Medial Malleolar Malreduction with Syndesmotic Disruption.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
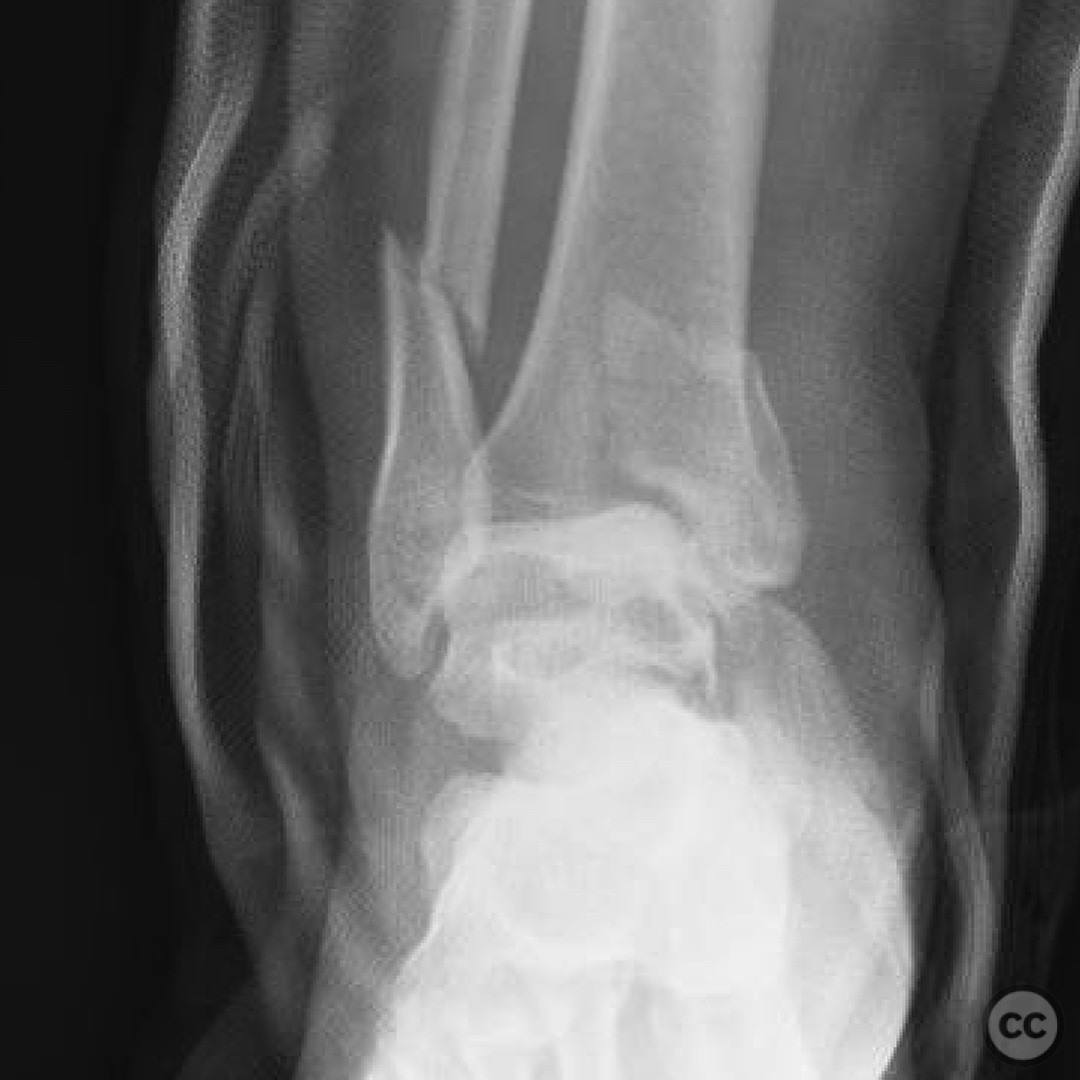
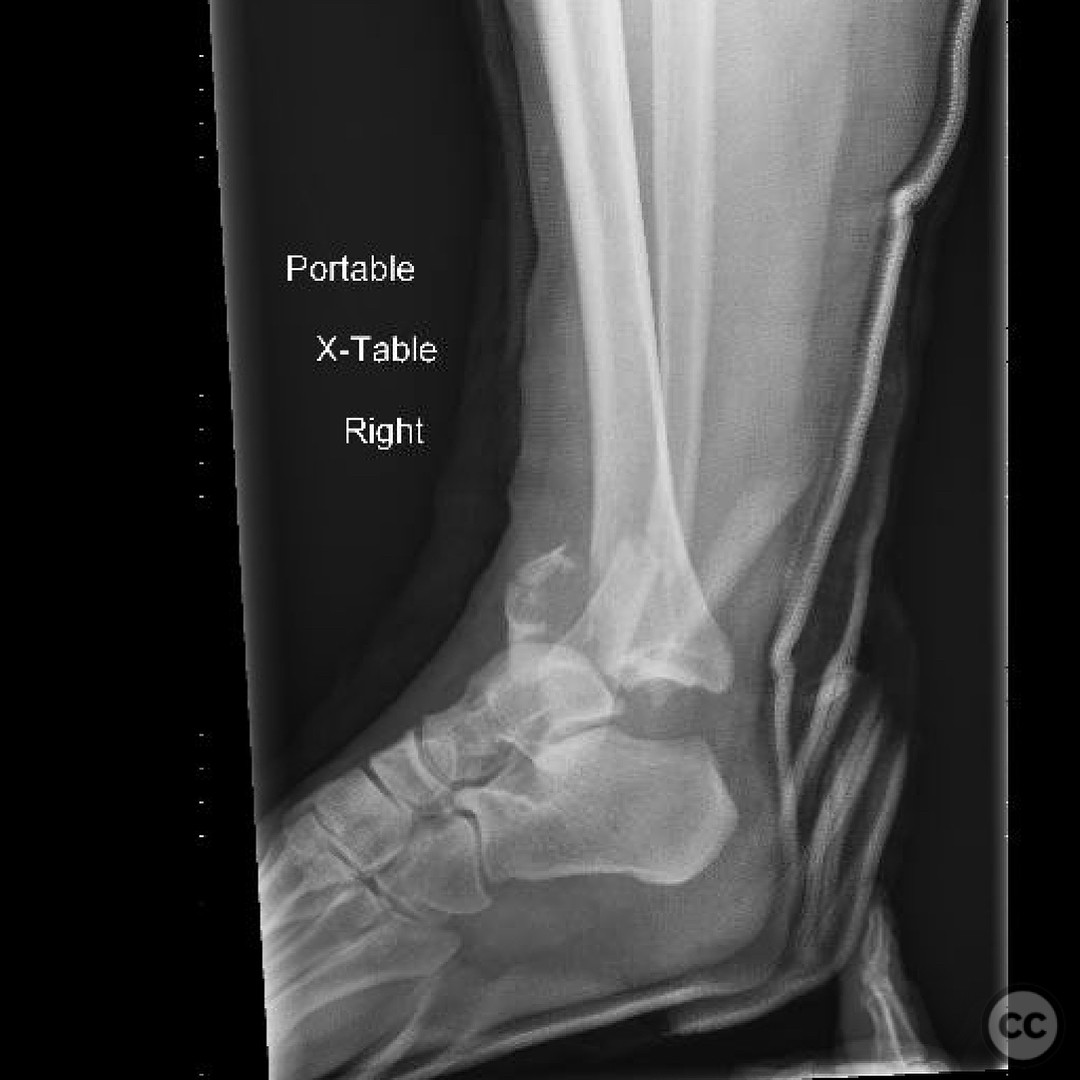
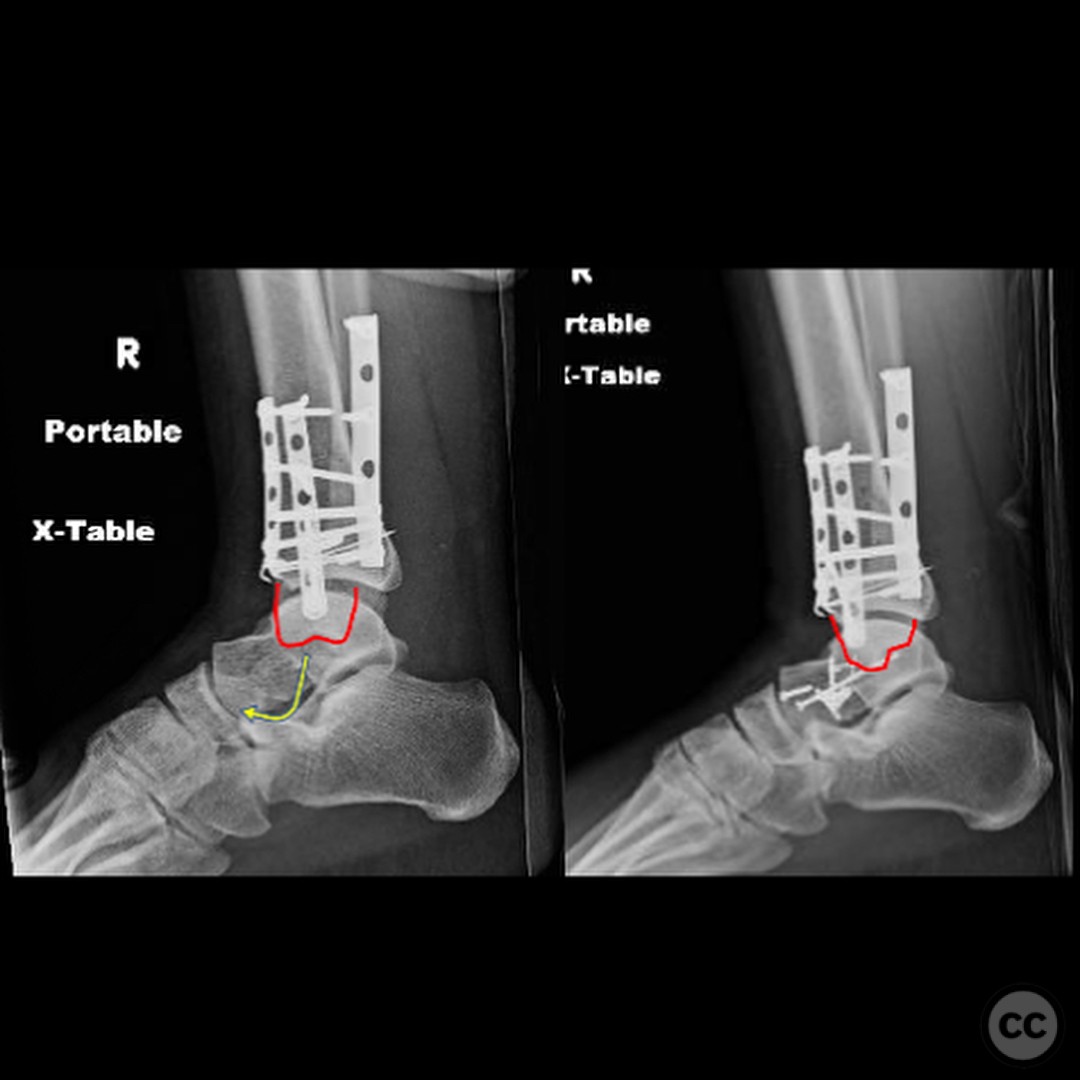
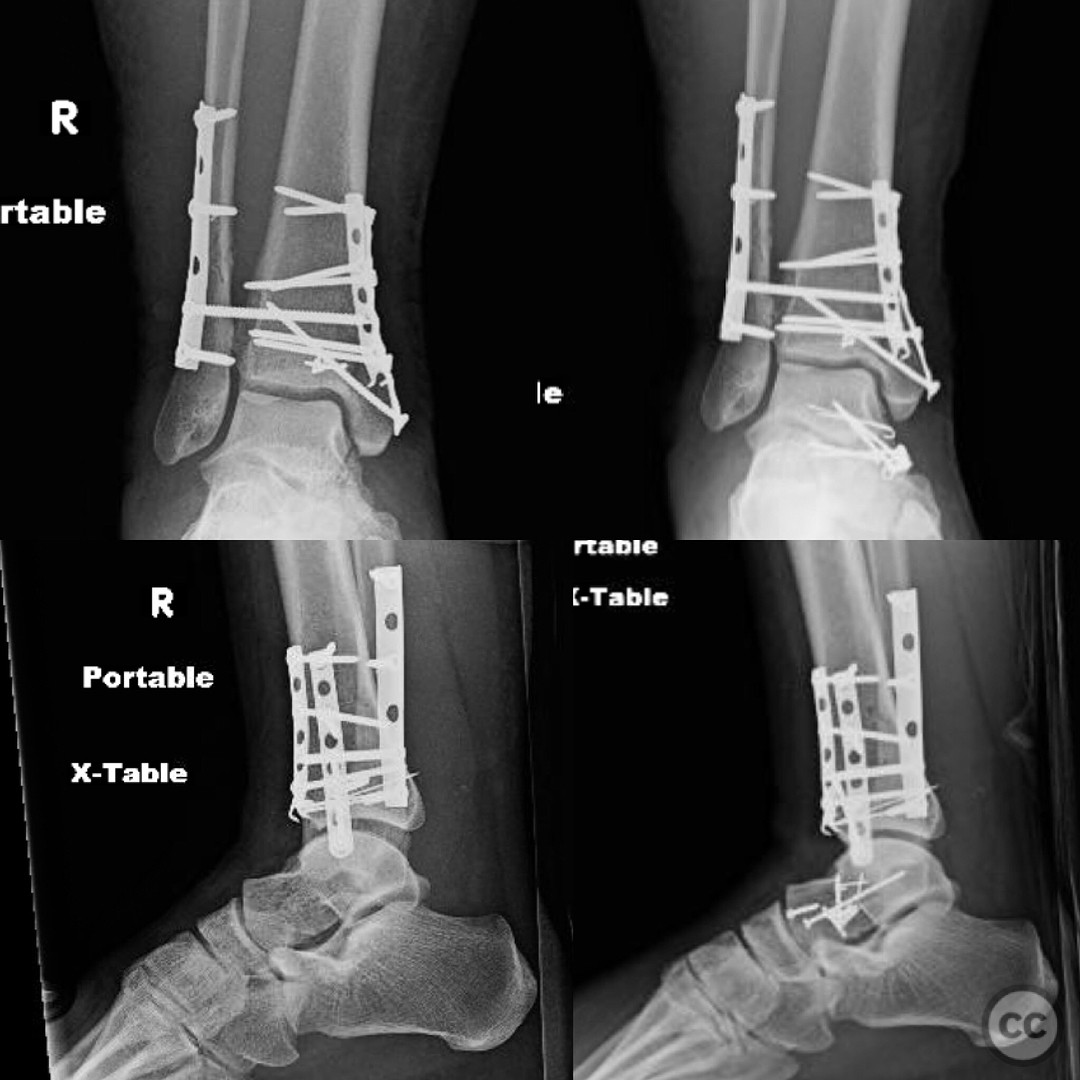
Clinical and radiological findings: A patient presented with an anterior dislocation of the ankle joint, accompanied by disruption of the syndesmosis. Initial radiological assessment revealed that the medial malleolus and distal fibula were displaced along with the talus, indicating a complete disruption of posterior ligaments while the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL) and deltoid ligament remained intact. Postoperative imaging identified a malreduction of the medial malleolus, particularly evident in the lateral view, leading to anterior displacement of the talus due to deltoid ligament tension.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved an anatomical reduction of the fibula and medial malleolus through a direct medial approach to address the malreduction. The surgical strategy included ensuring proper alignment and fixation of the medial malleolus to prevent anterior displacement of the talus and subsequent syndesmotic malalignment.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with a bump under the ipsilateral hip to facilitate access to the medial aspect of the ankle.
Anatomical surgical approach: A direct medial approach was utilized, involving an incision over the medial malleolus. Careful dissection was performed to expose the fracture site, allowing for direct visualization and reduction of the malleolar fragment. The syndesmosis was addressed through a separate lateral incision
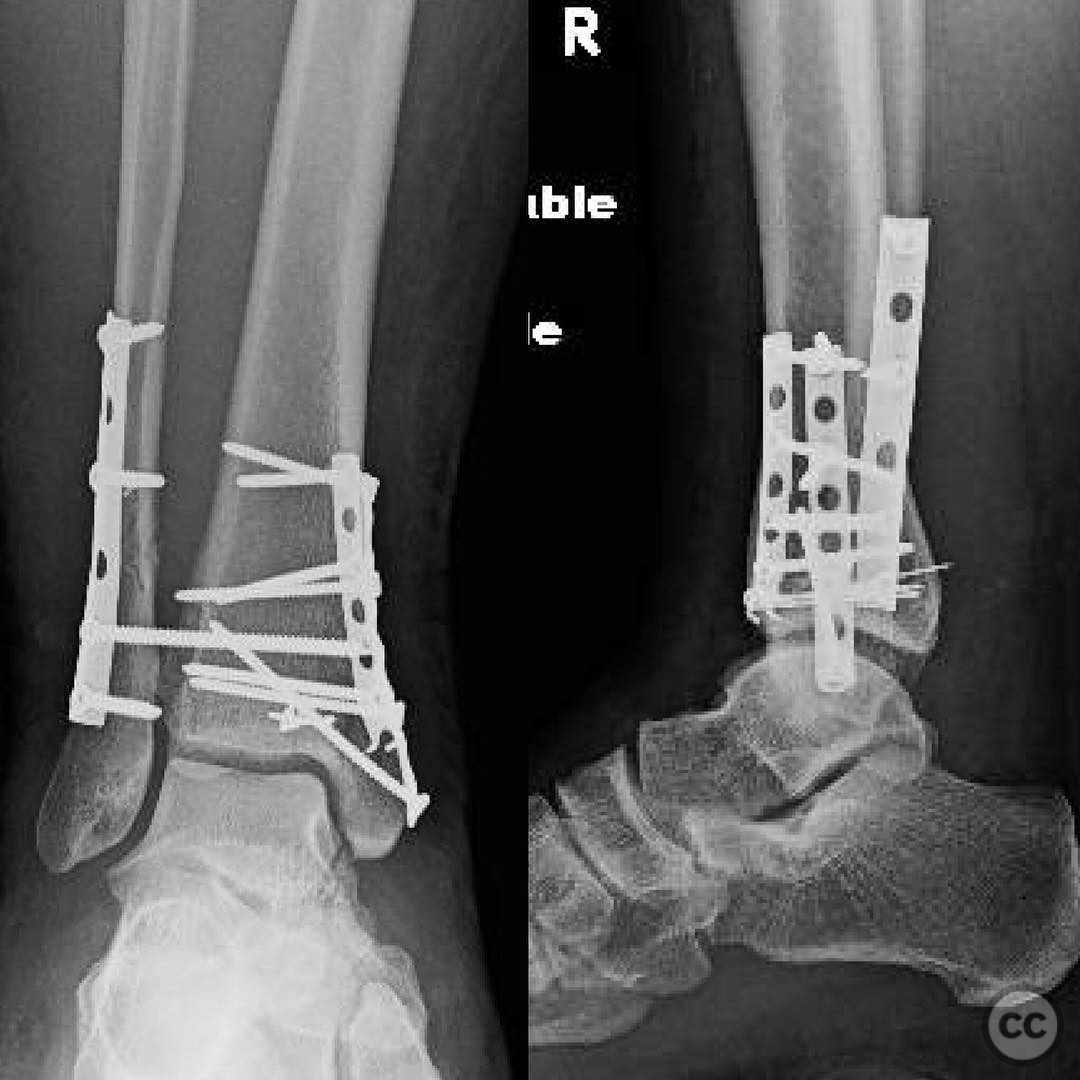
Operative remarks:Intraoperative findings confirmed a rotational and lengthening malreduction of the medial malleolus, which had resulted in anterior displacement of the talus. The deltoid ligament's tension was corrected by achieving an anatomical reduction of the medial malleolus, thereby realigning the talus and fibula within the syndesmosis. The surgeon emphasized the importance of obtaining true lateral imaging intraoperatively to confirm proper reduction.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included immobilization in a short leg cast for 4 weeks, followed by progressive weight-bearing as tolerated. Physical therapy was initiated at 6 weeks postoperatively to restore range of motion and strength.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Medial malleolar screws, syndesmotic fixation screws.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 182 times
25 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Medial Malleolar Malreduction with Syndesmotic Disruption.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 42837052 Published Online Jul 25 2025.