Open Trimalleolar Equivalent Fracture with Medial Wound and Fibular Nonunion.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
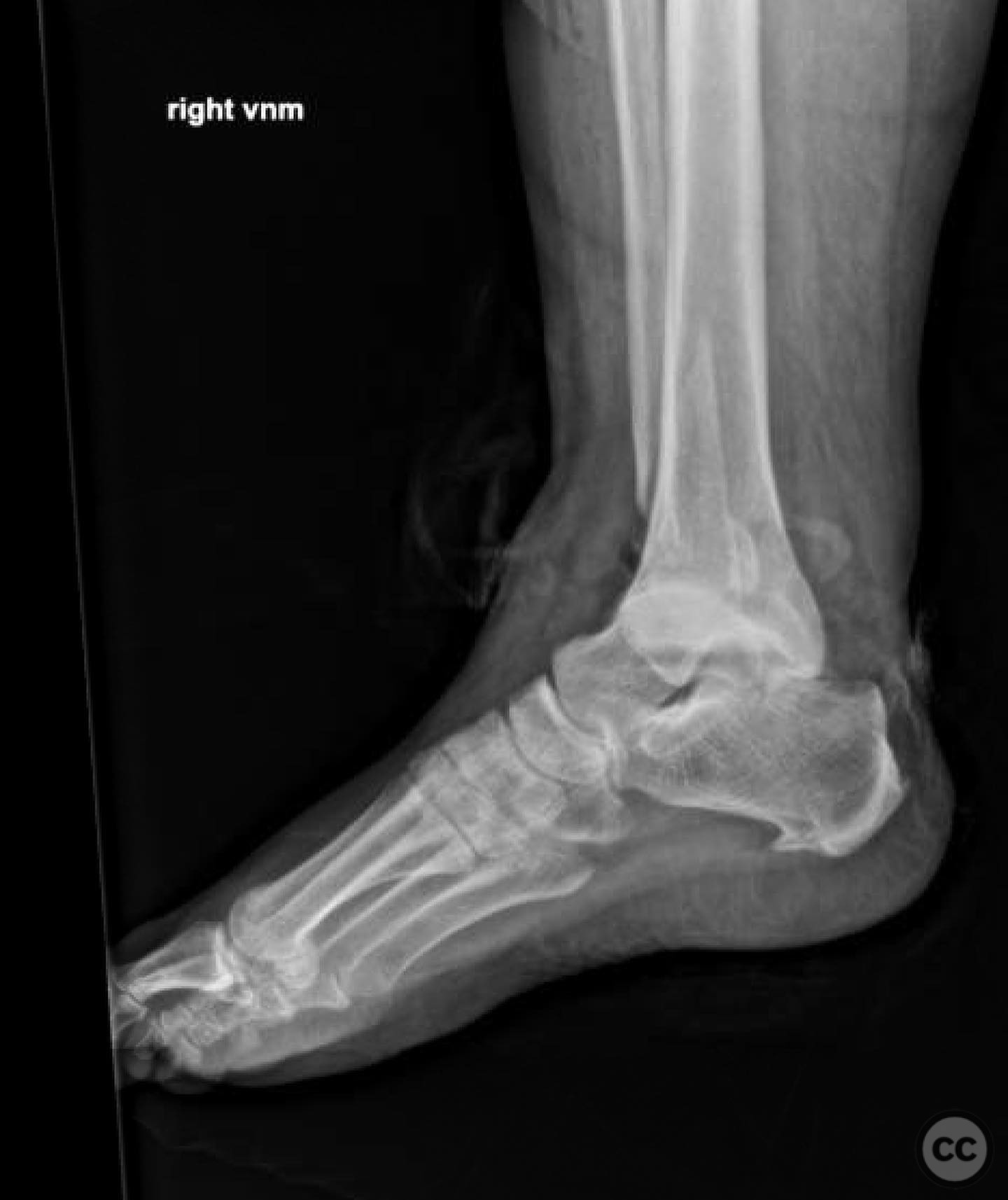
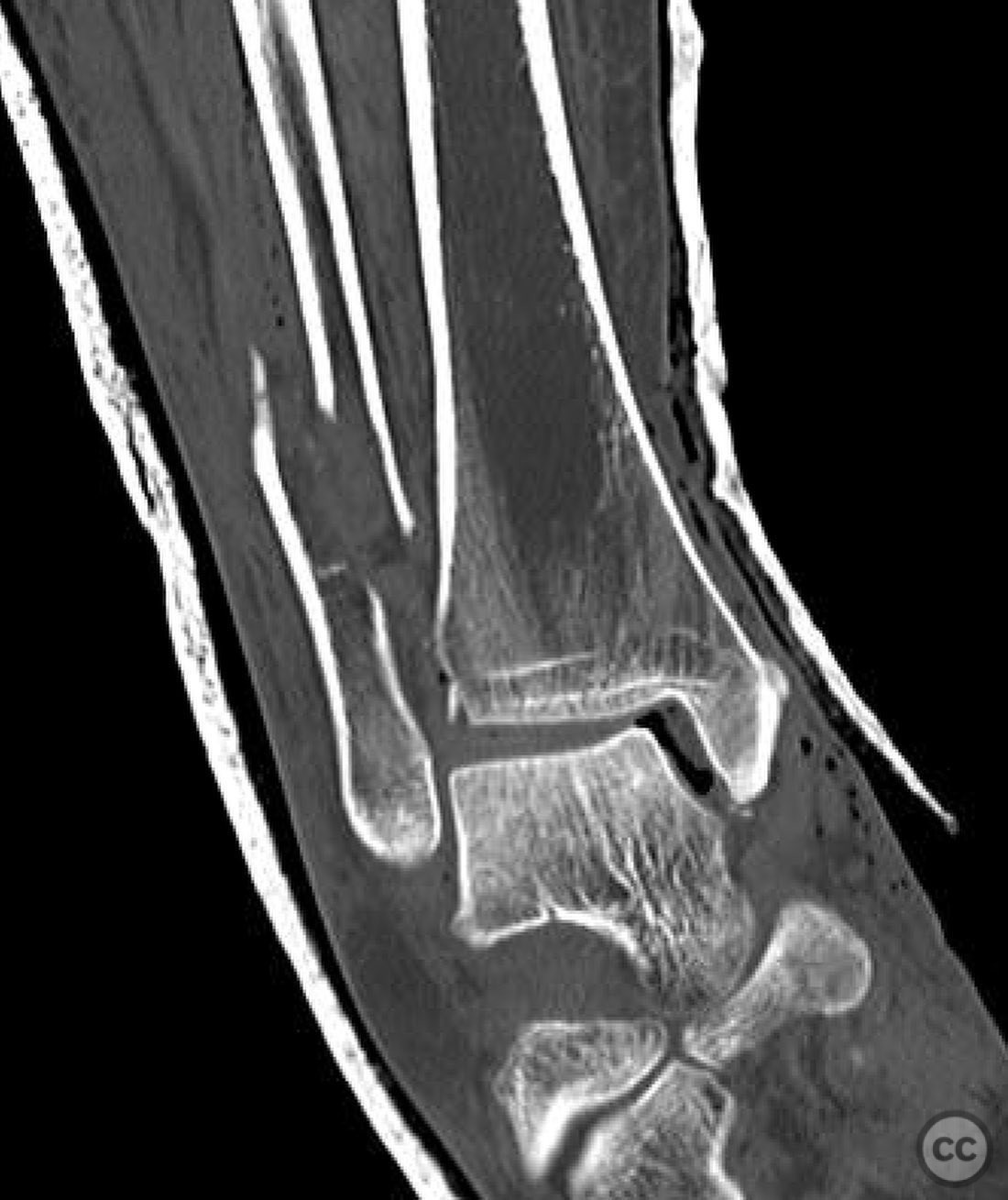
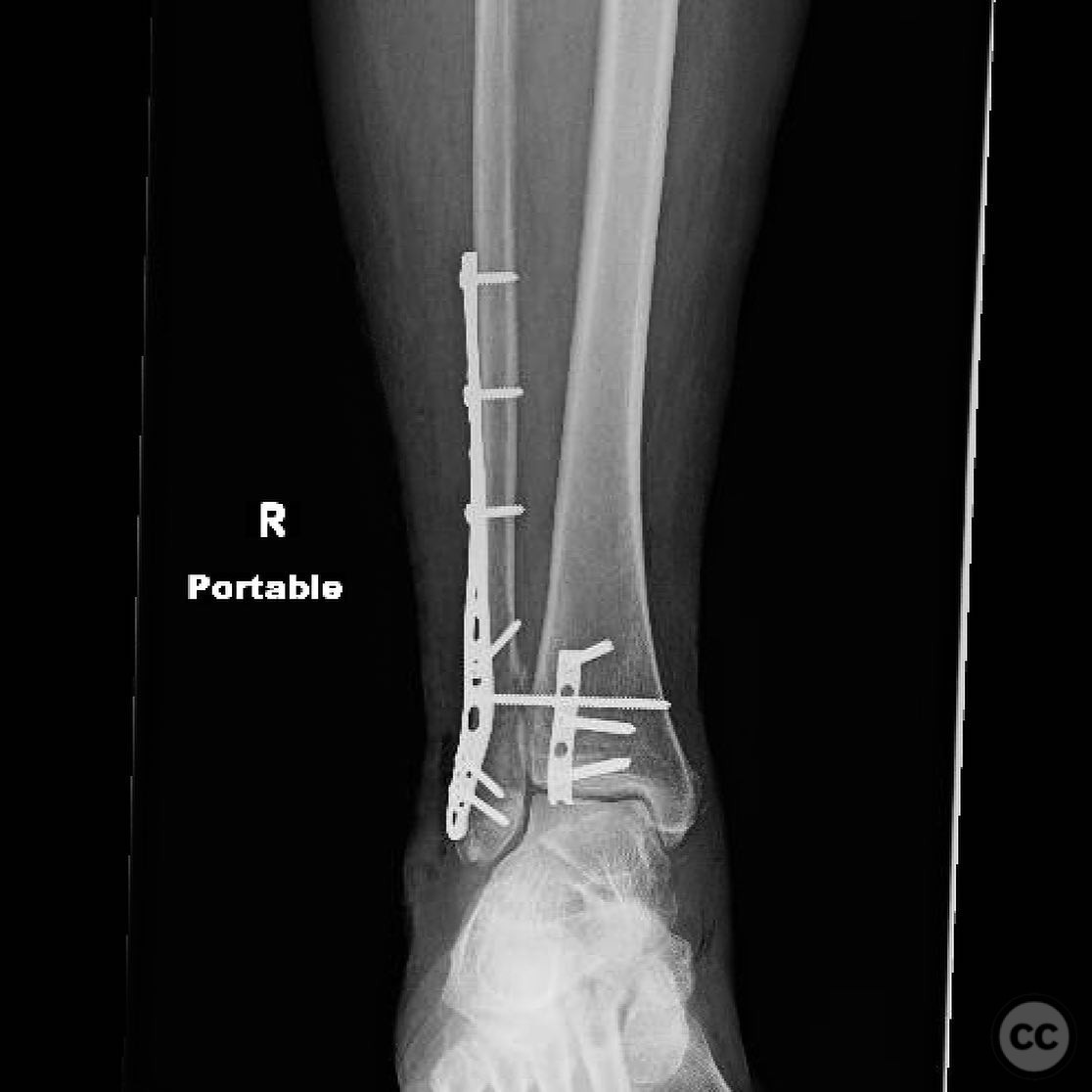
Clinical and radiological findings: A 60-year-old female presented following a slip off a curb in the rain, resulting in an open trimalleolar equivalent fracture dislocation of the ankle. The patient has a medical history of hypothyroidism. Clinical examination revealed a 6 cm transverse open wound on the medial aspect of the ankle, indicative of tension failure of the skin. Radiographs confirmed the fracture pattern, and there was no significant lateral soft tissue injury. The fracture was classified as an AO/OTA 44-B3 fracture.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a single-stage surgical intervention due to the low-energy nature of the open fracture and the absence of severe contamination or soft tissue compromise. The surgical approach included fixation of the posterior malleolus to aid in syndesmotic reduction and stability, without additional syndesmotic fixation unless necessary.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table, with the affected limb elevated and supported to allow for optimal access to the lateral, posterior, and medial aspects of the ankle.
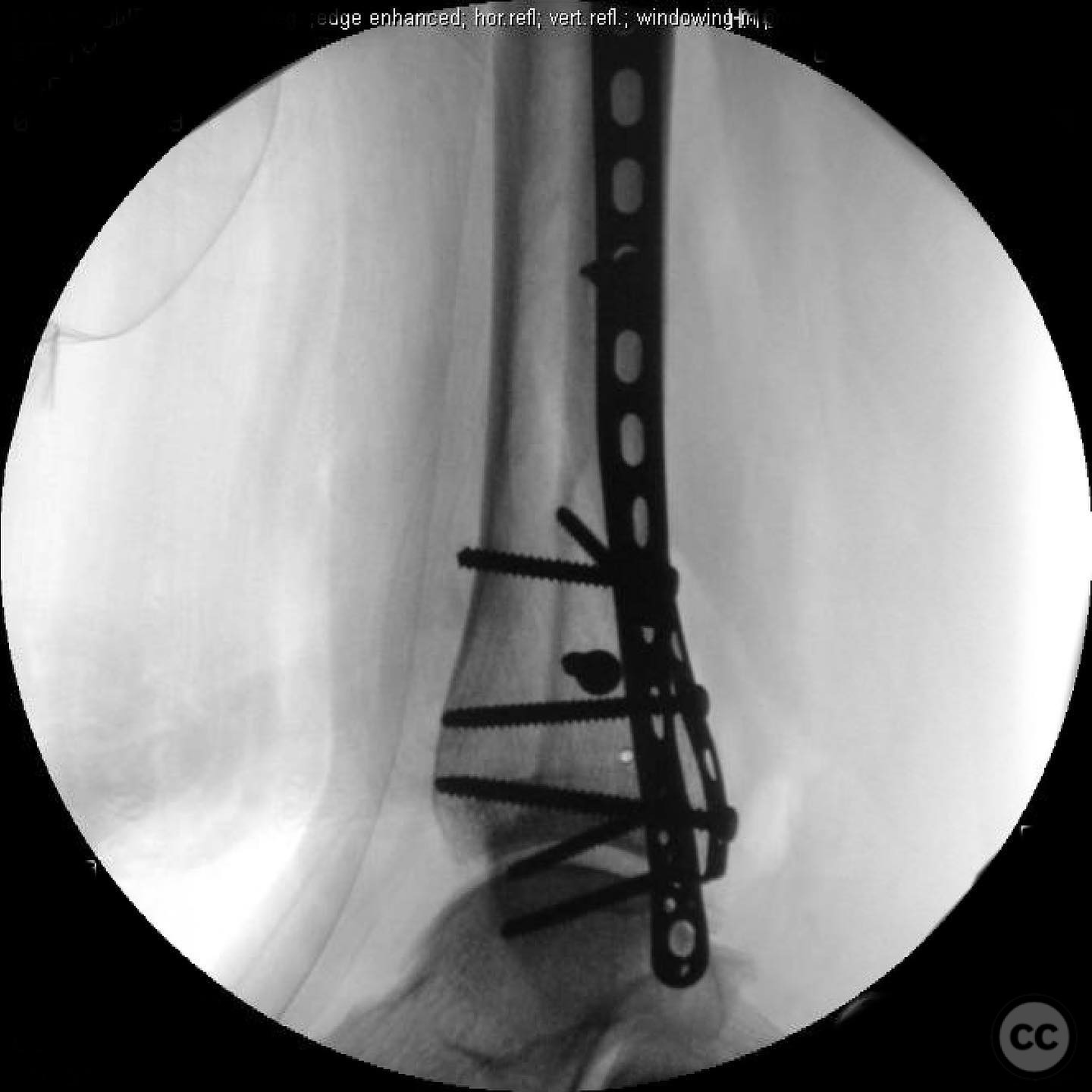
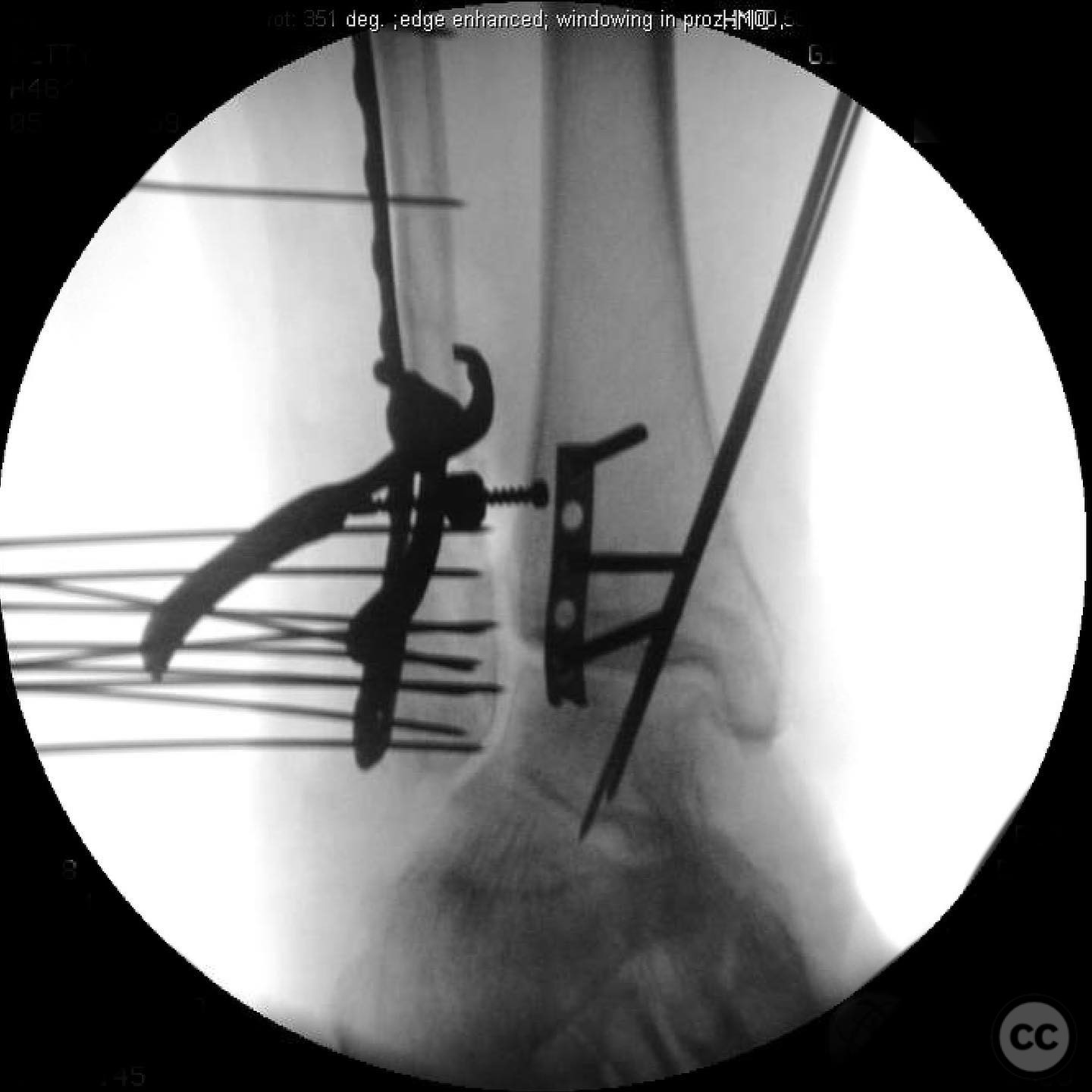
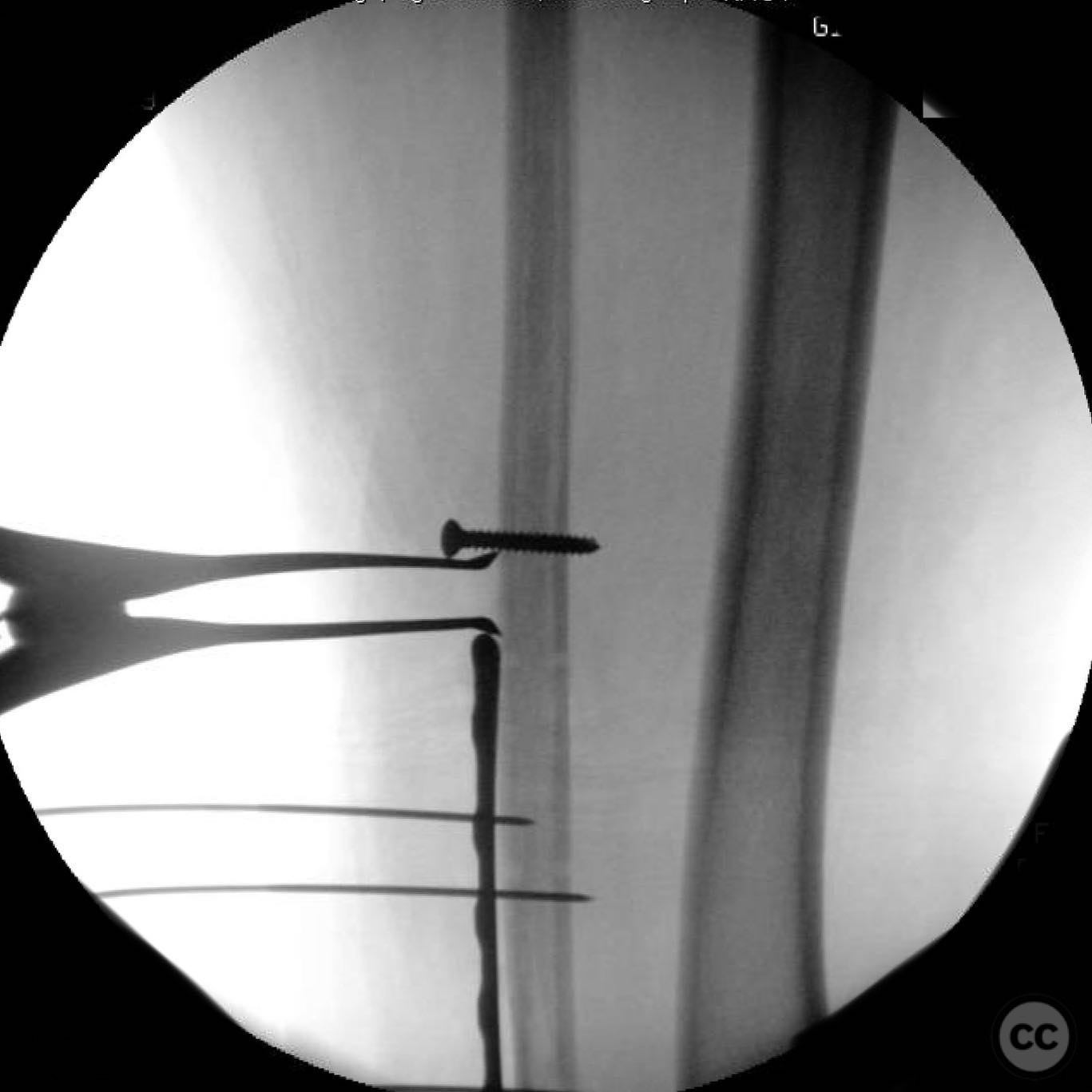
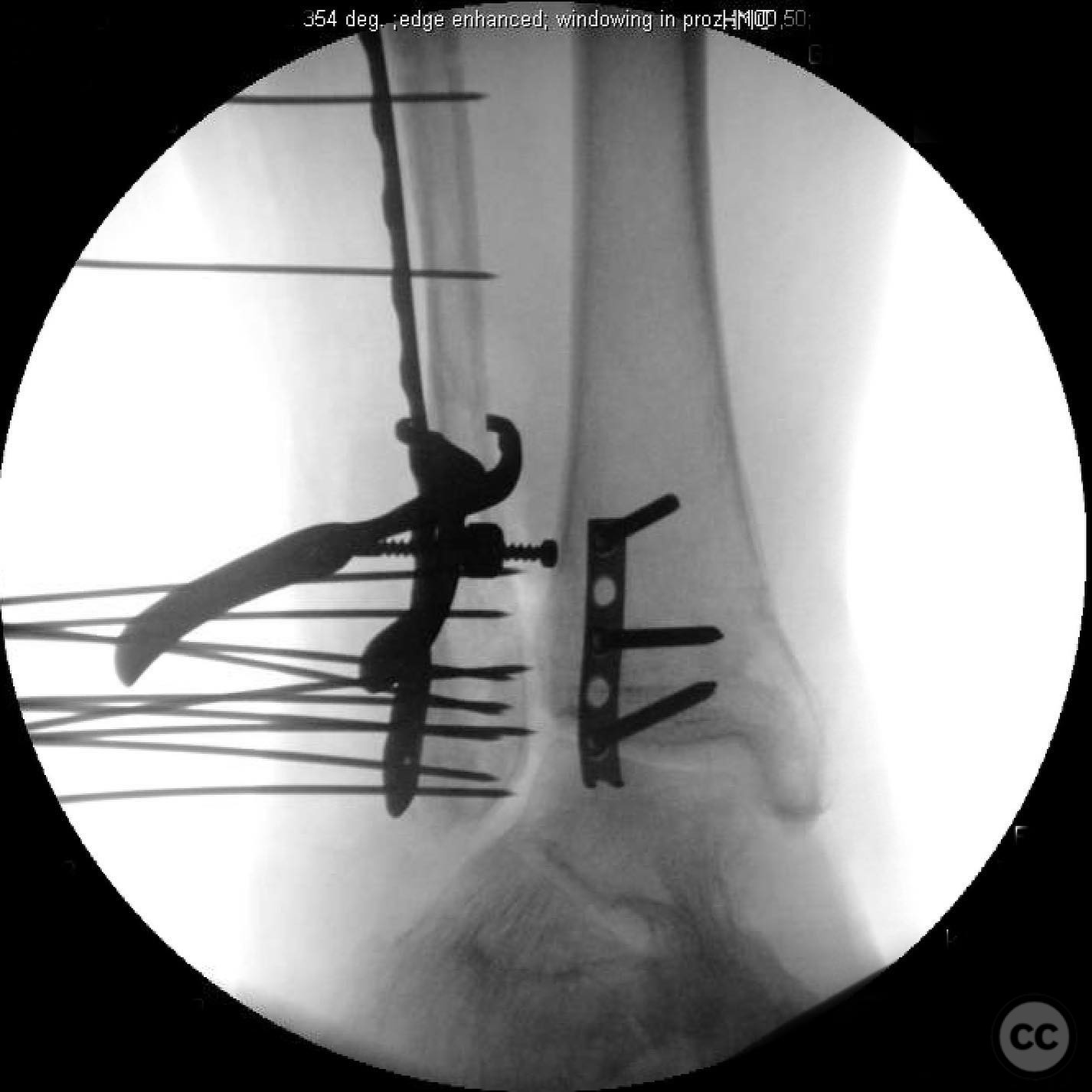
Anatomical surgical approach: A posterolateral approach was utilized for fixation of the posterior malleolus, followed by an anterolateral approach for syndesmotic stabilization. A modified medial approach was employed for addressing the medial gutter and deltoid ligament reconstruction. Extensive debridement of scar tissue from the syndesmosis and medial gutter was performed.
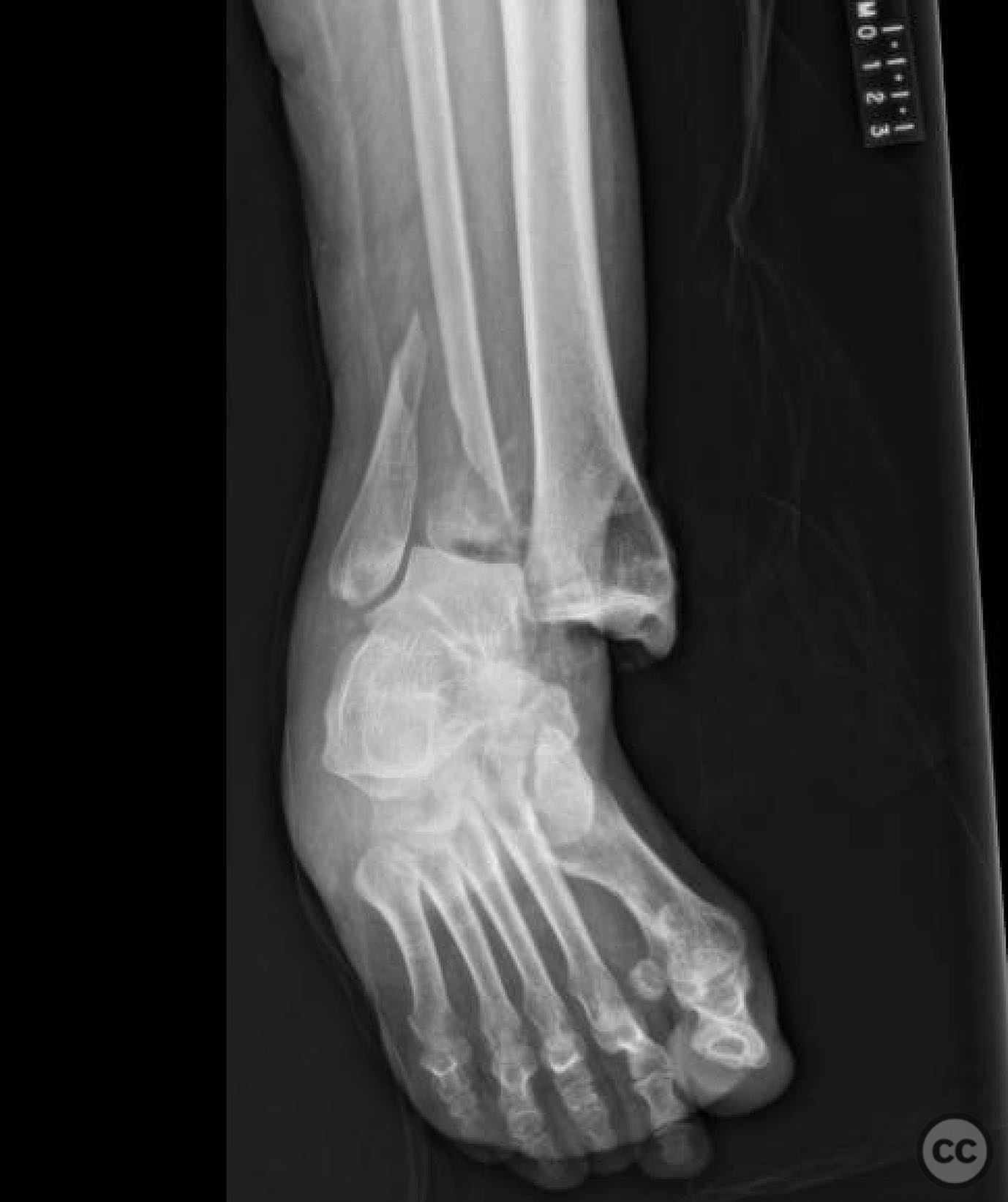
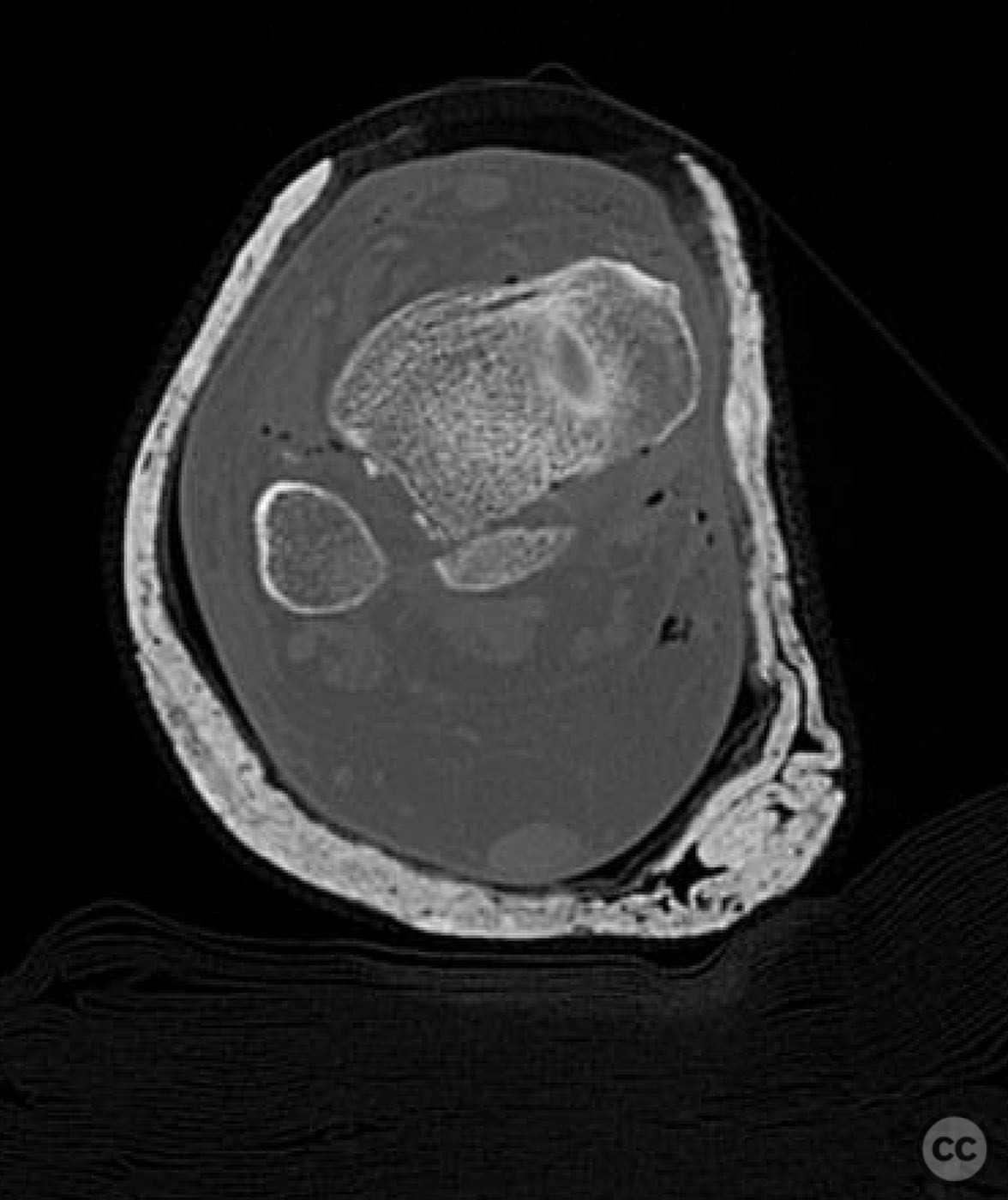
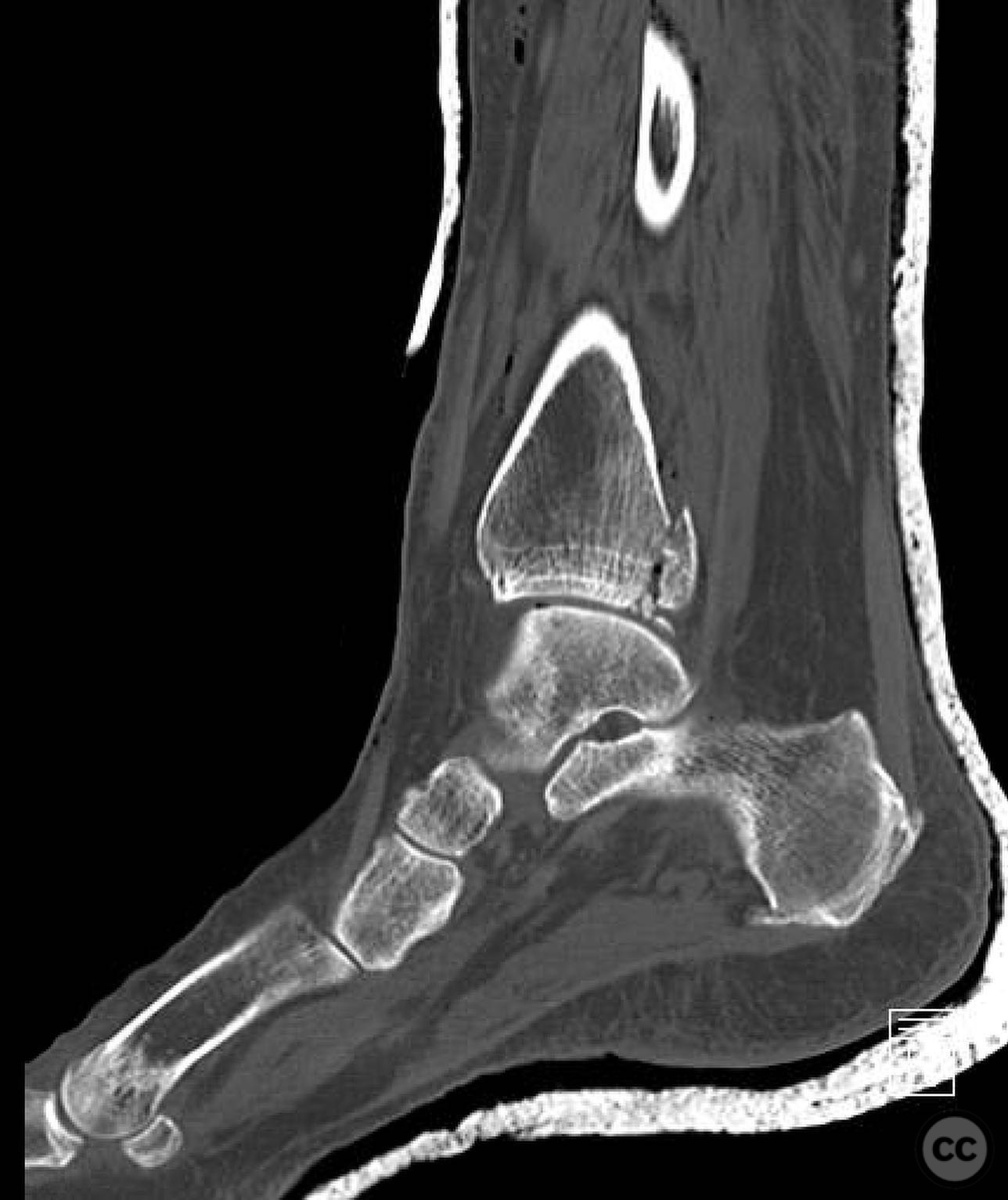
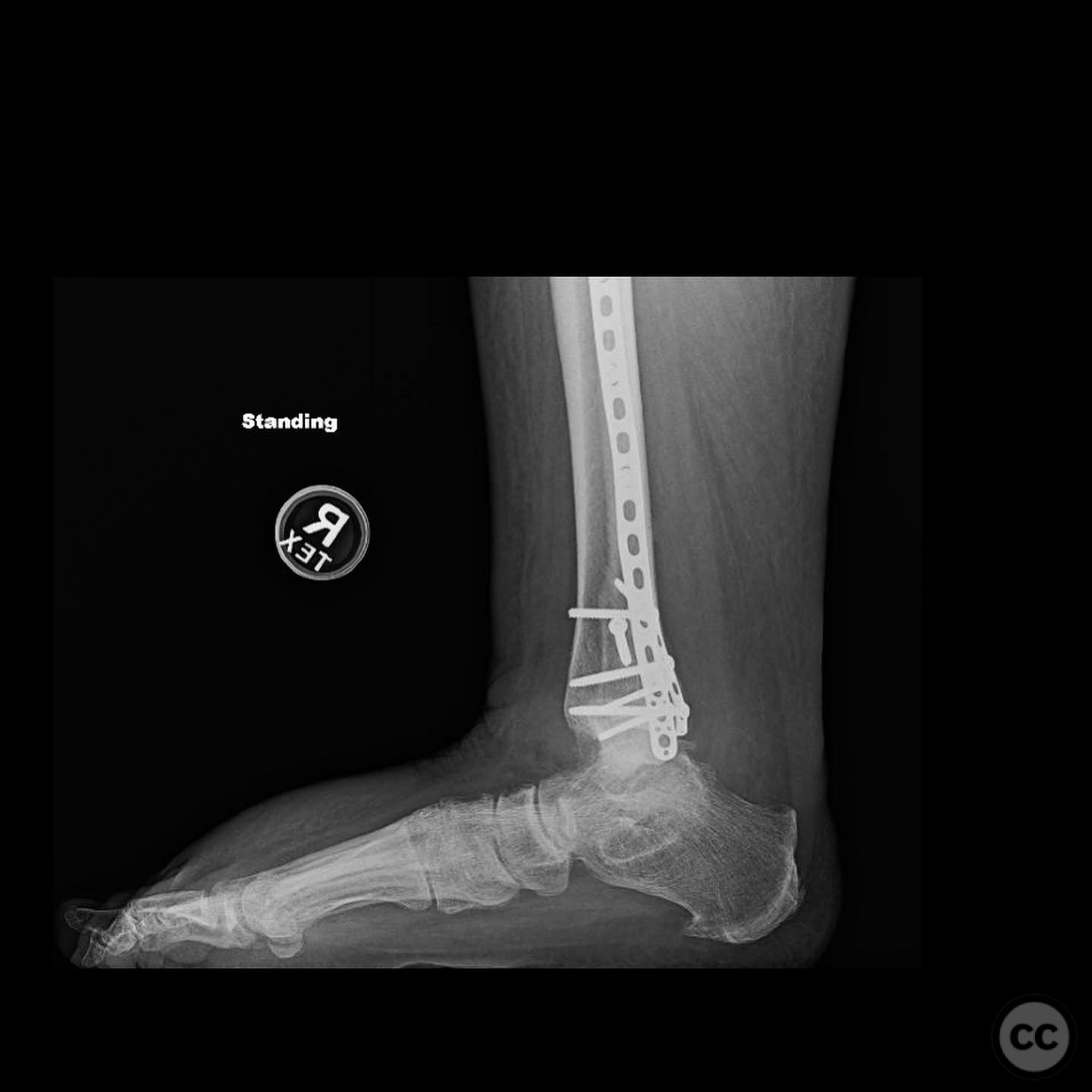
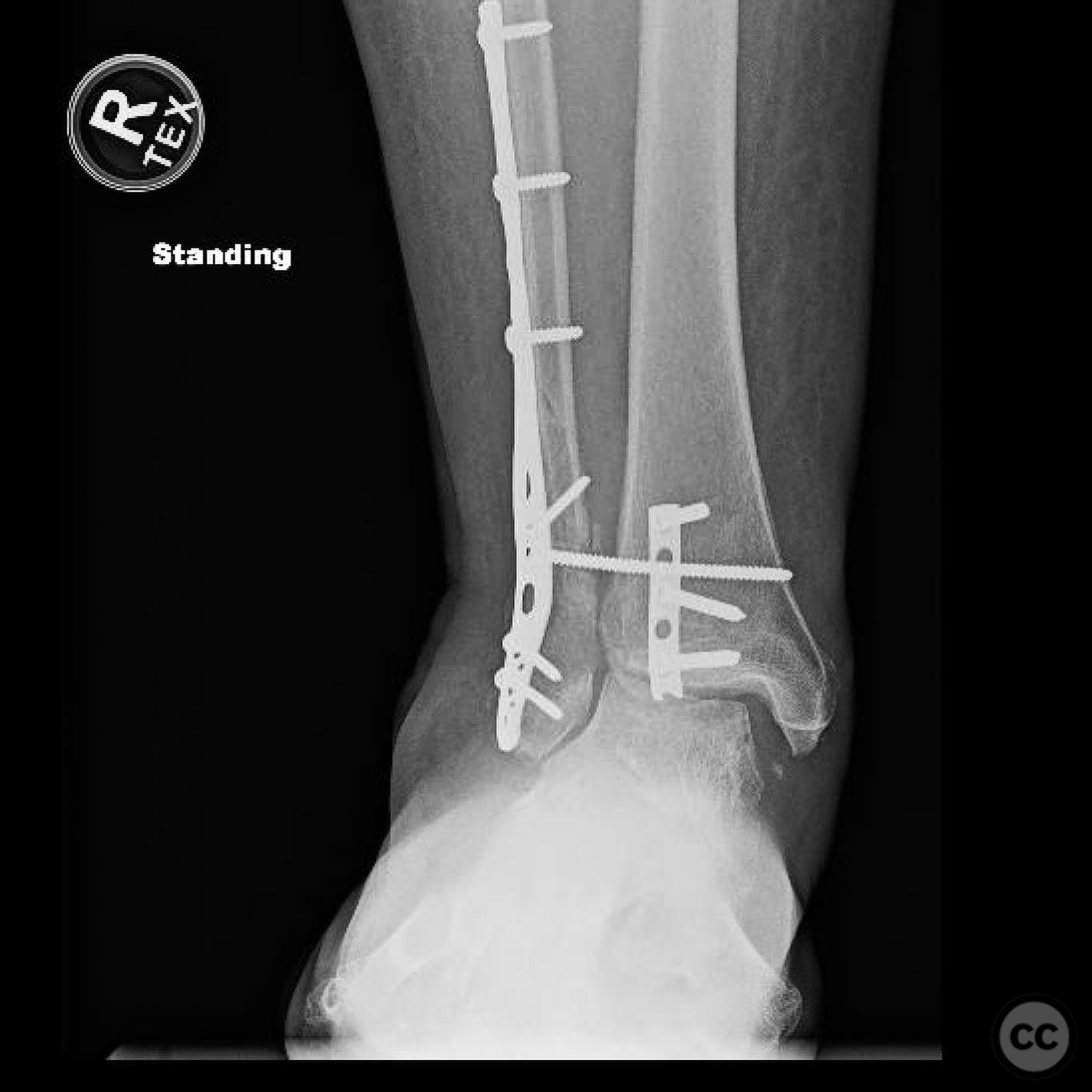
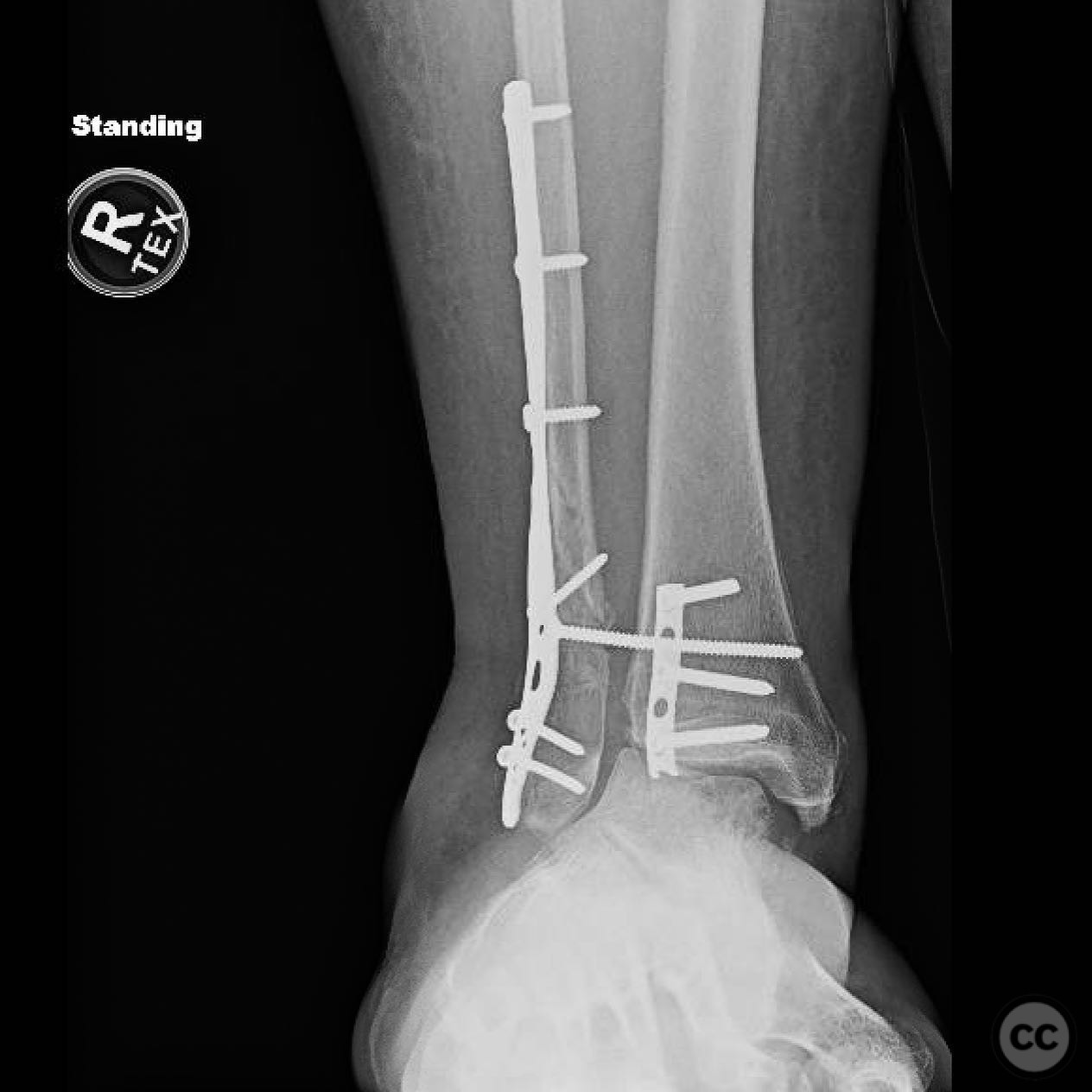
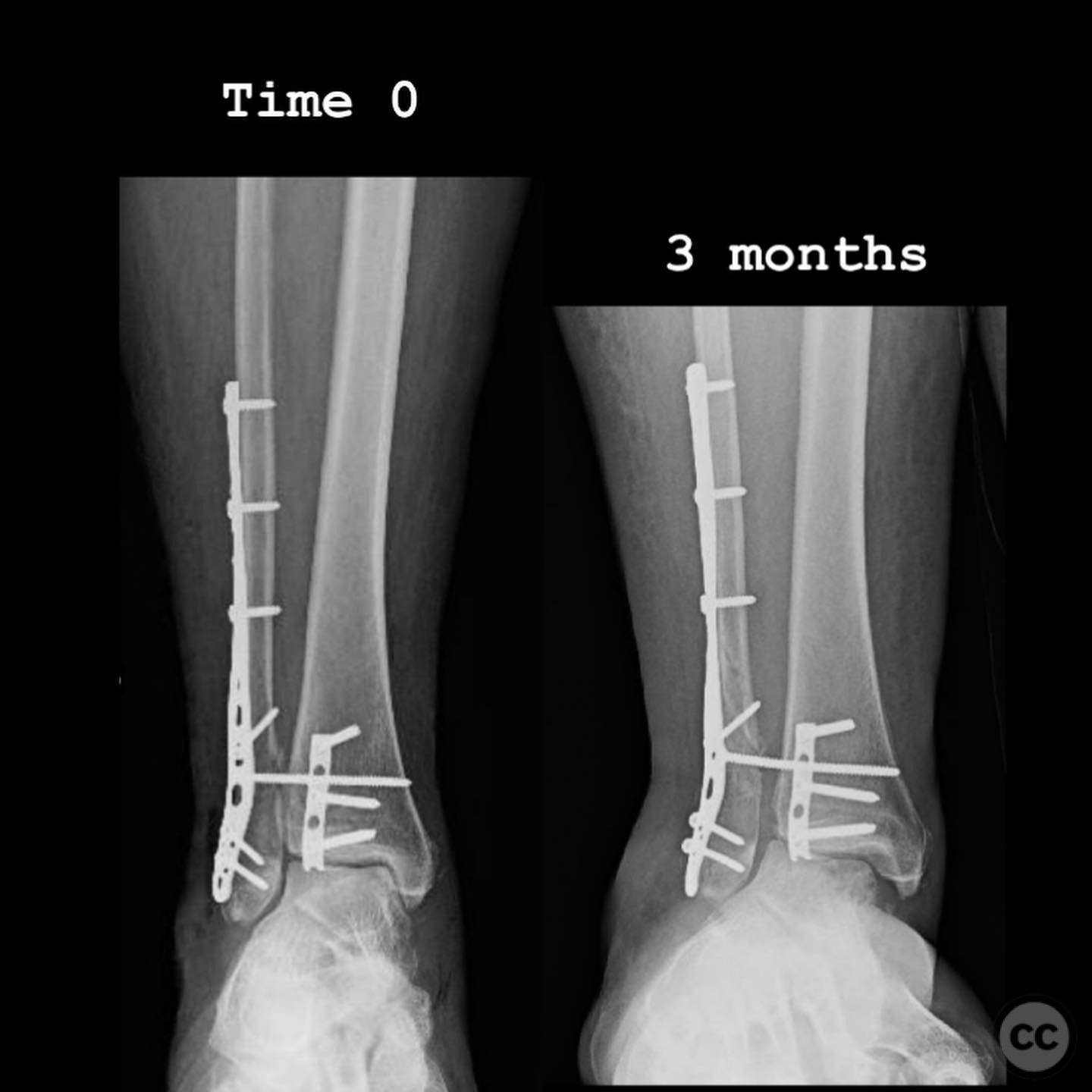
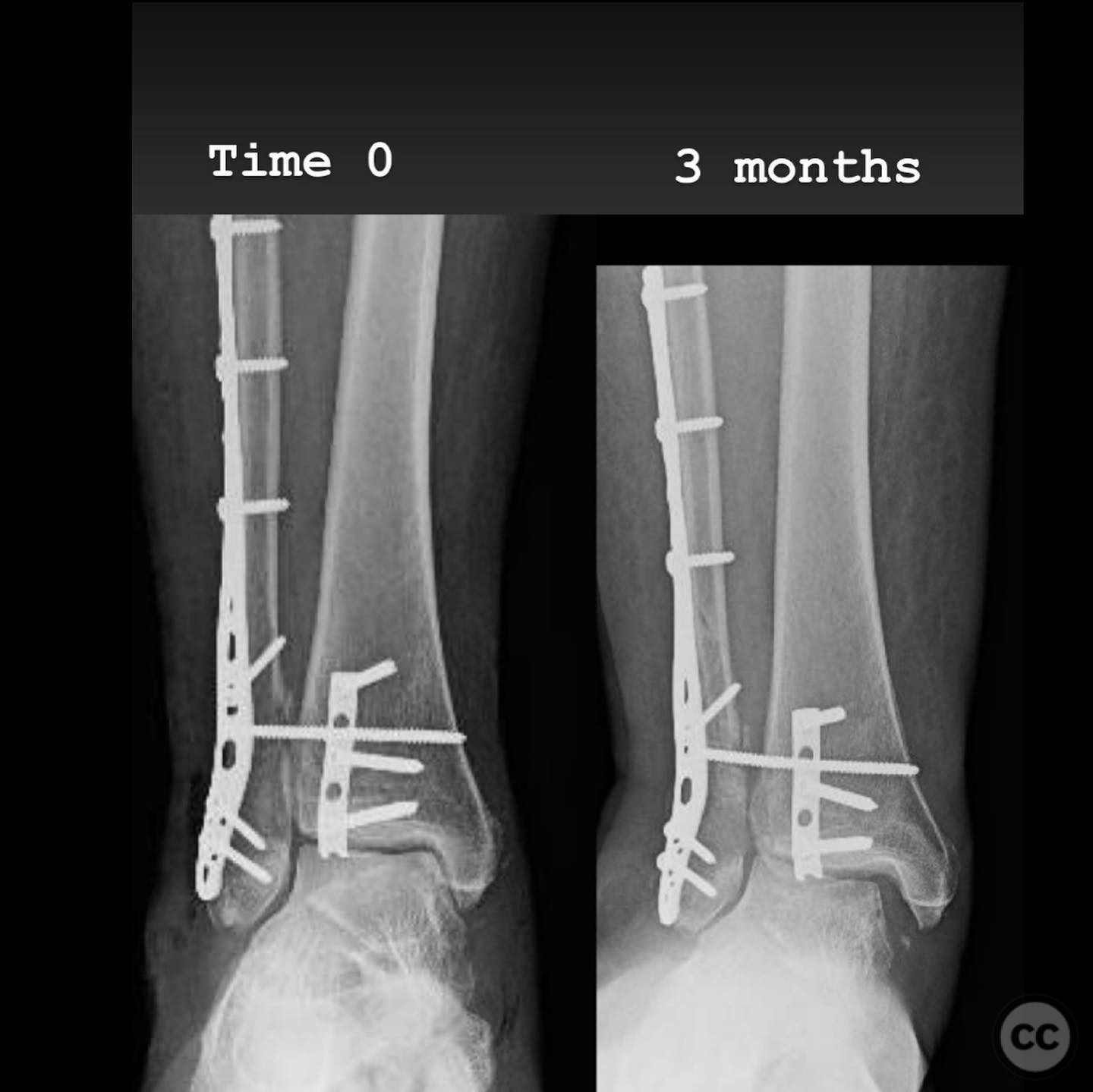
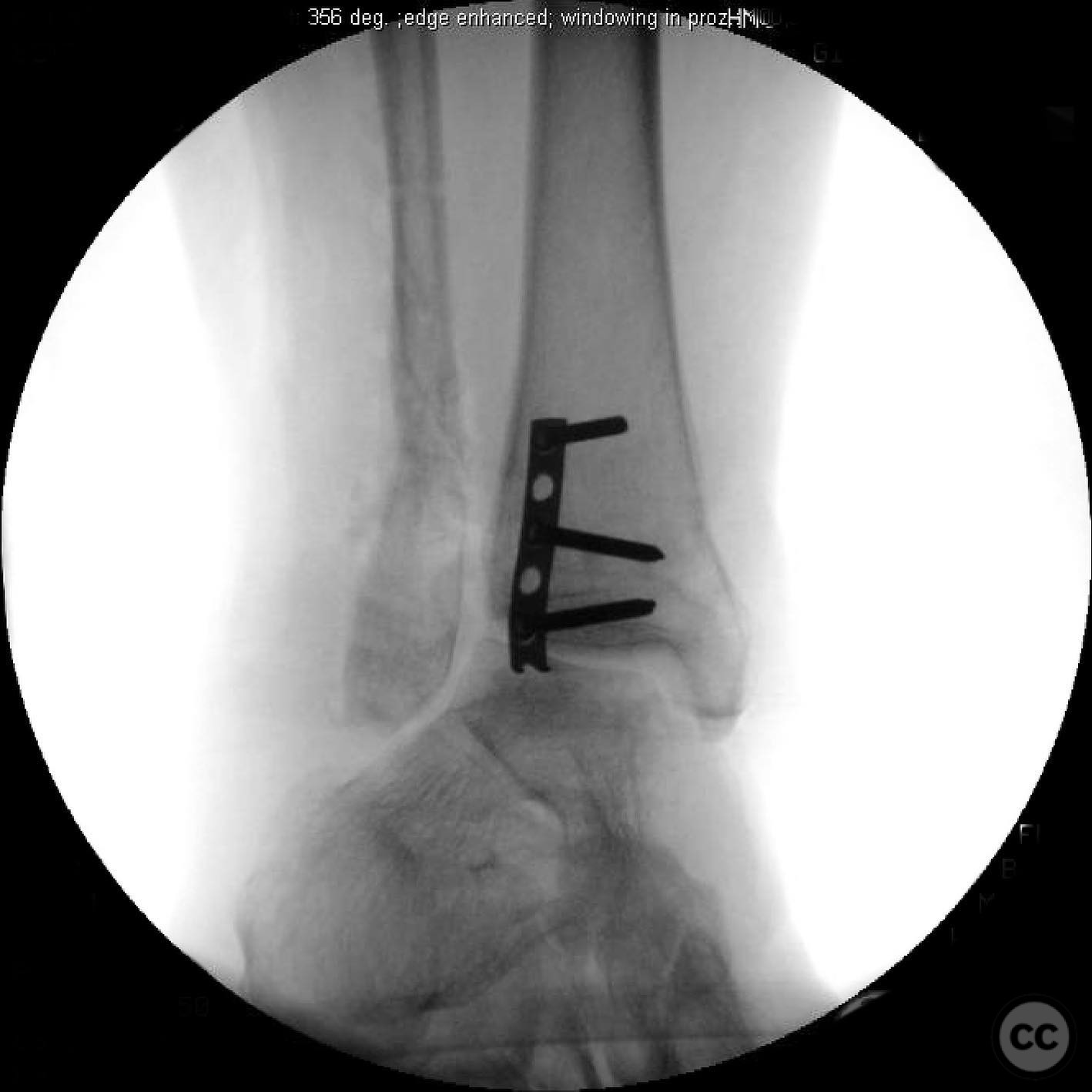
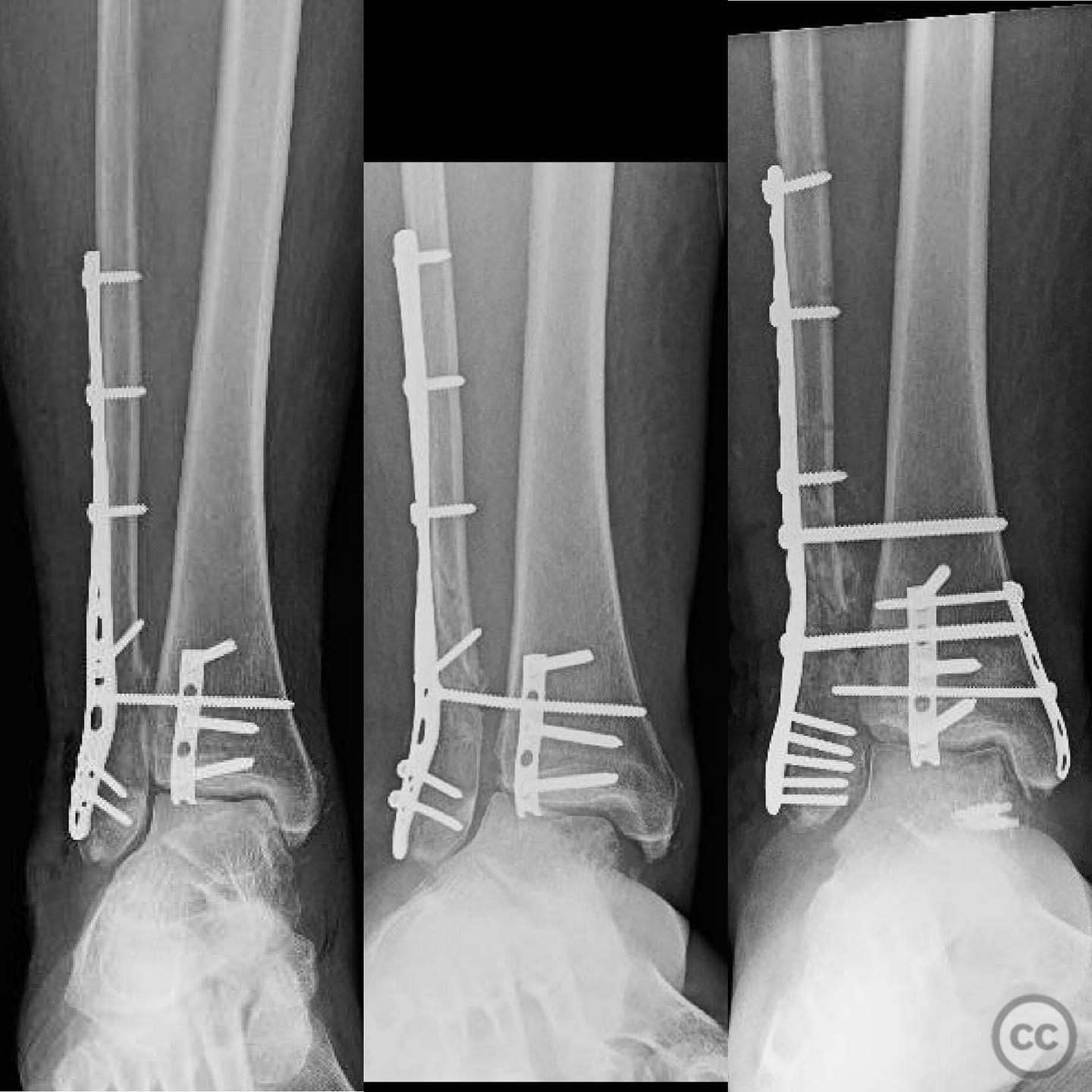
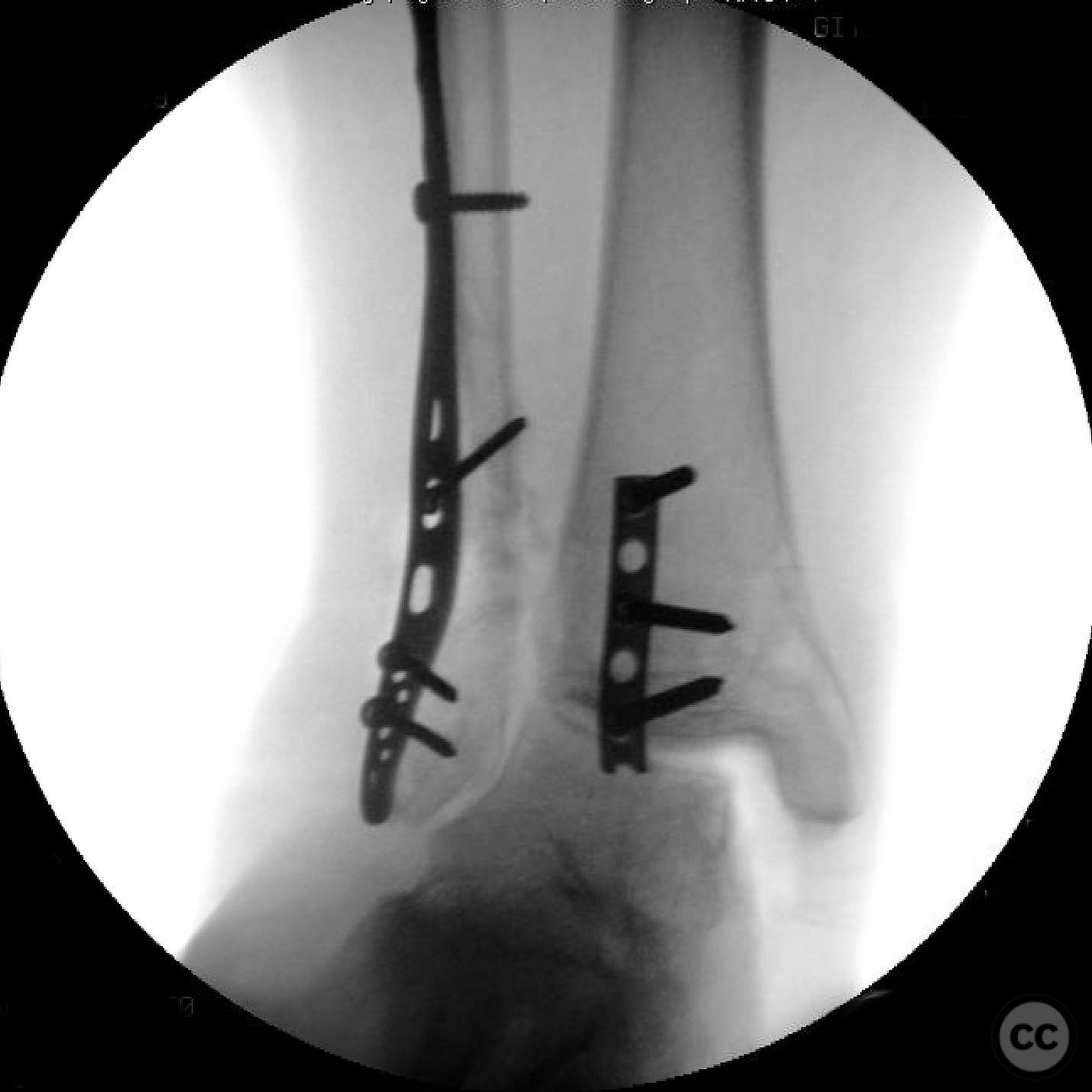
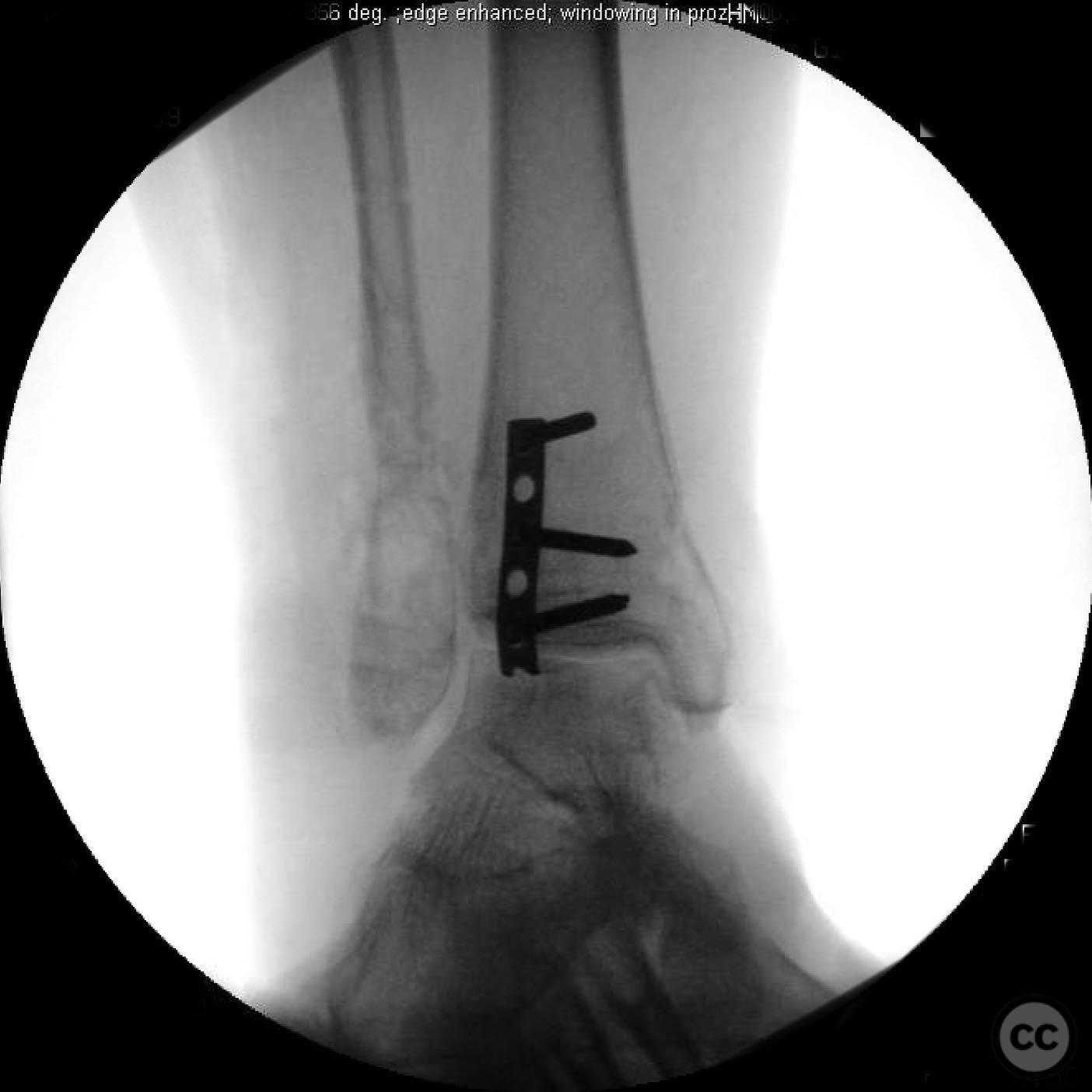
Operative remarks:Intraoperatively, a mobile nonunion of the fibula was identified, contributing to valgus loading and failure of initial fixation. The fibula was lengthened to match the contralateral side and stabilized with locking plate fixation. Deltoid ligament reconstruction and syndesmotic stabilization were performed using screws and anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL) repair. Autologous distal tibial bone grafting combined with osteogenic synthetic material was used to address the fibular nonunion.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient followed a conservative rehabilitation protocol with non-weight bearing for three months. Early active and passive range of motion exercises were initiated with physical therapy once the wound had healed.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Locking plate for fibular fixation, syndesmotic screws, AITFL repair constructs, distal tibial autograft, osteogenic synthetic material for fibular nonunion.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 174 times
15 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Open Trimalleolar Equivalent Fracture with Medial Wound and Fibular Nonunion.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 34038144 Published Online Jul 15 2025.