Triceps Sparing Posterior Approach for Humeral Fracture Fixation
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
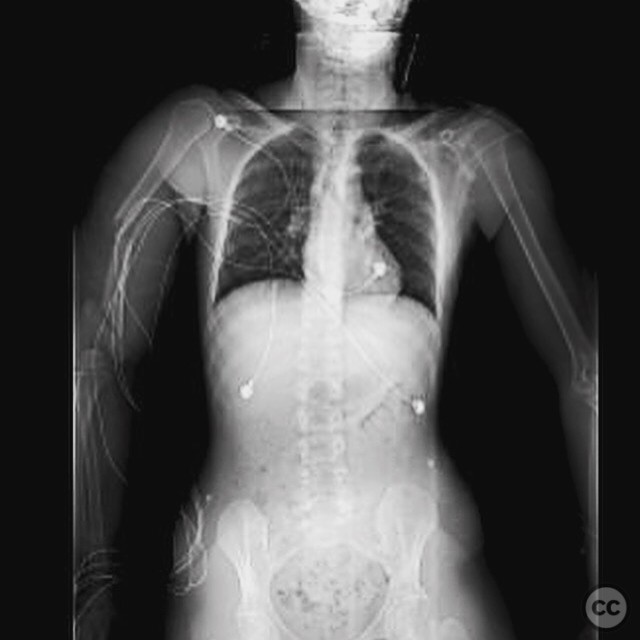
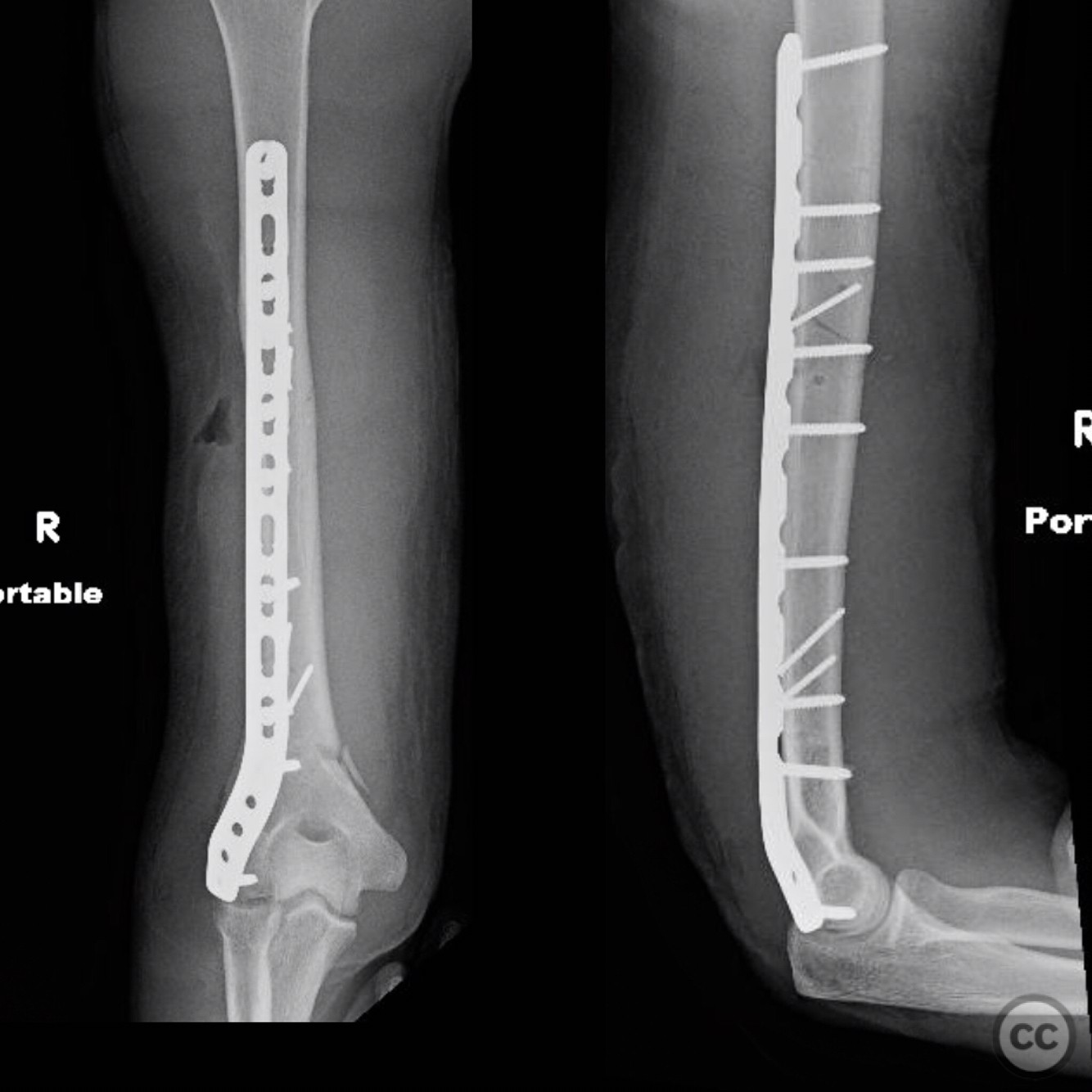
Clinical and radiological findings: A patient was urgently brought to the operating room for a multi-disciplinary surgical intervention involving neurosurgery, general surgery, and vascular surgery. During the procedure, an intraoperative consult was requested for orthopaedic trauma. The patient sustained a humeral fracture, with intraoperative imaging indicating a fracture extending from the surgical neck to the distal articular surface. The specific AO/OTA classification could not be determined from the available information.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved utilizing a triceps sparing posterior approach to access the humerus. This approach was chosen to allow exposure from the surgical neck to the distal articular surface while preserving the integrity of the triceps muscle and protecting the axillary and radial nerves.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned prone on the operating table to facilitate access to the posterior aspect of the humerus.
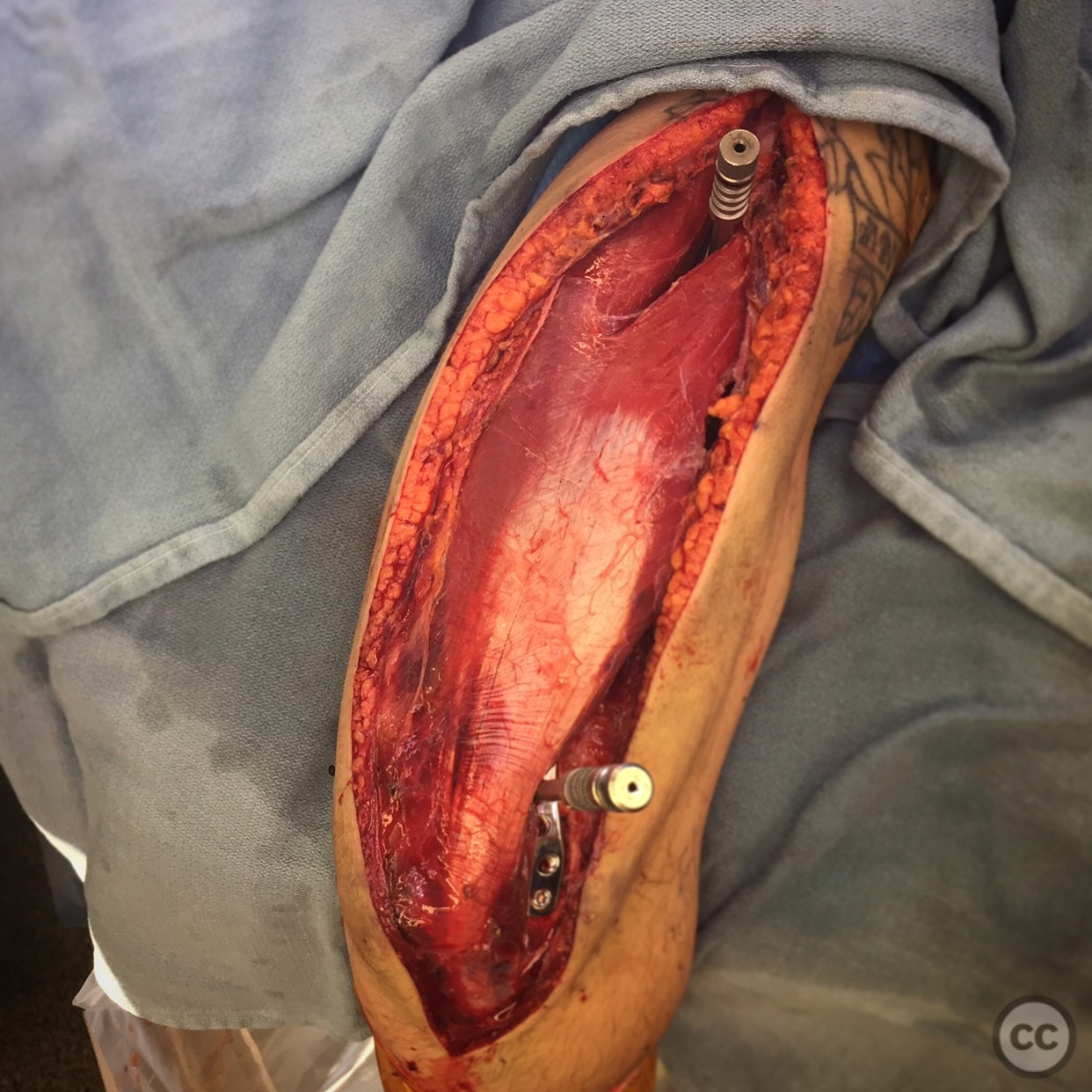
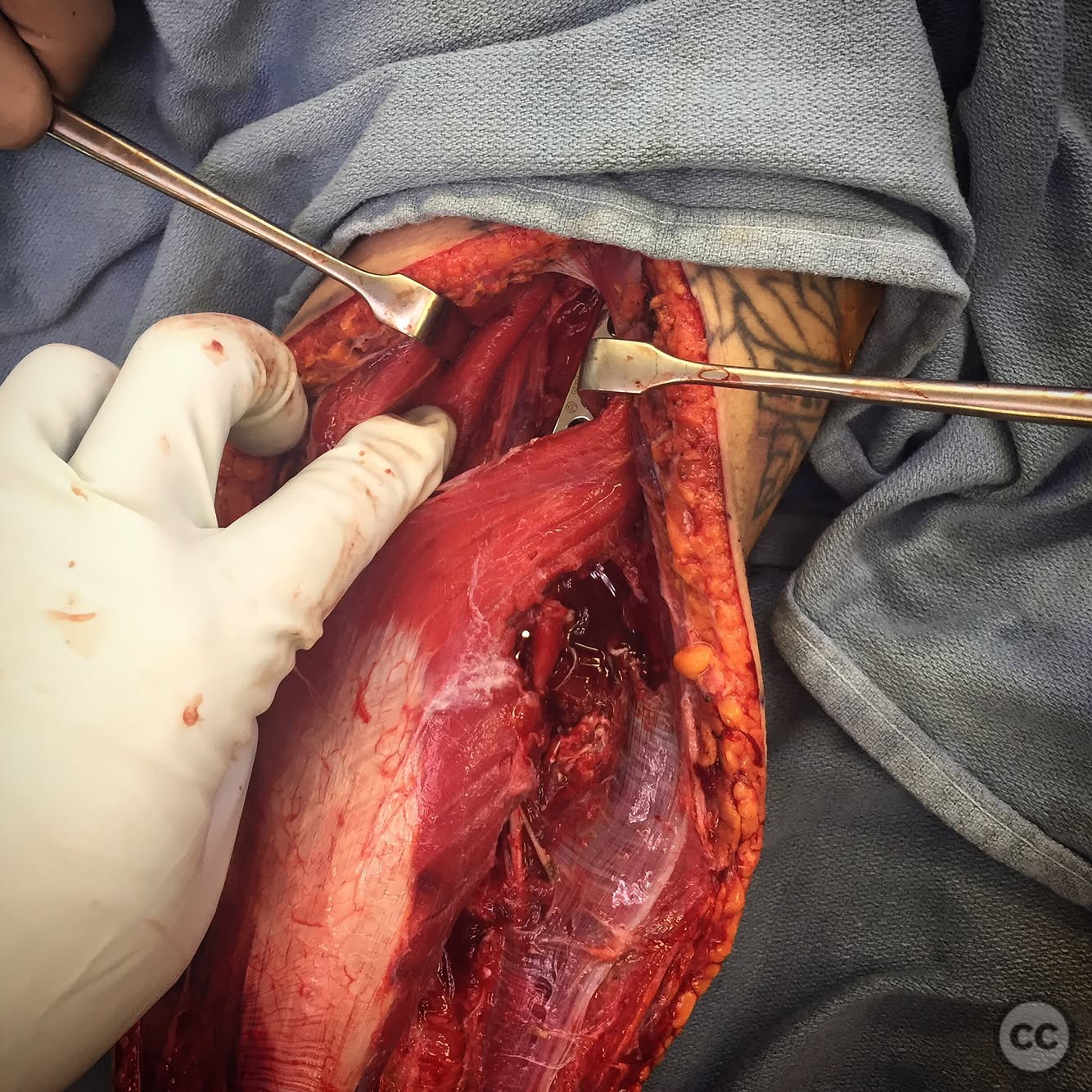
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal incision was made along the posterior aspect of the arm. The triceps muscle was carefully retracted laterally, sparing its insertion, to expose the humeral shaft. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to visualize the fracture site while maintaining awareness of the axillary and radial nerves.
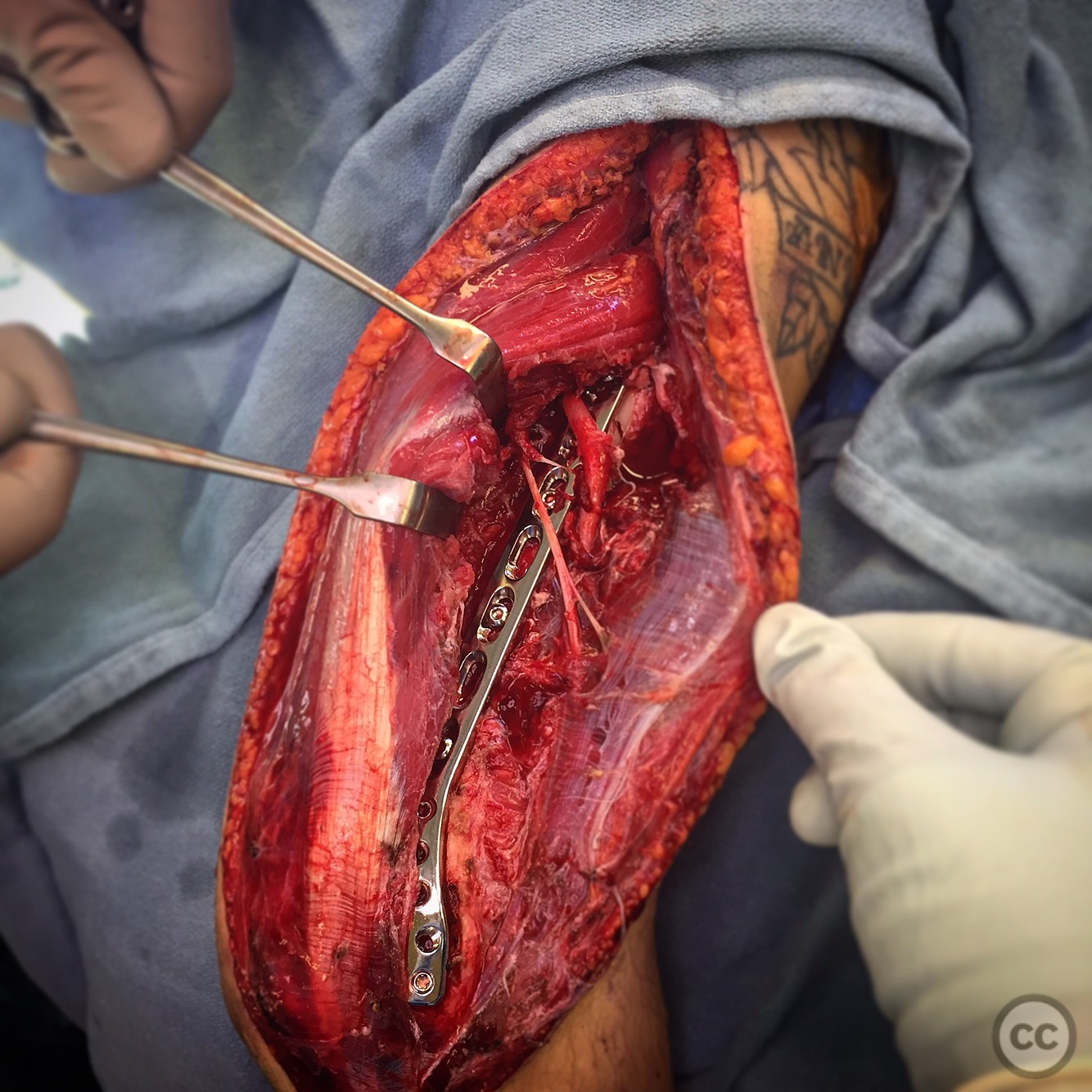
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of understanding the anatomy of the axillary and radial nerves when performing a posterior approach to the humerus. The approach allowed for adequate exposure of the humerus from the surgical neck to the distal articular surface, enabling effective fracture fixation.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early mobilization with range of motion exercises initiated as tolerated. Weight-bearing restrictions were applied based on fracture stability and fixation.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used were not specified in the provided information.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 145 times
26 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Triceps Sparing Posterior Approach for Humeral Fracture Fixation. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 41499912 Published Online Jul 26 2025.