H-pattern Sacral and Bilateral Pubic Ramus Fractures Stabilized with CurvaFix Medullary Device
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
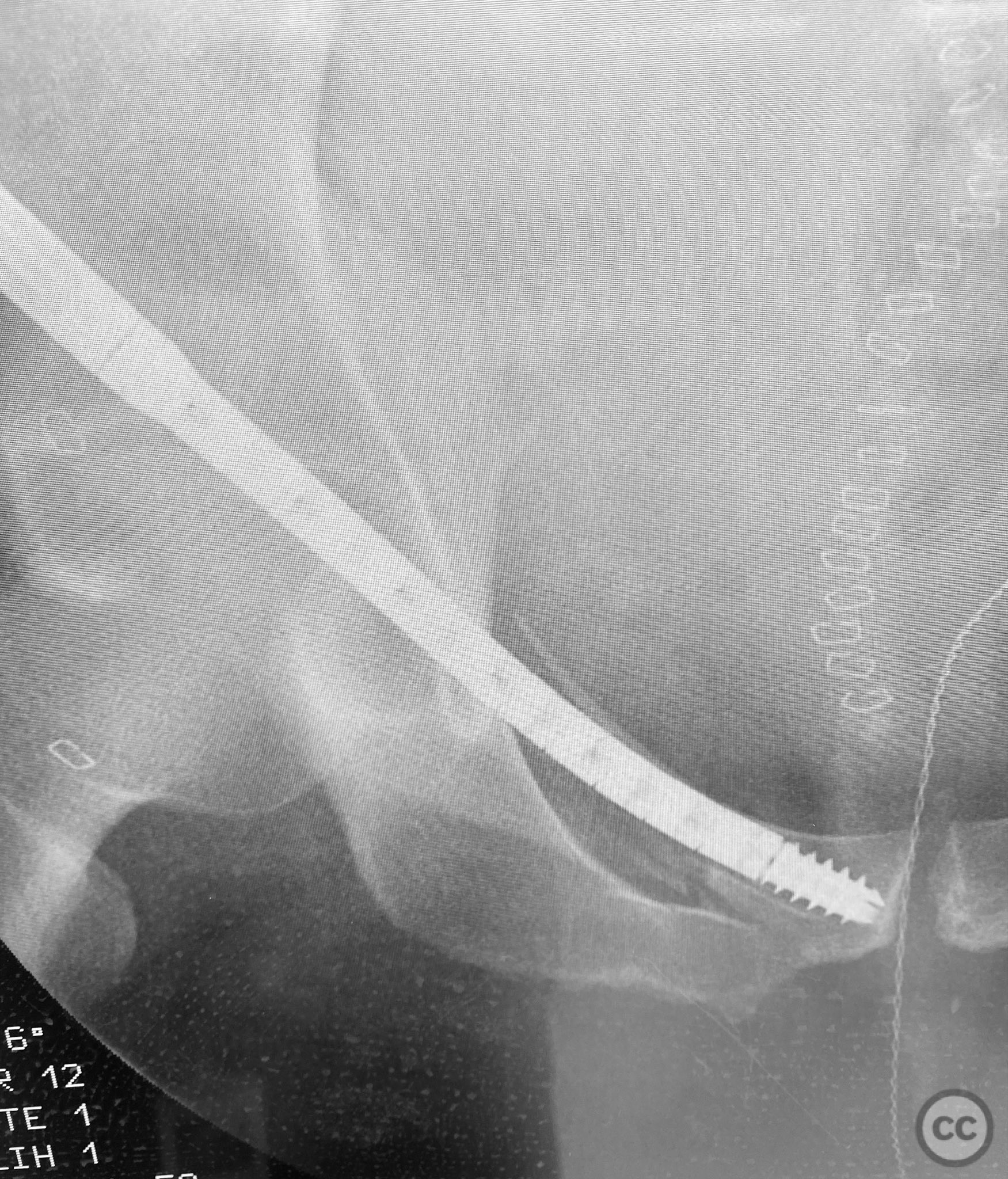
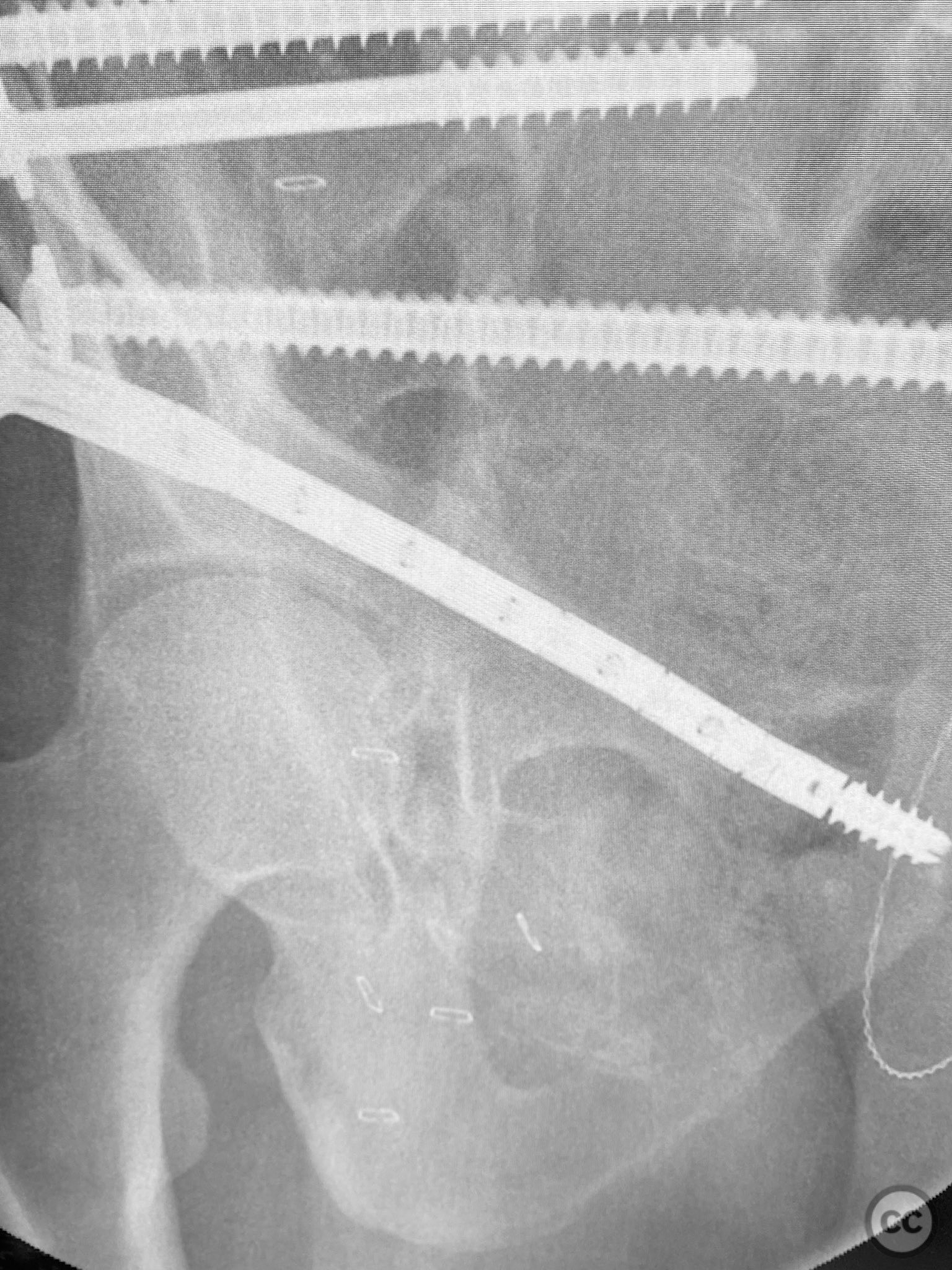
Clinical and radiological findings: A patient sustained a high-energy lap belt injury resulting in an H-pattern sacral fracture (AO/OTA 61-C1.3) and bilateral pubic ramus fractures (AO/OTA 61-C1.3). Initial clinical assessment revealed a hemodynamically stable patient with no neurological deficit. Radiological evaluation with pelvic radiographs and computed tomography demonstrated a complete H-type sacral fracture involving both sacral ala and the central sacral body, as well as displaced bilateral superior and inferior pubic ramus fractures. No associated acetabular or hip dislocation was identified.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan was to achieve stabilization of the bilateral pubic ramus fractures using a 7.5mm CurvaFix medullary device, selected for its ability to conform to the curved osseous pathway of the pubic ramus. Percutaneous fixation of the sacral fracture was planned using standard iliosacral screw technique.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on a radiolucent table to facilitate fluoroscopic imaging of the pelvis in multiple planes.
Anatomical surgical approach: A percutaneous approach was utilized for the pubic ramus fixation. A small stab incision was made over the anterior aspect of the pubic tubercle. Blunt dissection was carried down to bone, and a guidewire was advanced under fluoroscopic guidance along the intramedullary canal of the superior pubic ramus, traversing the fracture site. The 7.5mm CurvaFix medullary device was then inserted over the guidewire, conforming to the osseous curvature and achieving stable fixation across the fracture. The procedure was repeated for the contralateral side. For sacral fixation, percutaneous iliosacral screws were placed under fluoroscopic guidance through small lateral incisions over the posterior ilium.
Operative remarks:The use of the CurvaFix medullary device allowed for anatomic alignment and stable fixation of the bilateral pubic ramus fractures by accommodating the natural curvature of the osseous pathway, which is often challenging with traditional straight implants. This technique provided robust fixation in a fracture pattern that is historically difficult to stabilize, minimizing soft tissue disruption and facilitating early mobilization.
Postoperative protocol: The postoperative rehabilitation protocol included immediate non-weight bearing mobilization with a walker for 6 weeks, followed by progressive weight bearing as tolerated. Range of motion exercises for the hip and knee were initiated on postoperative day one.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: 7.5mm CurvaFix Medullary Device (bilateral). Cannulated iliosacral screws.
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities


Article viewed 138 times
11 Sep 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Routt, ML. (2025). H-pattern Sacral and Bilateral Pubic Ramus Fractures Stabilized with CurvaFix Medullary Device. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 39919681 Published Online Sep 11 2025.