Posterior Column Shearing Fracture with Lateral Displacement
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
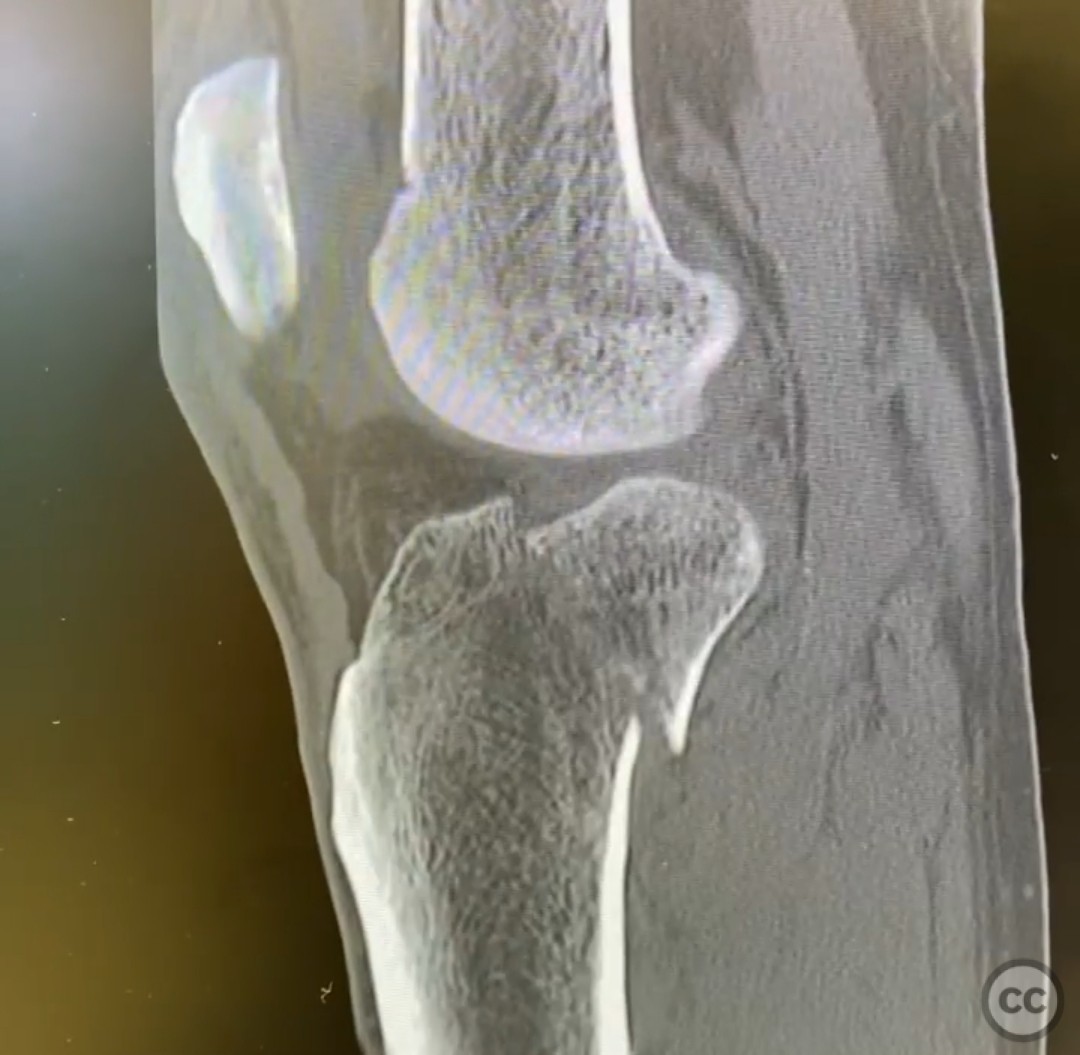
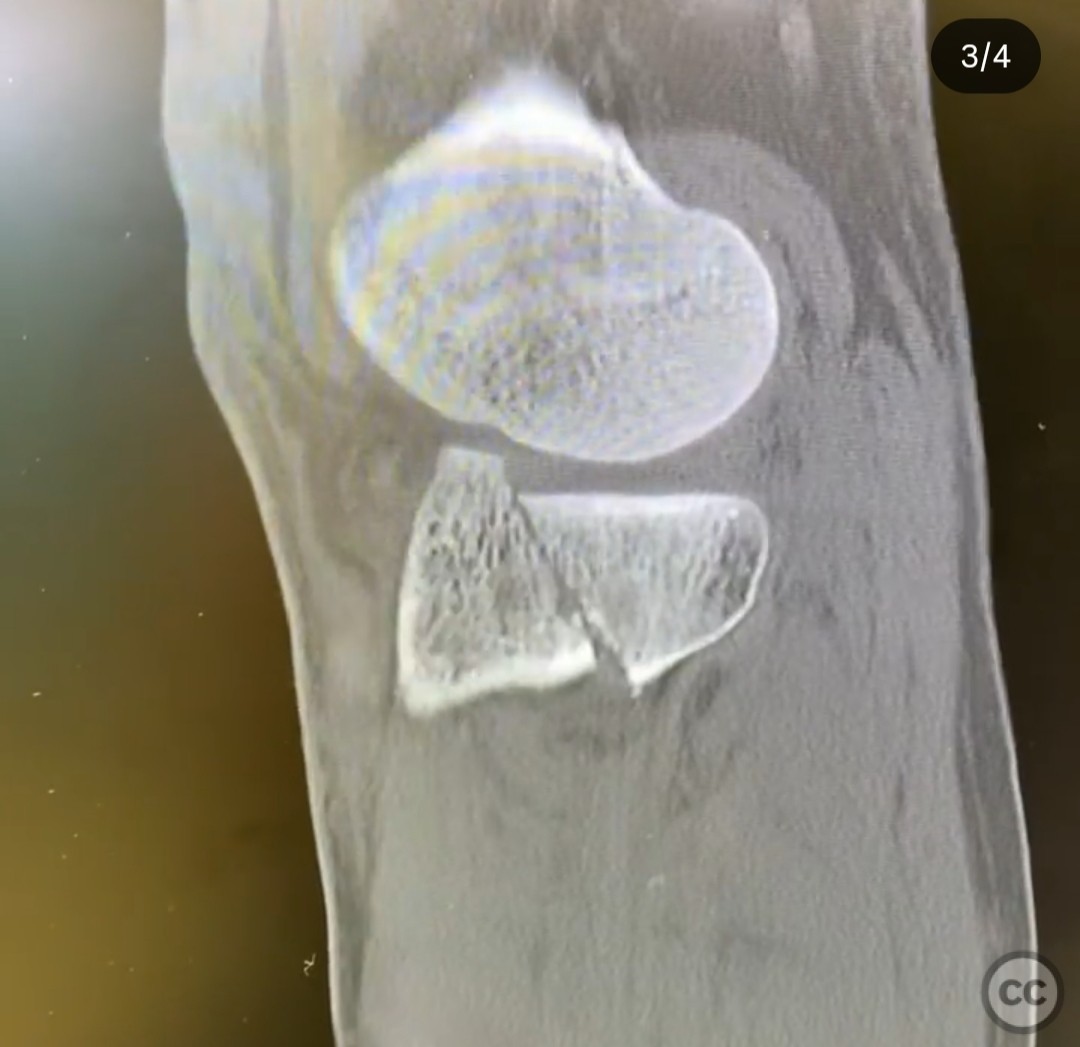
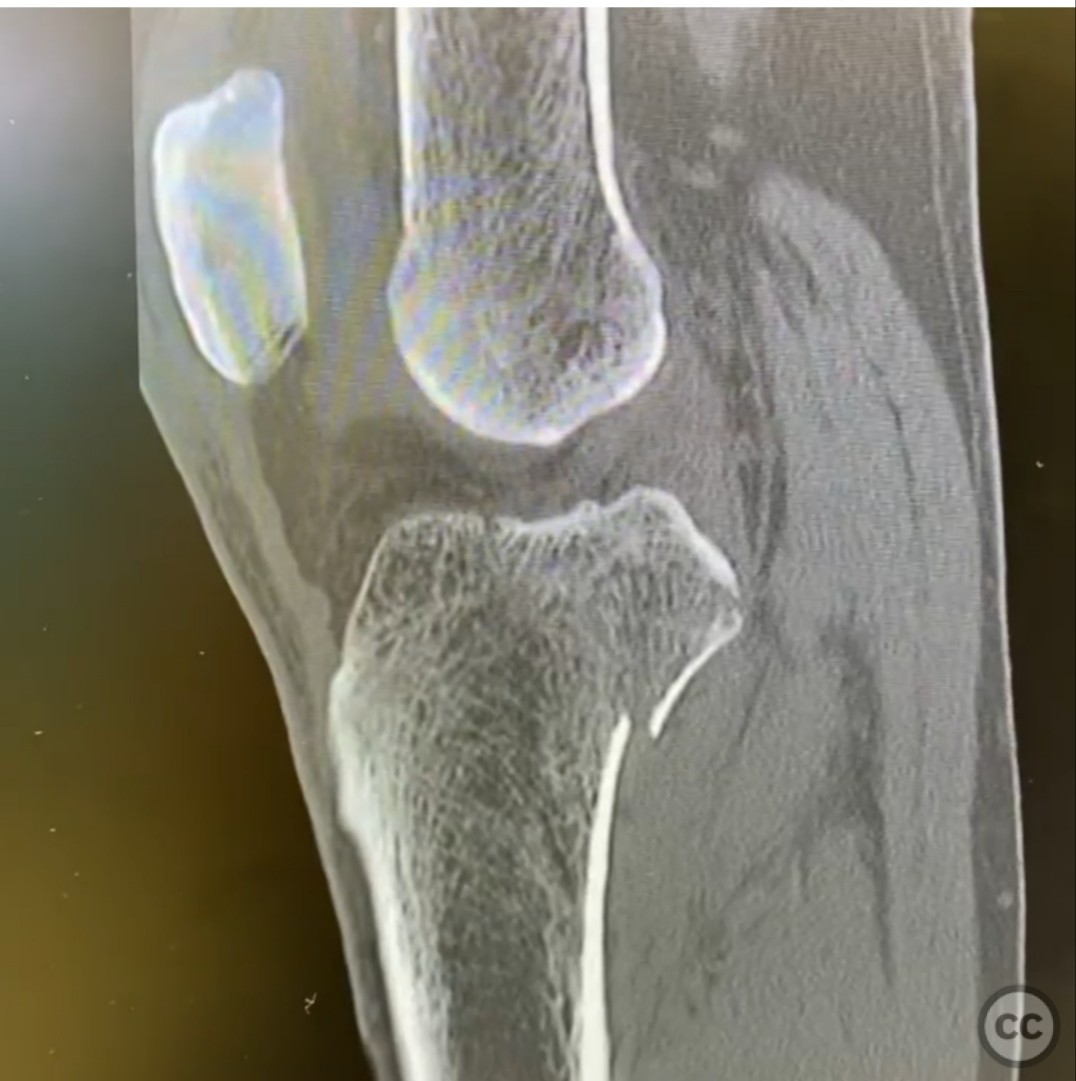
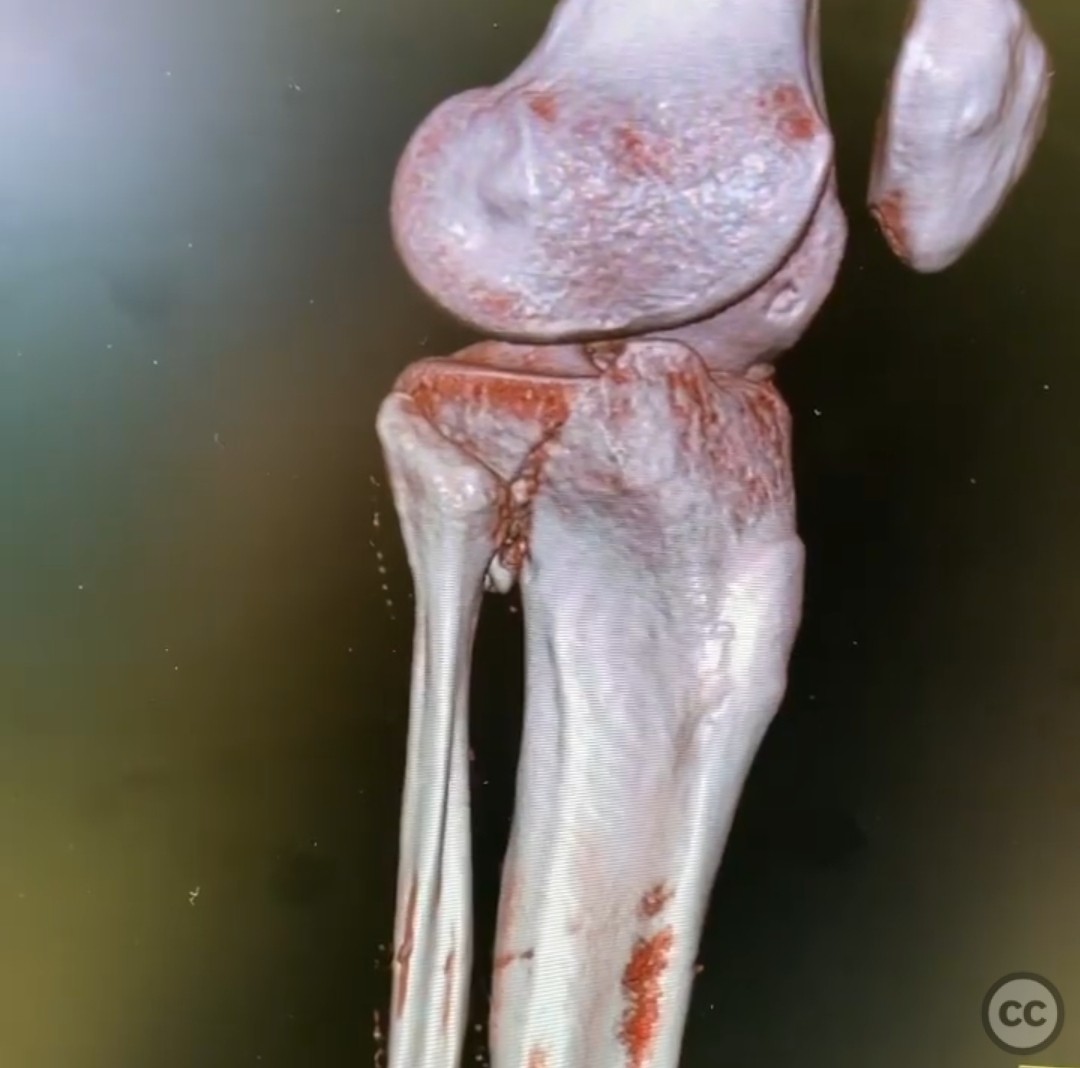
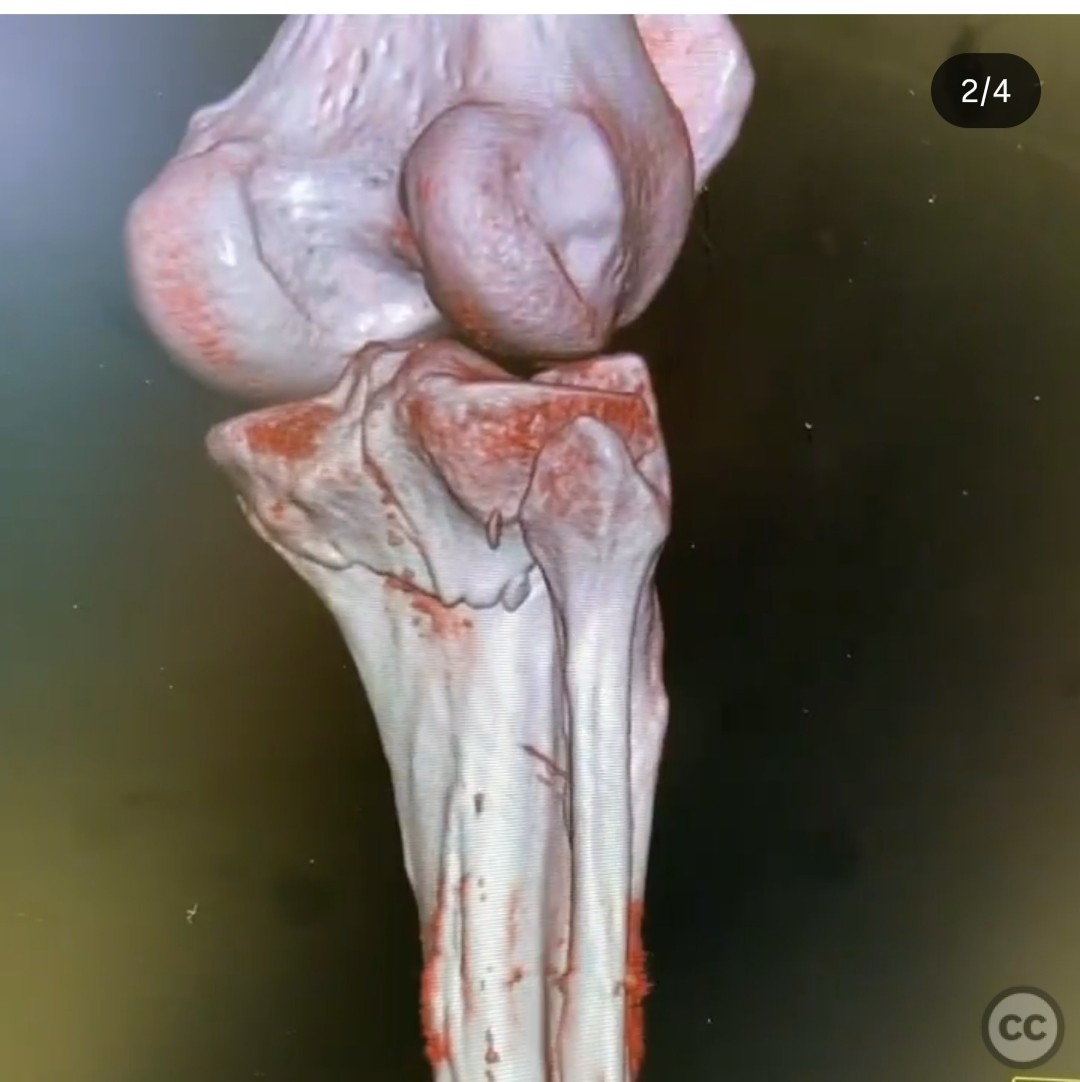
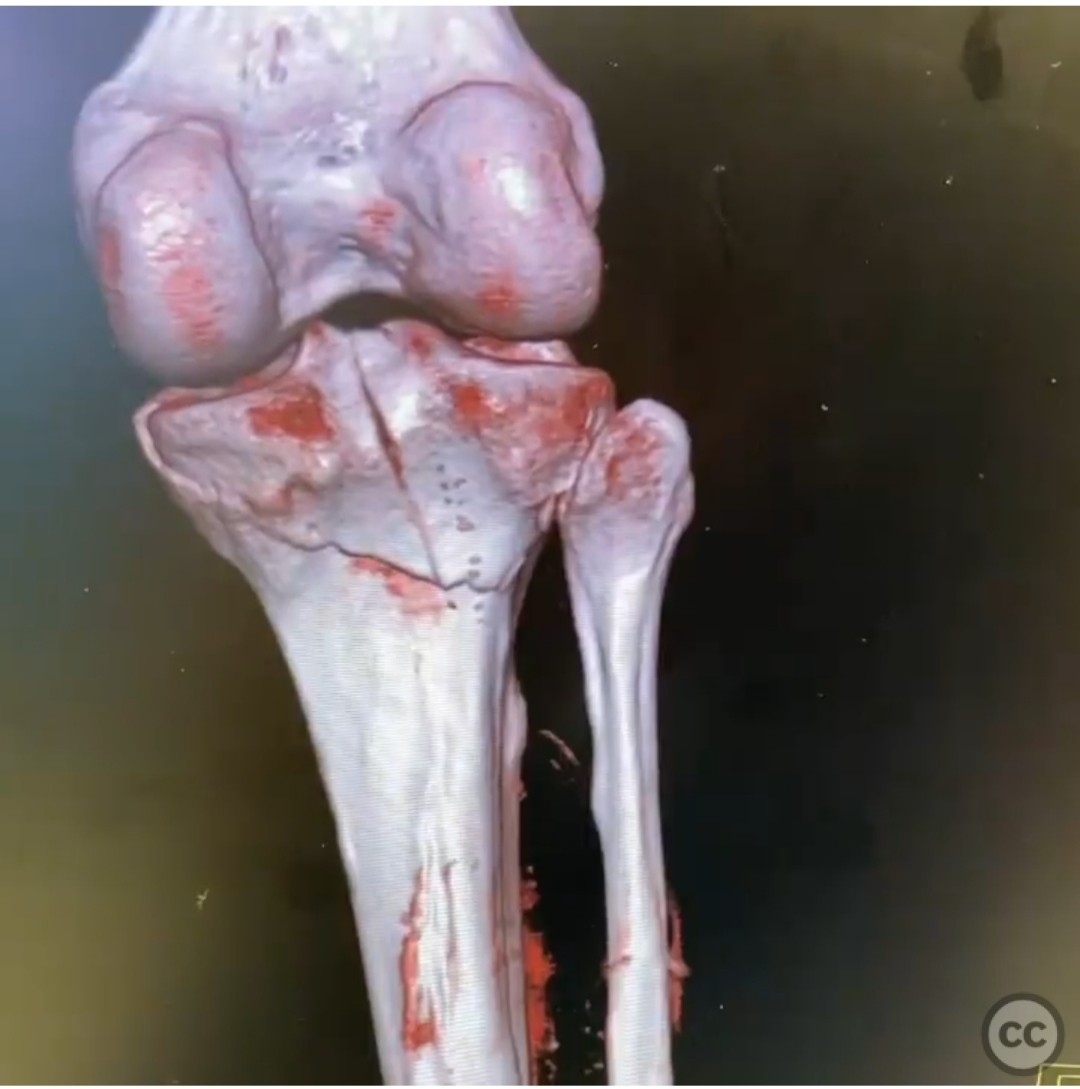
Clinical and radiological findings: The patient presented with an unusual posterior column shearing pattern, more displaced on the lateral side than the medial. The fracture is classified as an OTA B type articular fracture, characterized by failure in shear.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involves direct reduction, interfragmentary compression, and buttress plating. The surgical approach is planned through a posteromedial incision, given the patient's lean physique, allowing access to the entire posterior plateau.
Surgical Discussion
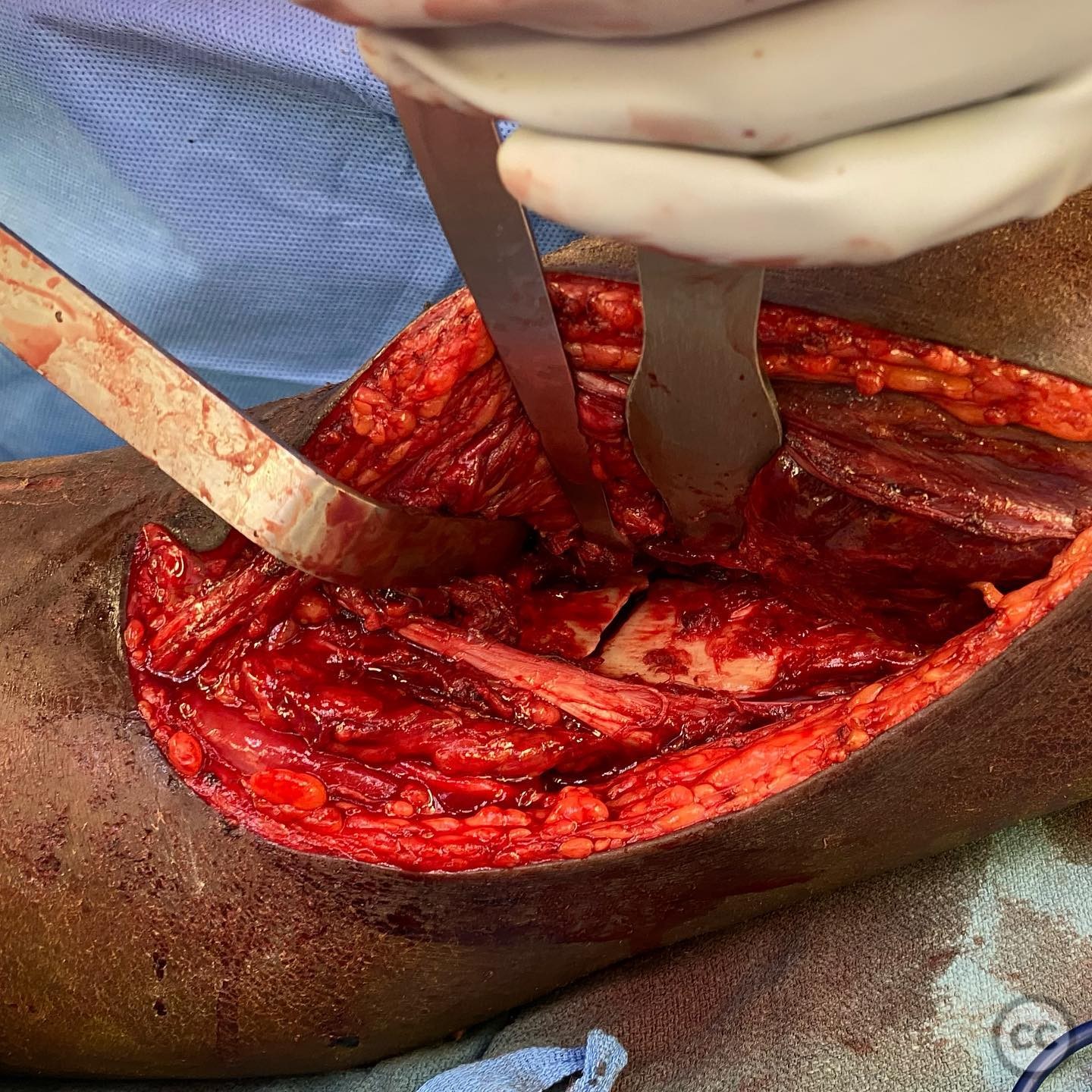
Patient positioning: Prone positioning was selected for optimal access to the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau.
Anatomical surgical approach: A posteromedial approach was utilized. The incision was made along the medial border of the tibia, with careful dissection through the subcutaneous tissue and fascia. The medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle was retracted laterally to expose the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau. Care was taken to protect the neurovascular structures in proximity.
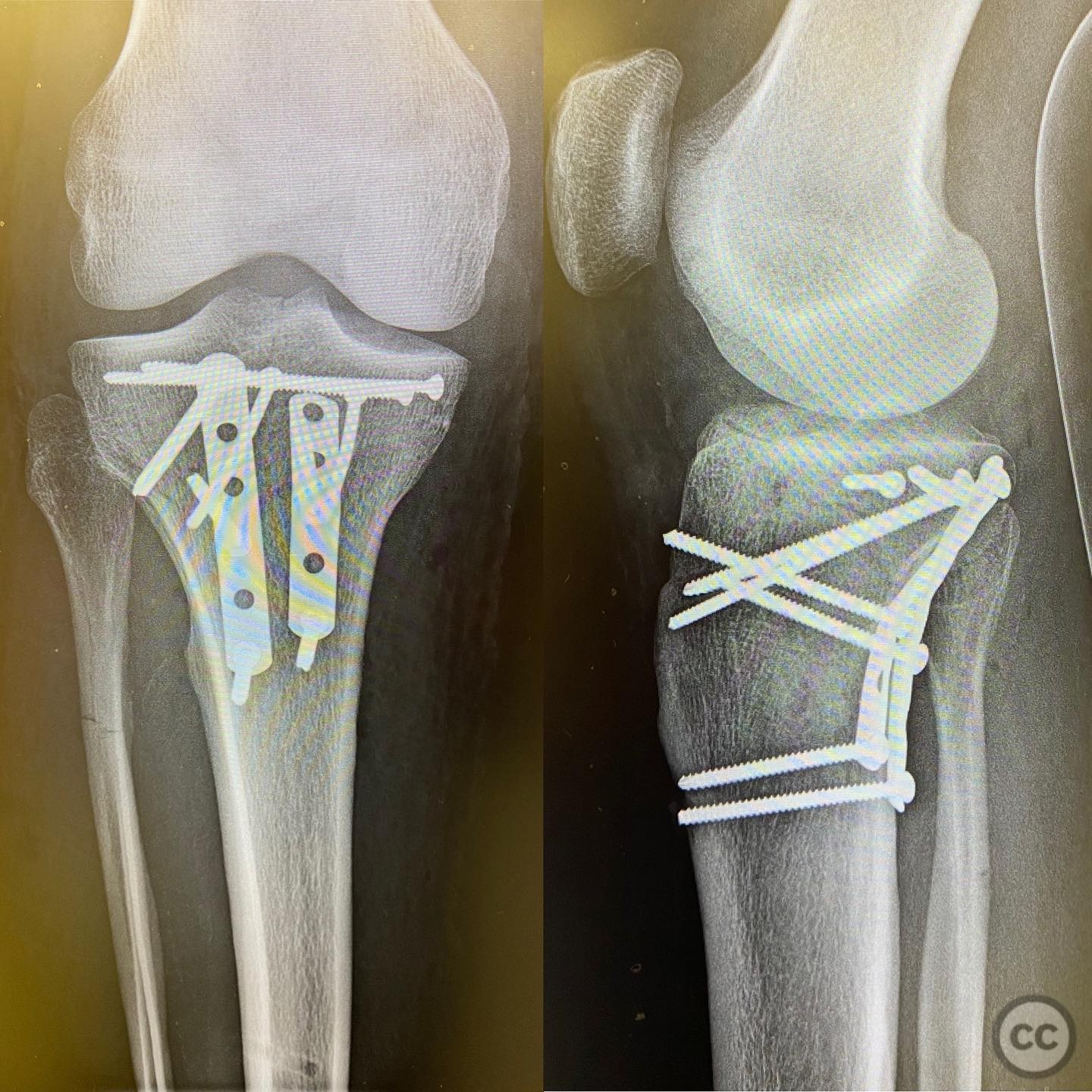
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that the lateral displacement of the posterior column required meticulous reduction and stabilization. Interfragmentary compression was achieved using lag screws at the articular surface, followed by buttress plating at the apex to provide stability. The reduction was confirmed intraoperatively with fluoroscopy.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included non-weight bearing with crutches for 6 weeks, followed by gradual weight-bearing as tolerated. Range of motion exercises were initiated early to prevent stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Buttress plate, lag screws
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 167 times
12 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Posterior Column Shearing Fracture with Lateral Displacement. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 37823540 Published Online Jul 12 2025.