Intramedullary Nailing of a Proximal Humerus Fracture with Large Butterfly Fragment in a Young Adult
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
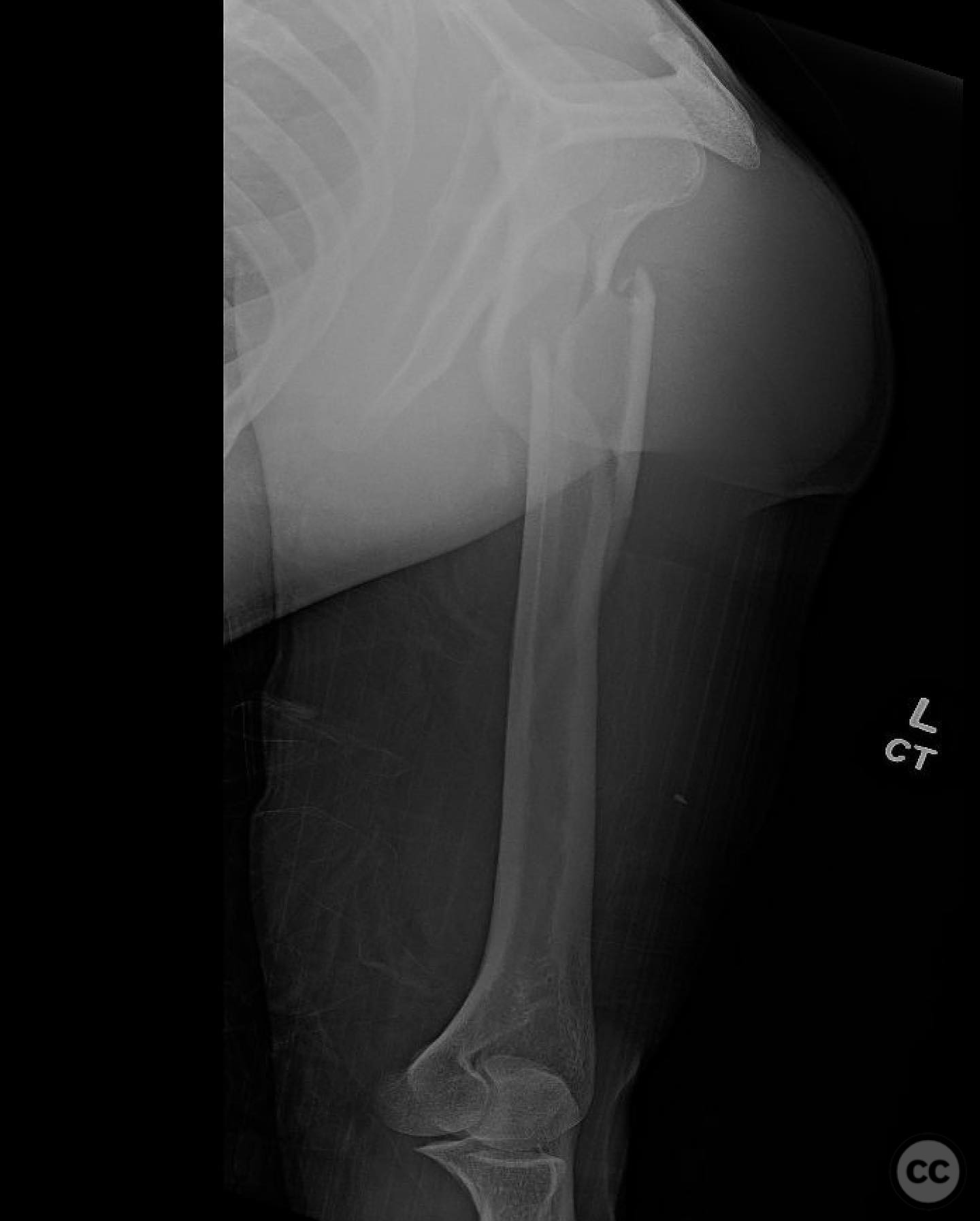
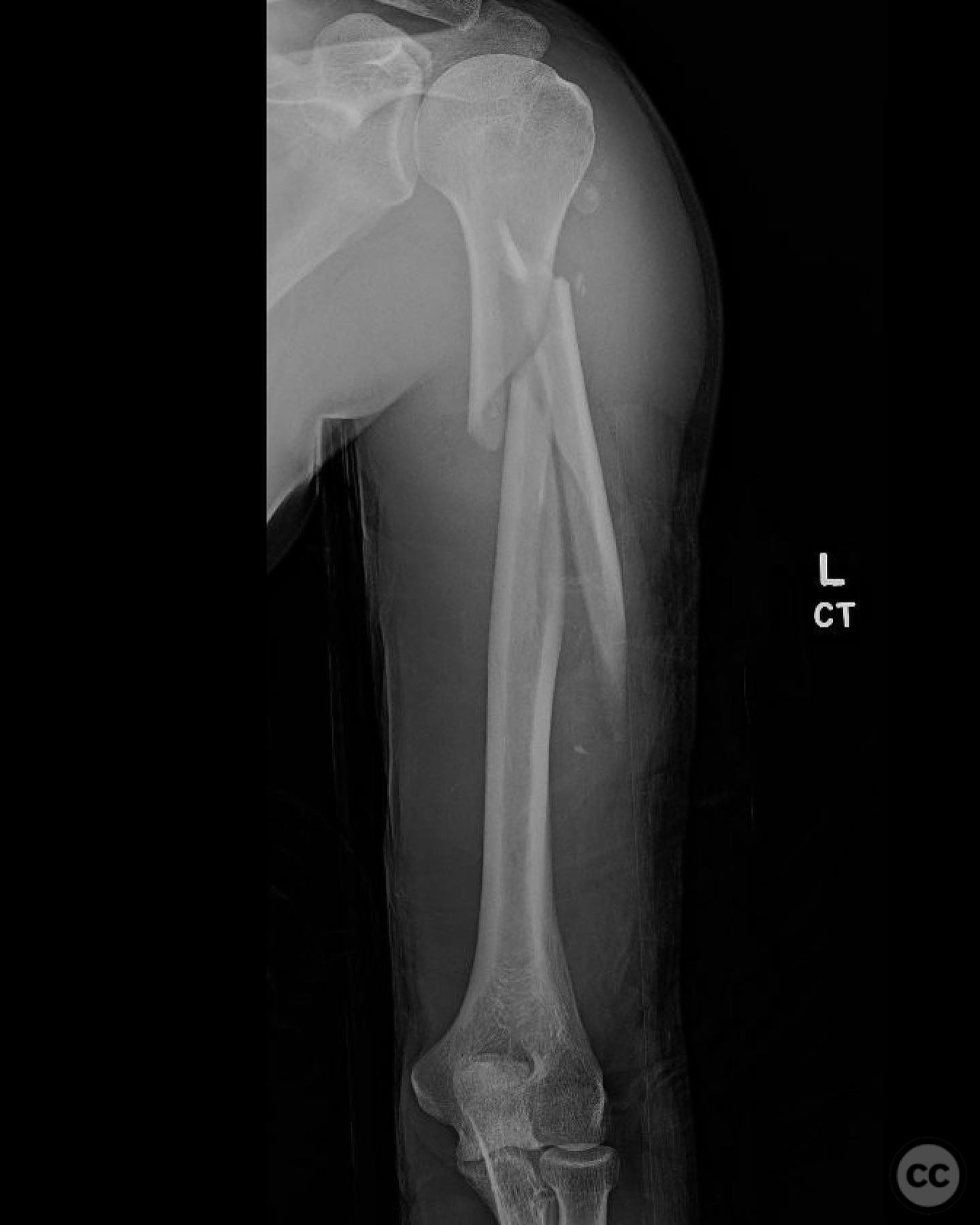
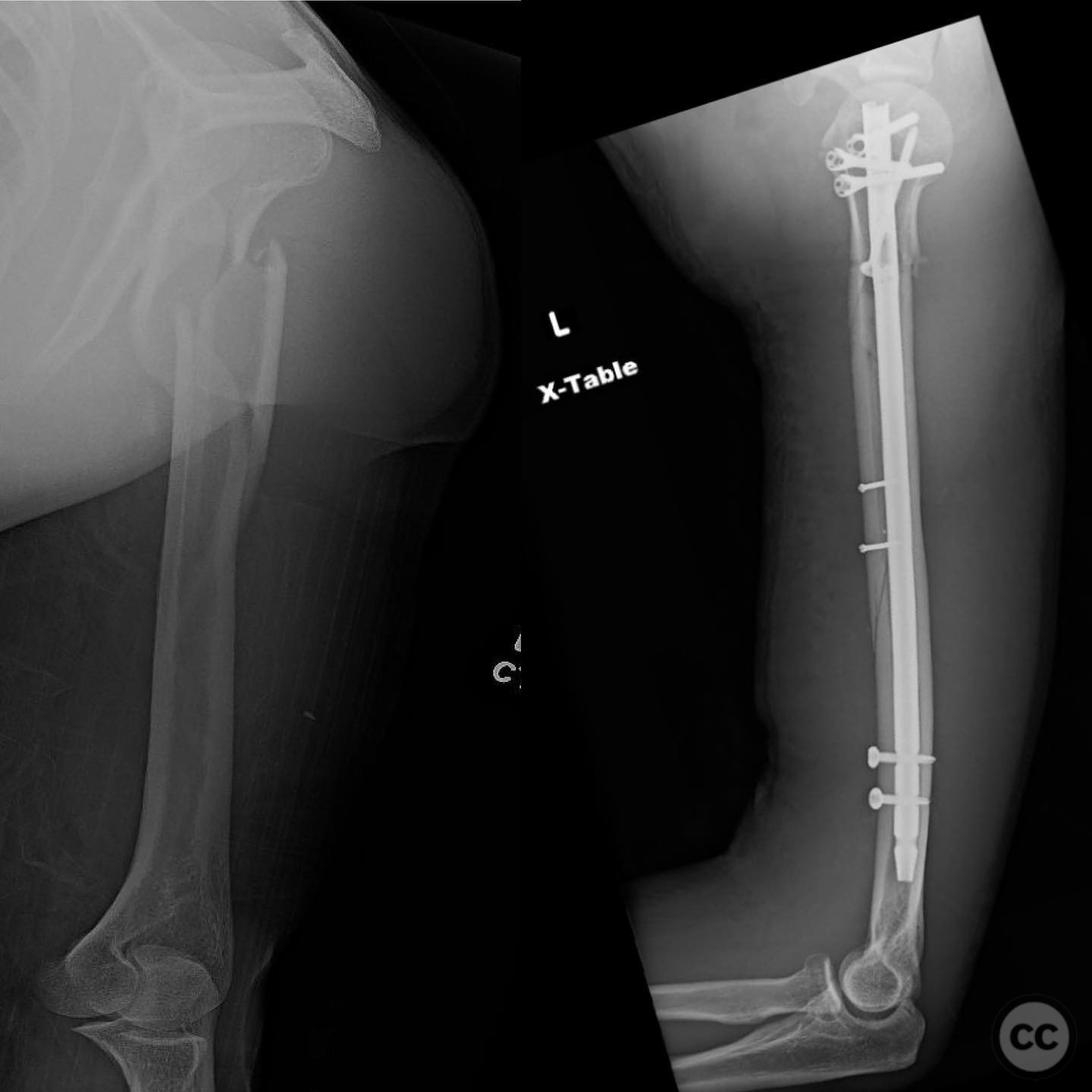
Clinical and radiological findings: A 29-year-old male involved in a high-speed motorcycle collision presented with a closed proximal humerus fracture. The patient had a normal neurovascular examination, and the injury was isolated with no other significant injuries affecting the treatment plan. Radiological assessment revealed a simple fracture pattern with a large butterfly fragment.
Preoperative Plan
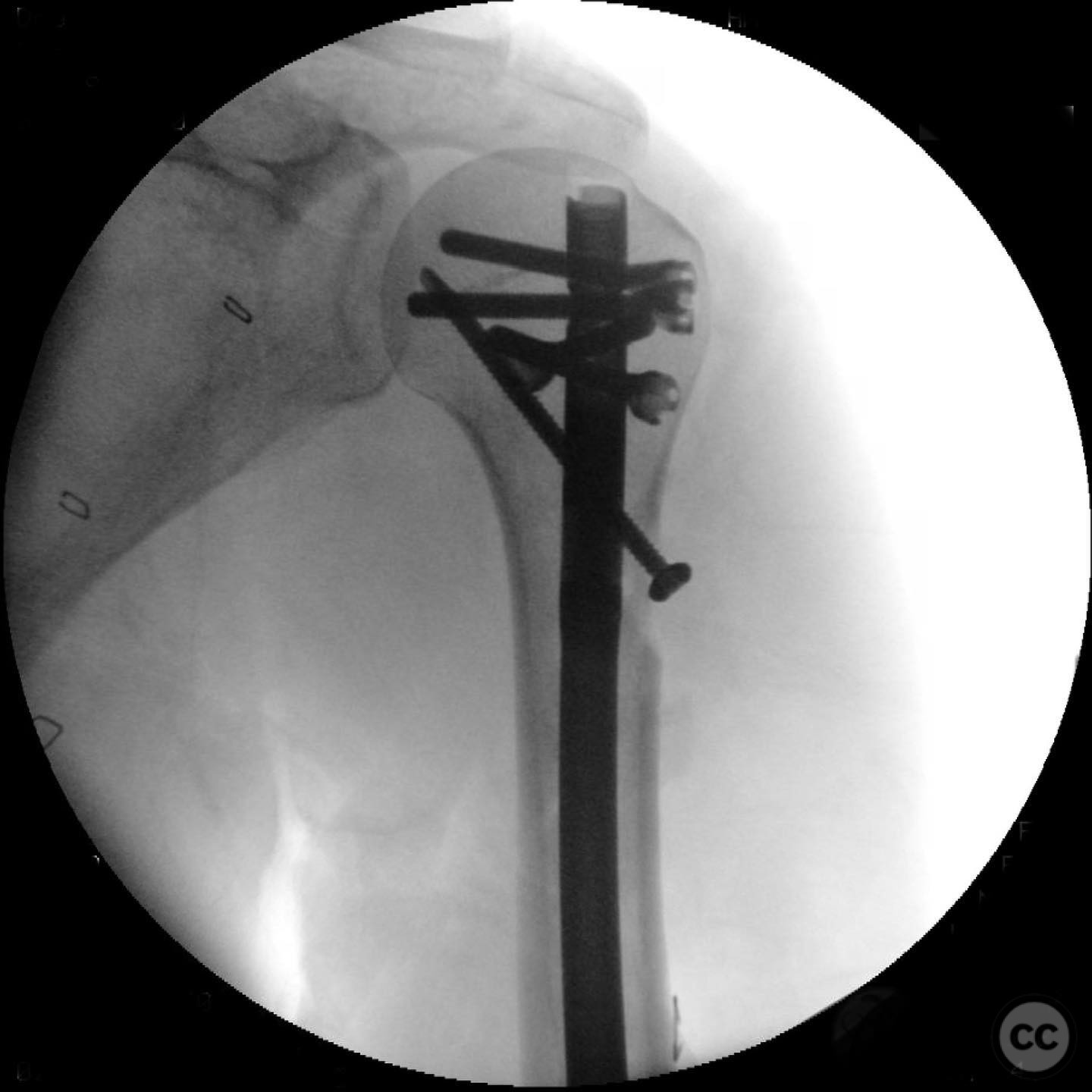
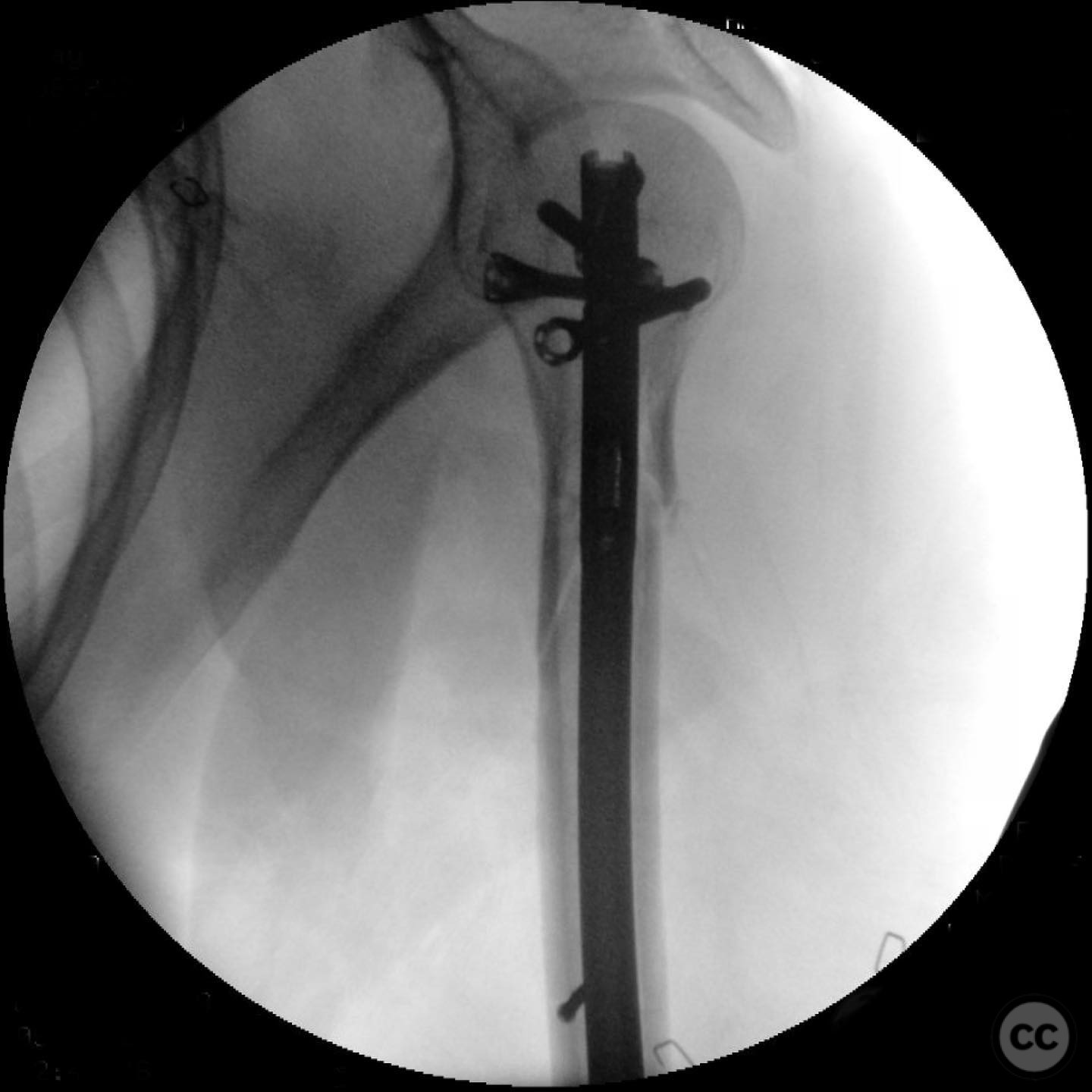
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved intramedullary nailing due to the fracture's long pattern and the presence of a large butterfly fragment. A limited anterolateral approach was chosen for direct reduction and clamping of the fracture fragments. The plan included the use of interfragmentary screws to maintain reduction during nailing.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with the affected arm draped free to allow for manipulation and reduction of the fracture.
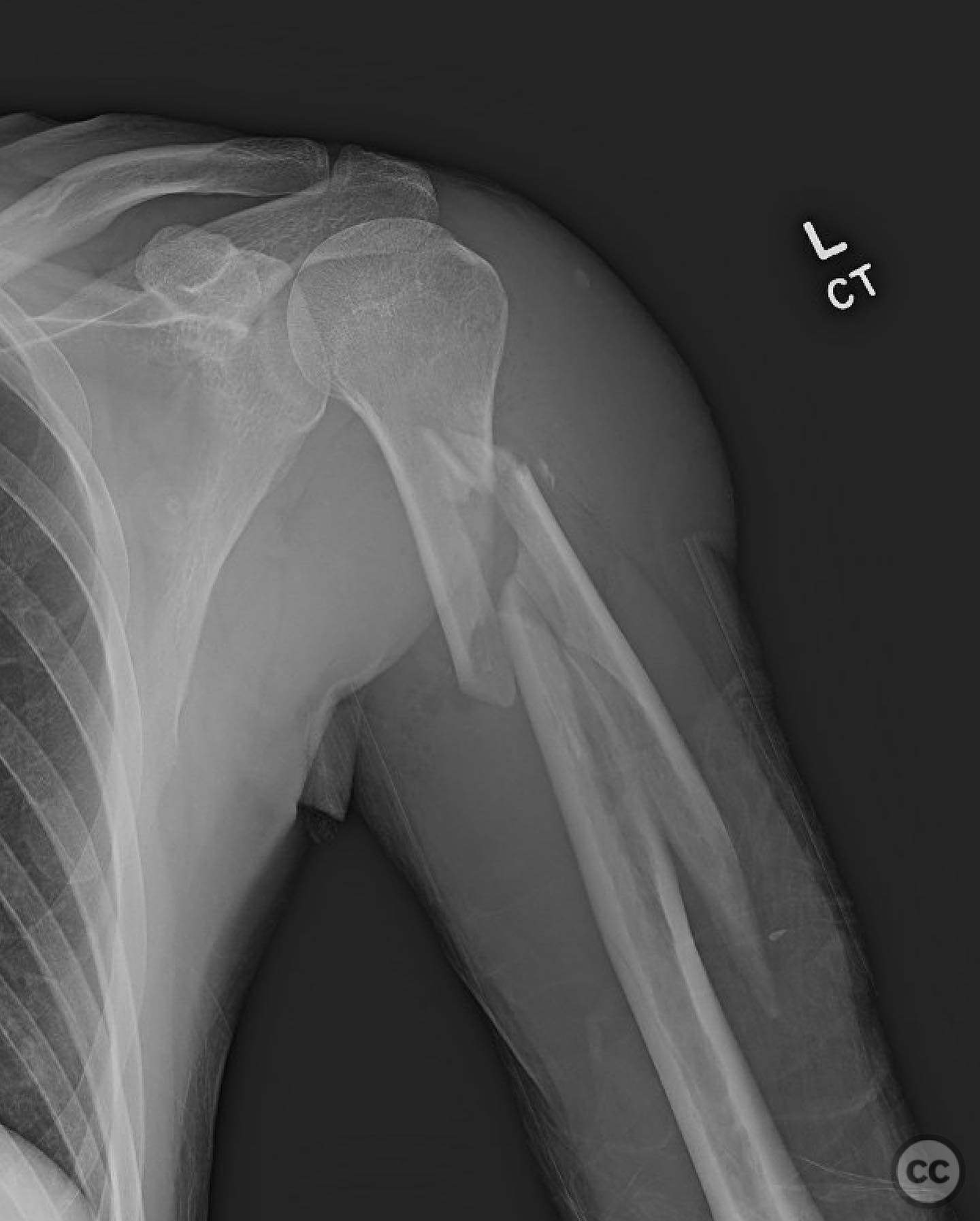
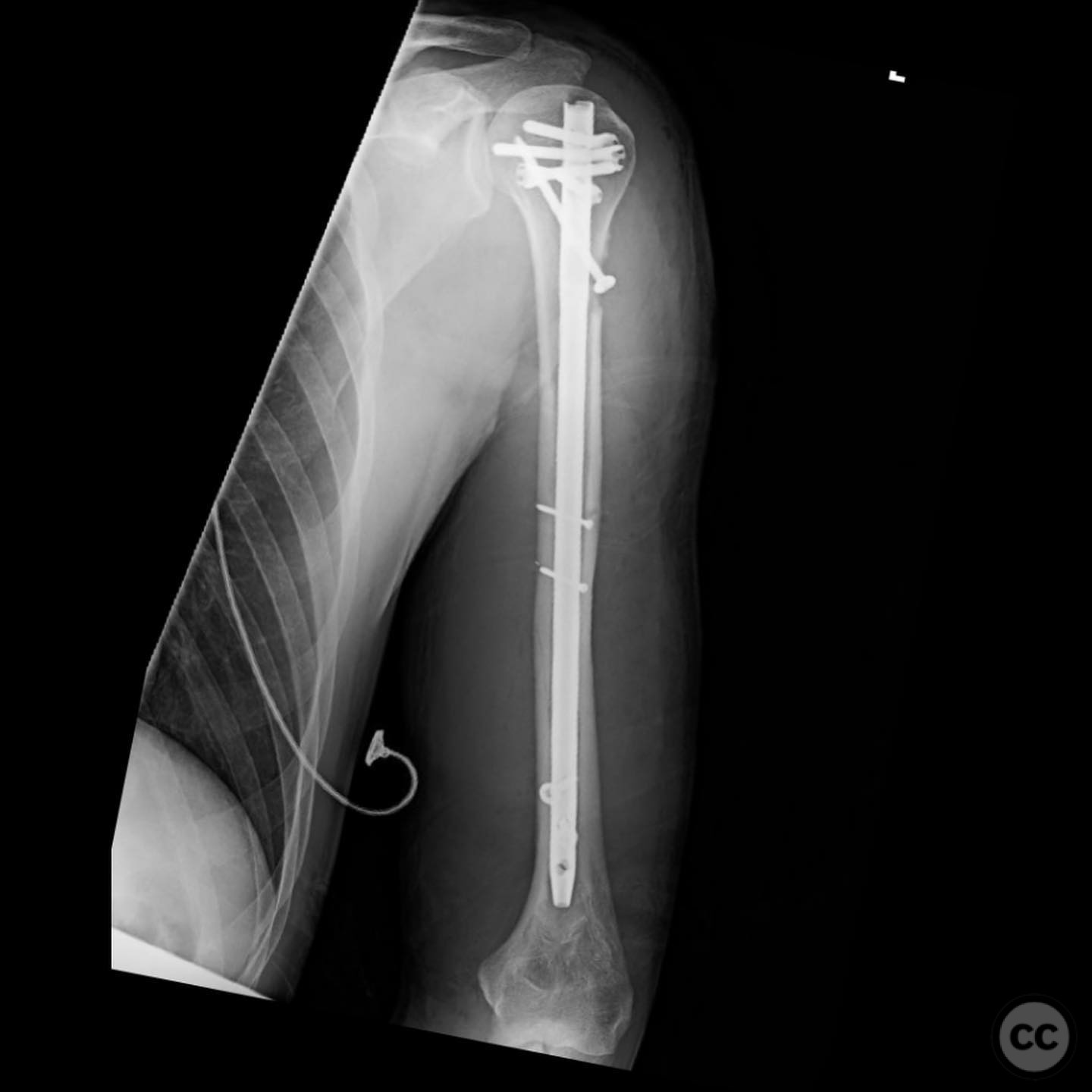
Anatomical surgical approach: A limited anterolateral approach was utilized, involving a careful split of the deltoid muscle to access the fracture site. The rotator cuff was split and protected during the procedure. Direct clamping of the fracture fragments was performed, followed by placement of interfragmentary screws to maintain reduction.
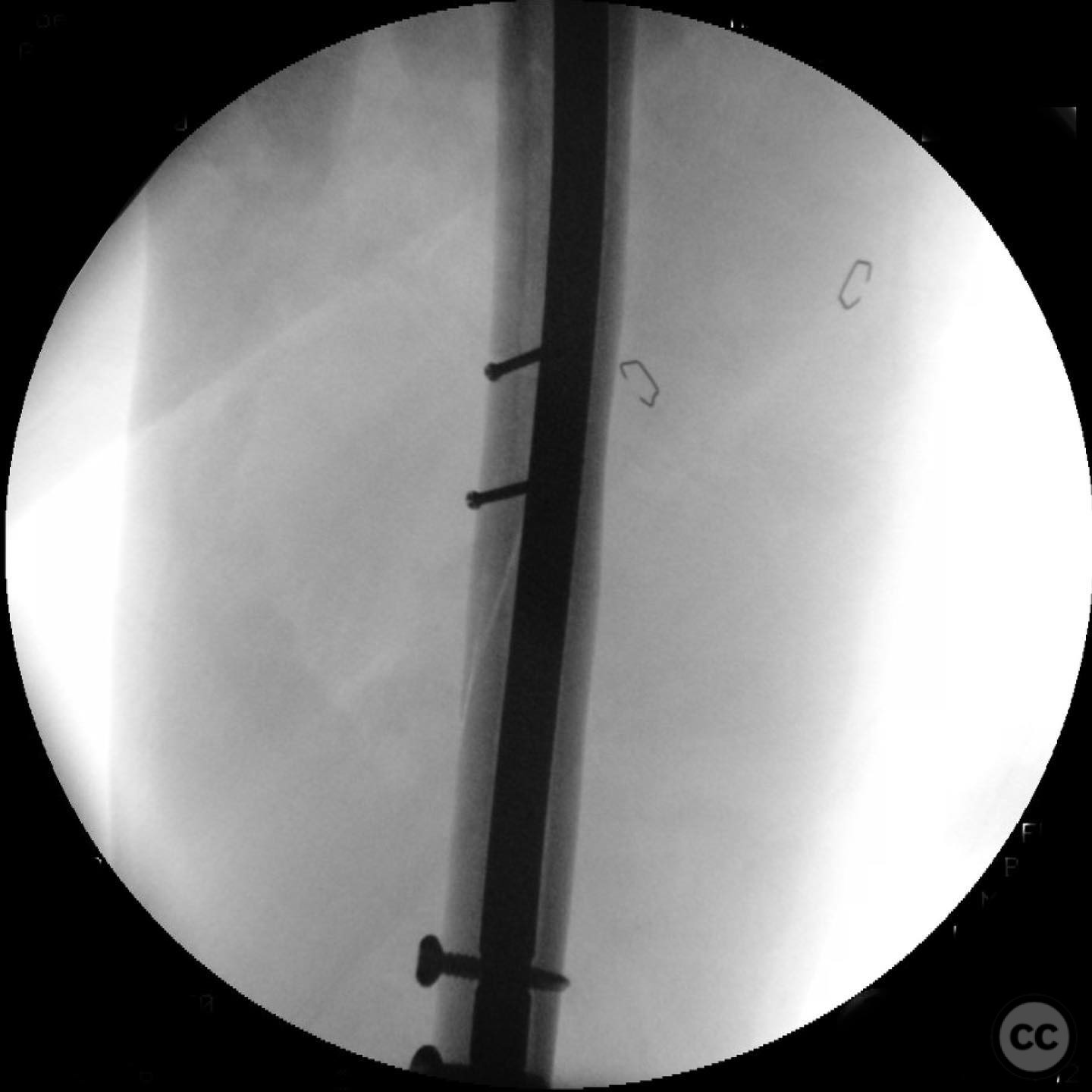
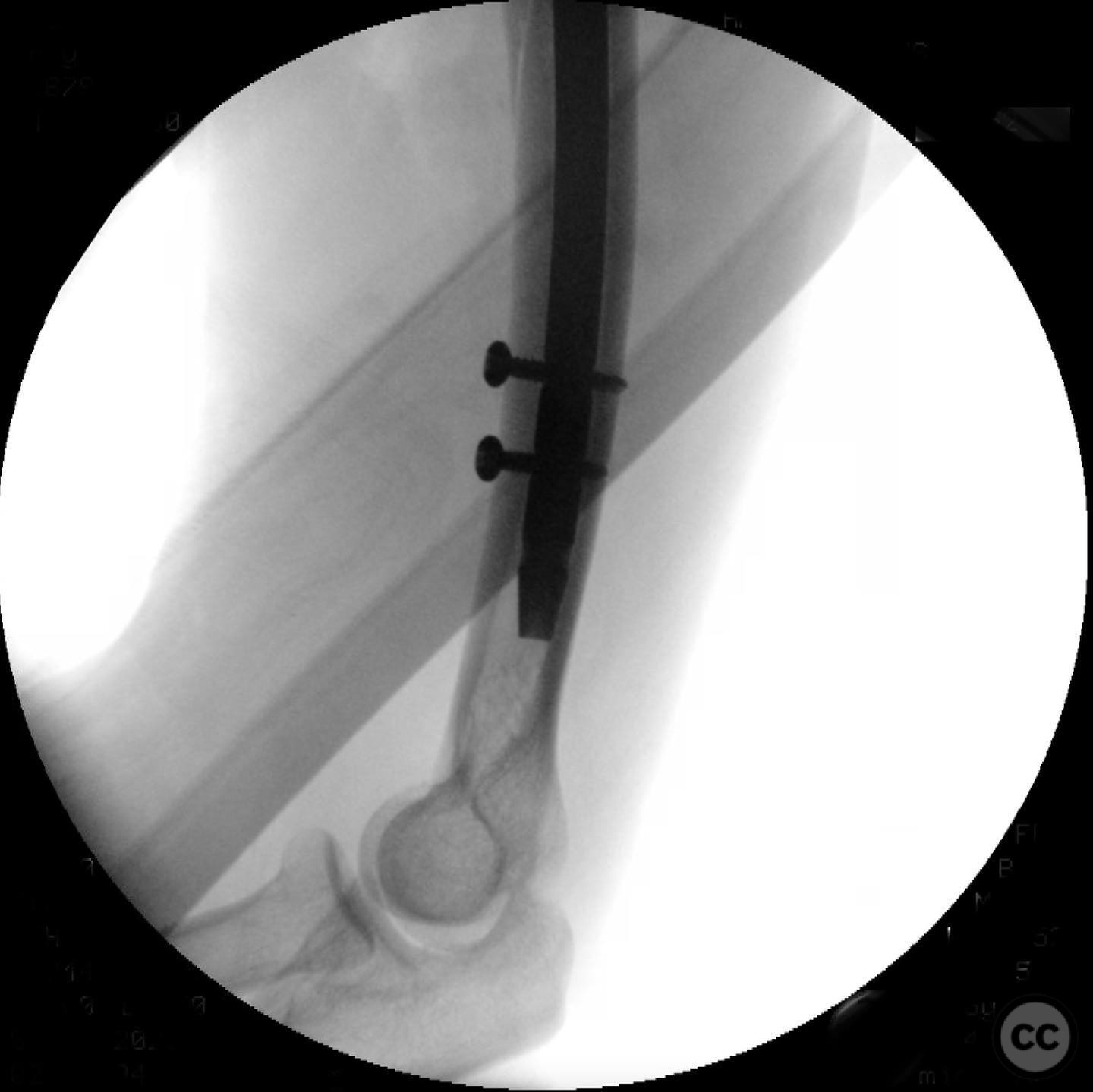
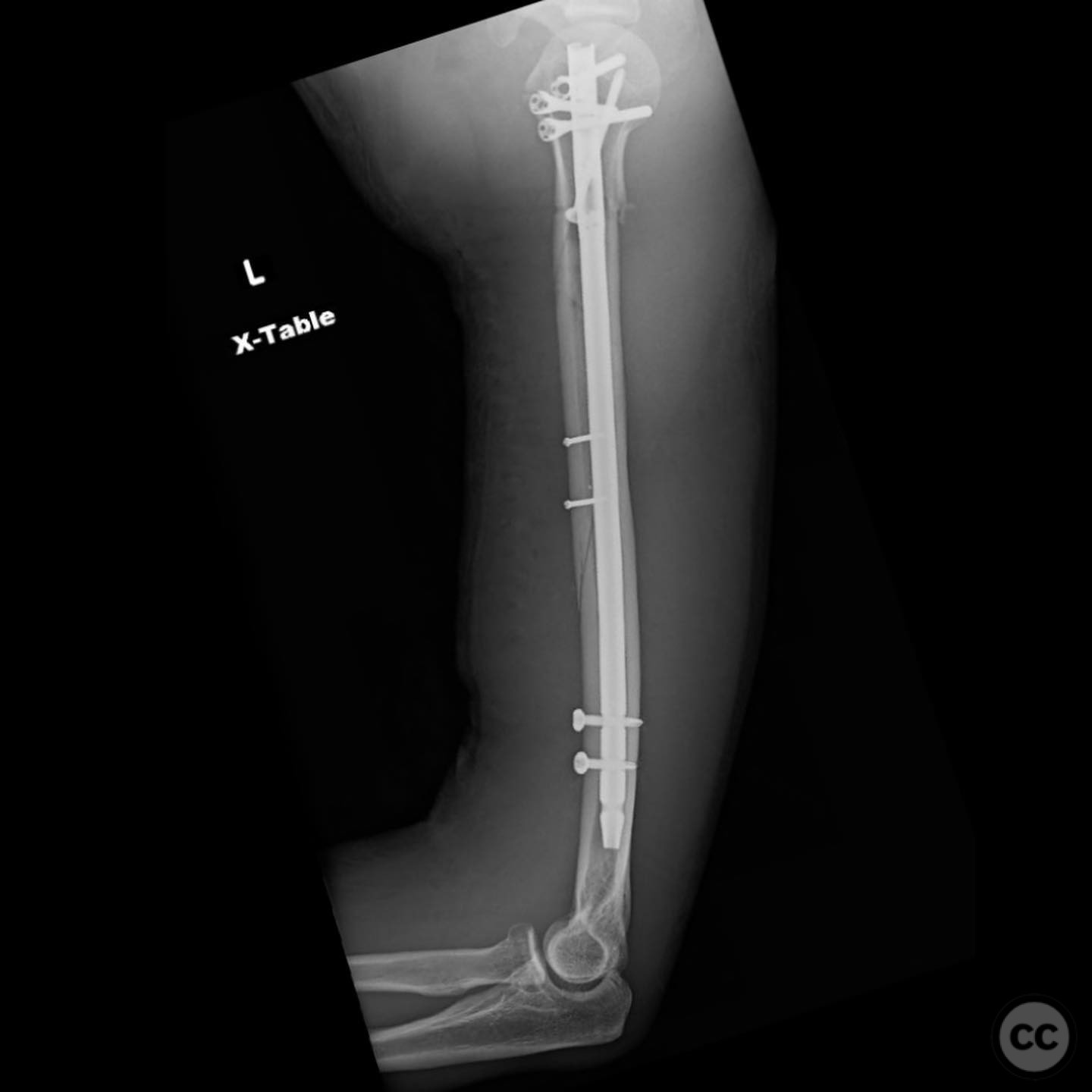
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that using an intramedullary nail minimized exposure, blood loss, and risk to the radial nerve compared to plating. A straight nail was bent using a tabletop bender to match the natural bow of the humerus, addressing potential issues with coronal and sagittal plane alignment and preventing distal humerus fracture. This technique was highlighted as a unique approach by the surgeon.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early mobilization with a focus on regaining range of motion and strength. Weight-bearing restrictions were not specified, but emphasis was placed on a rapid return to function.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail, 2.4 mm interfragmentary screws.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 258 times
11 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Intramedullary Nailing of a Proximal Humerus Fracture with Large Butterfly Fragment in a Young Adult. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 33528501 Published Online Jul 11 2025.