Segmental Tibia Fracture Managed with Open Reduction and Intramedullary Nailing.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
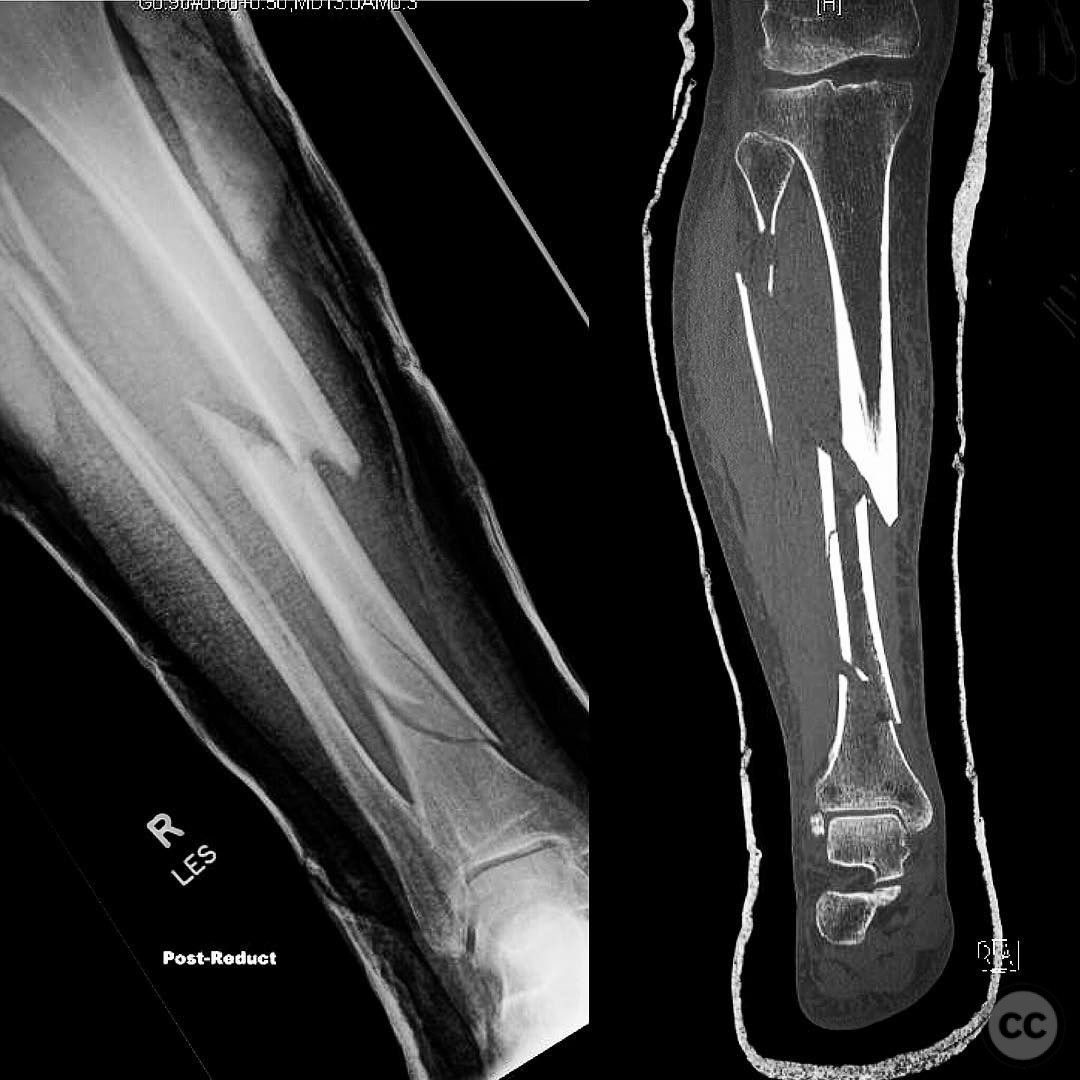
Clinical and radiological findings: A patient sustained a closed segmental tibia fracture after being struck by a truck while evading law enforcement. The injury was characterized by significant swelling but no compartment syndrome or articular involvement. There were no significant soft tissue wounds noted.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved open reduction of the fracture through two small posteromedial incisions. The fracture was to be directly reduced, provisionally plated, and subsequently stabilized with intramedullary nailing. A semi-extended position with a supra-patellar approach was selected for the nailing procedure.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine with the knee in a semi-extended position to facilitate the supra-patellar approach for intramedullary nailing.
Anatomical surgical approach: Two small posteromedial incisions were made to access the fracture sites. The fractures were directly reduced and provisionally stabilized with plates. A supra-patellar approach was utilized for the insertion of the intramedullary nail.
Operative remarks:The surgeon opted for open reduction and provisional plating of the segmental tibia fracture prior to intramedullary nailing, a technique that can be controversial in closed fractures. The provisional plate on the diaphyseal segment was removed before compressing the fracture and locking the nail. The provisional plate on the metaphyseal segment was removed after the locking bolts were placed, ensuring stability of the construct.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included weight-bearing as tolerated with progression based on clinical and radiographic healing.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail, provisional plates (removed post-fixation).
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 178 times
05 Aug 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Segmental Tibia Fracture Managed with Open Reduction and Intramedullary Nailing.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 39955682 Published Online Aug 05 2025.