Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture with Non-displaced Medial Malleolar Fracture.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
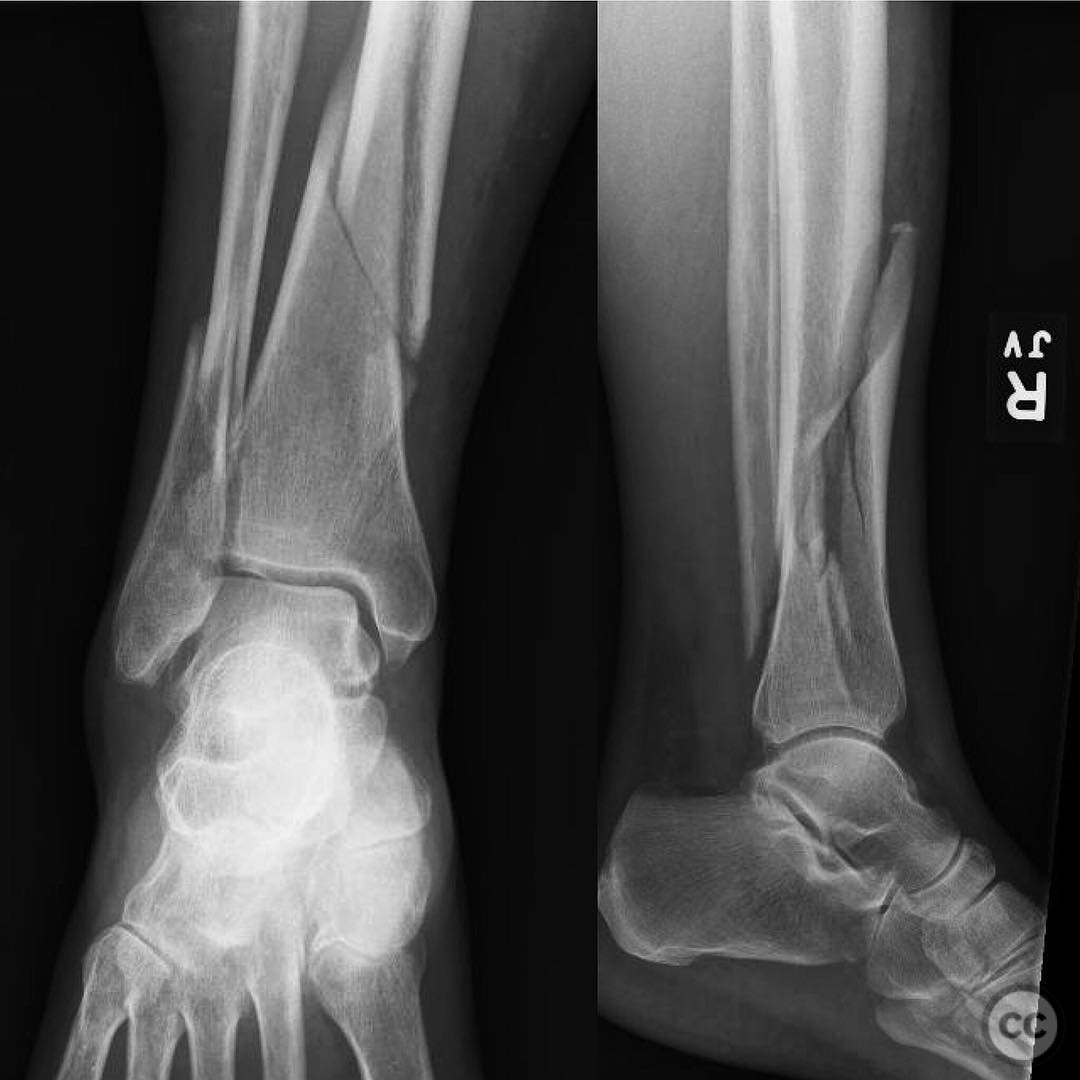
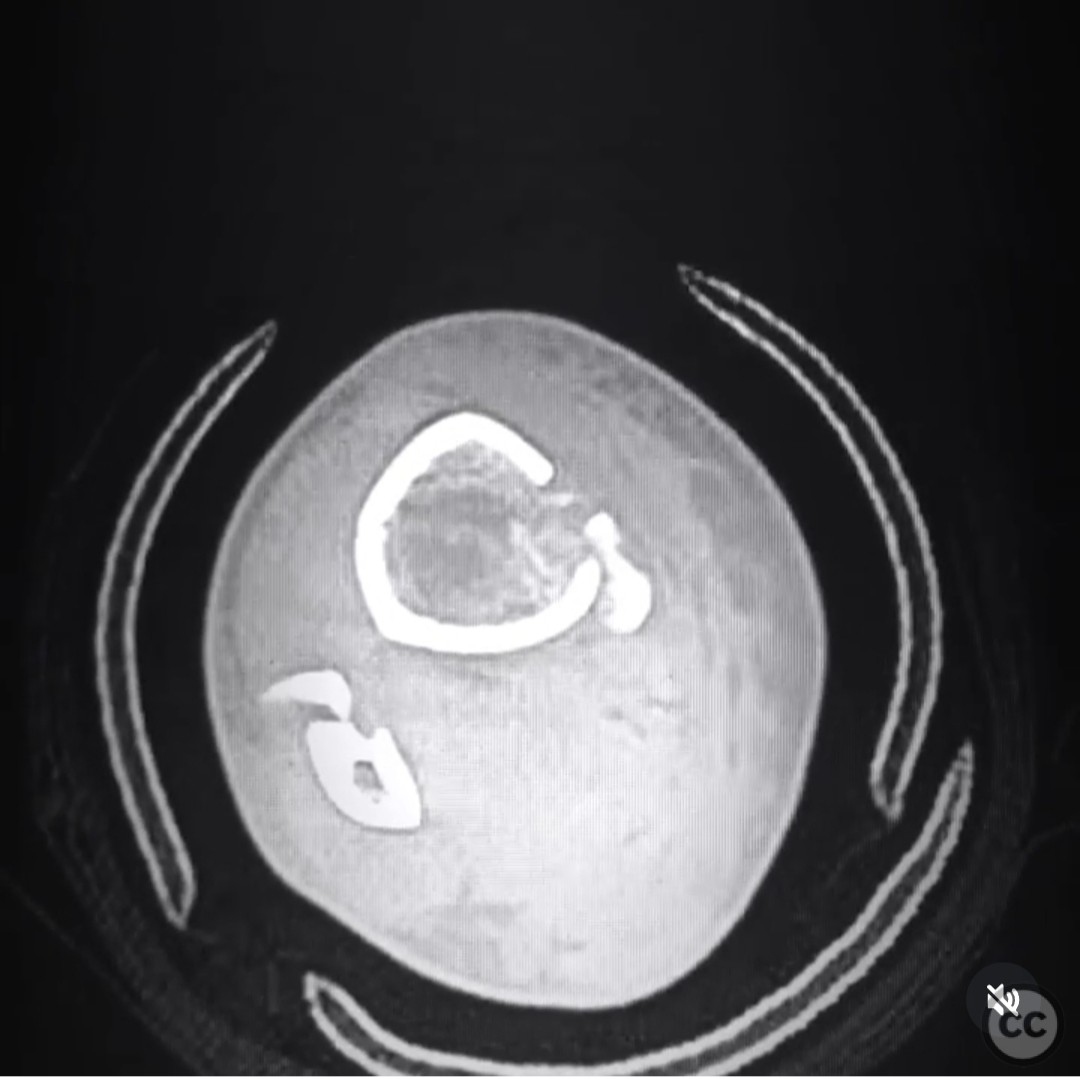
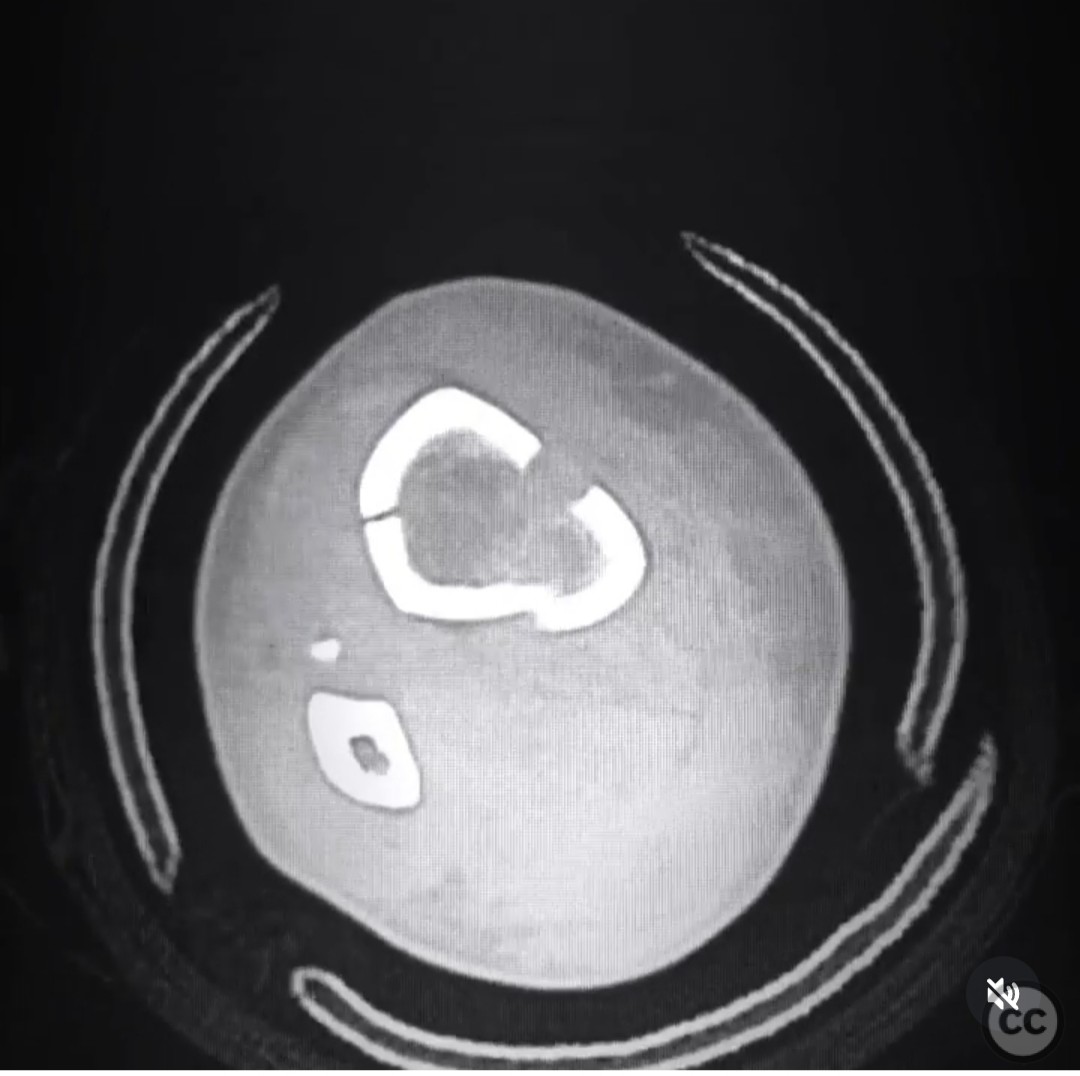
Clinical and radiological findings: A 37-year-old female sustained a distal tibial metaphyseal fracture with an associated non-displaced vertical medial malleolar fracture following a skiing accident. Initial radiographs and CT imaging confirmed the presence of a large, non-displaced contiguous medial malleolar fracture in conjunction with the distal tibial fracture. The fibula was not mentioned as being fractured or requiring fixation.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved intramedullary nailing of the distal tibial fracture. The decision was made to use a nail due to the ability to achieve stable fixation with three distal interlocking bolts, favoring the biomechanical advantages of a nail over a plate for long bone fractures. The medial malleolar fracture was deemed stable and non-displaced, thus not requiring fixation.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned in a semiextended position for the procedure, facilitating a supra-patellar approach for nail insertion.
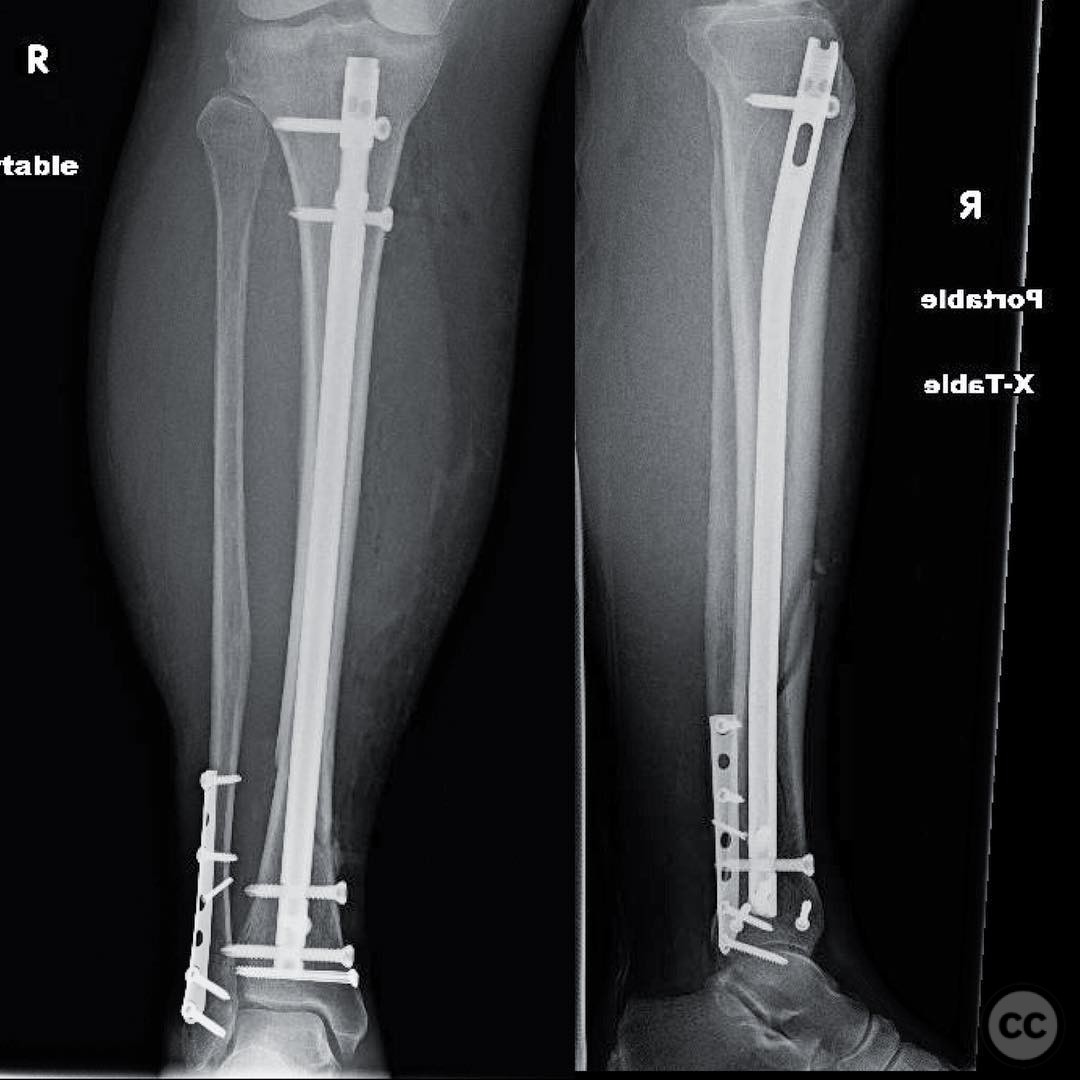
Anatomical surgical approach: A supra-patellar approach was utilized for intramedullary nailing. The entry point was established through the patellar tendon, and the nail was inserted through the proximal tibia into the medullary canal. Reduction of the tibial fracture was achieved using two percutaneously applied large Weber clamps prior to nail insertion.
Operative remarks:The surgeon opted for intramedullary nailing due to the ability to achieve stable fixation with three distal interlocking bolts in a short segment of the tibia. This choice was based on the biomechanical superiority of nails in long bone fractures. The medial malleolar fracture was left unfixed due to its non-displaced nature. The fibula was not addressed surgically, as it was not fractured or deemed necessary for stabilization.
Postoperative protocol: The postoperative rehabilitation protocol included early weight-bearing, allowing the patient to walk at 2 weeks post-surgery. This approach contrasts with a plating strategy, which would have required non-weight bearing for at least 6 weeks.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail with three distal interlocking bolts.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 255 times
28 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture with Non-displaced Medial Malleolar Fracture.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 35548295 Published Online Jul 28 2025.