Distal Femur Fracture Around Total Knee Arthroplasty: Nail-Plate Construct
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
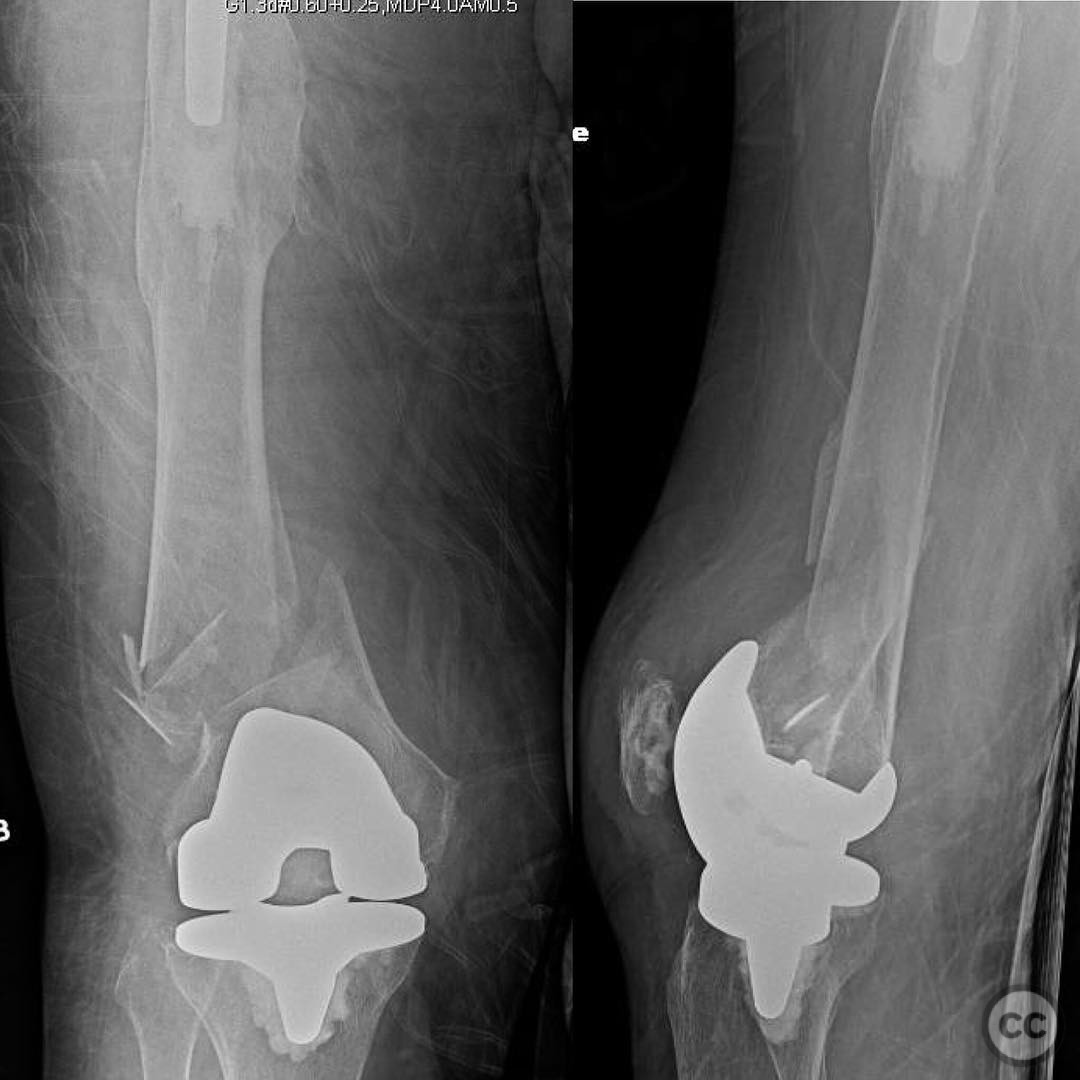
Clinical and radiological findings: A 71-year-old patient presented with a distal femur fracture around a total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The fracture was characterized by osteoporotic bone, complicating stable fixation. The patient was described as large/obese, further challenging the biomechanical stability of the construct. Radiological evaluation indicated a comminuted fracture pattern. The AO/OTA classification for this fracture is 33A3, indicating a distal femur fracture with metaphyseal involvement.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved achieving anatomic reduction with attention to length, alignment, and rotation. A combined nail-plate construct was chosen to provide stable fixation while maintaining relative stability. The surgical approach included a knee arthrotomy and a small lateral incision for lateral plate insertion, avoiding opening the fracture site to preserve biological integrity.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table to facilitate access to the distal femur and knee joint.
Anatomical surgical approach: A lateral approach to the distal femur was utilized. A small lateral incision was made for the insertion of the lateral plate. A knee arthrotomy was performed to aid in the reduction and fixation process. The femoral canal was not reamed to minimize biological insult.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of stable fixation in osteoporotic bone, noting that a lateral plate alone is not ideal due to biomechanical considerations. The use of a nail allows load transmission along the anatomic axis of the femur, reducing the risk of varus failure. The combination of a nail and plate provides protection for the entire femur, preventing stress risers between the nail and TKA stem. The construct was designed to be biologically friendly, with minimal surgical insult and respect for the fracture's biology.
Postoperative protocol: The postoperative rehabilitation protocol focused on early mobilization. The patient was encouraged to begin ambulation the day after surgery to prevent complications such as pneumonia, blood clots, and bedsores.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Nail-plate construct with oblique interlocking bolts for posterior condylar fixation.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 anatomic reduction- length_ alignment_ rotation. Chec(.jpg)
Article viewed 165 times
26 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Distal Femur Fracture Around Total Knee Arthroplasty: Nail-Plate Construct. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 34170986 Published Online Jul 26 2025.