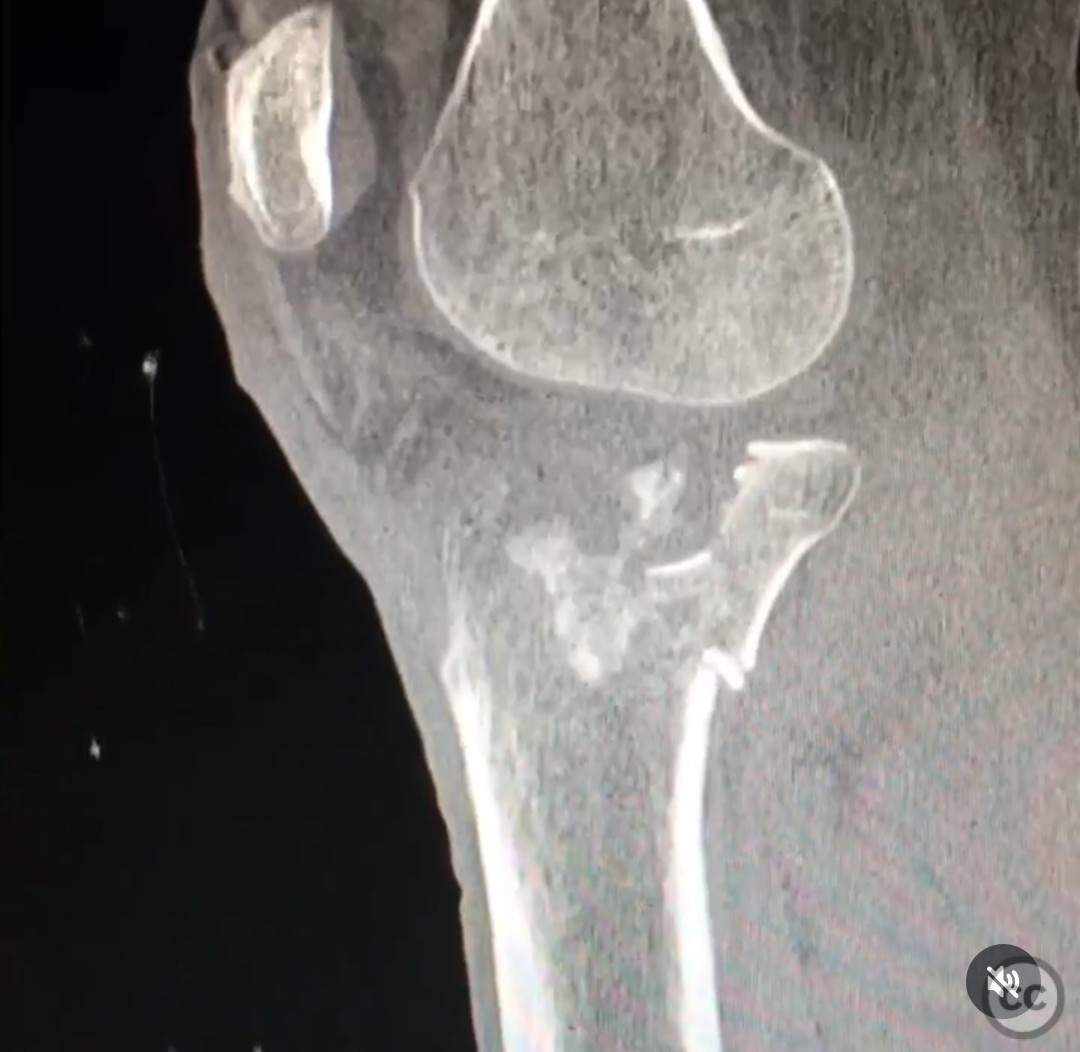
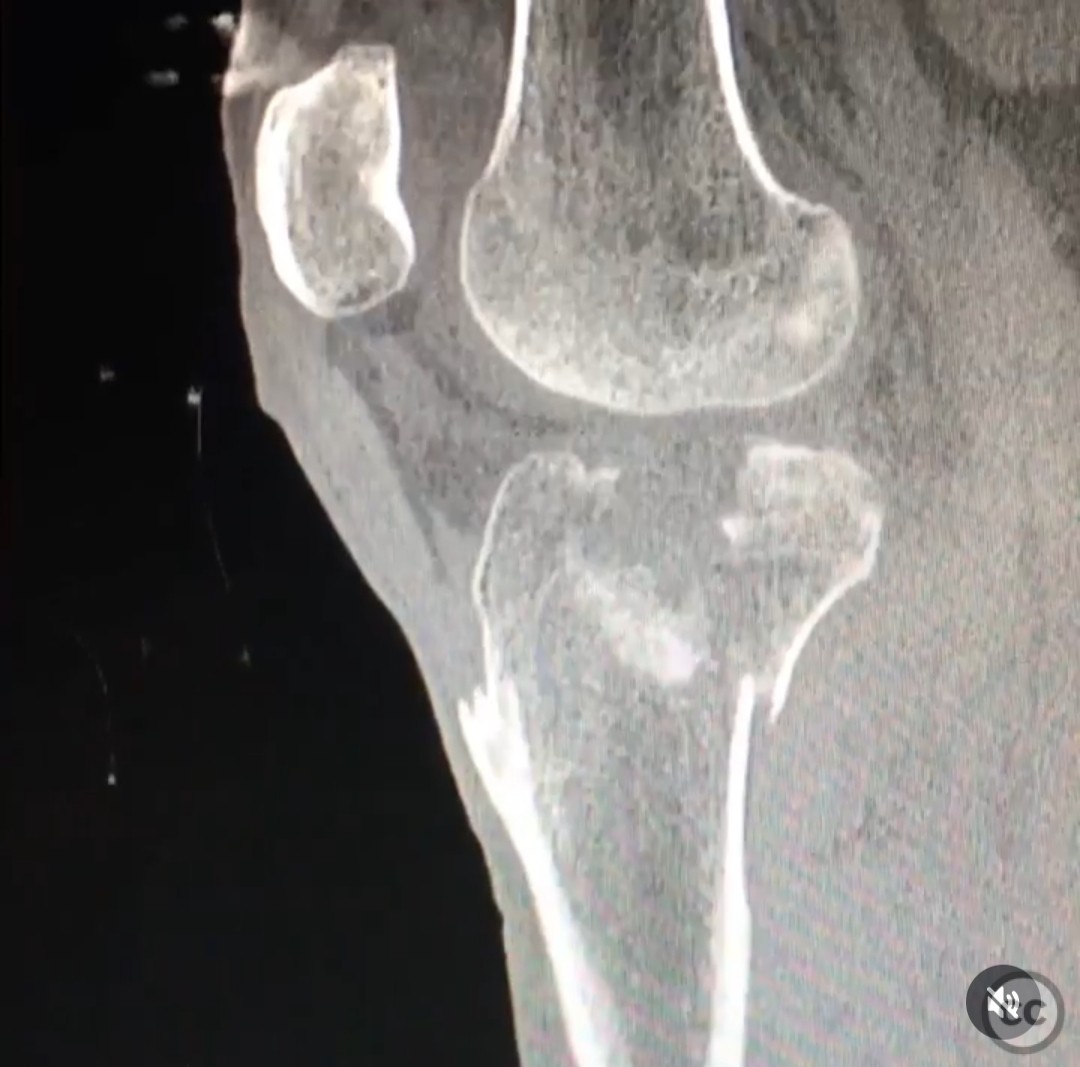
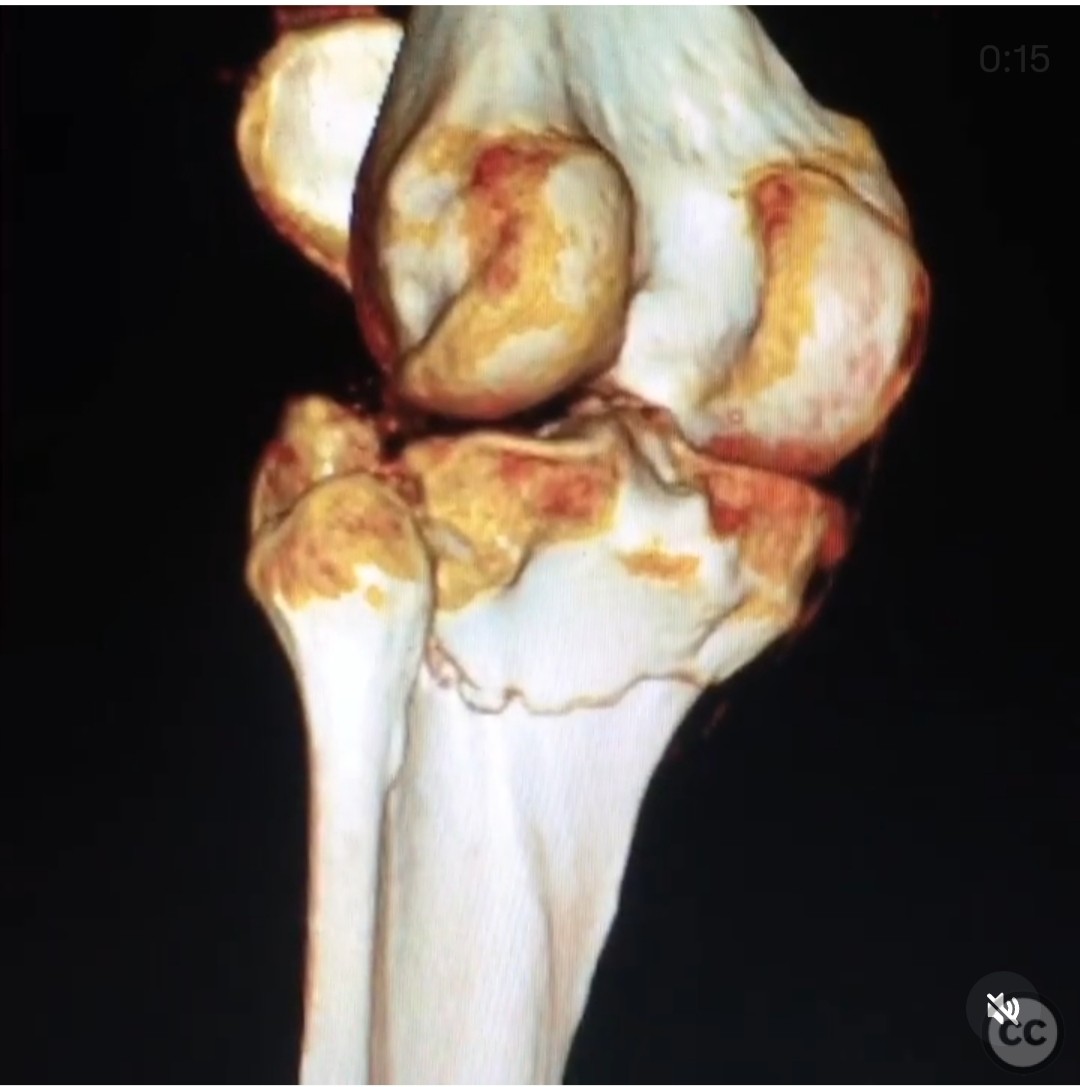
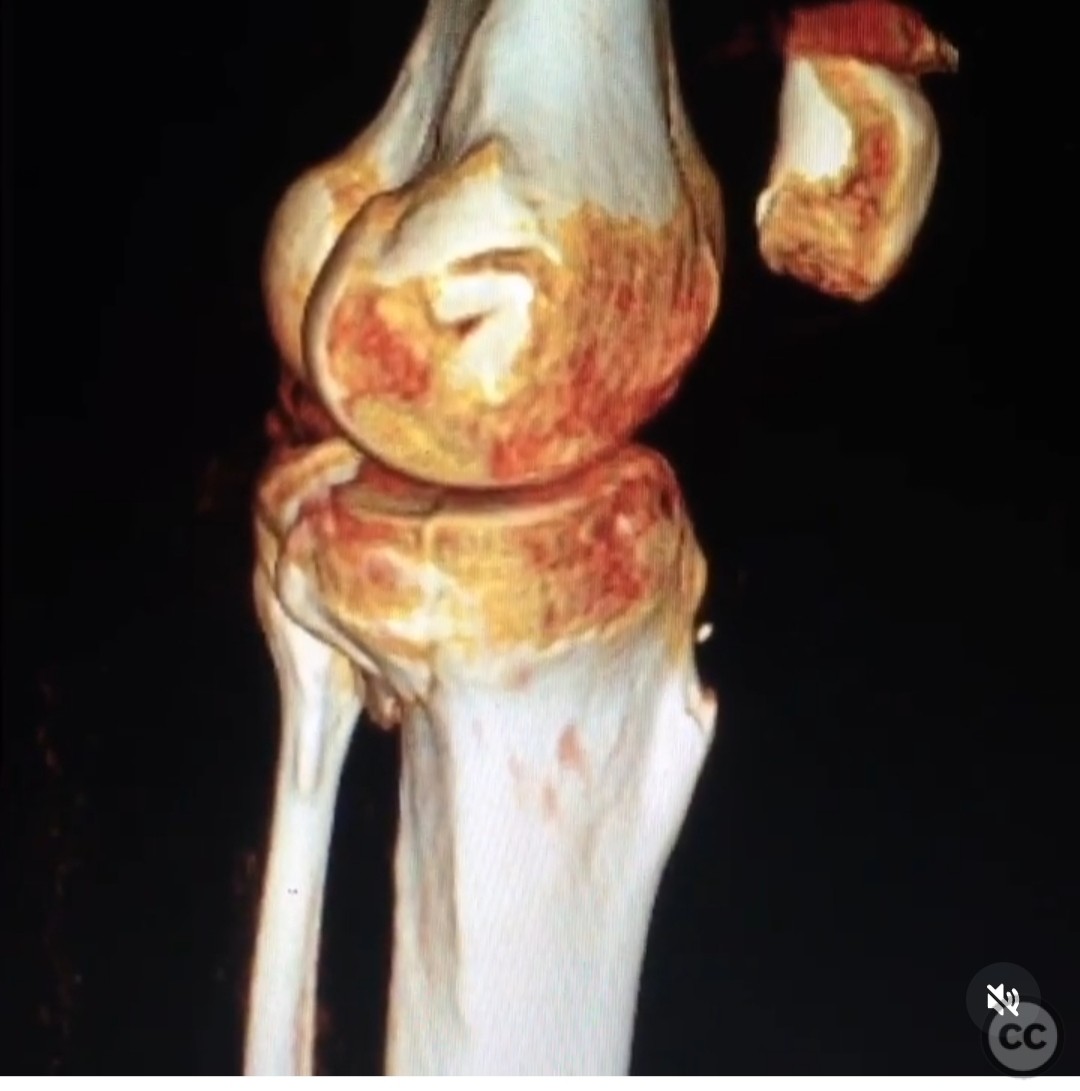
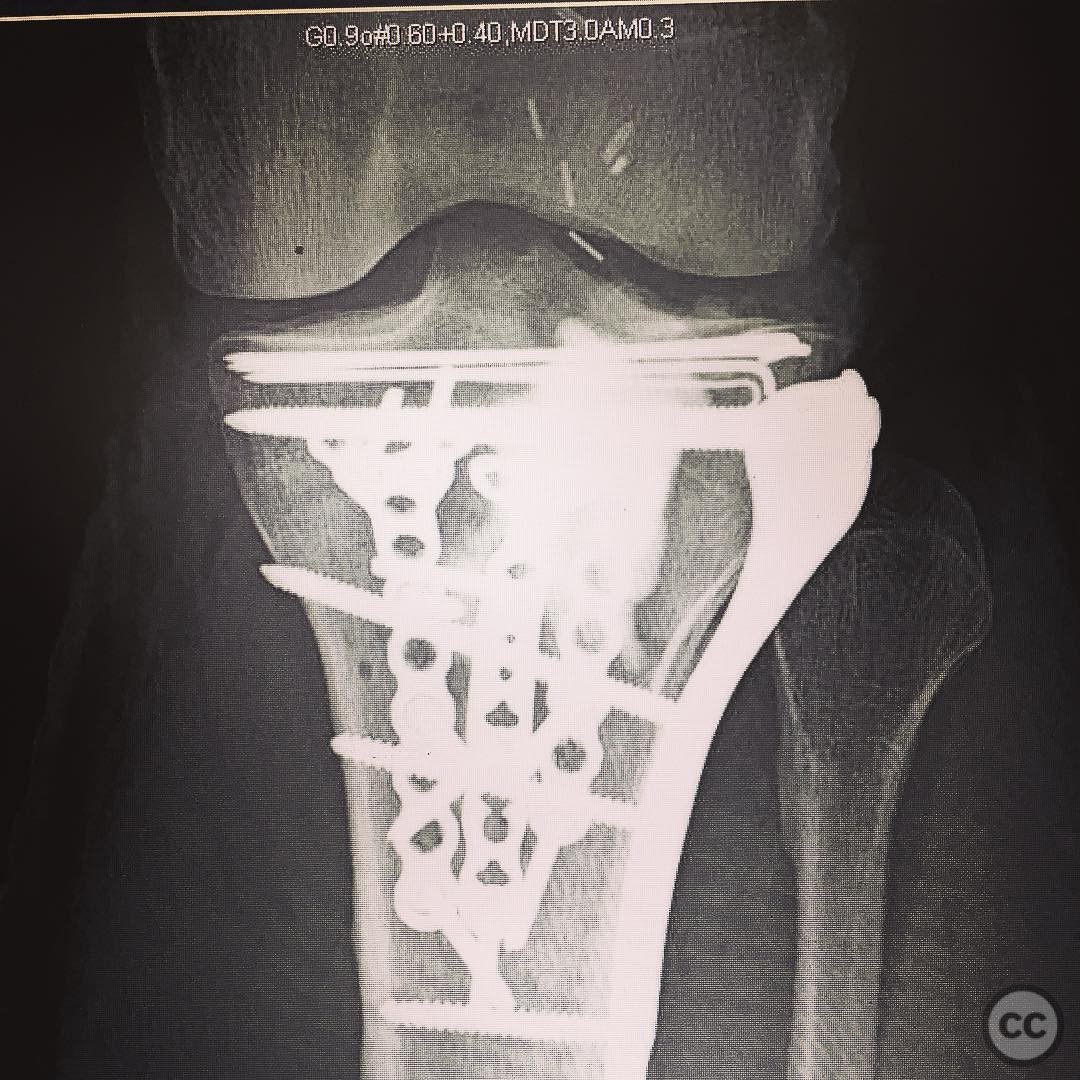
Coronal shear tibial plateau fracture with extensive lateral comminution.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
Clinical and radiological findings: The patient presented with a coronal shear fracture involving both condyles of the tibial plateau, as identified on sagittal CT imaging. There was significant comminution of the lateral articular surface. The fracture pattern indicated a complex injury requiring a strategic surgical approach to address both the coronal shear and the lateral comminution.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a two-stage surgical approach. Initially, a prone direct posterior approach was planned to address the coronal shear fracture traversing the entire posterior plateau. This was to be followed by a supine standard anterolateral approach to manage the lateral articular comminution.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was initially positioned prone for the direct posterior approach, and subsequently repositioned to supine for the anterolateral approach.
Anatomical surgical approach: The direct posterior approach involved a midline incision with dissection through the popliteal fossa to access the posterior tibial plateau. The anterolateral approach involved a longitudinal incision over the lateral aspect of the knee, splitting the iliotibial band and performing subperiosteal elevation from Gerdy's tubercle to expose the lateral condyle.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of recognizing the full extent of the coronal shear fracture across the posterior plateau. A posteromedial approach was deemed inadequate for accessing this fragment, as it would not allow proper reduction on the lateral side. The chosen dual approach facilitated comprehensive access and reduction of both the coronal shear and lateral comminution.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included non-weight bearing for 6 weeks, followed by gradual progression to partial weight bearing as tolerated. Range of motion exercises were initiated early to prevent stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included locking plates and screws for stabilization of the tibial plateau fracture.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 305 times
05 Aug 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Coronal shear tibial plateau fracture with extensive lateral comminution.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 3325773 Published Online Aug 05 2025.