Distal Humerus Fracture with Anteromedial Coronoid Fragment
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
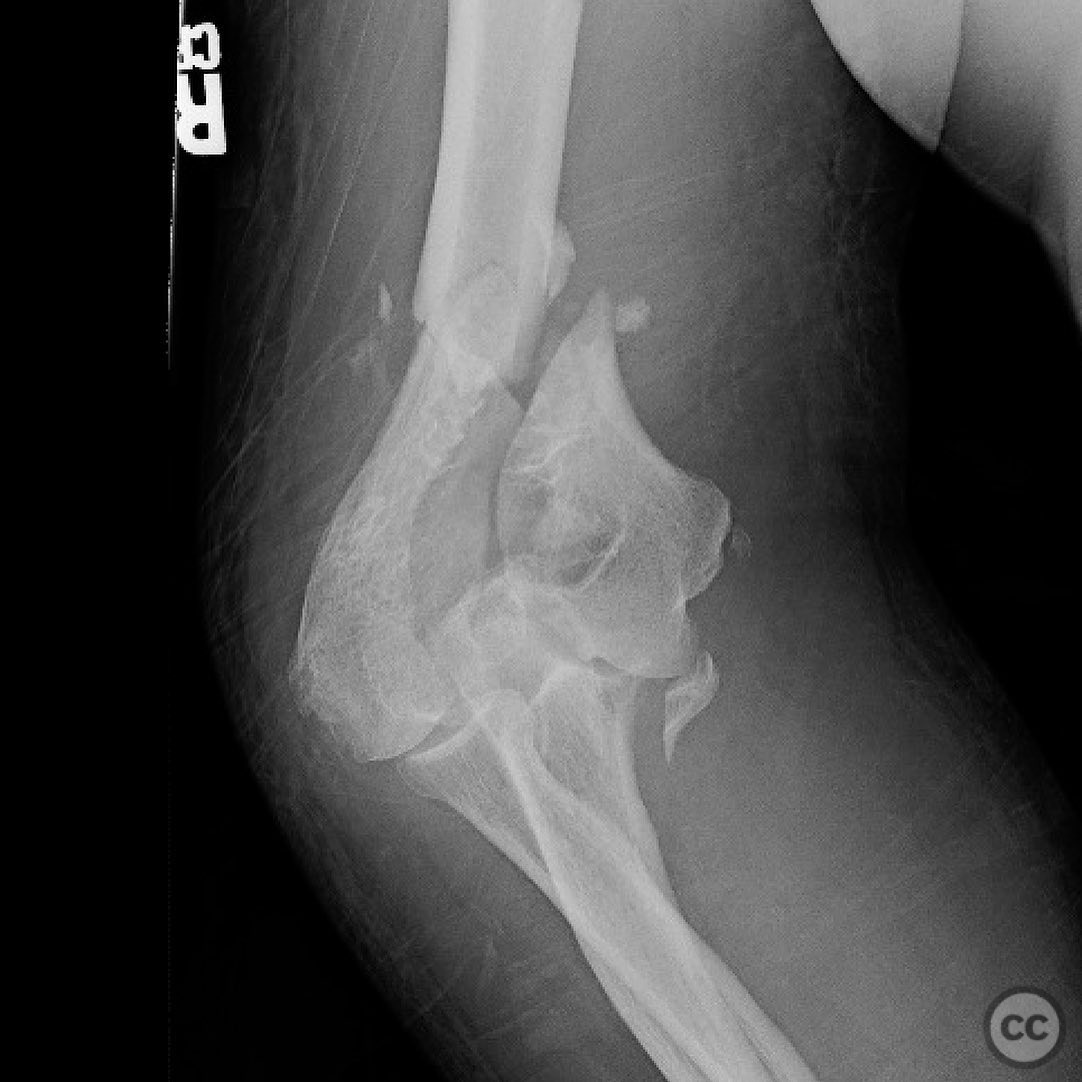
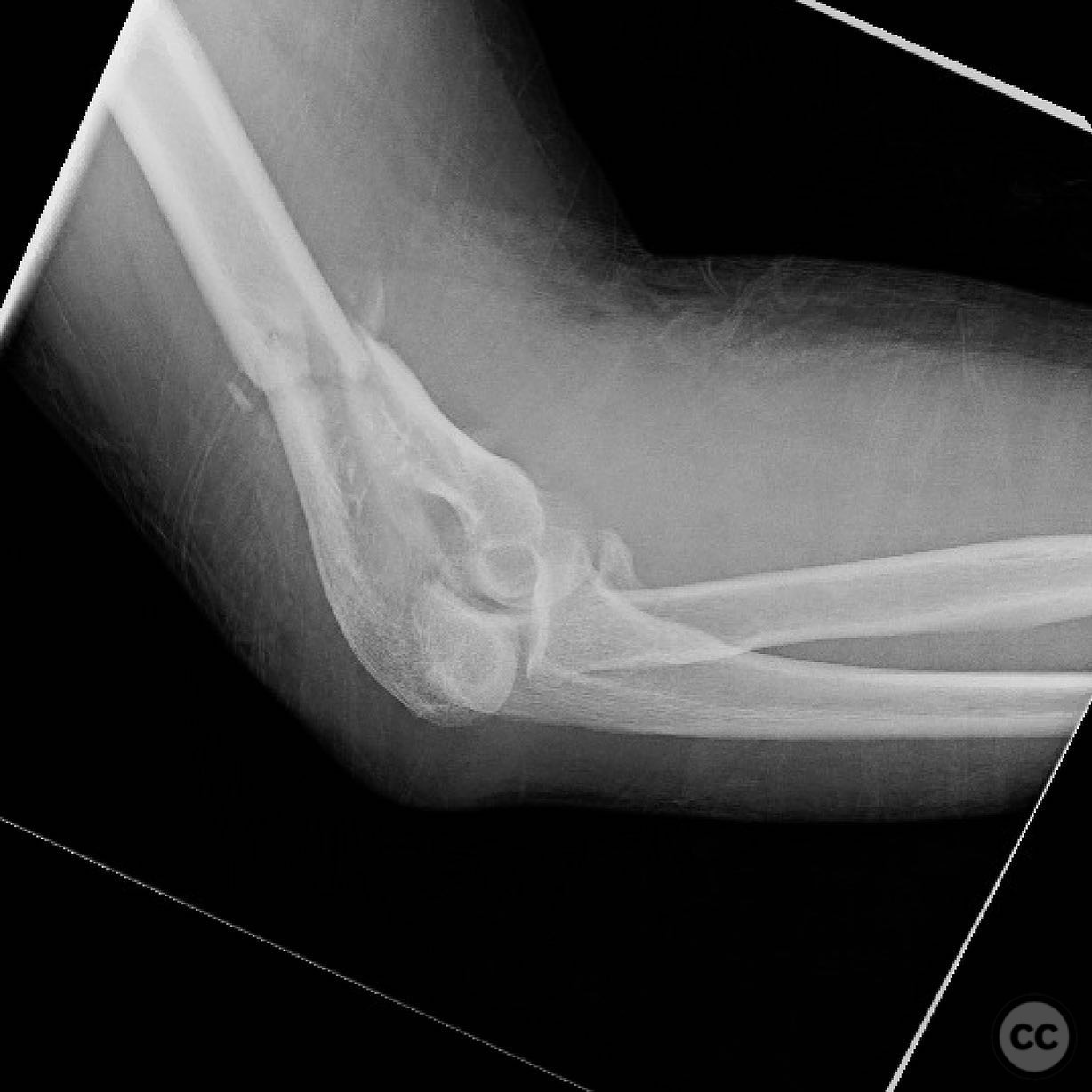
Clinical and radiological findings: A patient presented with a supracondylar intracondylar distal humerus fracture, accompanied by an anteromedial coronoid fragment. Initial imaging revealed a routine distal humerus fracture with the additional presence of the coronoid fragment following the medial epicondyle. The fragment was noted to be significant due to its potential impact on elbow stability, as it is associated with the insertion of the anterior bundle of the medial collateral ligament (MCL). The injury was further complicated by posteromedial instability.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved addressing the distal humerus fracture via a paratricipital approach, with consideration for an osteotomy if necessary due to impaction and central comminution. The anteromedial coronoid fragment was planned to be approached through a flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) split, potentially requiring a separate medial approach depending on intraoperative findings.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine to facilitate access to both the distal humerus and the anteromedial coronoid fragment.
Anatomical surgical approach: A paratricipital approach was utilized initially, with subsequent conversion to an olecranon osteotomy due to impaction and central comminution. For the anteromedial coronoid fragment, a flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) split was employed, allowing direct visualization and fixation of the fragment.
Operative remarks:Intraoperatively, the distal humerus fracture was addressed first, but the elbow remained unstable post-fixation, necessitating attention to the anteromedial coronoid fragment. The decision to perform an olecranon osteotomy was made intraoperatively due to the complexity of the fracture pattern, including impaction and comminution.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early mobilization with protected range of motion exercises. Weight-bearing restrictions were applied, with gradual progression based on clinical and radiological assessments.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included plates and screws for distal humerus fixation and additional fixation devices for the anteromedial coronoid fragment.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities










Article viewed 203 times
12 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Distal Humerus Fracture with Anteromedial Coronoid Fragment. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 42134777 Published Online Jul 12 2025.