Bilateral SI Joint Disruption and Right Anterior Column Posterior Hemitransverse Acetabular Fracture in a Morbidly Obese Patient.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
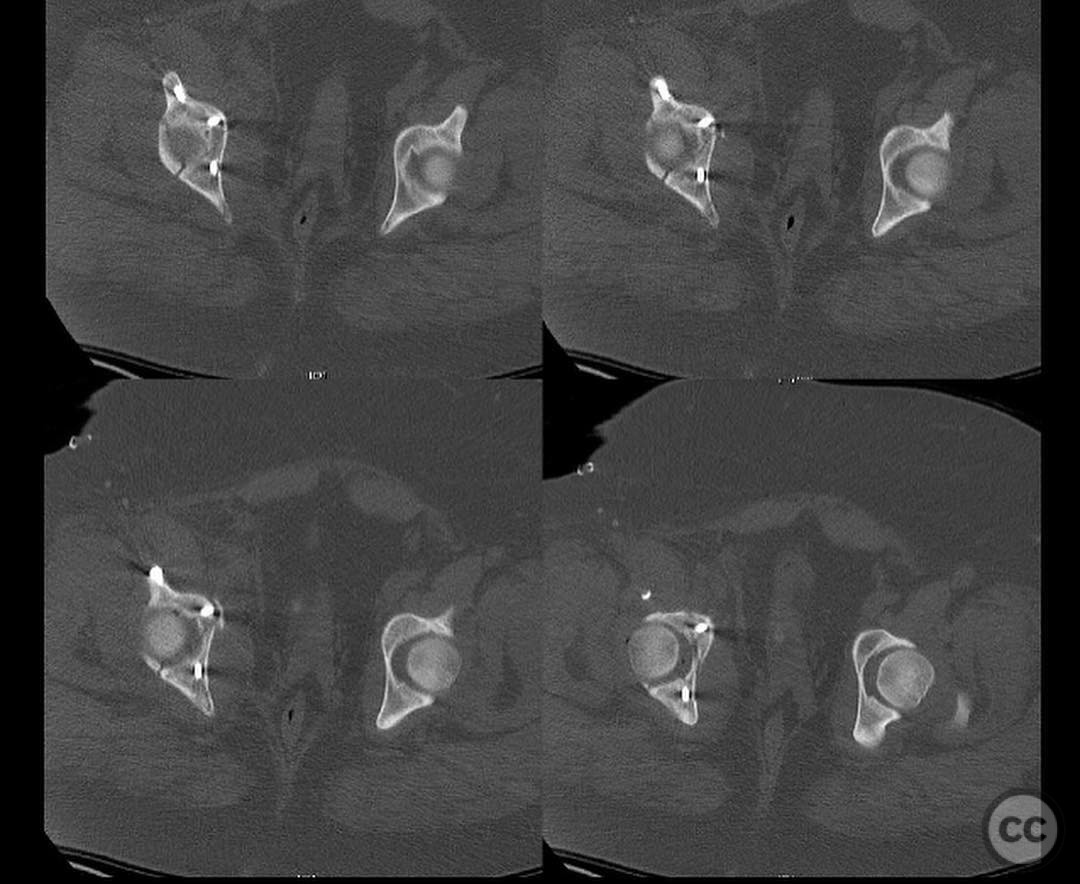
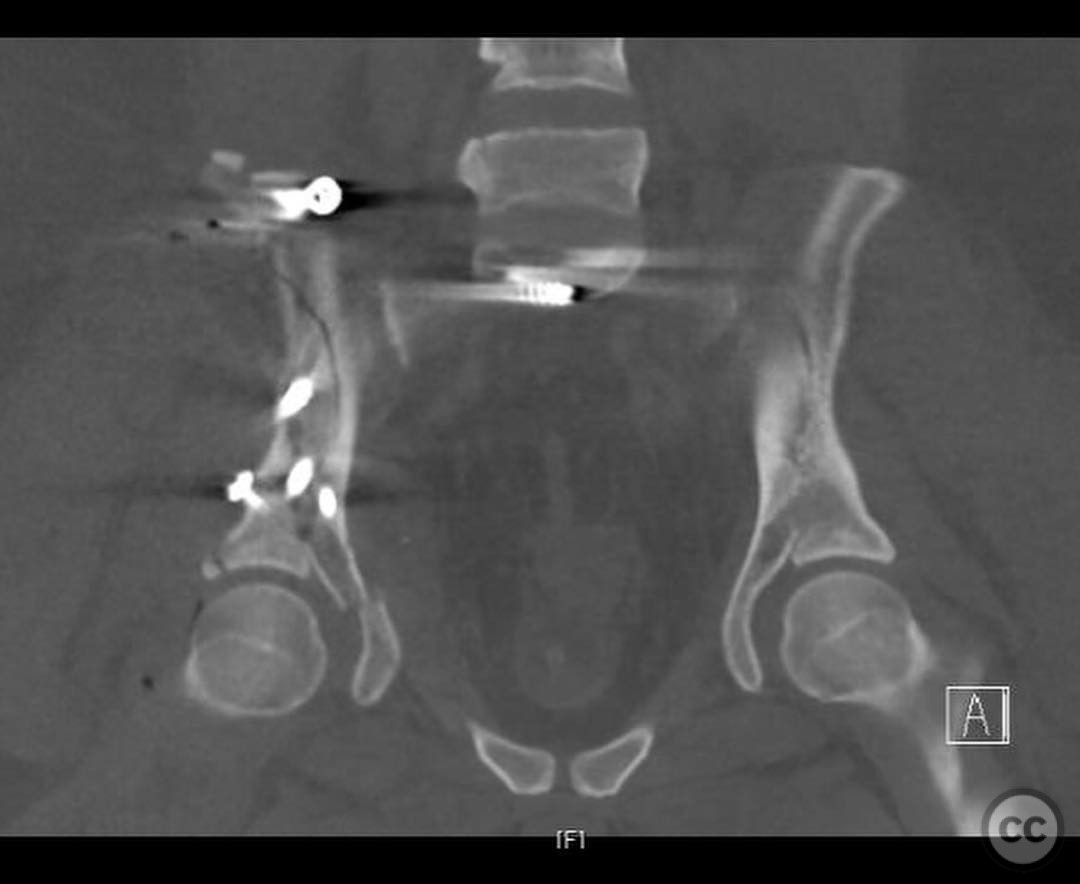
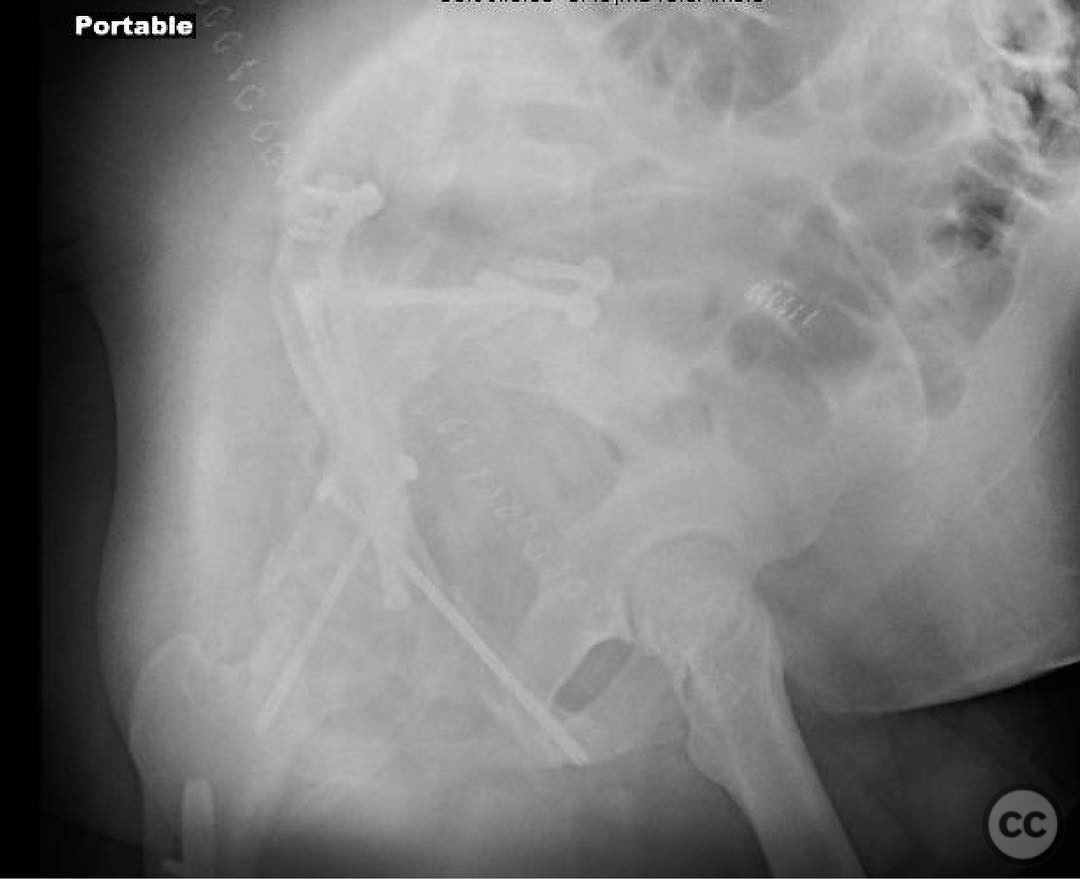
Clinical and radiological findings: A 22-year-old female pedestrian was struck by a truck, resulting in a combined pelvic ring and acetabular fracture. The patient is morbidly obese and has sustained a complete thoracic spinal cord injury. Radiological assessment revealed bilateral sacroiliac (SI) joint disruptions and a right-sided anterior column posterior hemitransverse acetabular fracture. The patient's obesity increases the risk of infection and influences the operative strategy.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan for this morbidly obese patient involved a minimally invasive approach to reduce infection risk. Percutaneous screw reduction and fixation were prioritized, with the use of a Starr frame considered for its potential to achieve satisfactory reduction despite the patient's body habitus. The surgical plan included percutaneous fixation of the left SI joint with partially threaded screws, followed by a lateral window approach to address the anterior column fracture.
Surgical Discussion
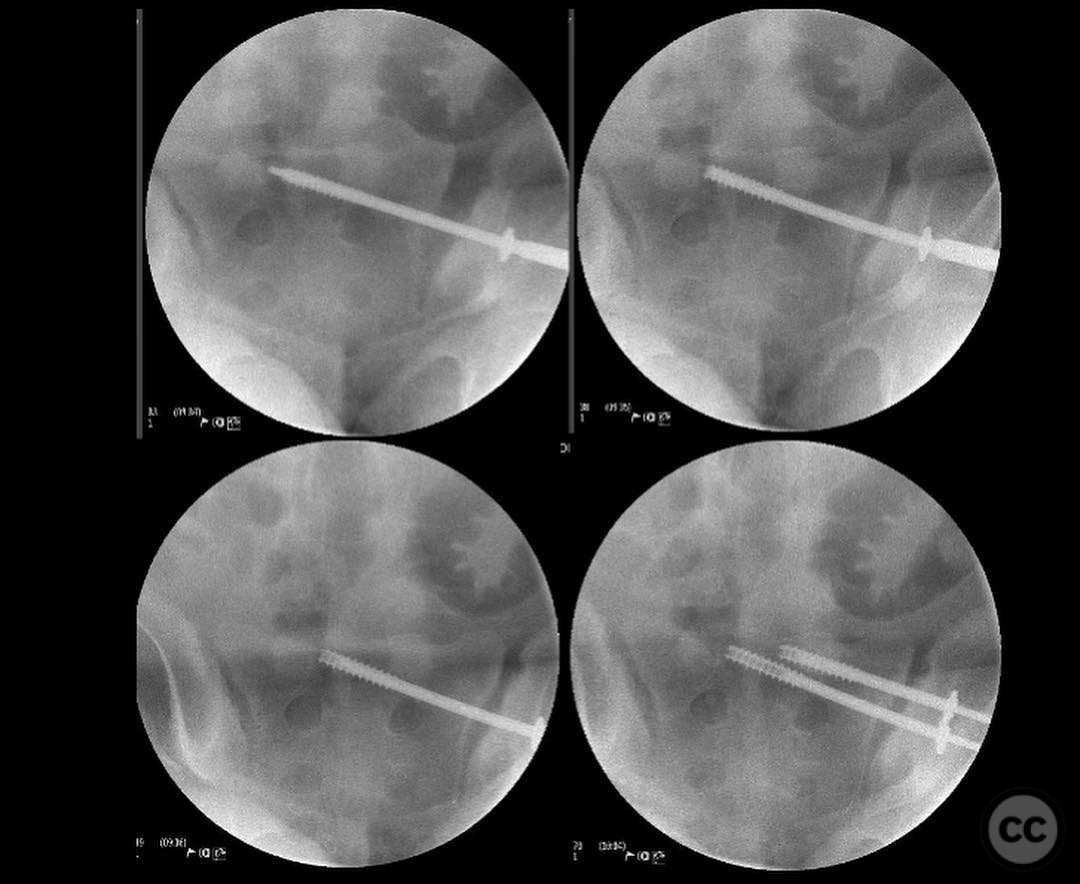
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table, with provisions made for intraoperative fluoroscopic imaging to guide percutaneous screw placement and reduction maneuvers.
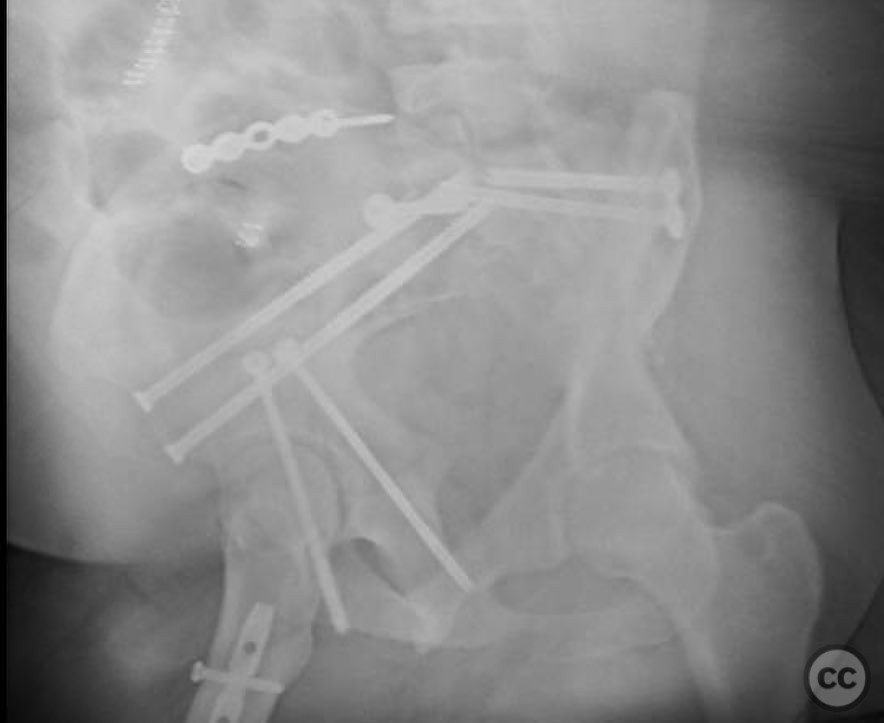
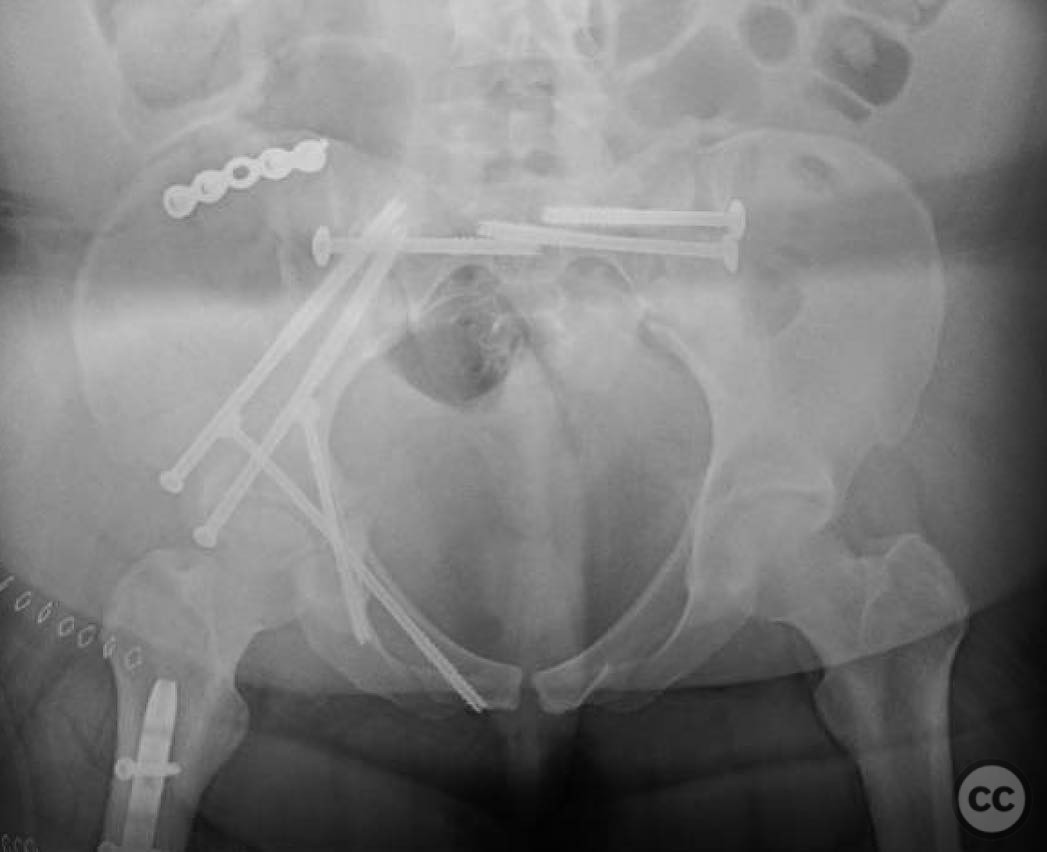
Anatomical surgical approach: A lateral window approach was utilized to access the anterior column. Schanz pins were strategically placed in the gluteal pillar and LC2 corridor to facilitate reduction of the anterior column at the iliac crest exit and brim. A crest plate was applied to maintain peripheral reduction, followed by placement of an LC2 style screw for compression. Additional fixation included an antegrade ramus lag screw, a posterior column lag screw, another LC2 style screw, and percutaneous right SI joint screw fixation.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that the lateral window approach provided a favorable balance between invasiveness and reduction quality, offering a lower infection risk compared to more extensive approaches such as ilioinguinal or Stoppa. The use of column screws minimized surface implants, further reducing infection risk. In a less obese patient, an anterior intrapelvic (Stoppa) approach might have been employed to enhance reduction quality.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation focused on minimizing weight-bearing stress on the pelvis. Initial non-weight-bearing status was maintained, with gradual progression to partial weight-bearing as tolerated, considering the patient's spinal cord injury and overall condition.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Partially threaded 7.0mm screws, Schanz pins, crest plate, LC2 style screws, antegrade ramus lag screw, posterior column lag screw.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body hab(.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_2.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_1.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_3.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_5.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_4.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_7.jpg)
 for a patient with this injury_ Islolated_ young_ healthy_ normal body ha_6.jpg)
Article viewed 171 times
23 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Bilateral SI Joint Disruption and Right Anterior Column Posterior Hemitransverse Acetabular Fracture in a Morbidly Obese Patient.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 2792092 Published Online Jul 23 2025.