Revision of Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Non-union with Plate and Nail Technique.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
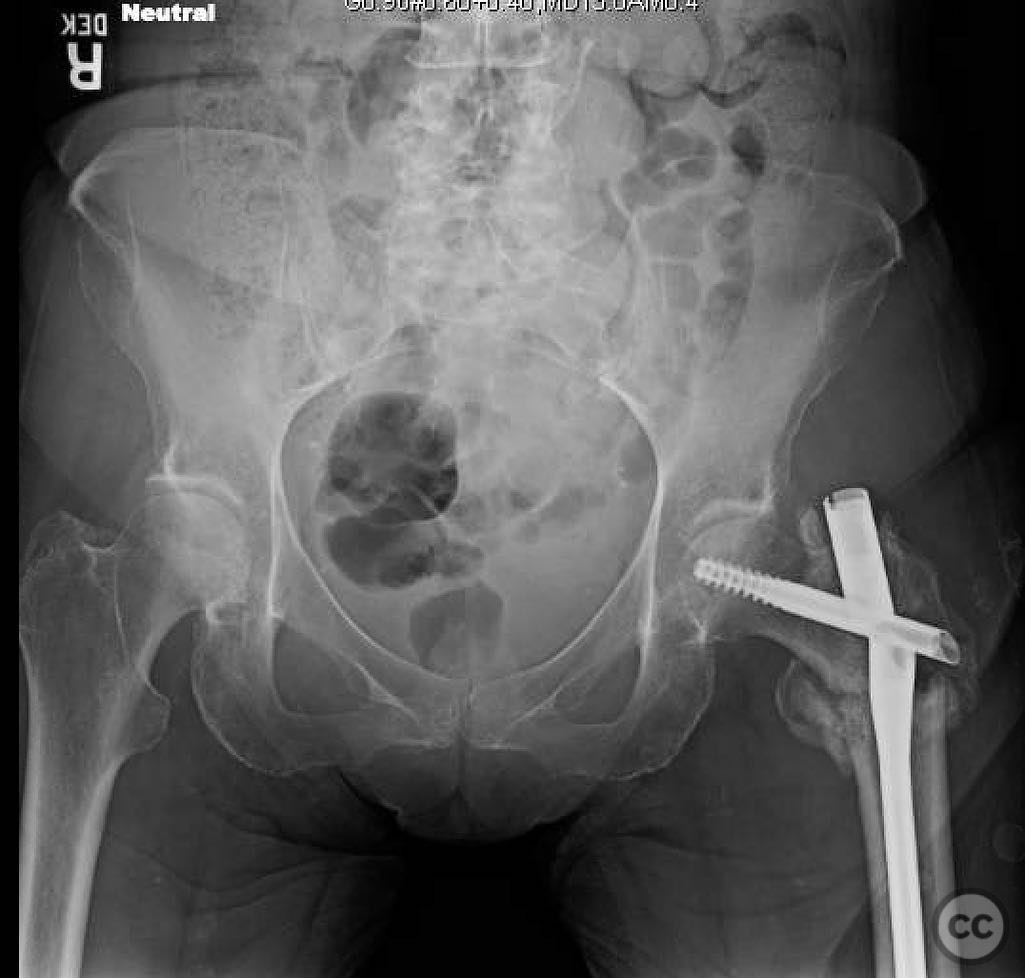
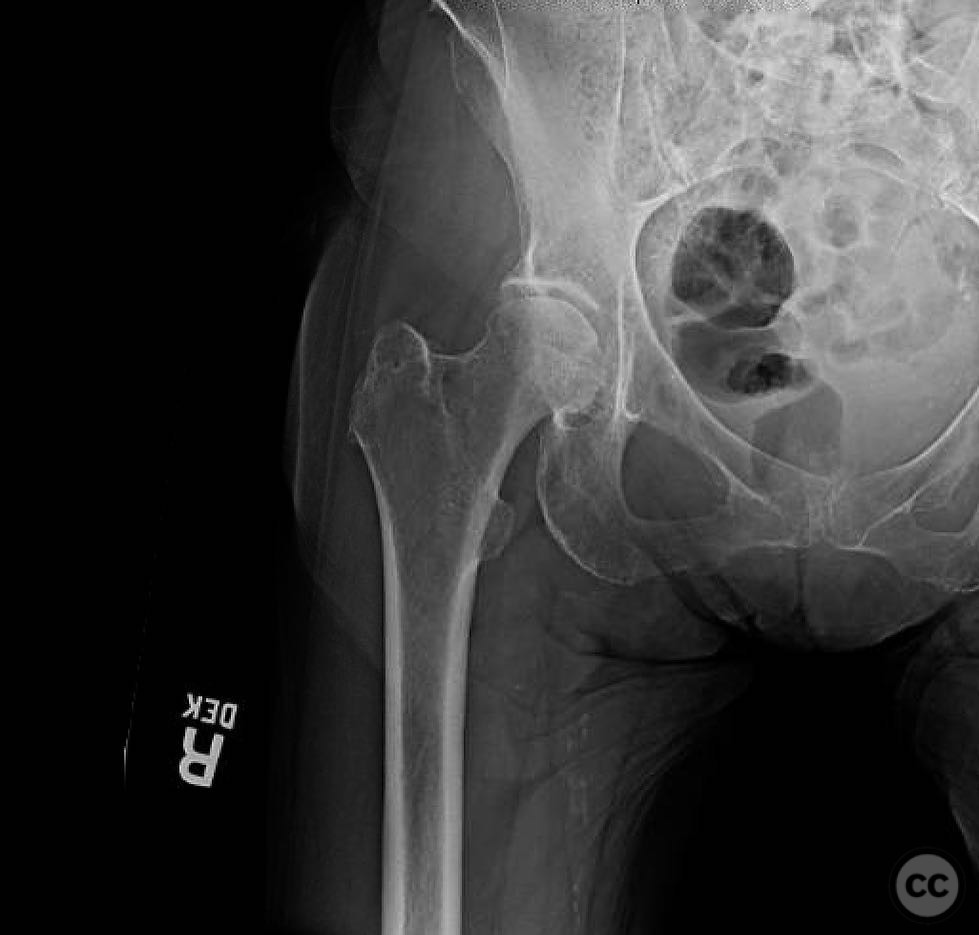
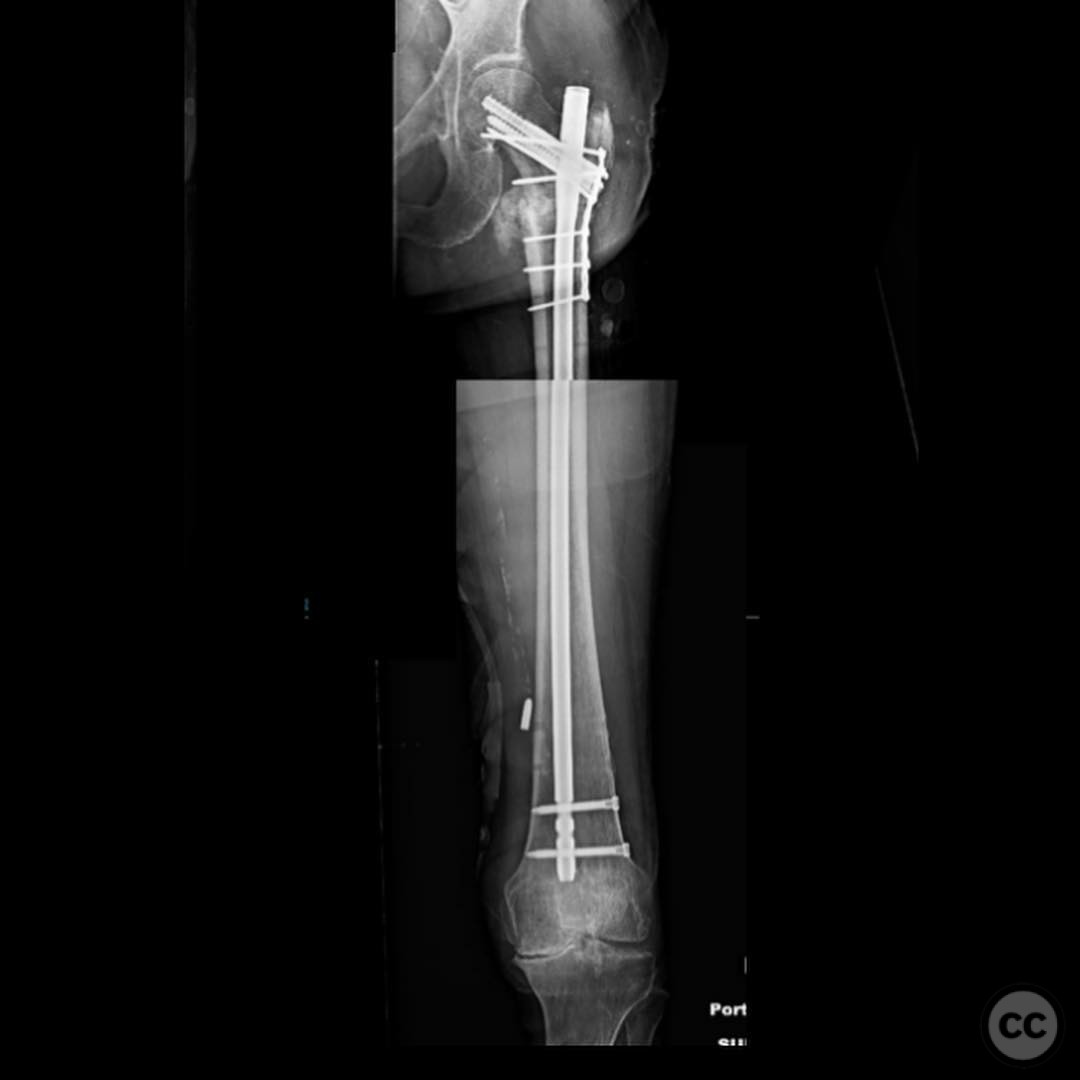
Clinical and radiological findings: A 74-year-old female presented with a 4-part intertrochanteric femur fracture following a ground-level fall. Initially treated with closed reduction and cephalomedullary (CM) nailing at an outside hospital, she was weight-bearing with a walker and showed improvement over six weeks. At seven weeks, she developed increasing pain, indicative of a non-union. Radiological evaluation revealed a hypertrophic non-union due to progressive varus collapse and fatigue failure of the implant, secondary to an inadequate initial reduction and too lateral an entry point.
Preoperative Plan
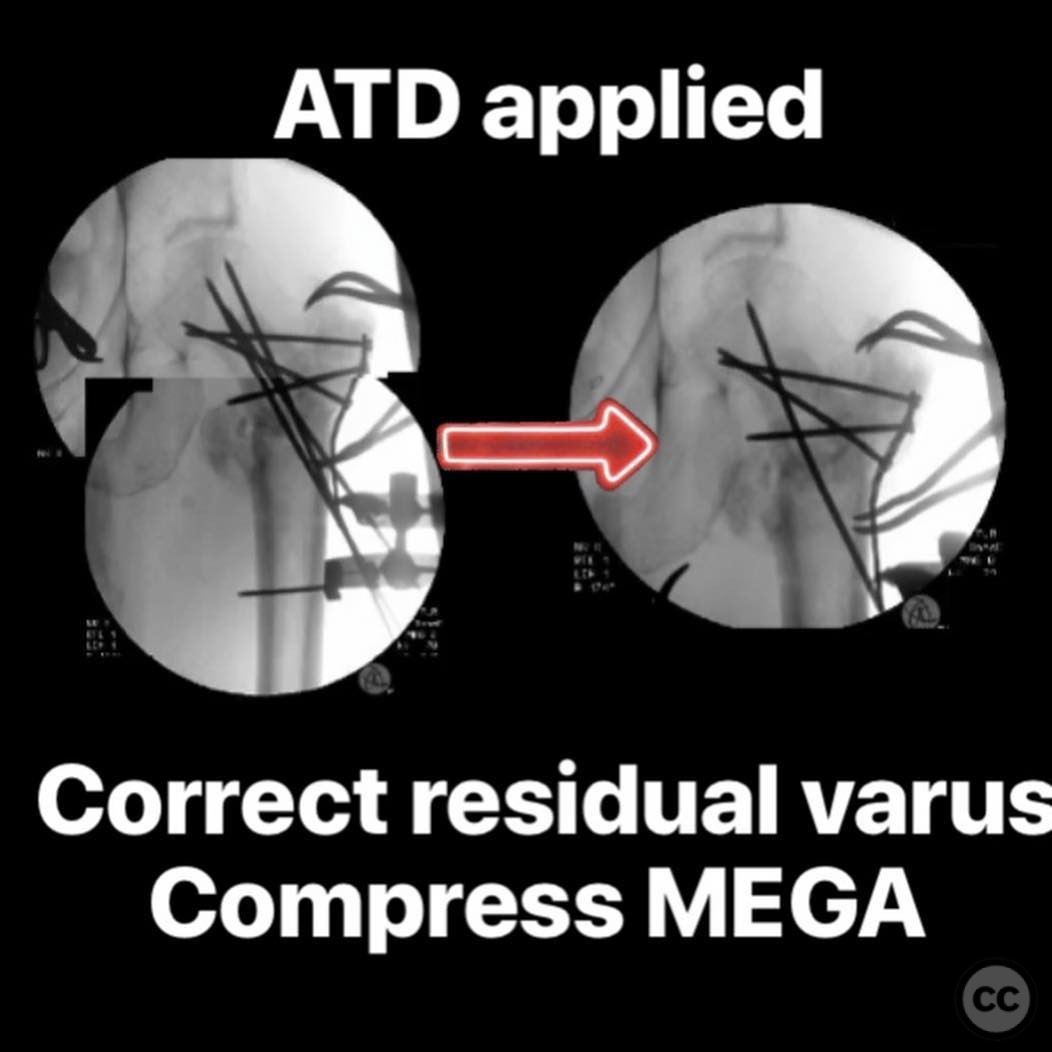
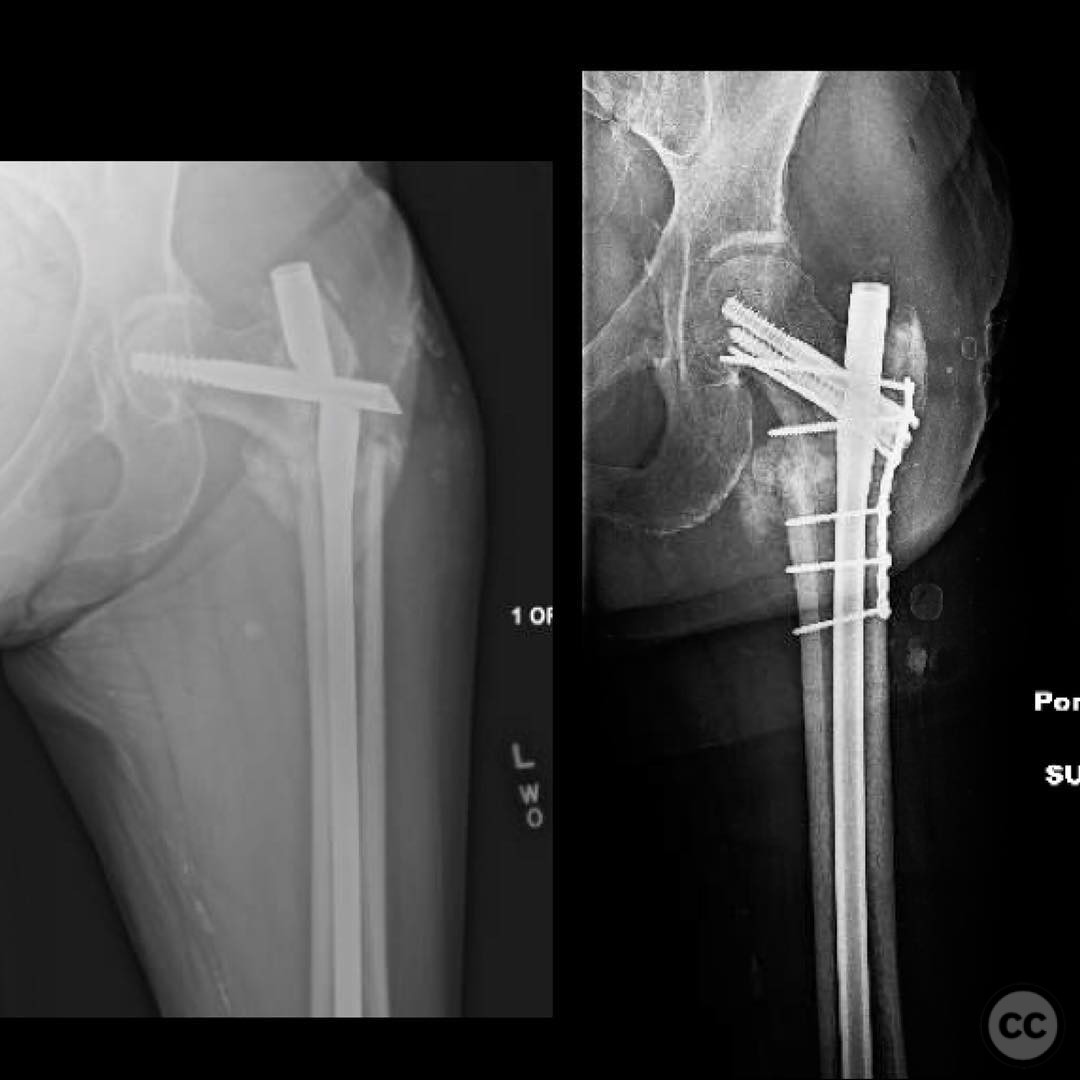
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved revision surgery to address the mechanical failure. The approach included removal of the existing nail, provisional reduction with Weber clamps, correction of version with Schanz pins, and fixation of a plate to the proximal segment. An anterolateral approach was planned for plate placement, avoiding interference with the subsequent nailing trajectory. The plan also included using an articulated traction device (ATD) for varus correction and compression.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned laterally to facilitate optimal surgical access.
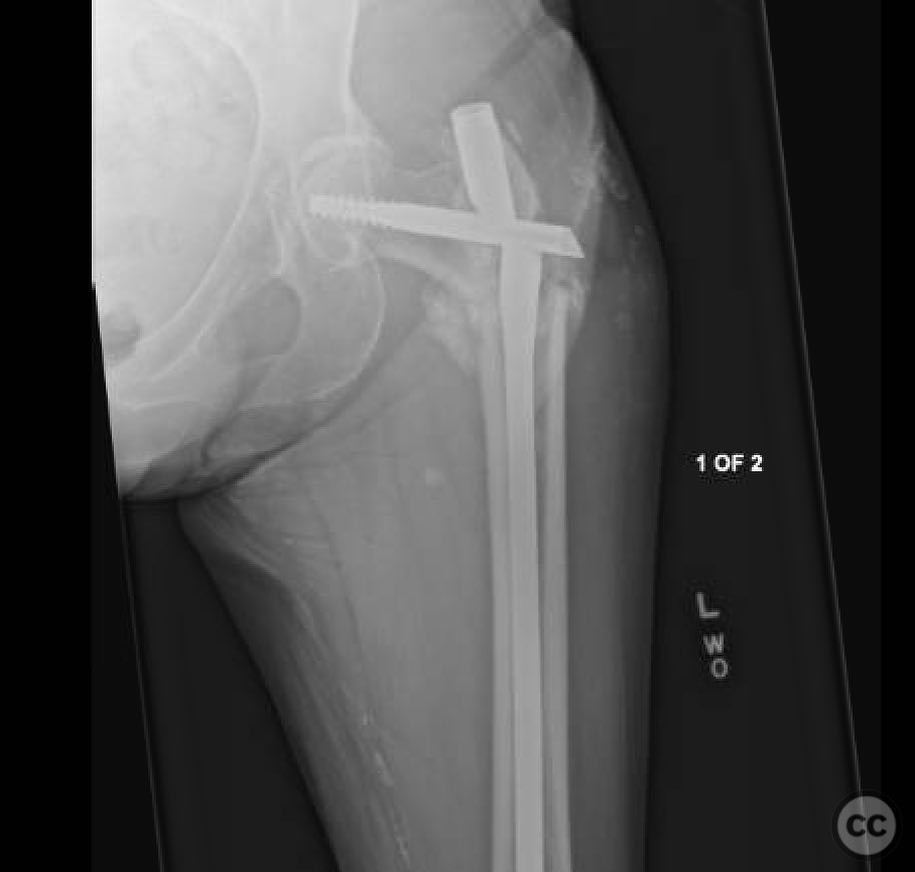
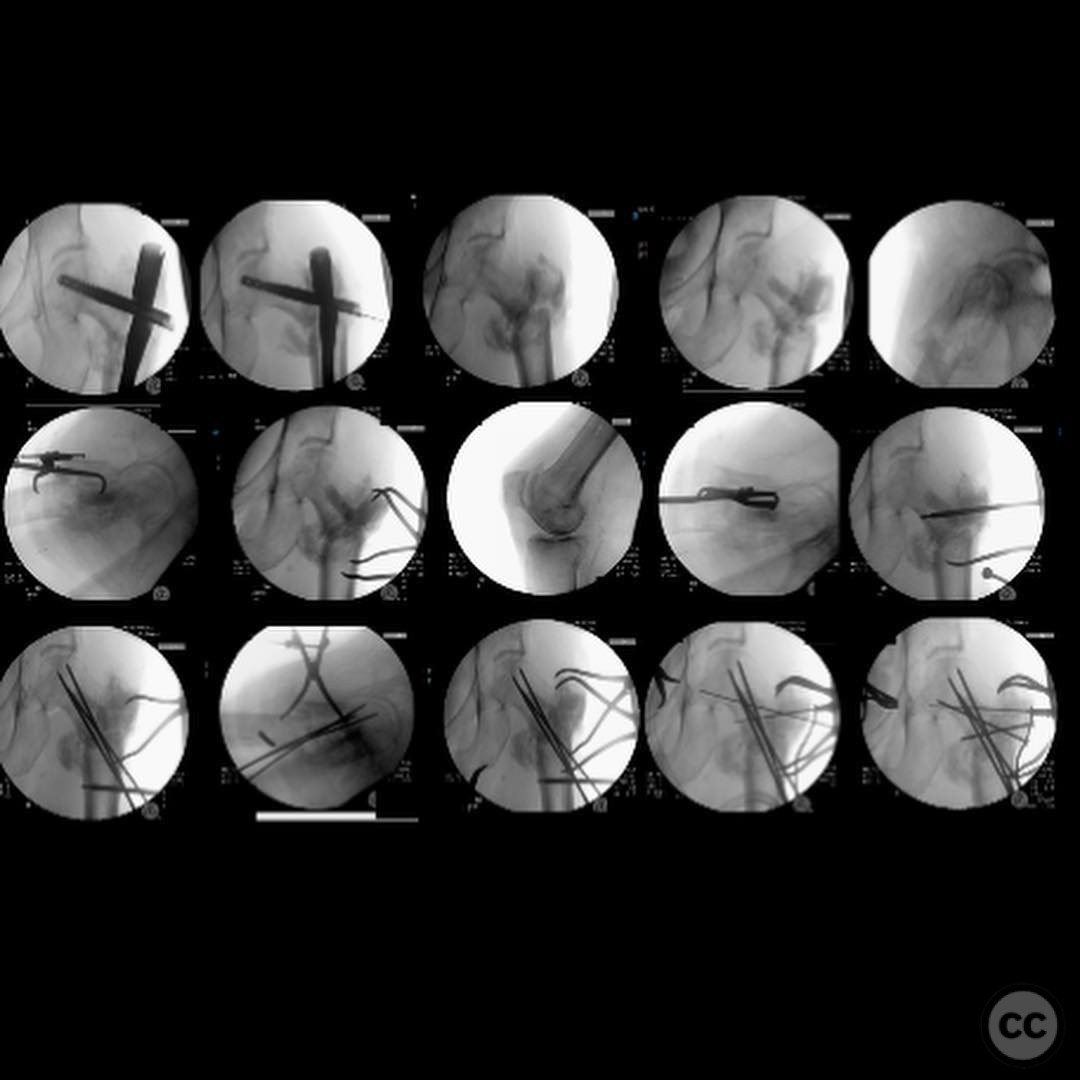
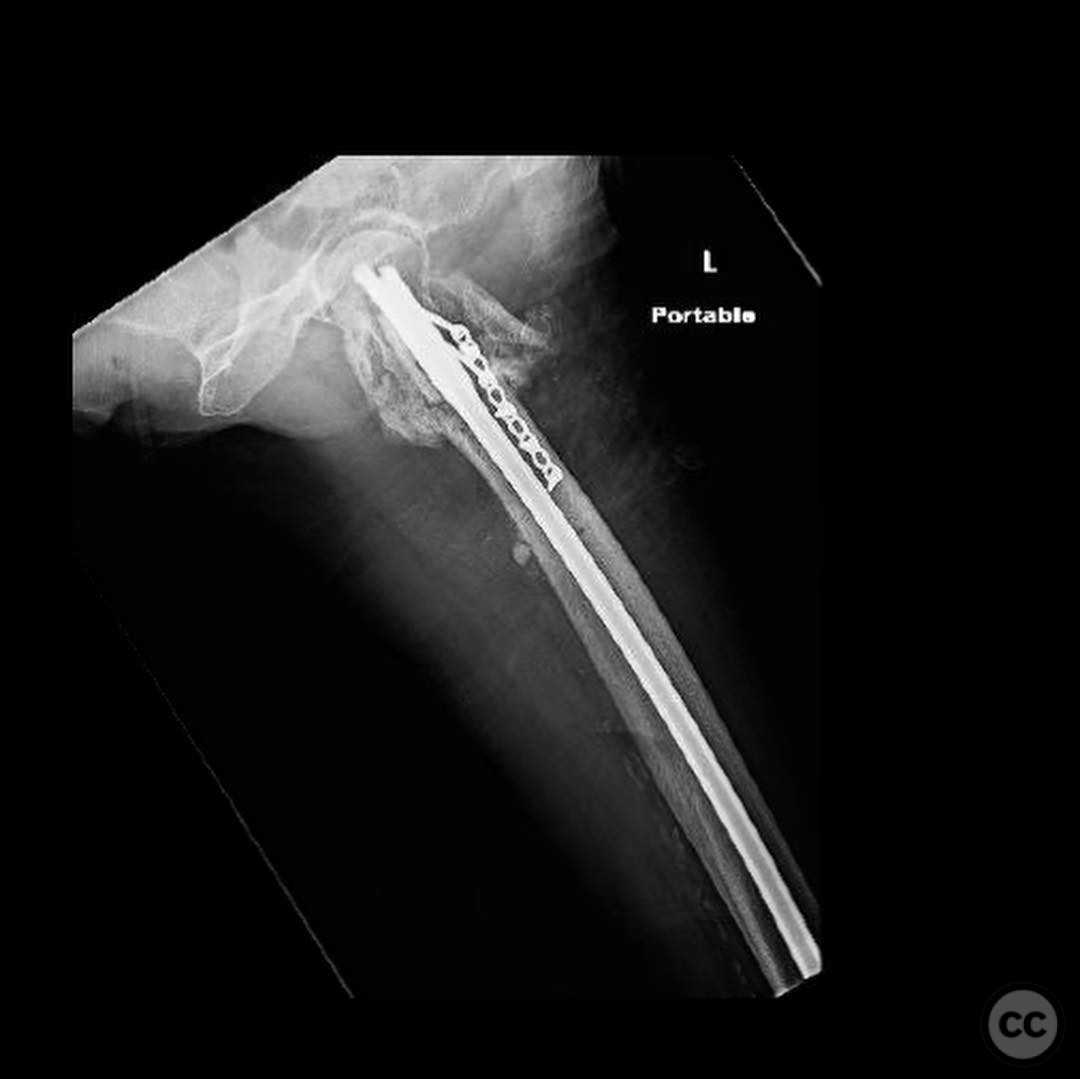
Anatomical surgical approach: An anterolateral approach was utilized, involving incision along the lateral aspect of the proximal femur. Dissection proceeded through the fascia lata and vastus lateralis muscle, allowing exposure of the proximal femur for plate application. The existing nail was removed, and reduction was achieved using Weber clamps and Schanz pins for version correction.
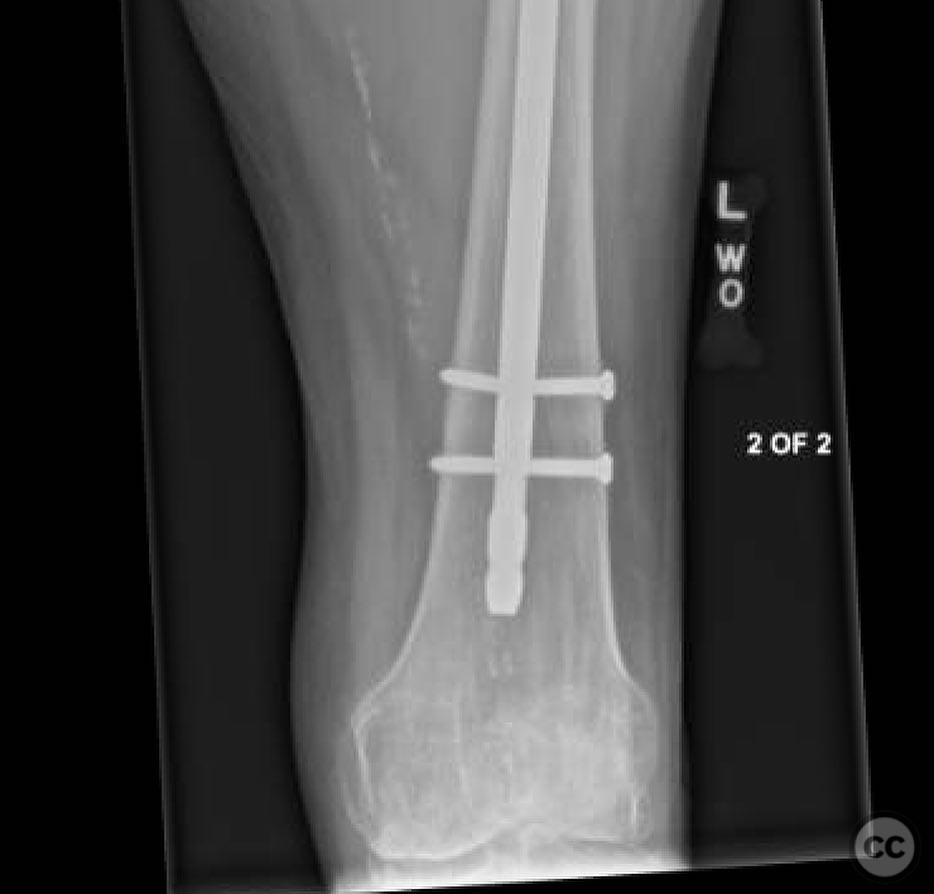
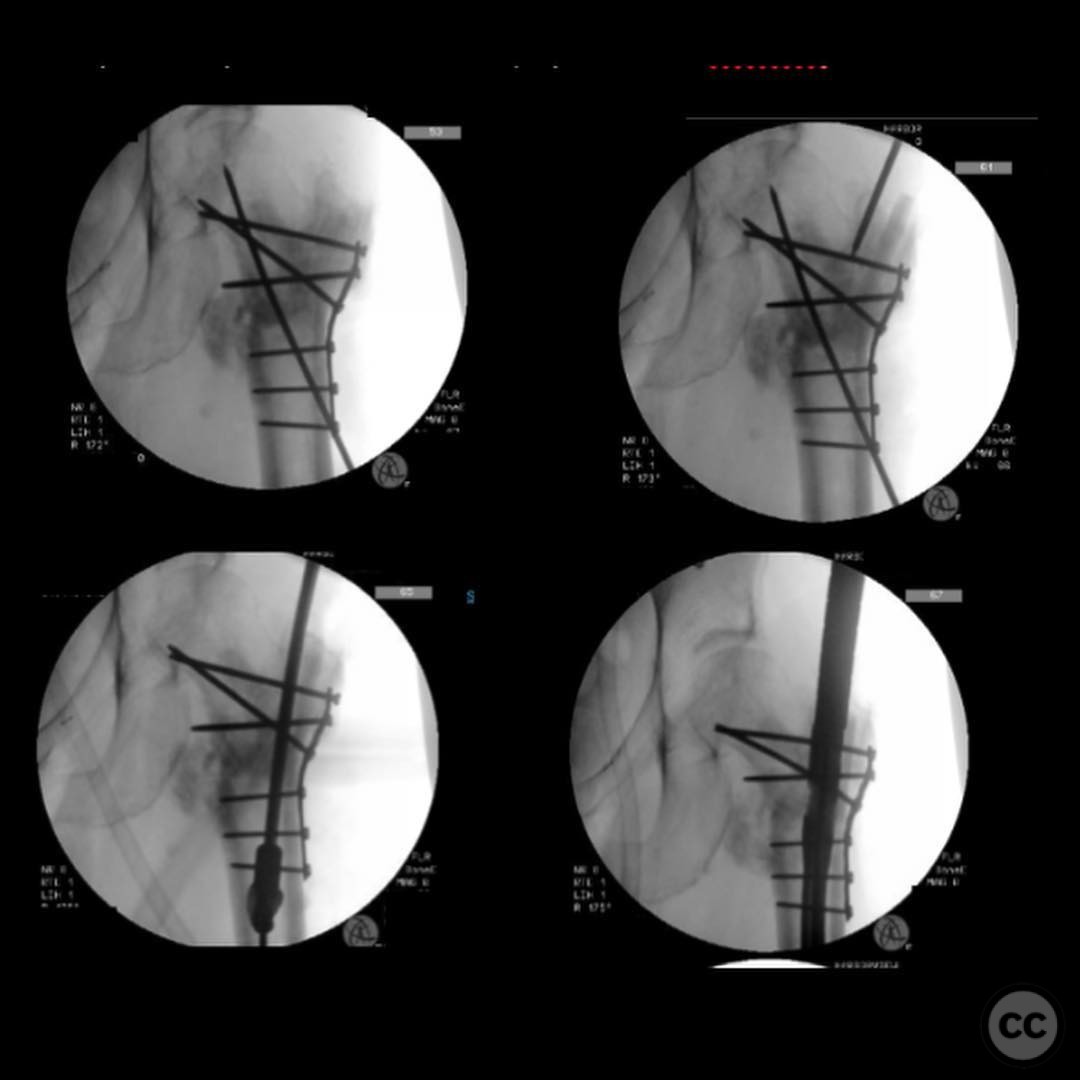
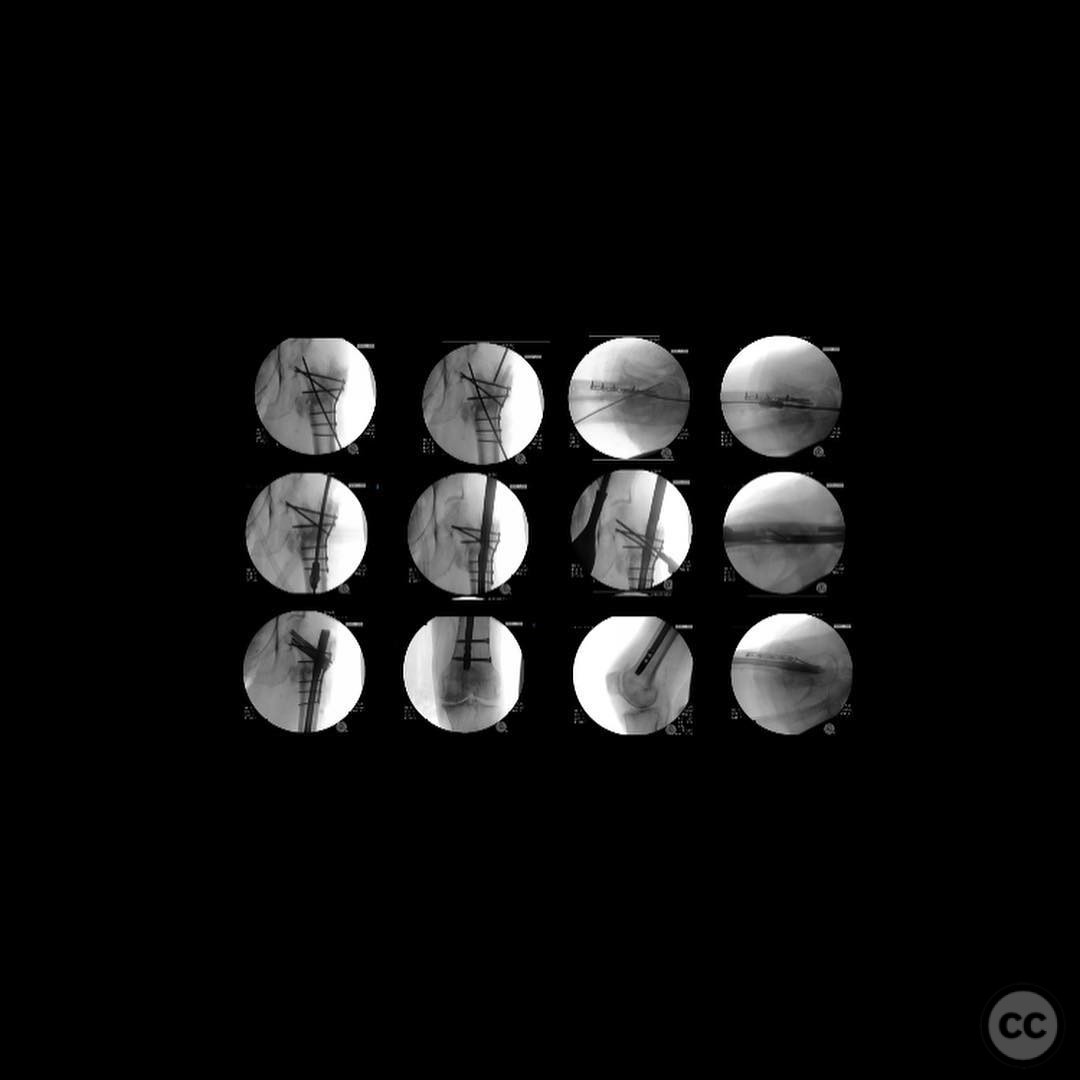
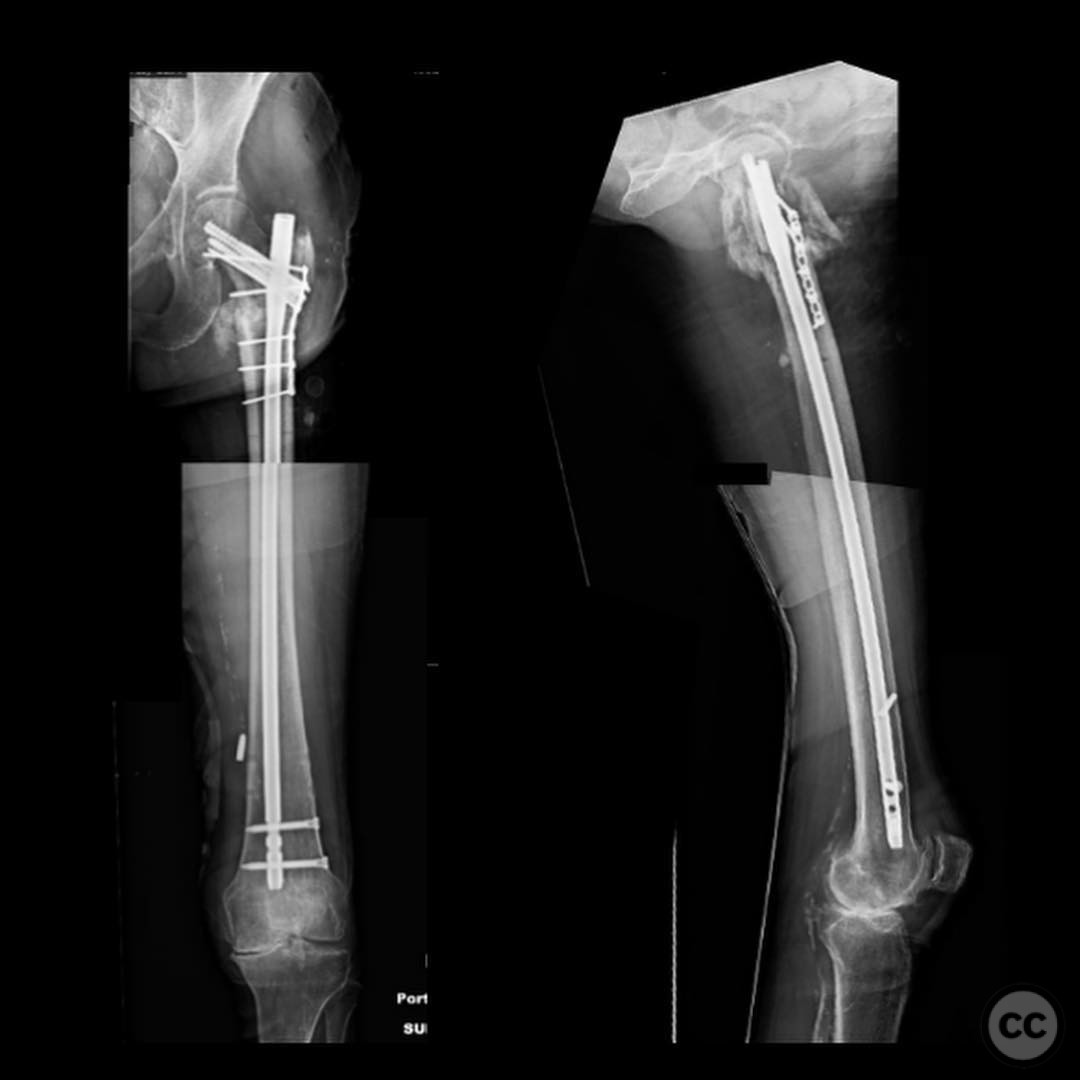
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that achieving native alignment and compression was critical. A fibula strut, bisected, was inserted into the old nail hole proximally to aid structural support. A new medial start site was created for careful reaming and insertion of the revision nail. The ATD facilitated significant compression at the non-union site, obviating the need for bone grafting.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included protected weight-bearing with progression as tolerated, focusing on maintaining alignment and promoting union through mechanical stability.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Proximal femoral plate, revision intramedullary nail, Weber clamps, Schanz pins, fibula strut graft.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 198 times
23 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Revision of Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Non-union with Plate and Nail Technique.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 29117795 Published Online Jul 23 2025.