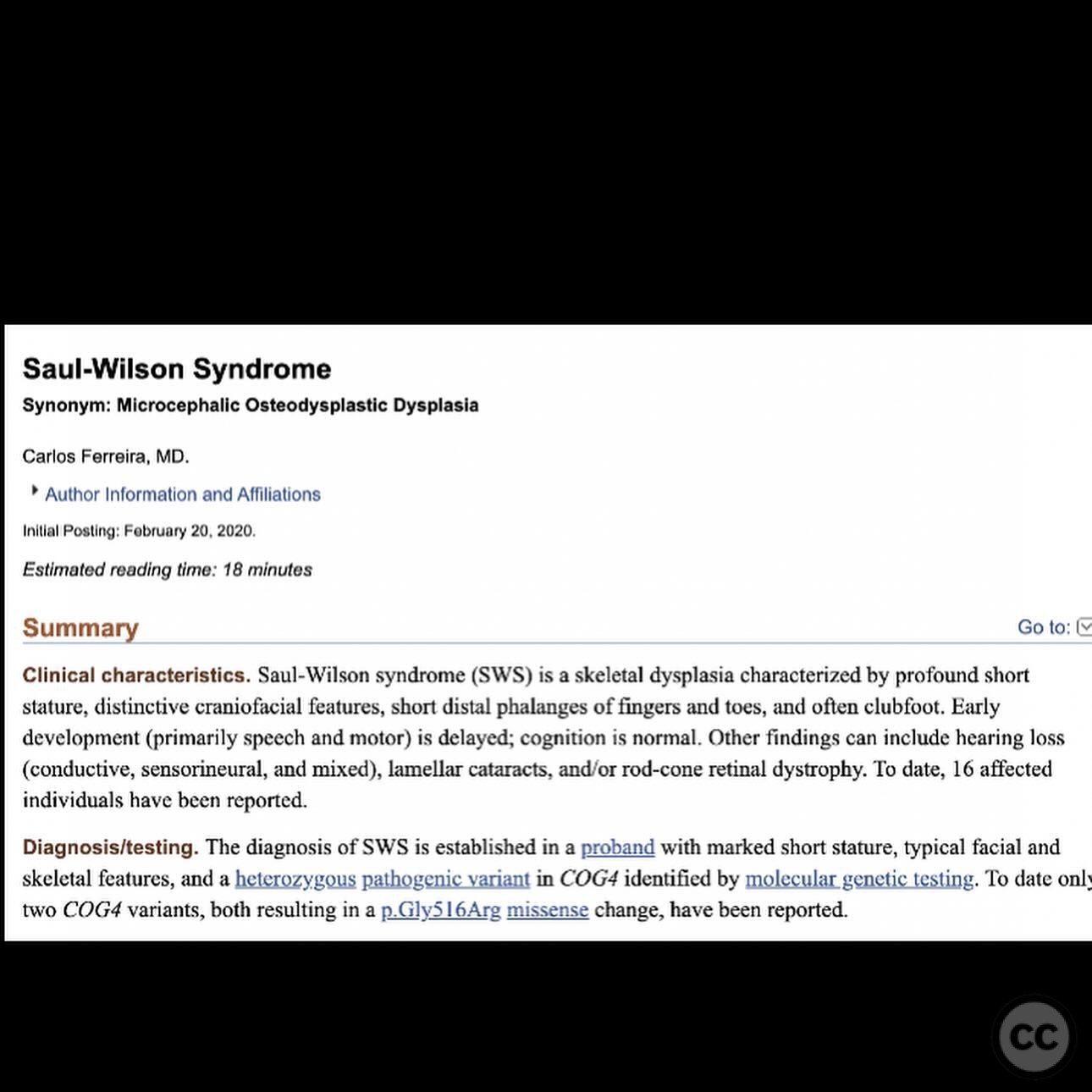
Diaphyseal Femur Fracture in Saul-Wilson Syndrome Managed with Double Plating
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
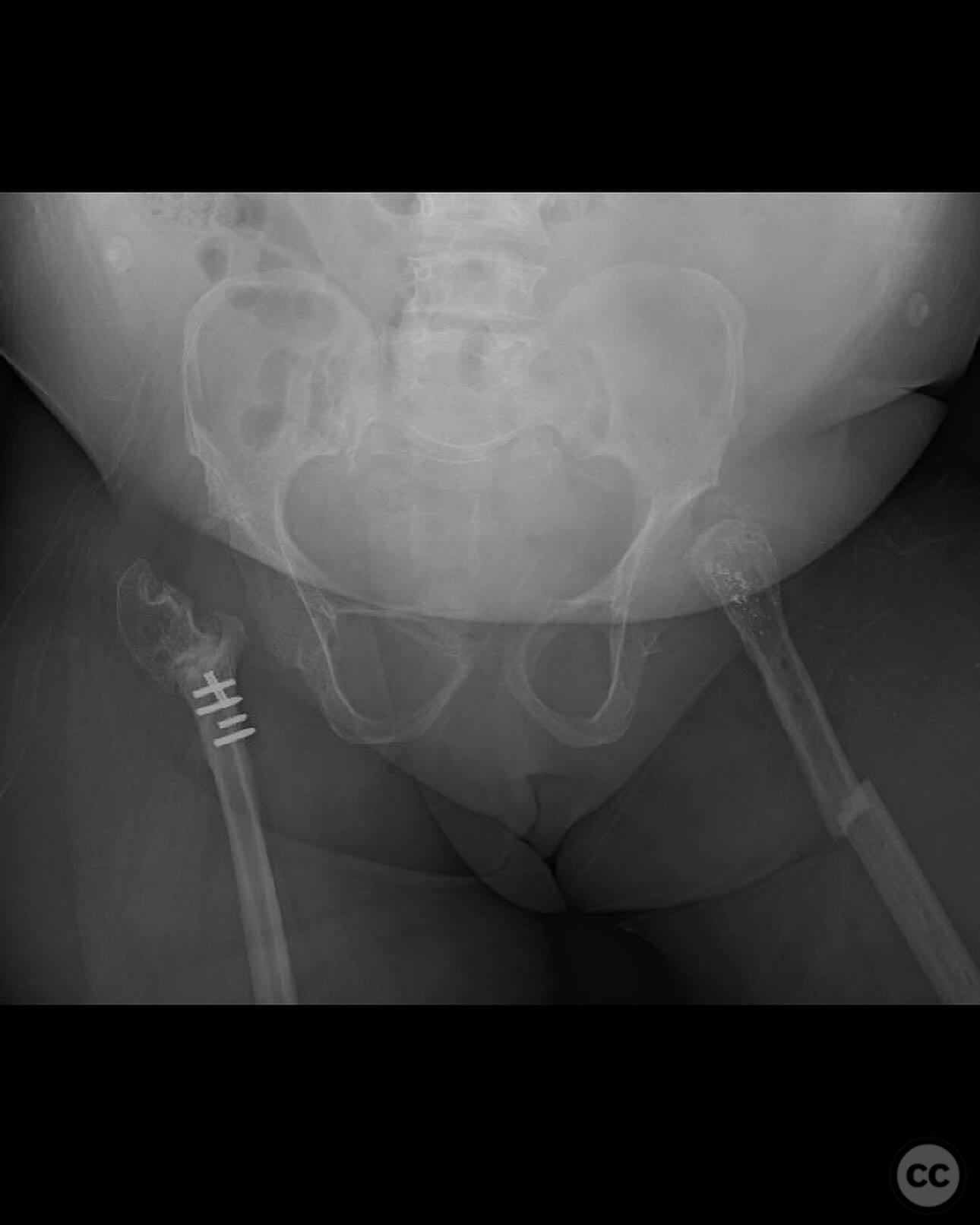
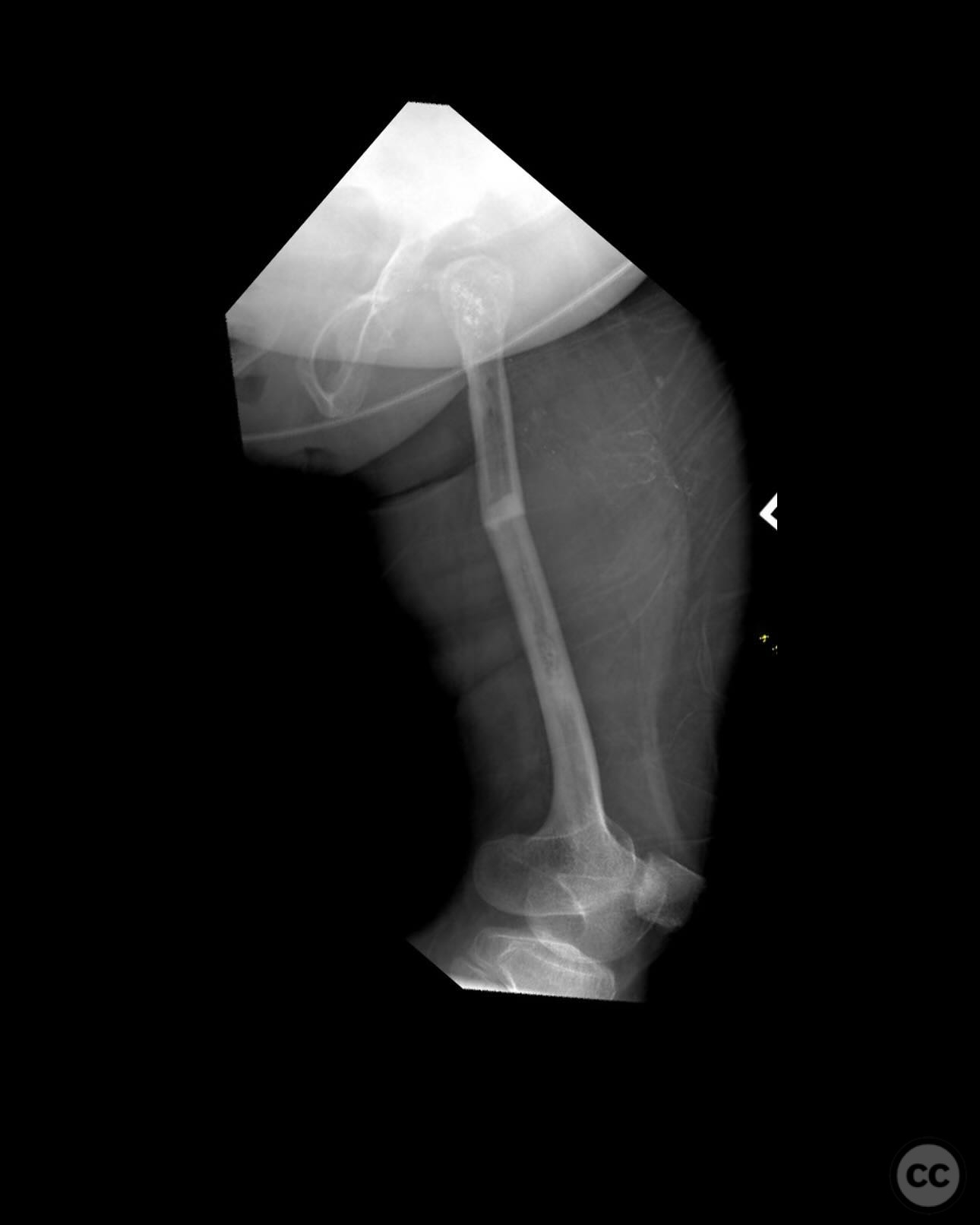
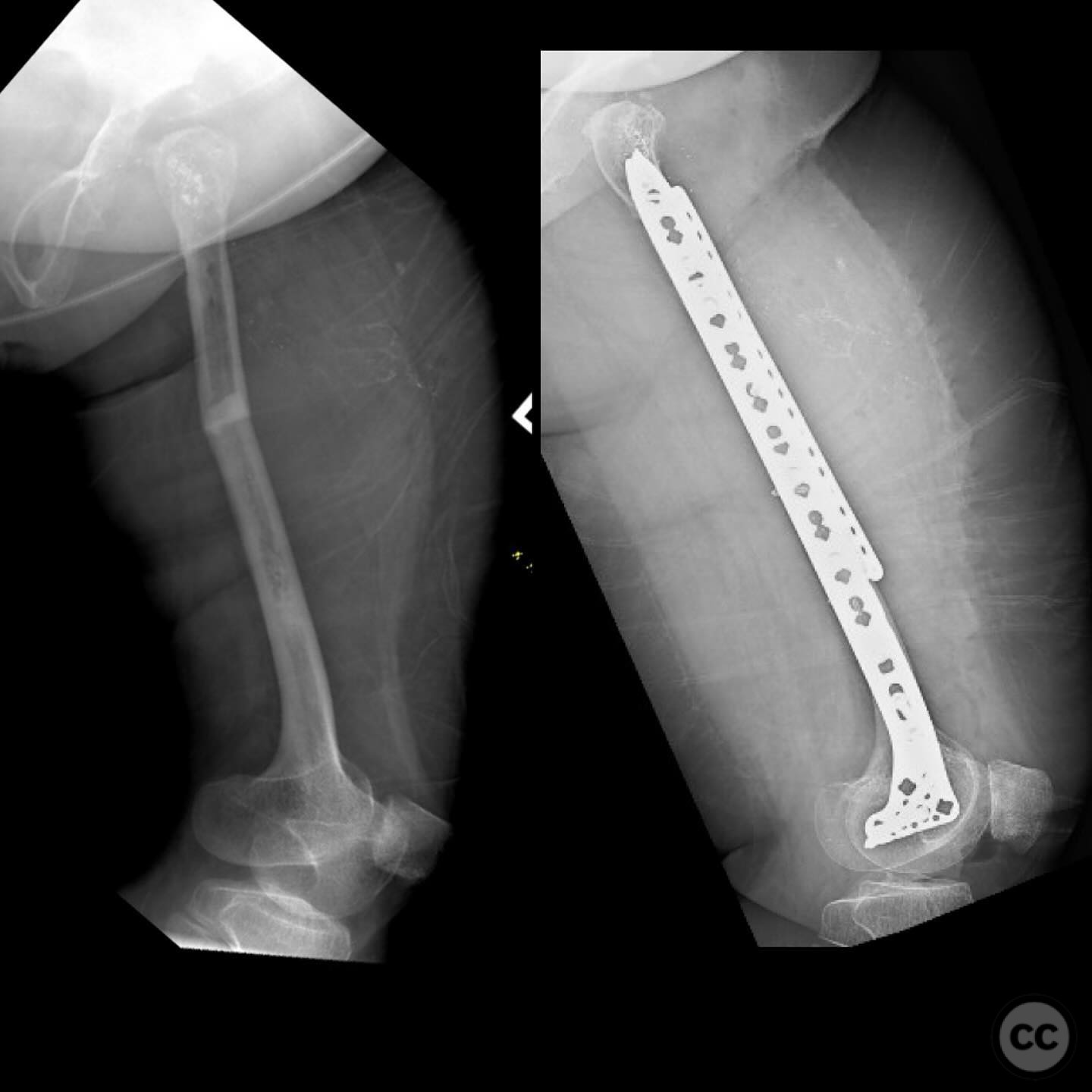
Clinical and radiological findings: A 34-year-old female with Saul-Wilson syndrome presented with a diaphyseal femur fracture following a fall. The patient, who is 3.5 feet tall and weighs 90 pounds, was fully ambulatory within the community without assistive devices prior to the injury. Radiological evaluation revealed a simple diaphyseal fracture with a narrow medullary canal measuring approximately 2.5-3mm at the isthmus, and obliteration distal to the fracture site.
Preoperative Plan
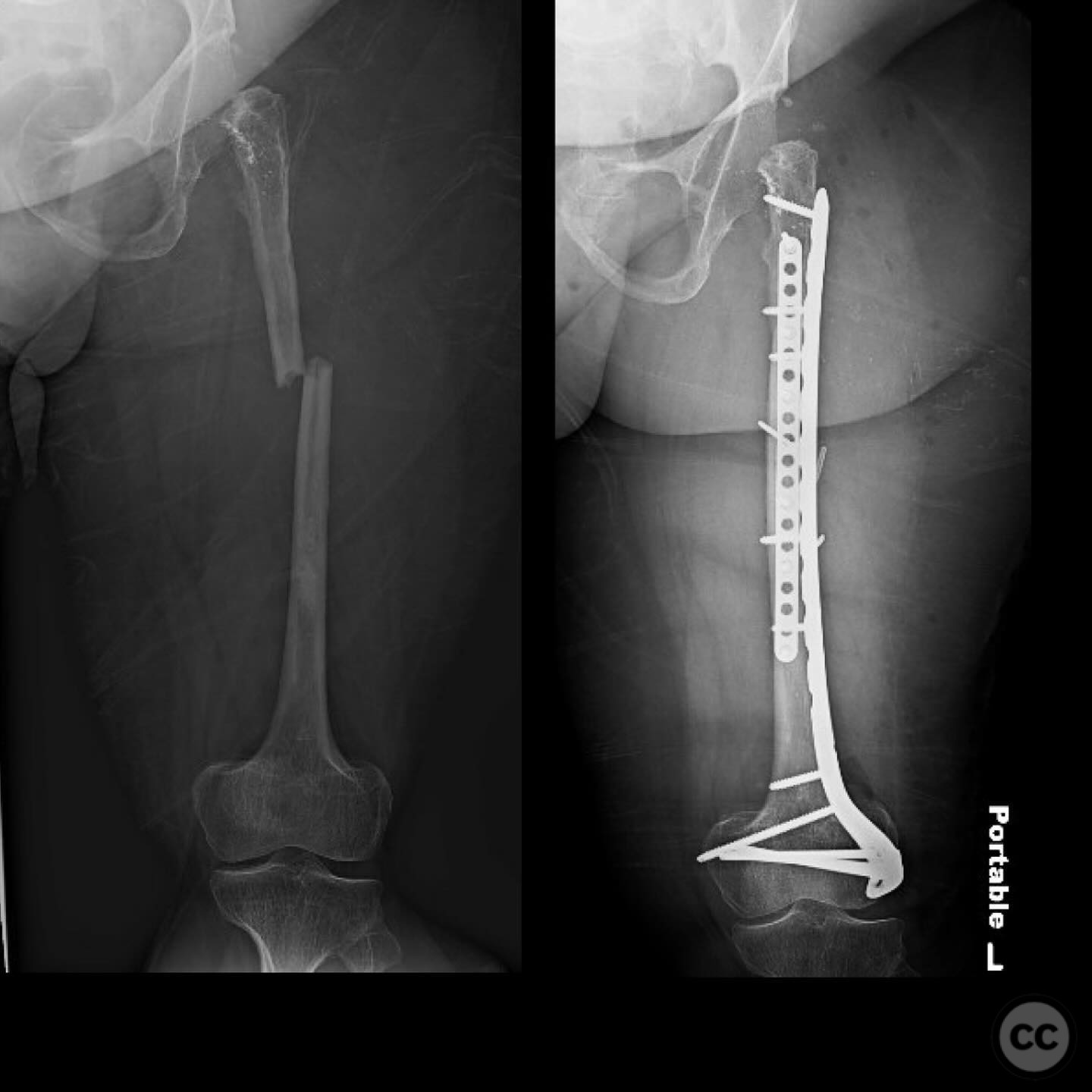
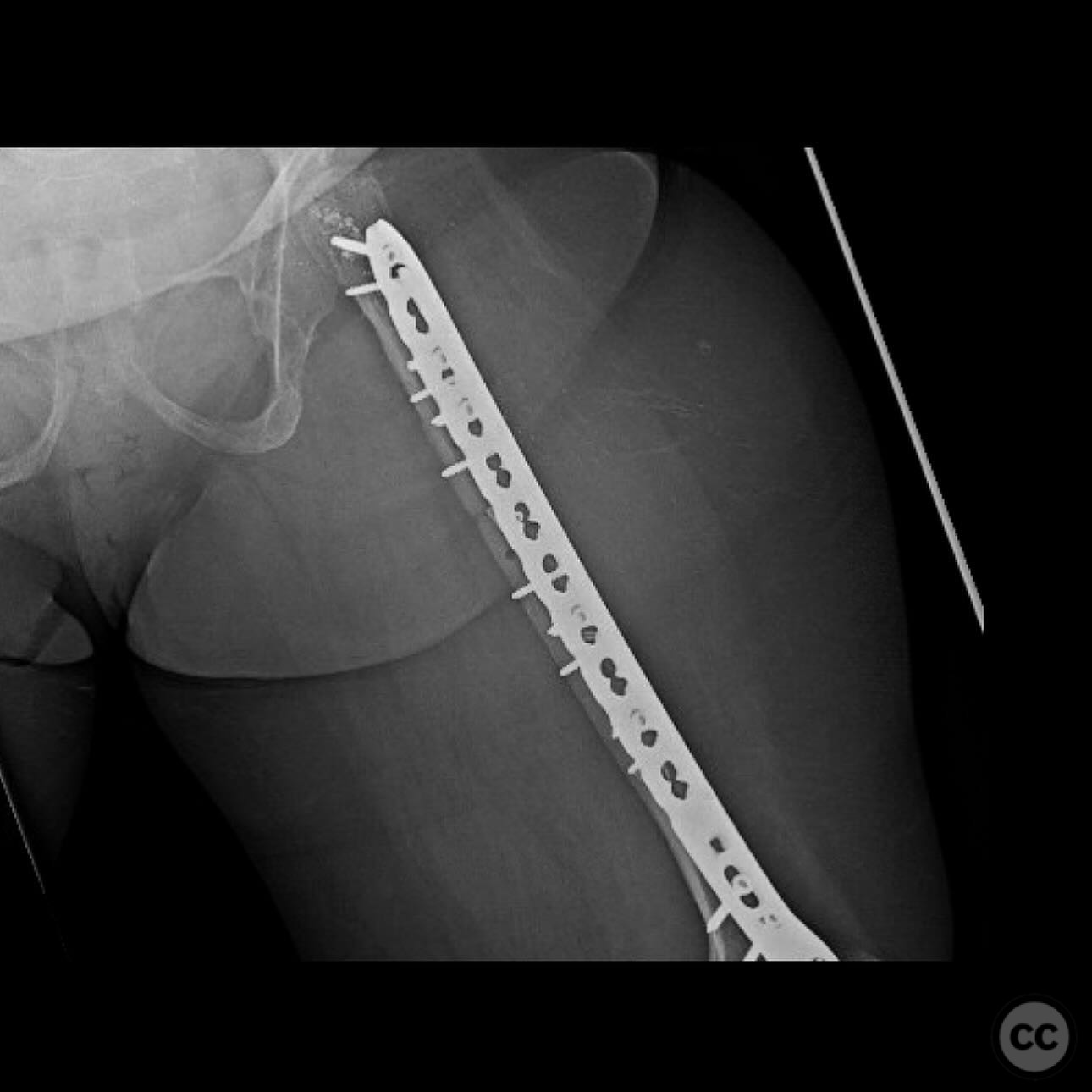
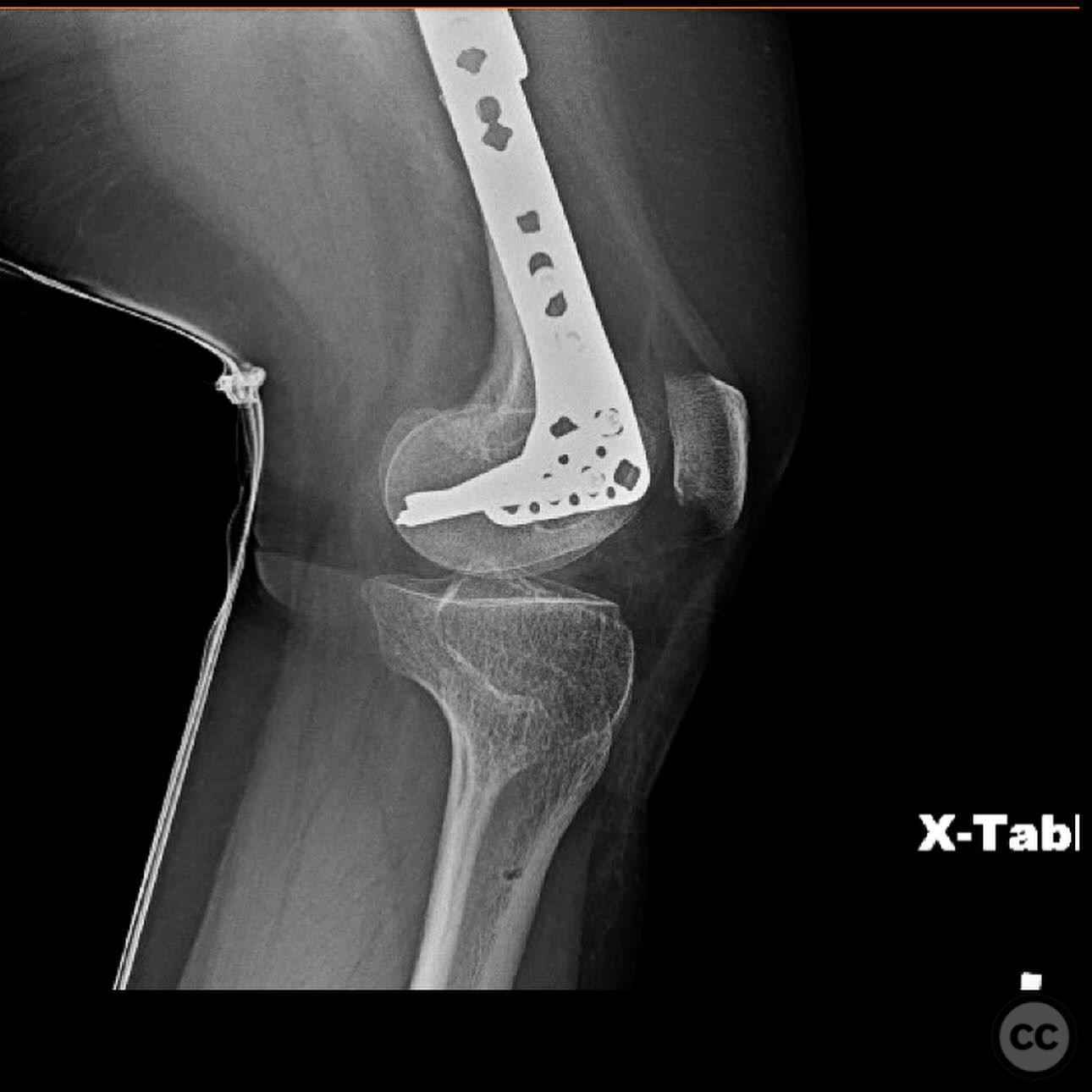
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a double plating technique due to the narrow and obliterated medullary canal, which precluded the use of intramedullary nailing. An anterior approach was planned for the application of a 2.7mm strength plate, and a lateral approach for the application of an upside-down 3.5mm tibial plateau plate.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine positioning on a radiolucent table was utilized to facilitate anterior and lateral access to the femur.
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal incision was made along the anterior aspect of the femur for the placement of the 2.7mm strength plate. A separate lateral incision was made for the application of the upside-down 3.5mm tibial plateau plate. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the diaphysis, allowing for accurate plate placement and fixation.
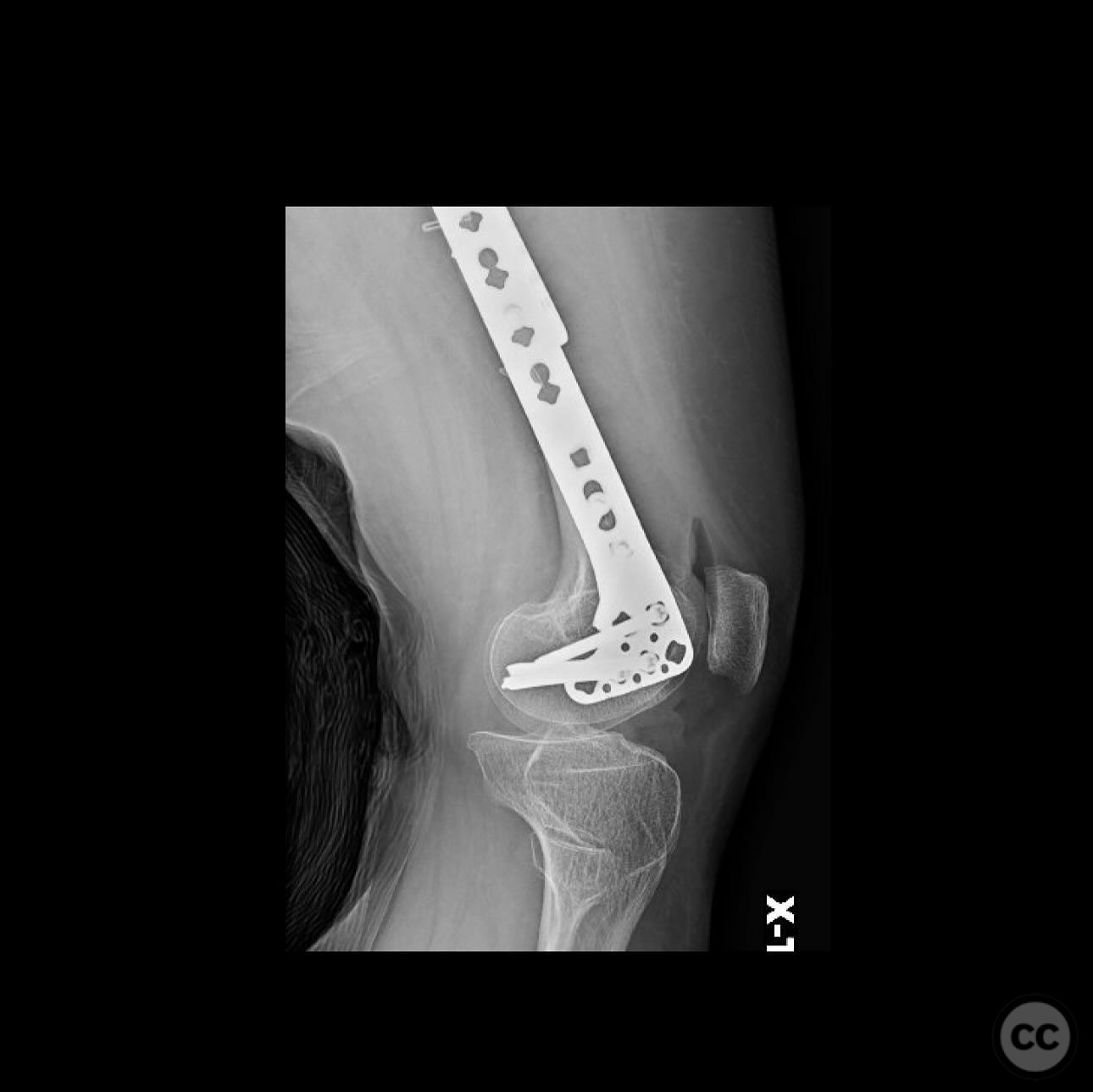
Operative remarks:The use of double plating was chosen due to the mechanical soundness and ability to protect against future fractures without compromising the thin cortex by reaming. The upside-down tibial plateau plate provided adequate support and has been effective in similar cases involving skeletal dysplasia.
Postoperative protocol: The postoperative rehabilitation protocol included protected weight-bearing as tolerated with gradual progression to full weight-bearing over several weeks, focusing on maintaining range of motion and strength.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: 2.7mm strength plate, 3.5mm upside-down tibial plateau plate
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 181 times
08 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Diaphyseal Femur Fracture in Saul-Wilson Syndrome Managed with Double Plating. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 33741501 Published Online Jul 08 2025.