Segmental Proximal Humerus and Shaft Fracture in a Rodeo Injury
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
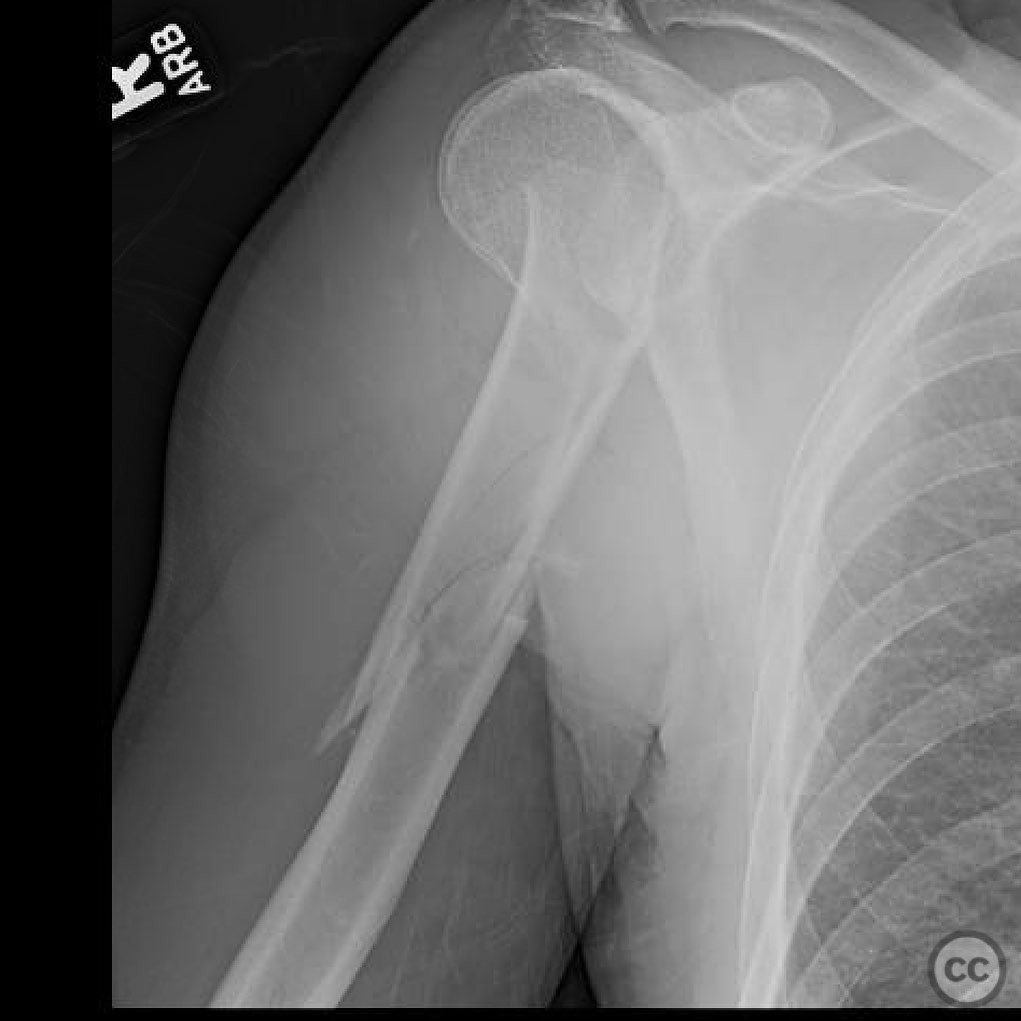
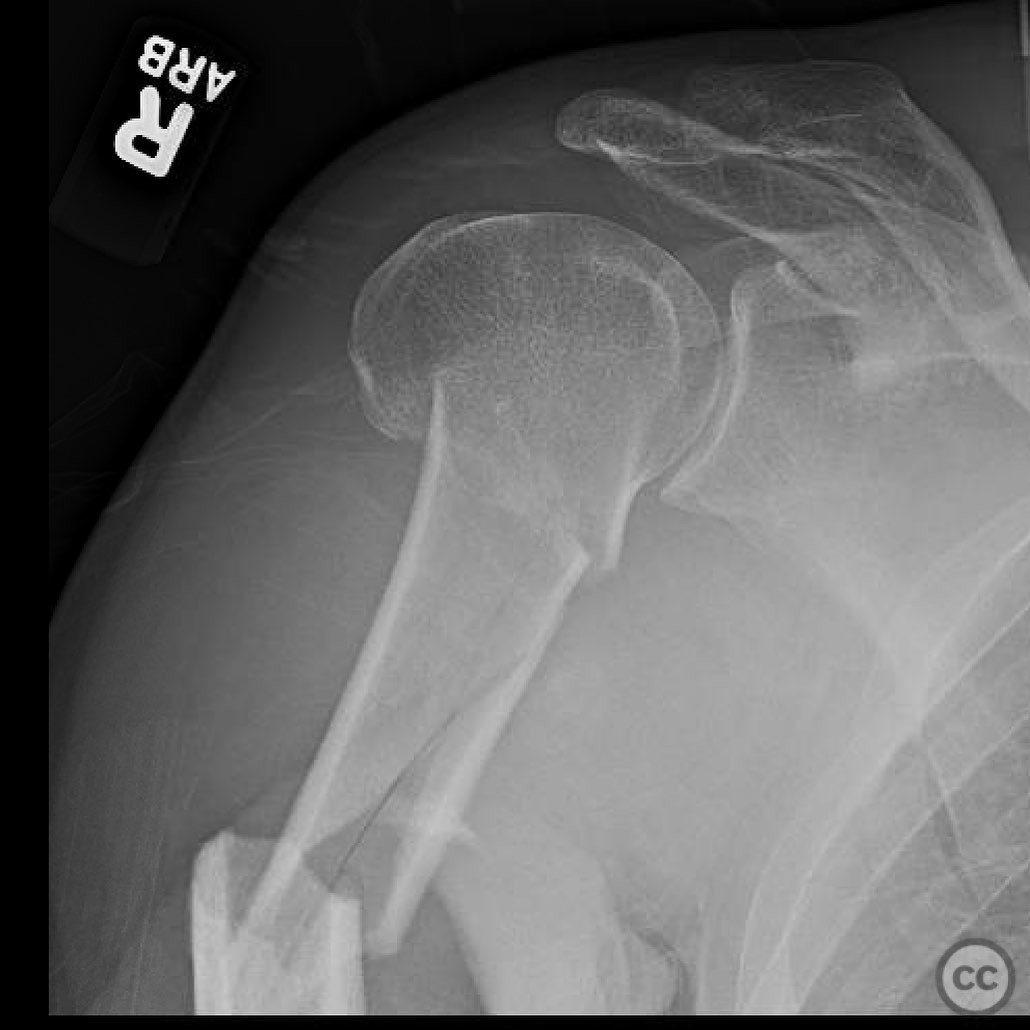
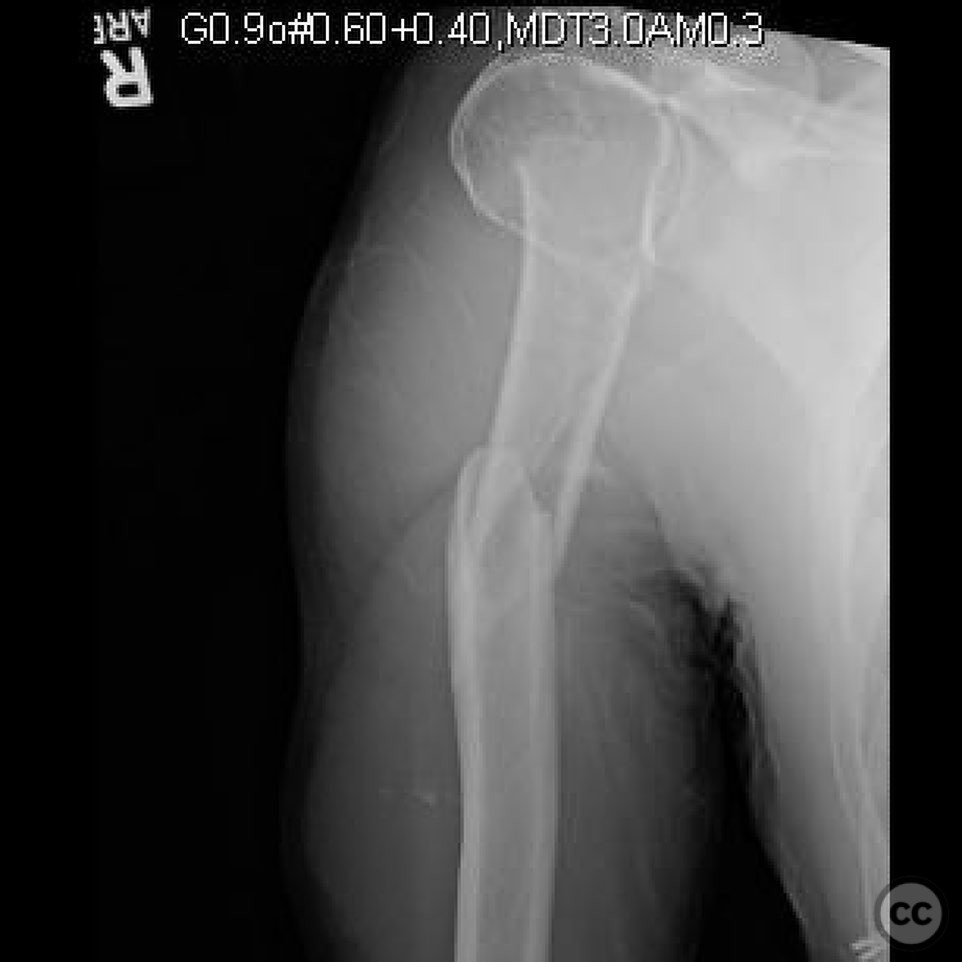
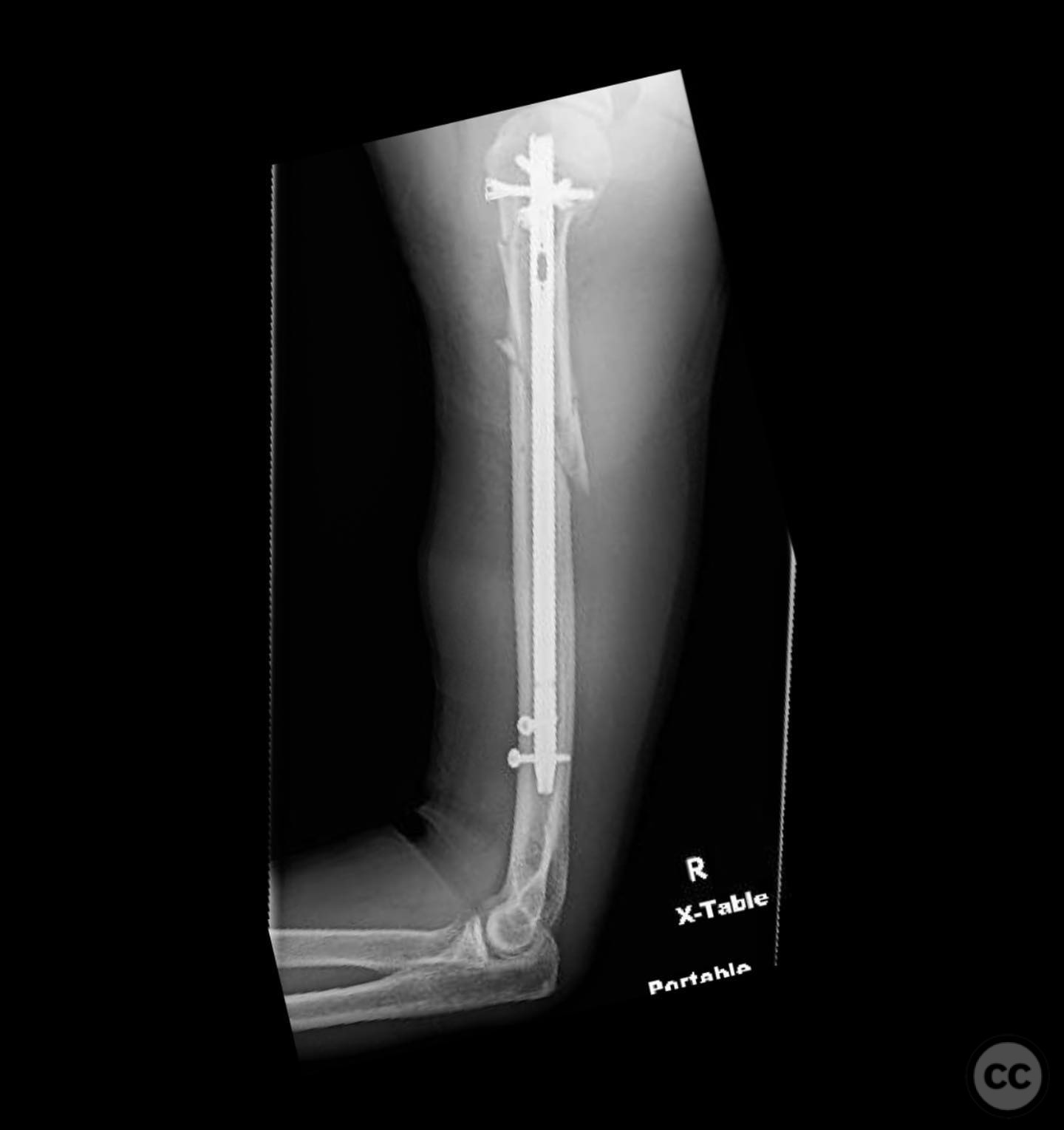
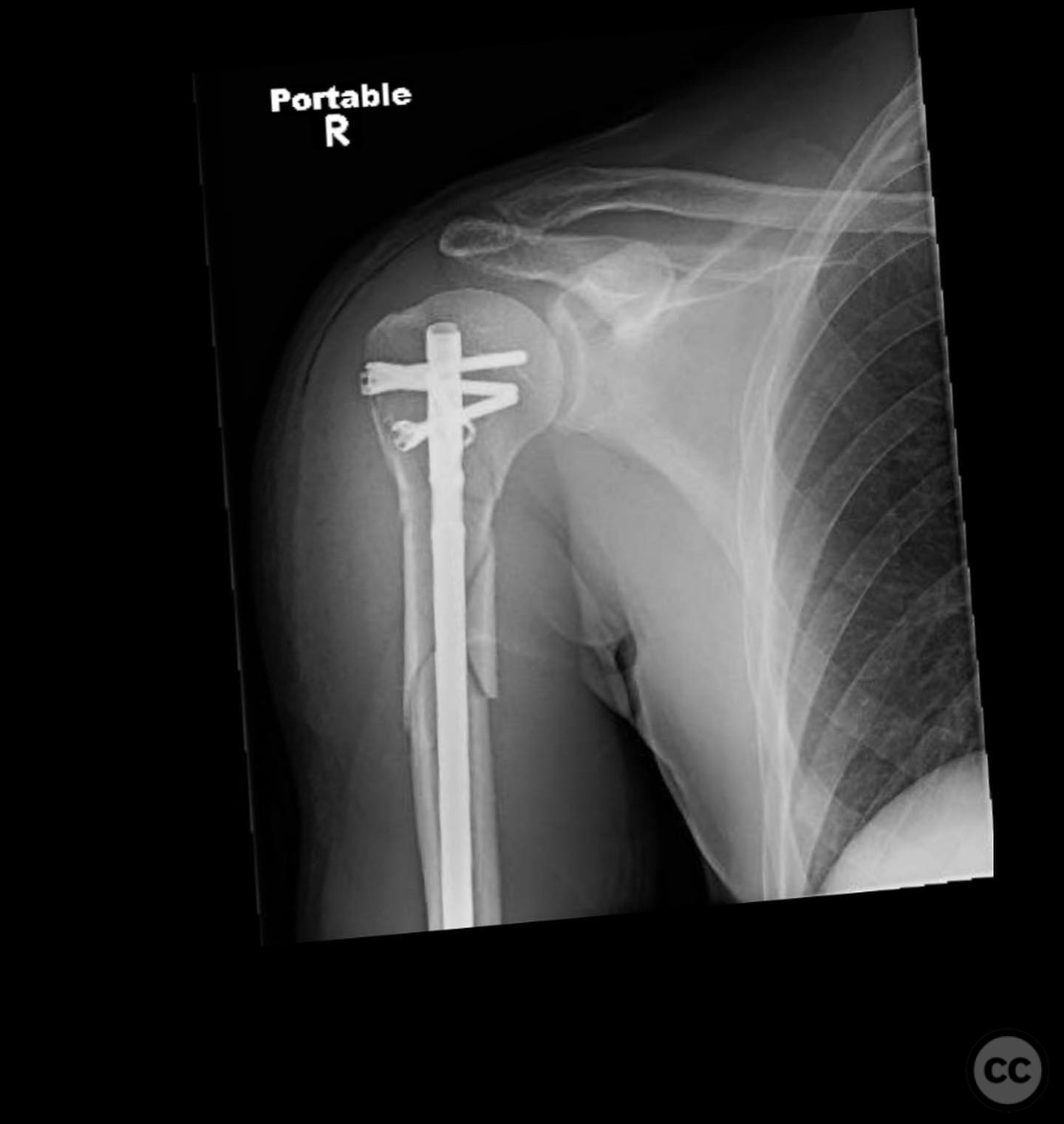
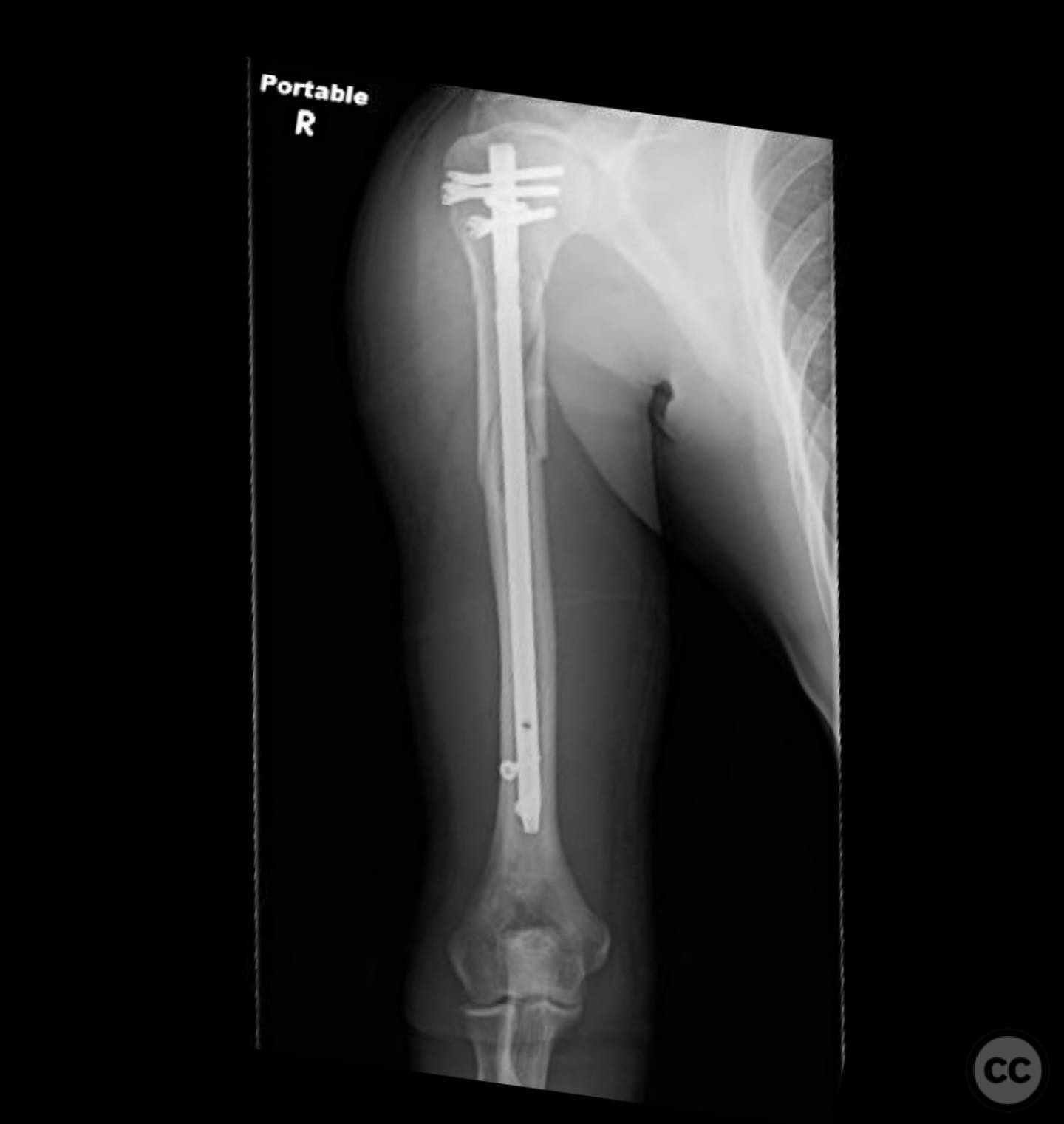
Clinical and radiological findings: A 46-year-old male sustained an injury while roping steer, resulting in a fall from a horse. The patient presented with a two-part proximal humerus fracture and a segmental contiguous shaft fracture. The injury was closed with no significant soft tissue damage noted. Neurovascular examination was unremarkable. Radiographs confirmed the fracture pattern.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved the use of an intramedullary nail for fixation, focusing on indirect reduction to maintain fracture hematoma and promote callus formation. The approach required careful consideration of nail length to avoid complications such as fracture distraction or distal humeral splitting.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on a flat-top operating table, positioned at the edge to facilitate C-arm access from the opposite side.
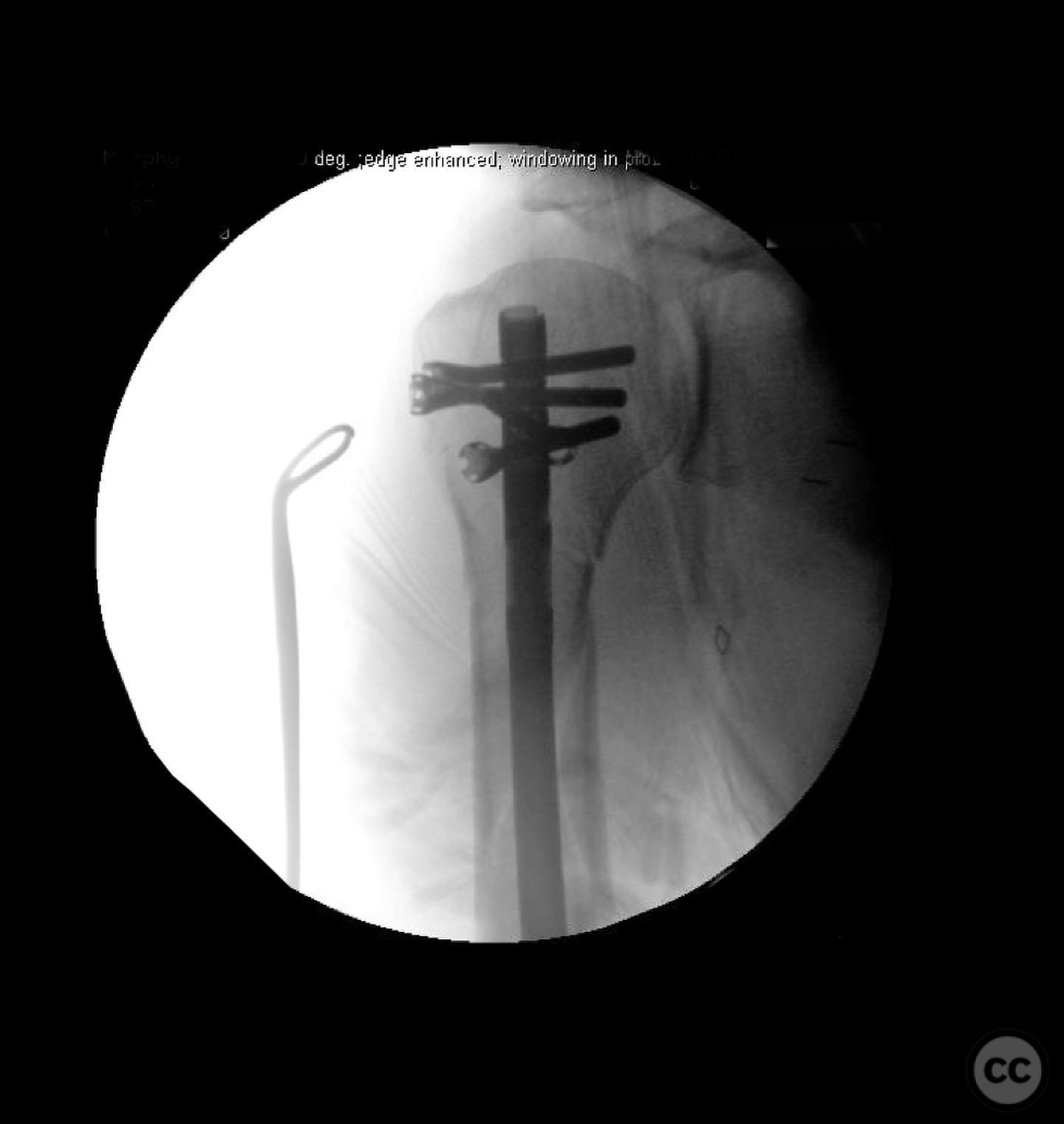
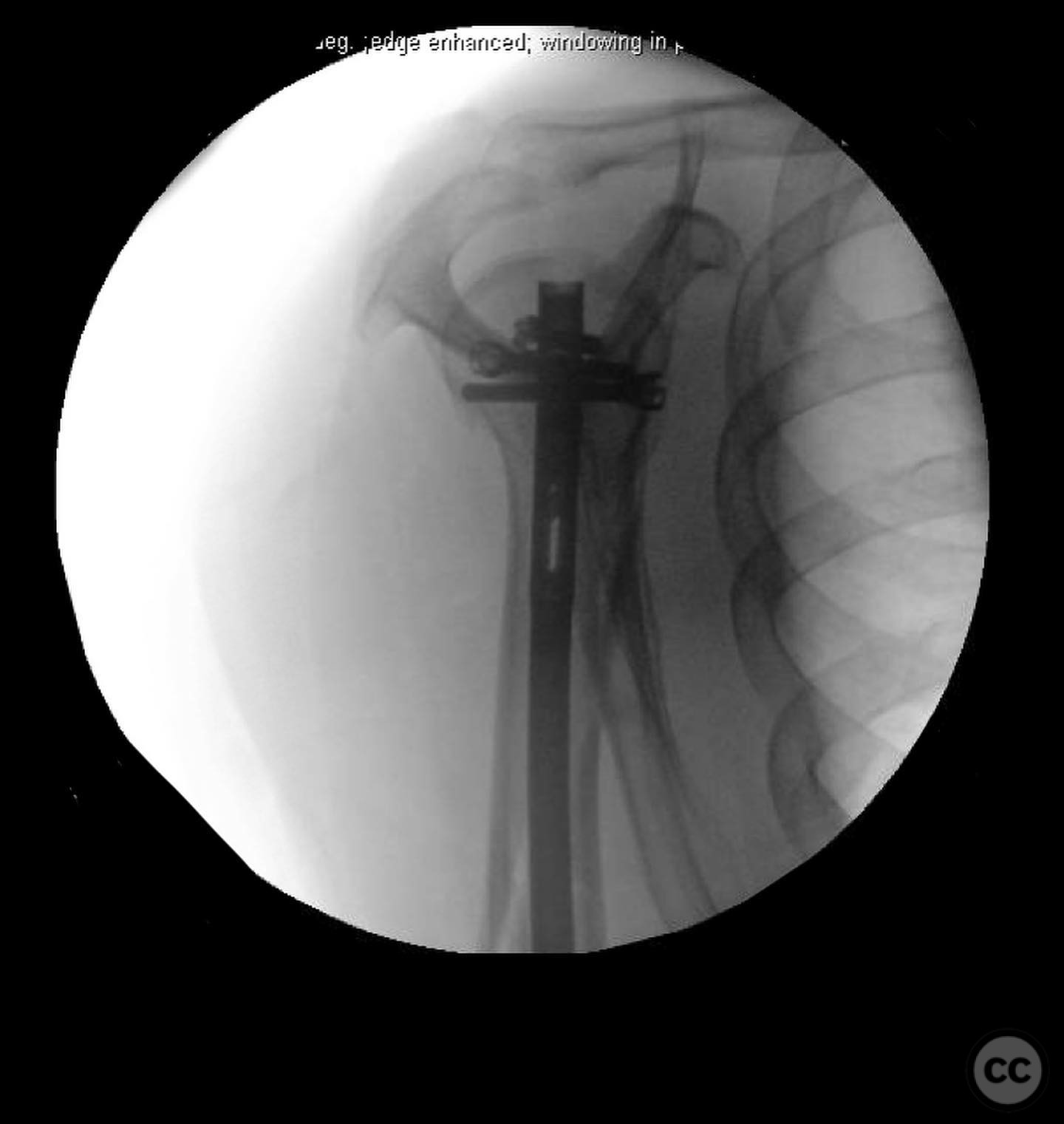
Anatomical surgical approach: A mini-open approach was utilized to access the start site for nailing. The rotator interval was opened, and stay sutures were placed in the rotator cuff for retraction. Care was taken to retract the cuff during reaming to prevent damage.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of selecting the correct nail length to avoid complications such as fracture distraction, distal humeral splitting, or leaving the nail proud in the shoulder joint. Distal interlocking screws were placed through a mini-open incision to avoid nerve injury. Attention was given to minimizing potential articular shoulder pain associated with intramedullary nailing.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early mobilization with protected weight-bearing as tolerated. Range of motion exercises were initiated early to prevent stiffness, with gradual progression to strengthening exercises.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail with distal interlocking screws.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 190 times
19 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Segmental Proximal Humerus and Shaft Fracture in a Rodeo Injury. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 26762406 Published Online Jul 19 2025.