Short Segment, Big Debate: Plating a Varus-Oriented Distal Tibial Fracture in a Polytrauma Case
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
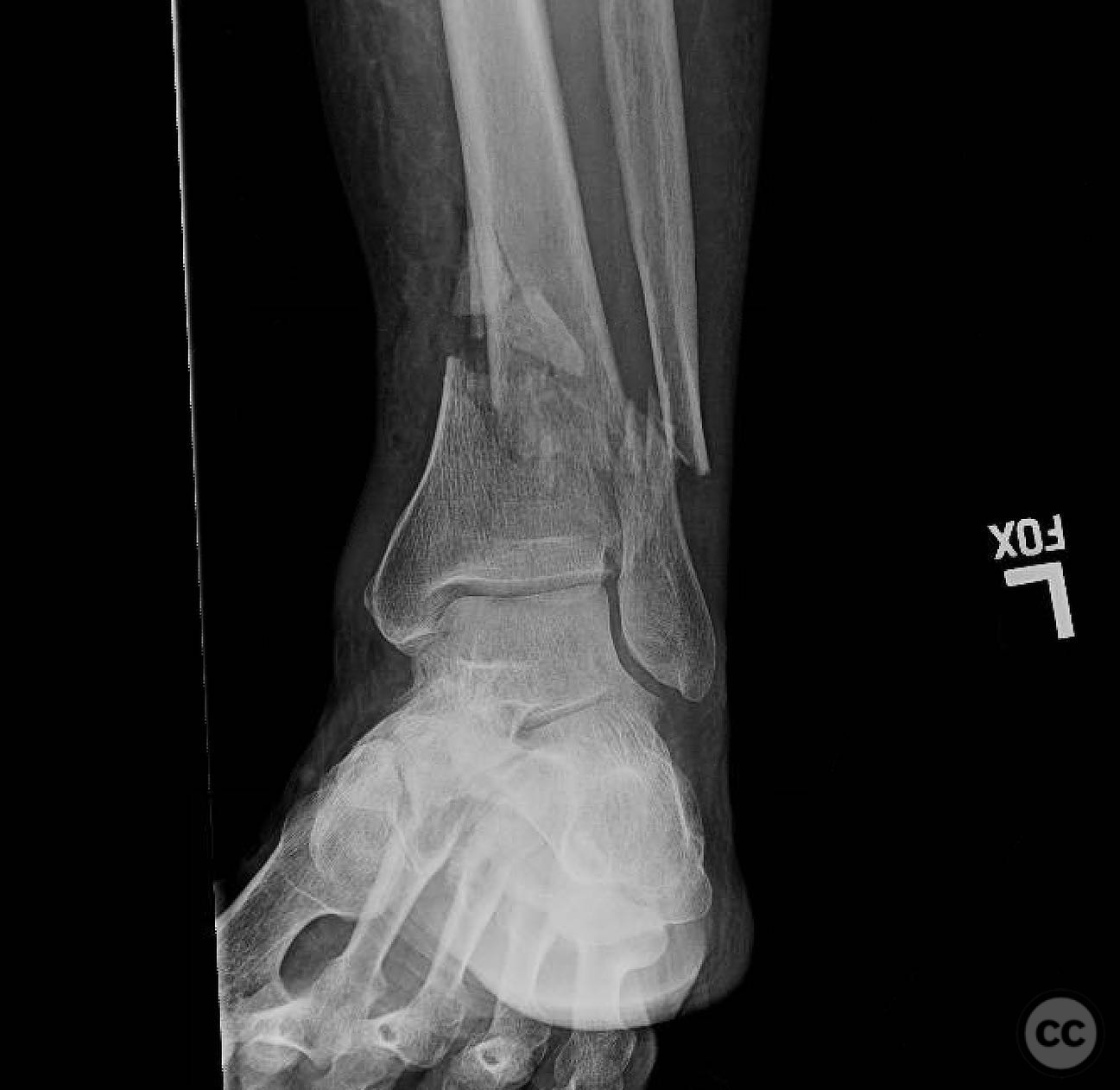
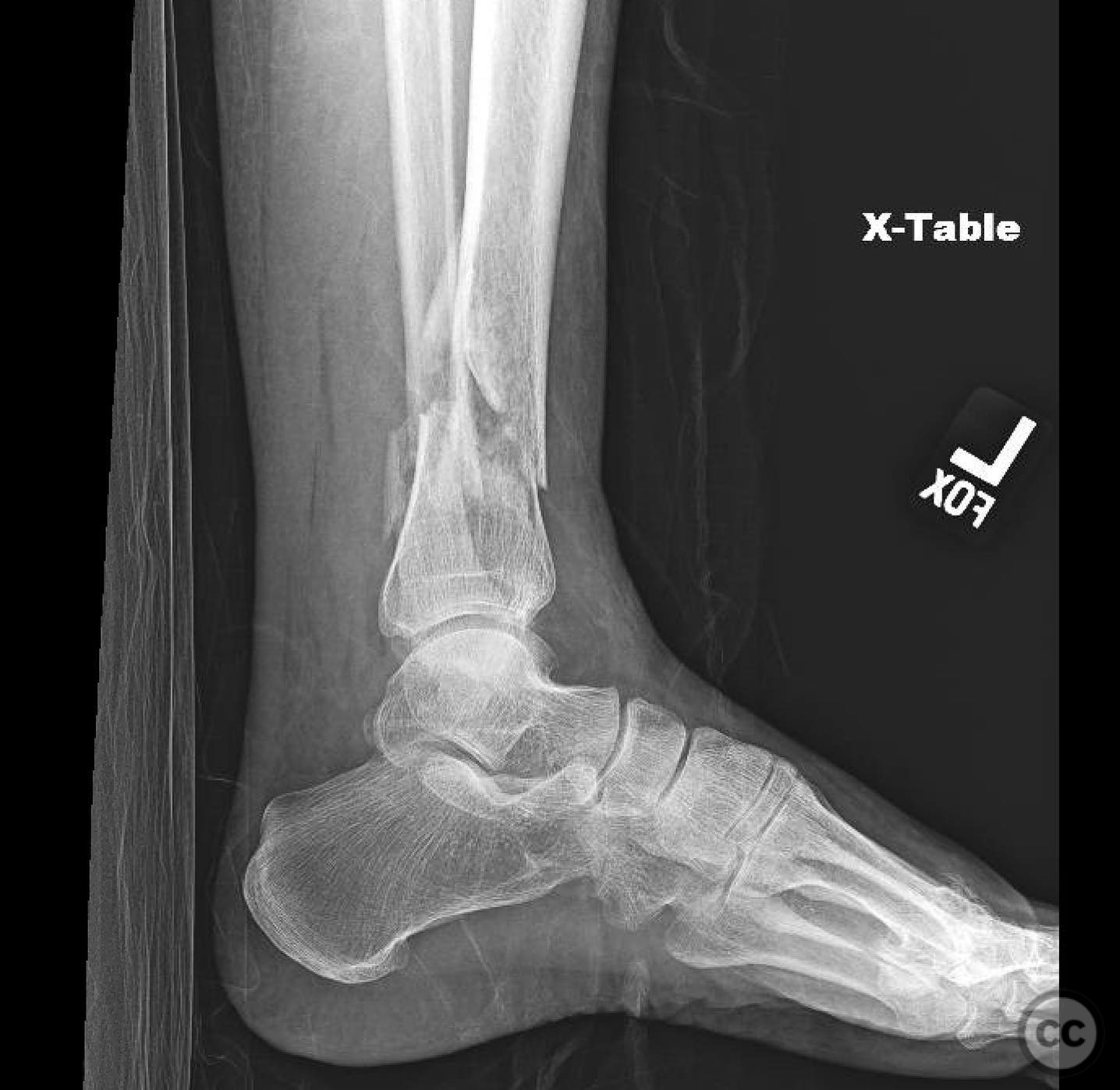
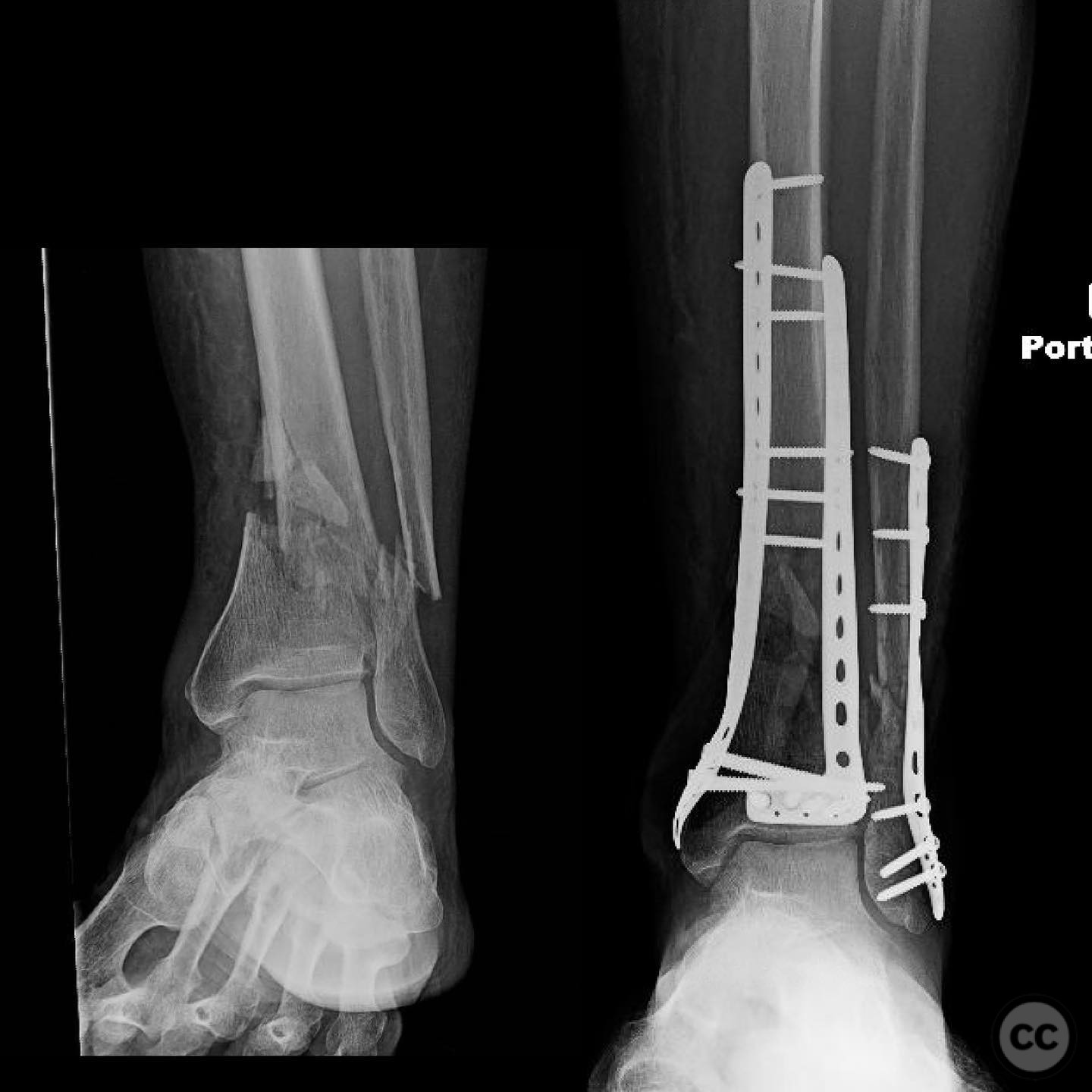
Clinical and radiological findings: A 68-year-old polytraumatized patient presented with a closed short metaphyseal fracture of the distal tibia, characterized by medial translation and varus angulation. The patient also sustained an acetabulum/ring injury. The soft tissue envelope was reassuring with mild to moderate swelling. The patient had no major medical problems or social issues.
Preoperative Plan
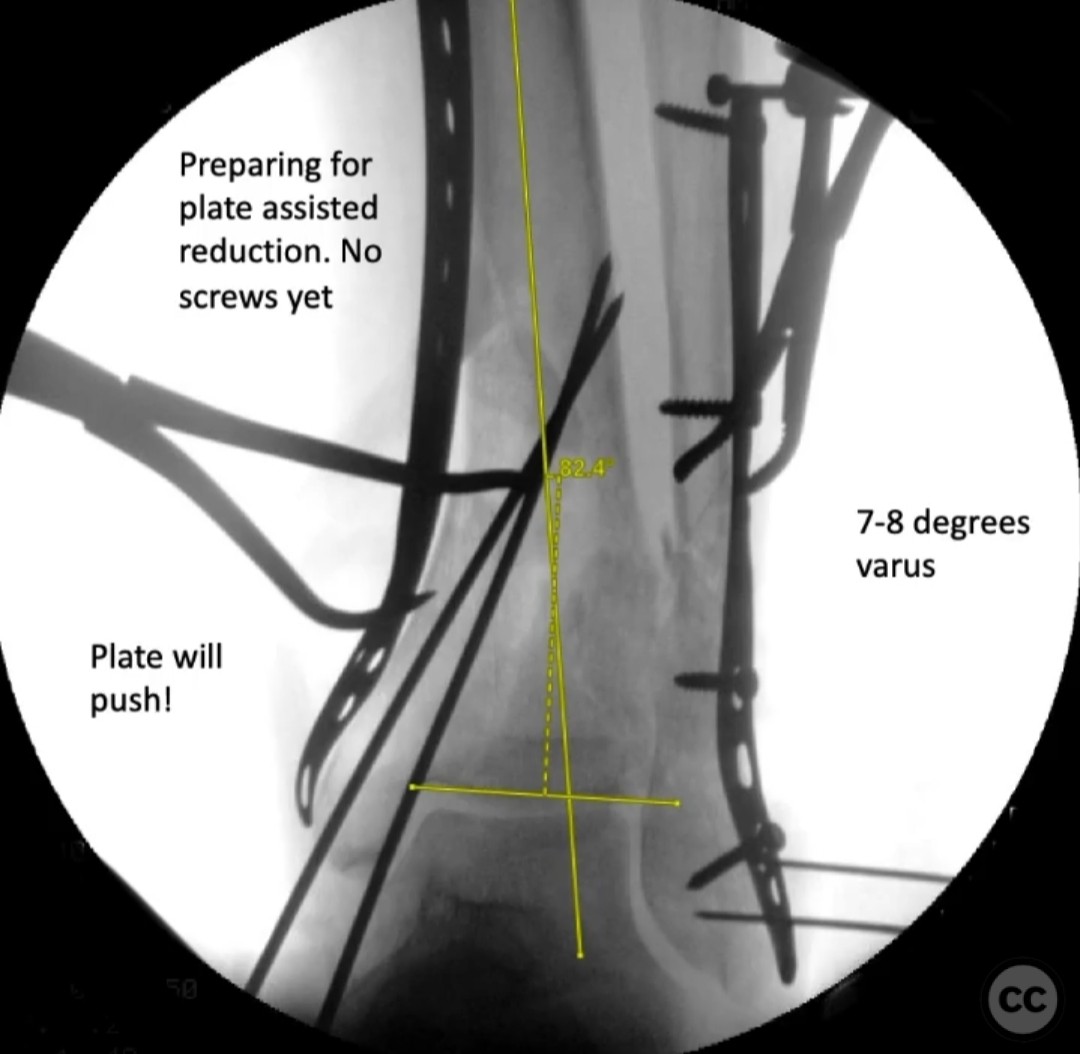
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved the use of a medial plate to address the medial translation and varus angulation of the fracture. The decision to plate was influenced by the fracture pattern, which required resistance to medial translation and varus deformity. The fibula was planned to be fixed lightly to assist in restoring length and alignment.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine position on a radiolucent table, allowing for intraoperative imaging and access to both the medial and lateral aspects of the lower extremity.
Anatomical surgical approach: A medial approach to the distal tibia was utilized. A longitudinal incision was made over the medial aspect of the distal tibia, followed by careful dissection to expose the fracture site. Subperiosteal elevation was performed to allow for placement of the plate.
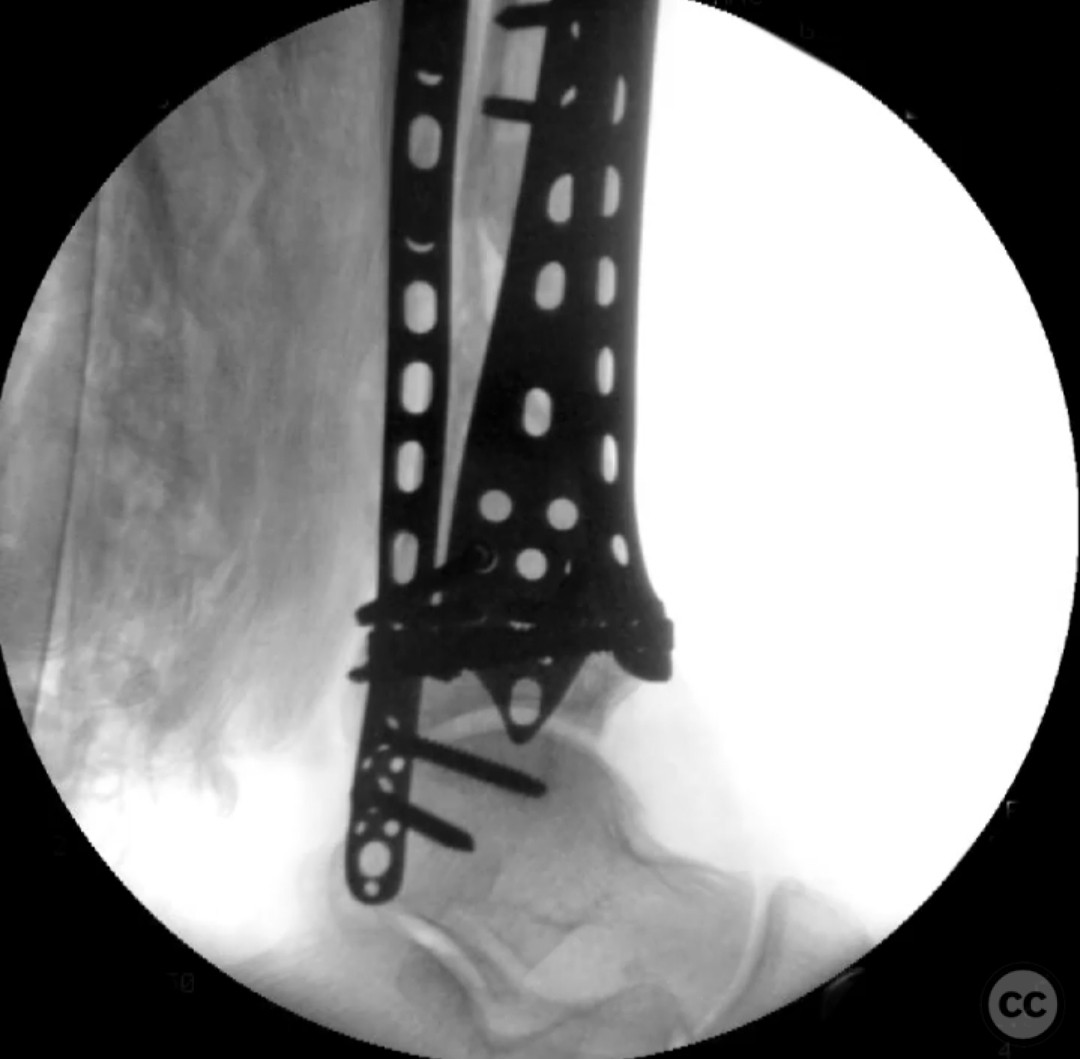
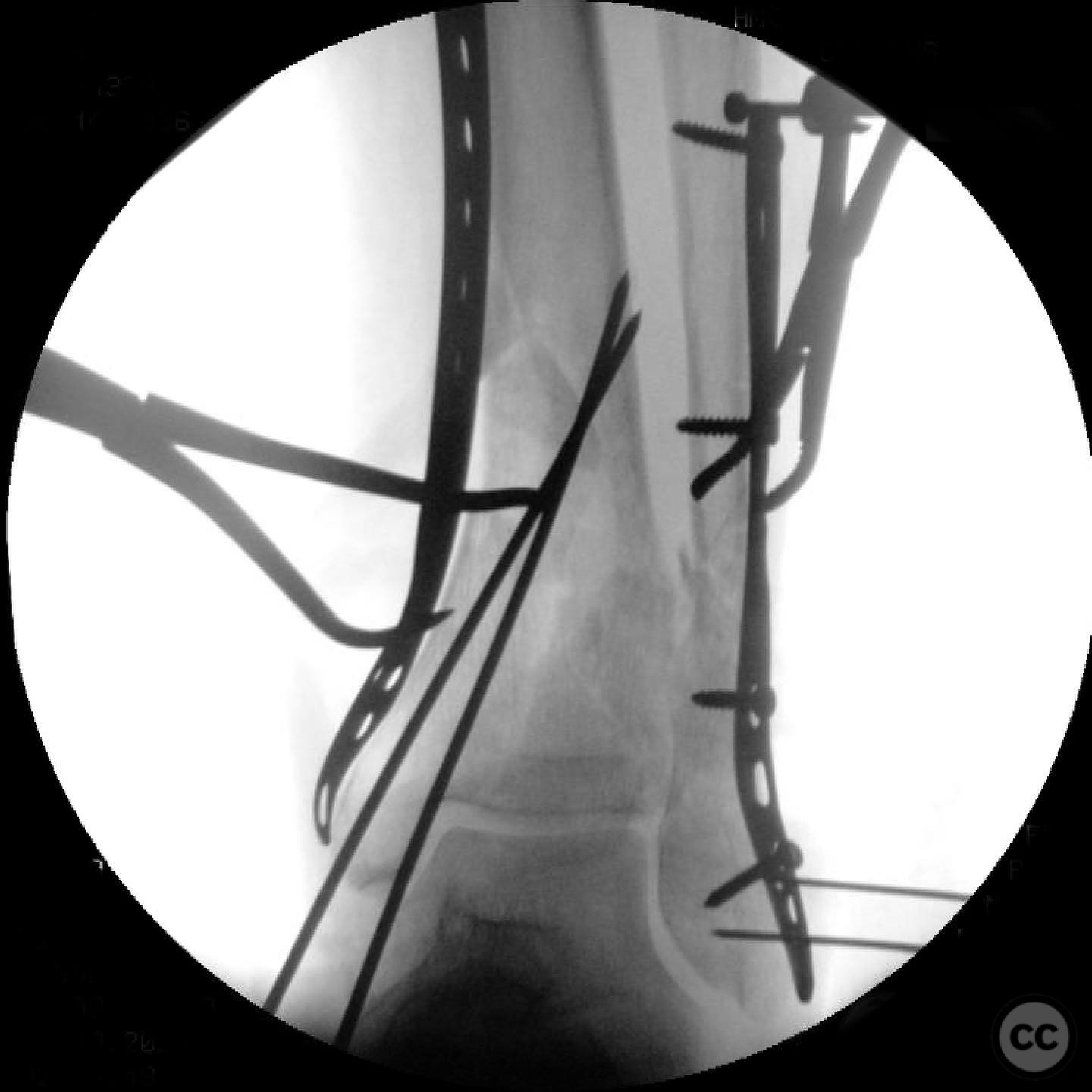
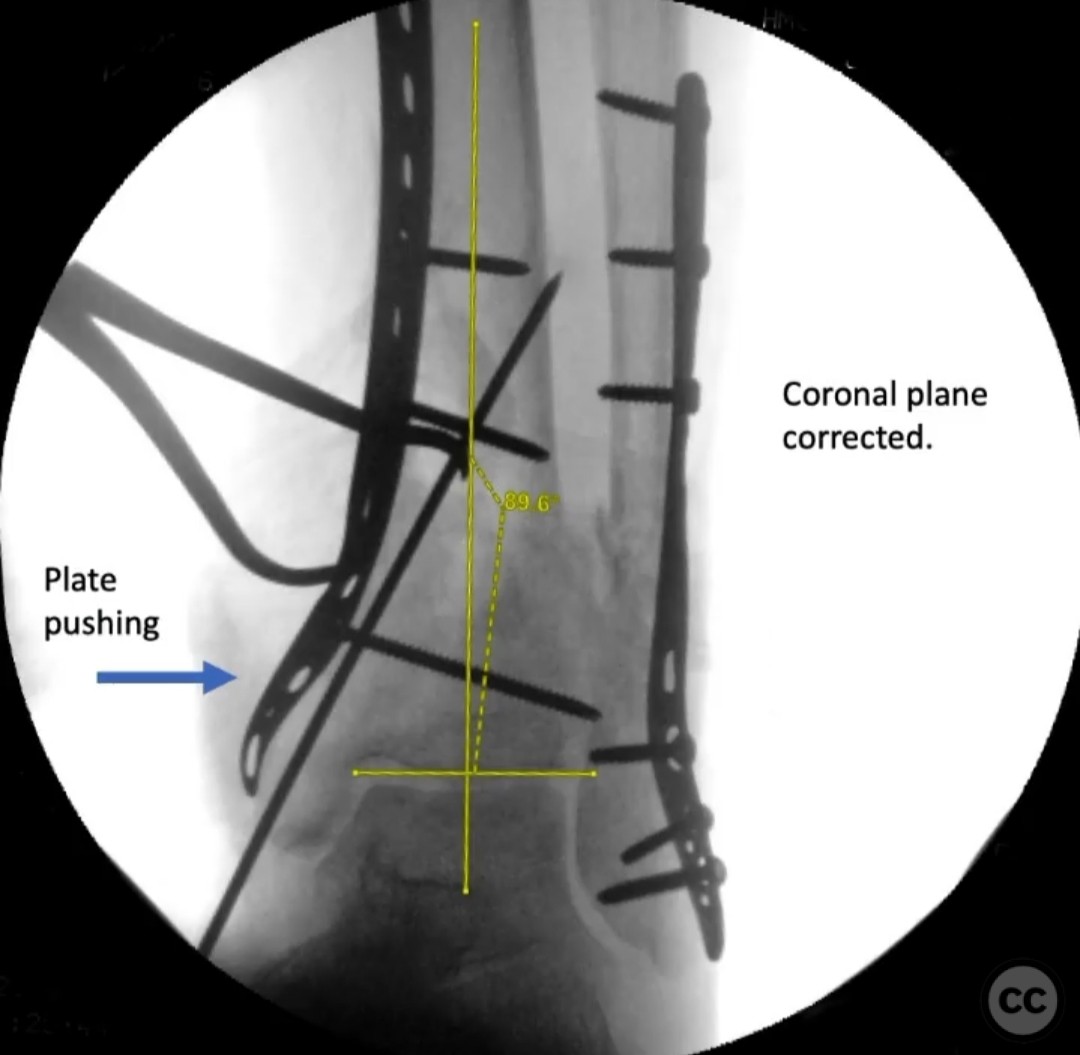
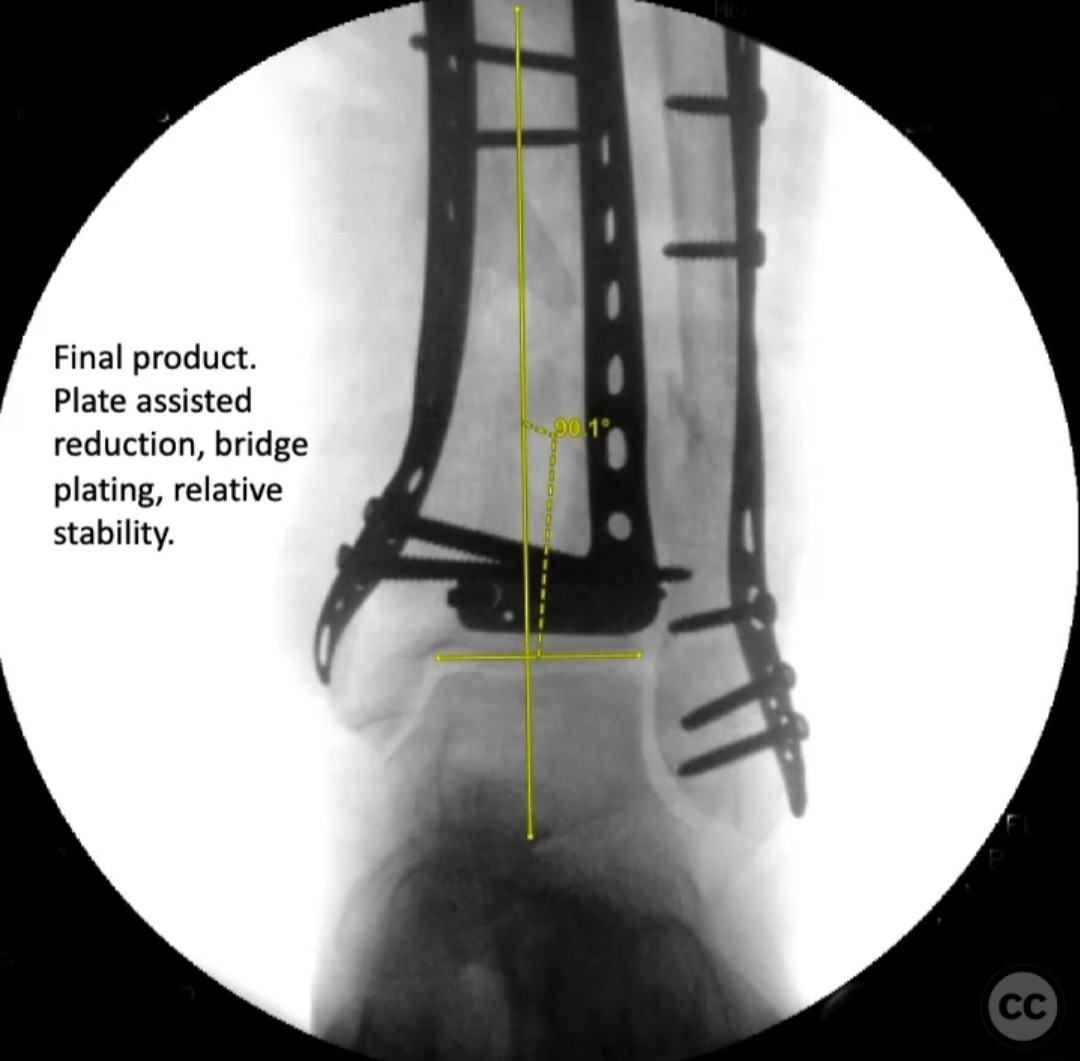
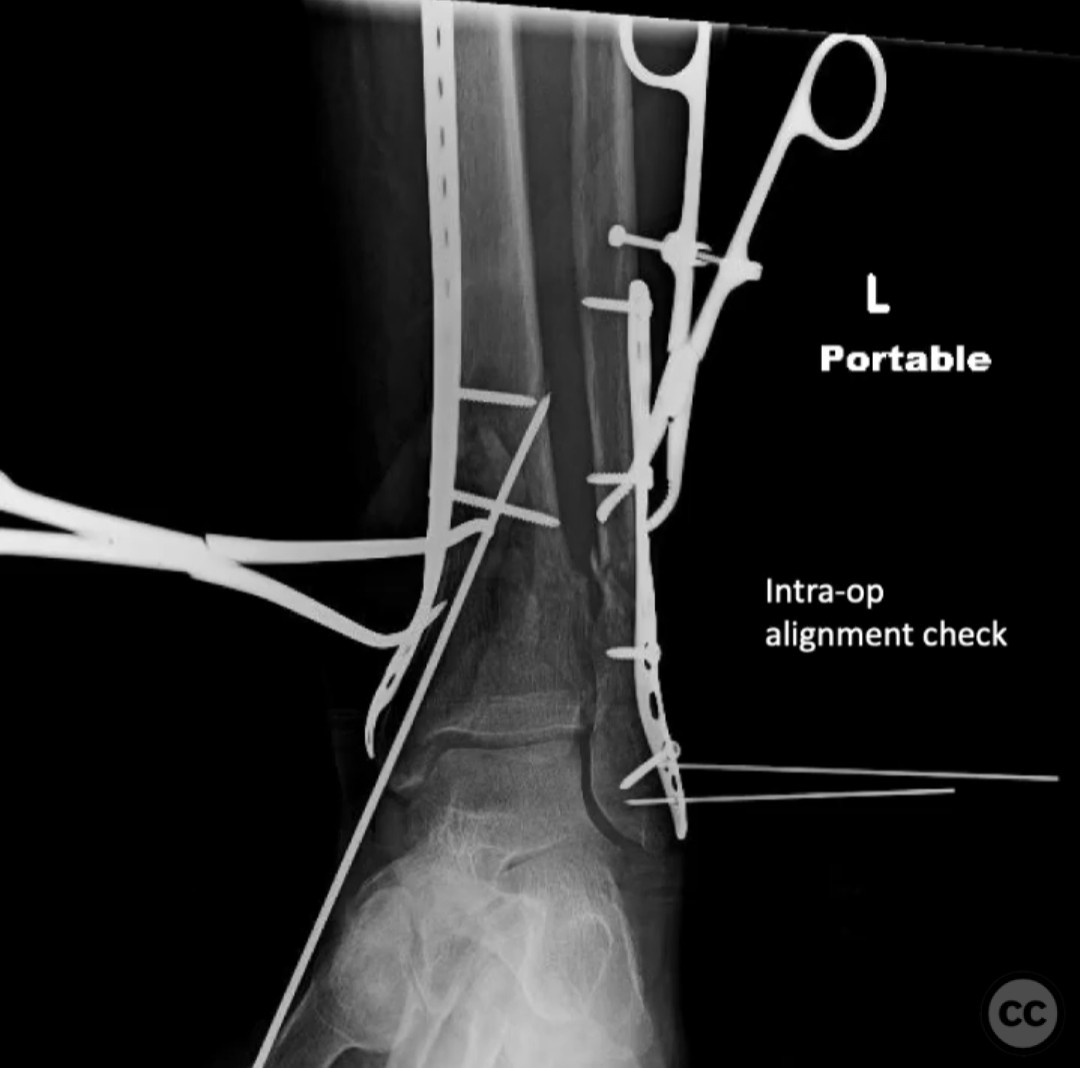
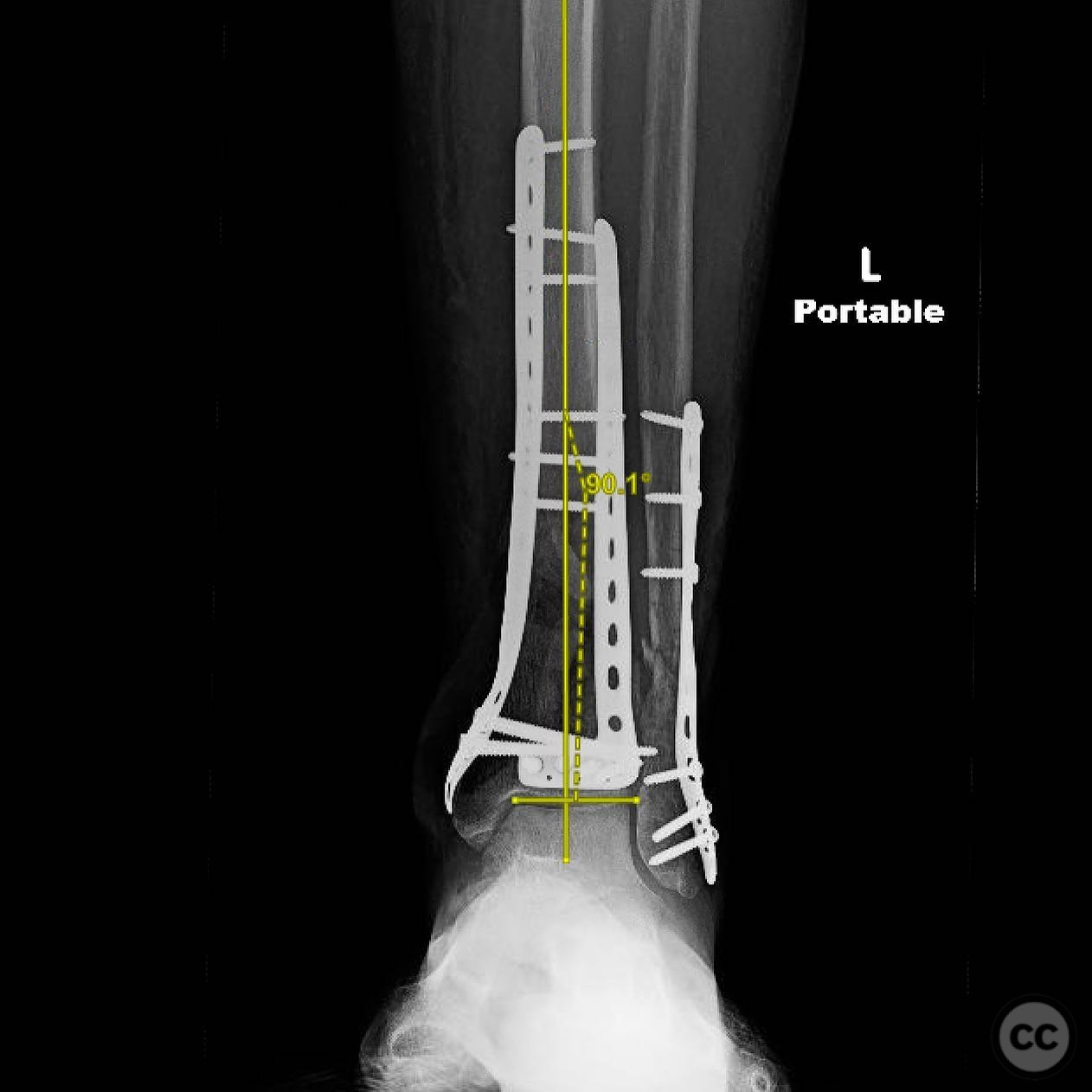
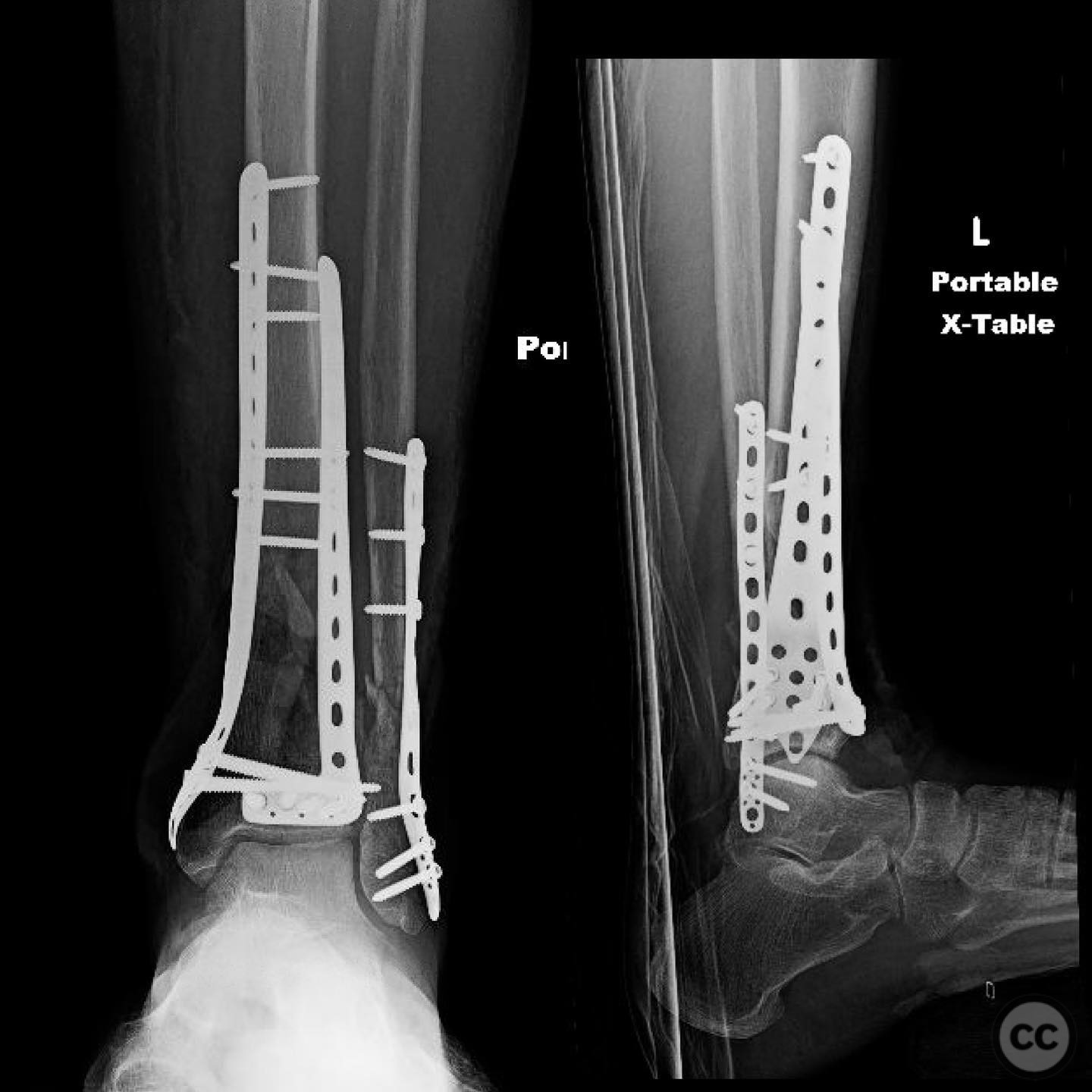
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted significant residual varus after initial reduction attempts using fibular fixation. An undercontoured medial plate was employed to push the articular block out of varus in a controlled manner, serving as an indirect reduction technique. This approach allowed for correction of the deformity that could not be achieved with a nail alone.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included protected weight-bearing initially, with progression based on radiographic healing and clinical assessment. Emphasis was placed on early range of motion exercises to prevent stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Medial tibial plate, fibular fixation screws
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 233 times
12 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Short Segment, Big Debate: Plating a Varus-Oriented Distal Tibial Fracture in a Polytrauma Case. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 38463953 Published Online Jul 12 2025.