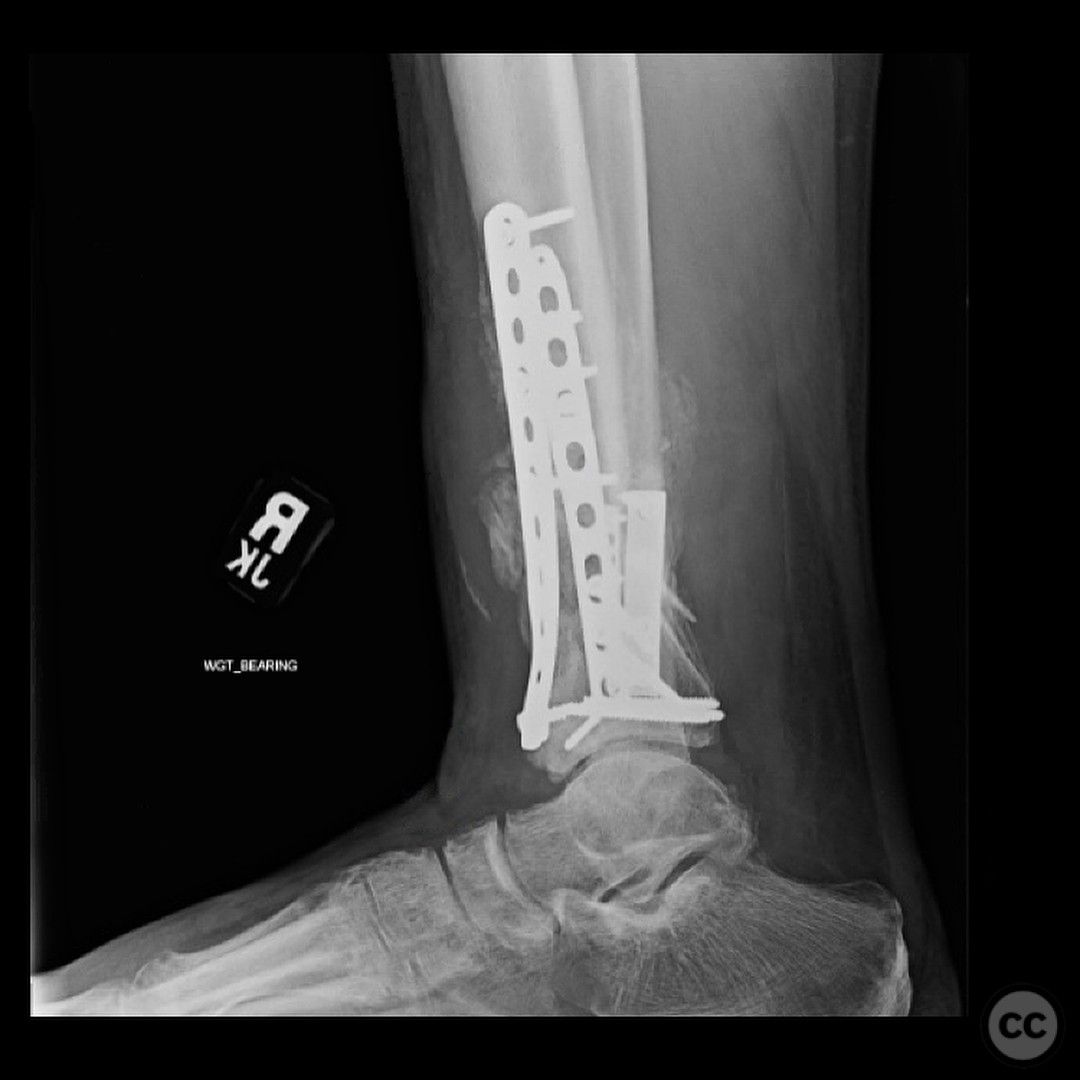
Follow up: At 6 months postoperatively, the patient returned for follow-up, ambulating without assistive devices but still using a CAM boot. He reported some medial side soreness after prolonged standing but overall satisfactory progress. Surgical and traumatic wounds healed uneventfully with no signs of infection.
Orthopaedic implants used: External fixator, fibular plate fixation, CAM boot.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 187 times
25 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Severely Contaminated OTA C3 Open Pilon Fracture from Rope Swing Fall: Challenges in Debridement, Staged Fixation, and Entrapment of Neurovascular Structures. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 43568305 Published Online Jul 25 2025.