Type 2 Open Distal Humerus Fracture with Posterior Approach and Osteotomy
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
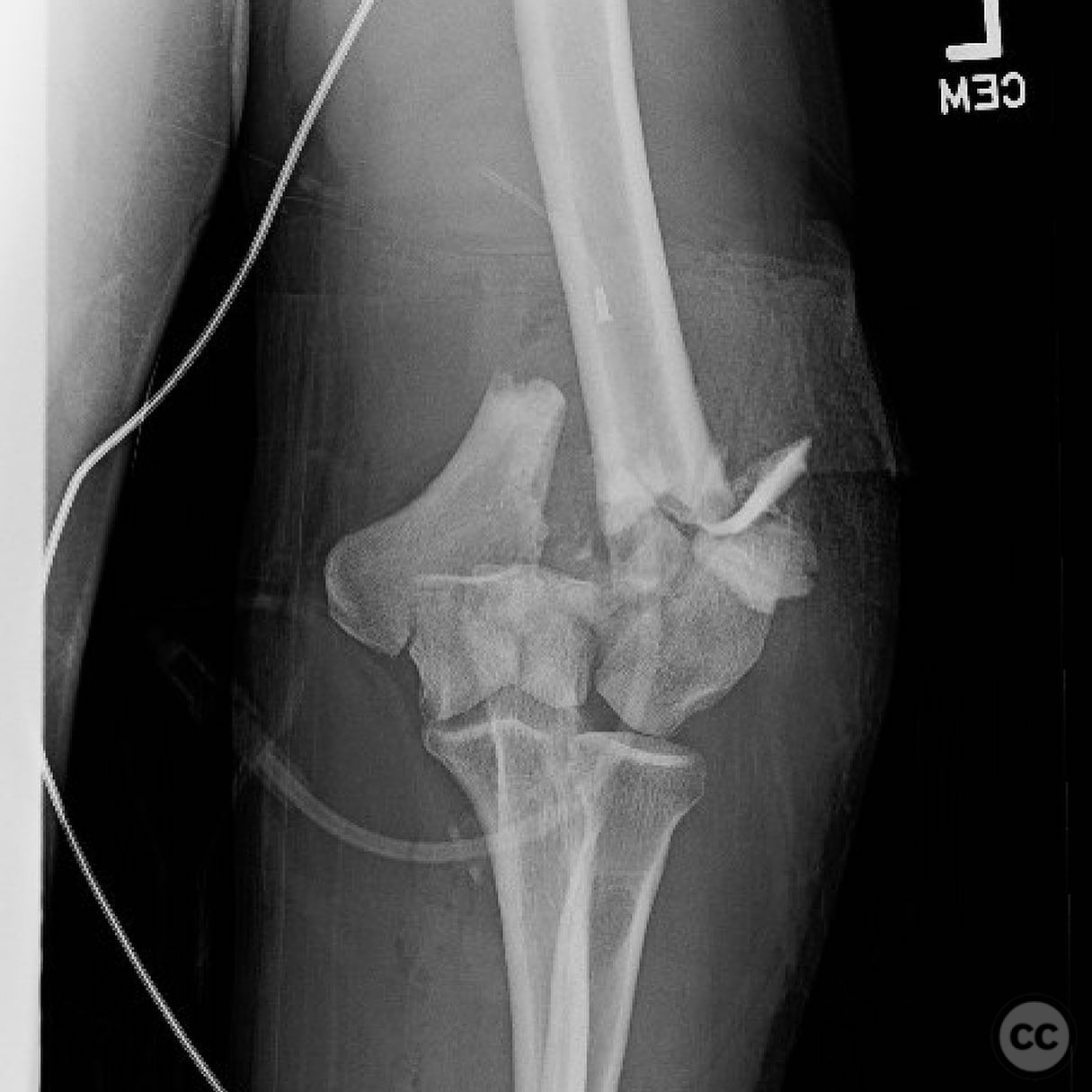
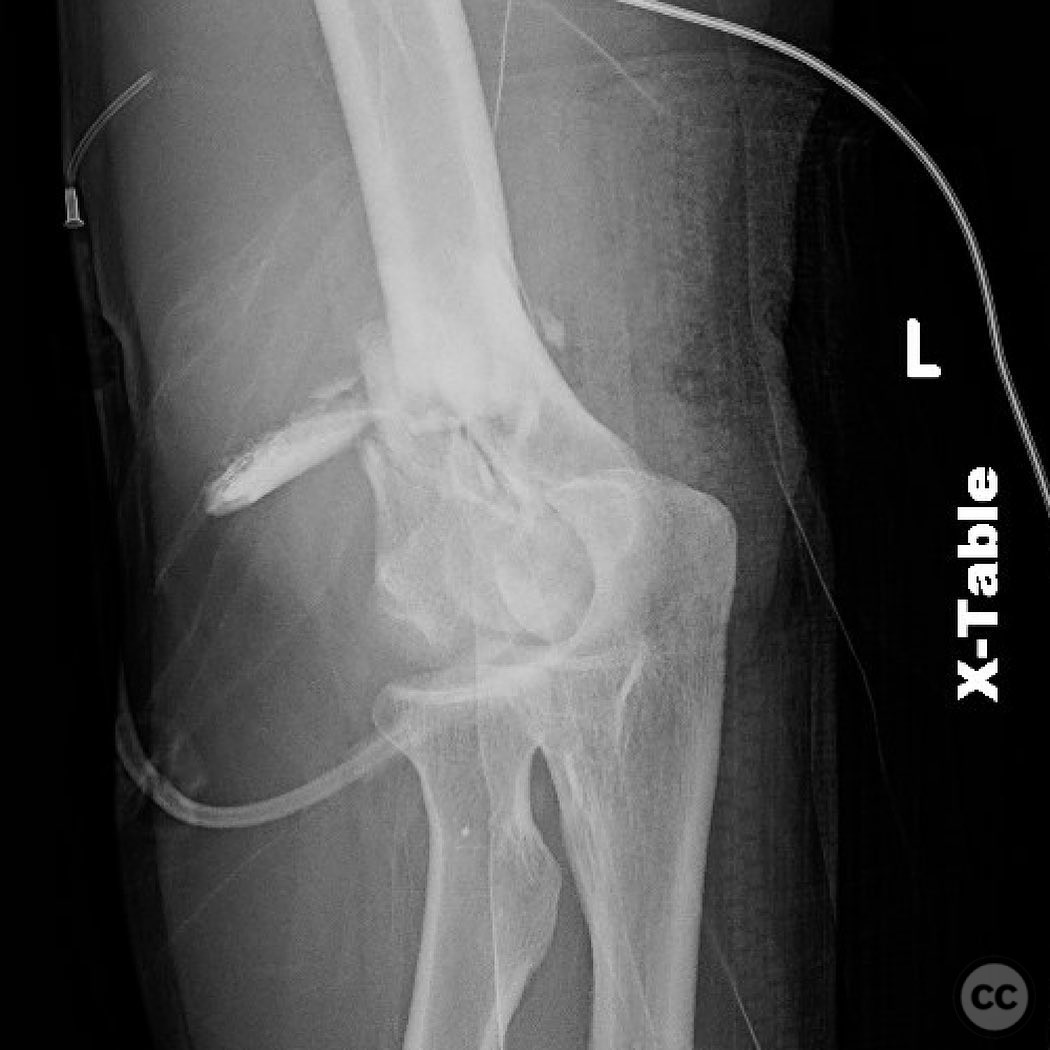
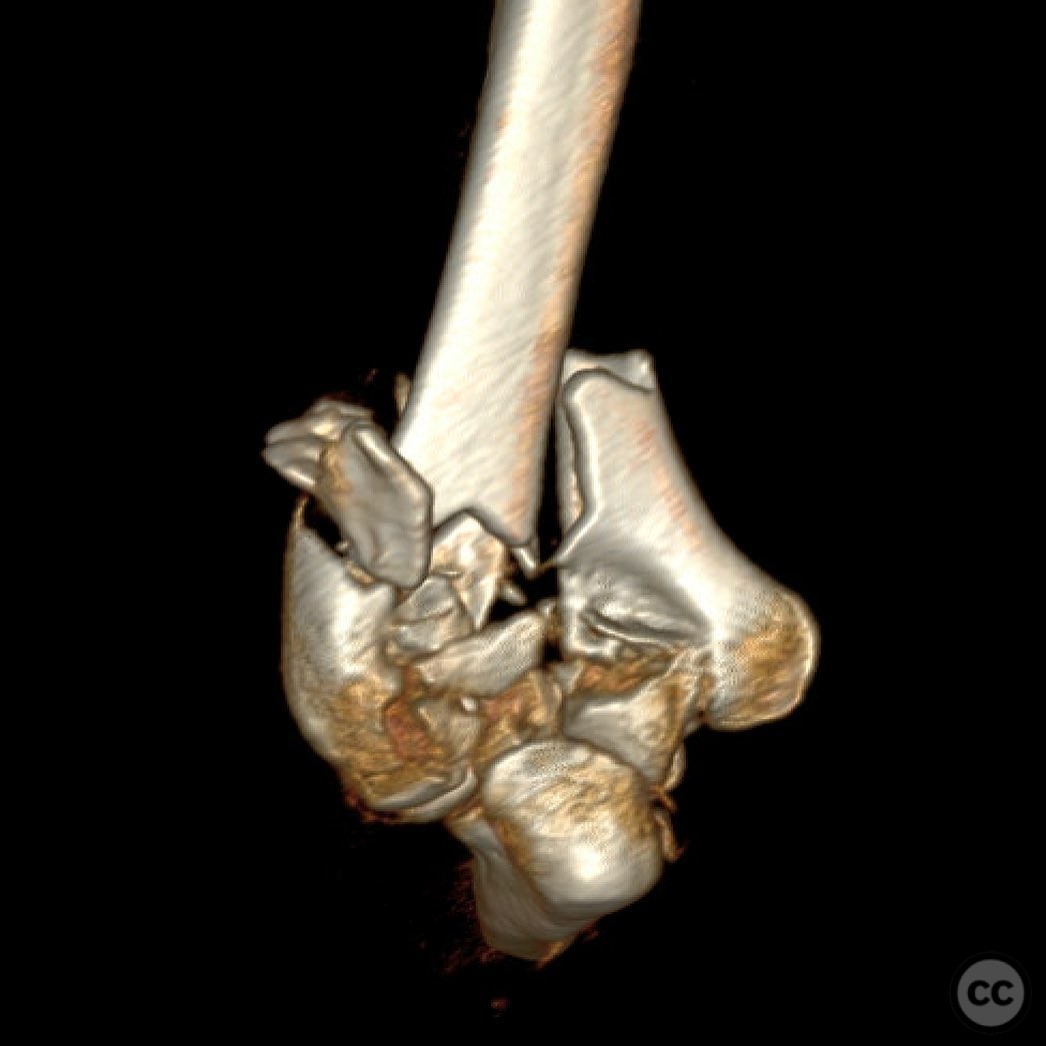
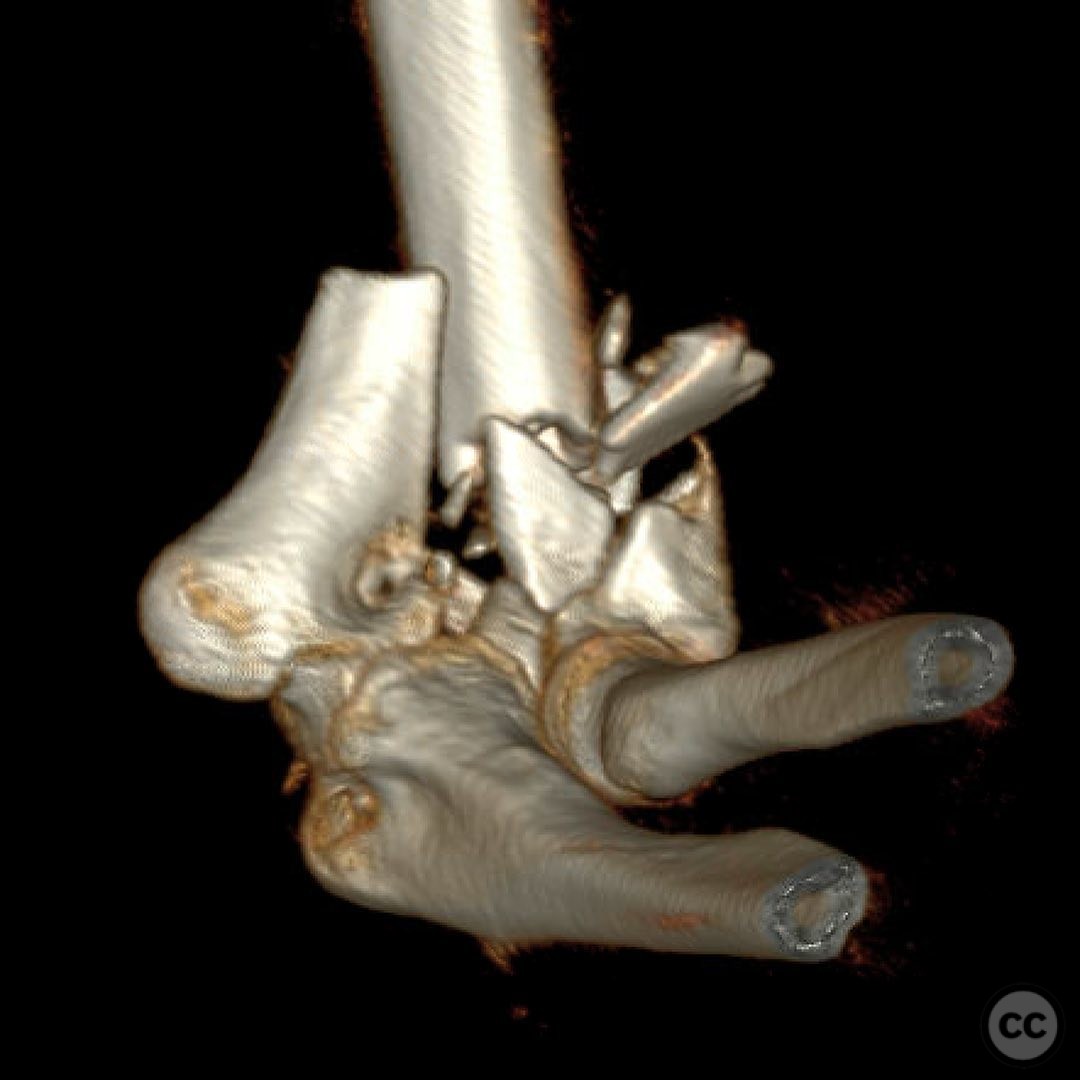
Clinical and radiological findings: The patient presented with a Type 2 open distal humerus fracture. Initial radiographs and clinical examination revealed a complex fracture pattern with significant articular fragmentation, particularly involving the trochlea and capitellum. The fracture was characterized by metaphyseal comminution and multifragmentary involvement of the lateral column. The neurovascular examination was unremarkable.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a direct posterior approach with an olecranon osteotomy to facilitate exposure and reduction of the articular surface. Given the complexity of the fracture, a flexible strategy for reduction and fixation was necessary, with potential use of fragment-specific fixation techniques.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned prone on the operating table, with the arm supported on a padded arm board to allow optimal access to the posterior aspect of the elbow.
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal posterior incision was made, followed by an olecranon osteotomy to enhance visualization of the distal humerus. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the fracture site, allowing for direct manipulation and reduction of the articular fragments.
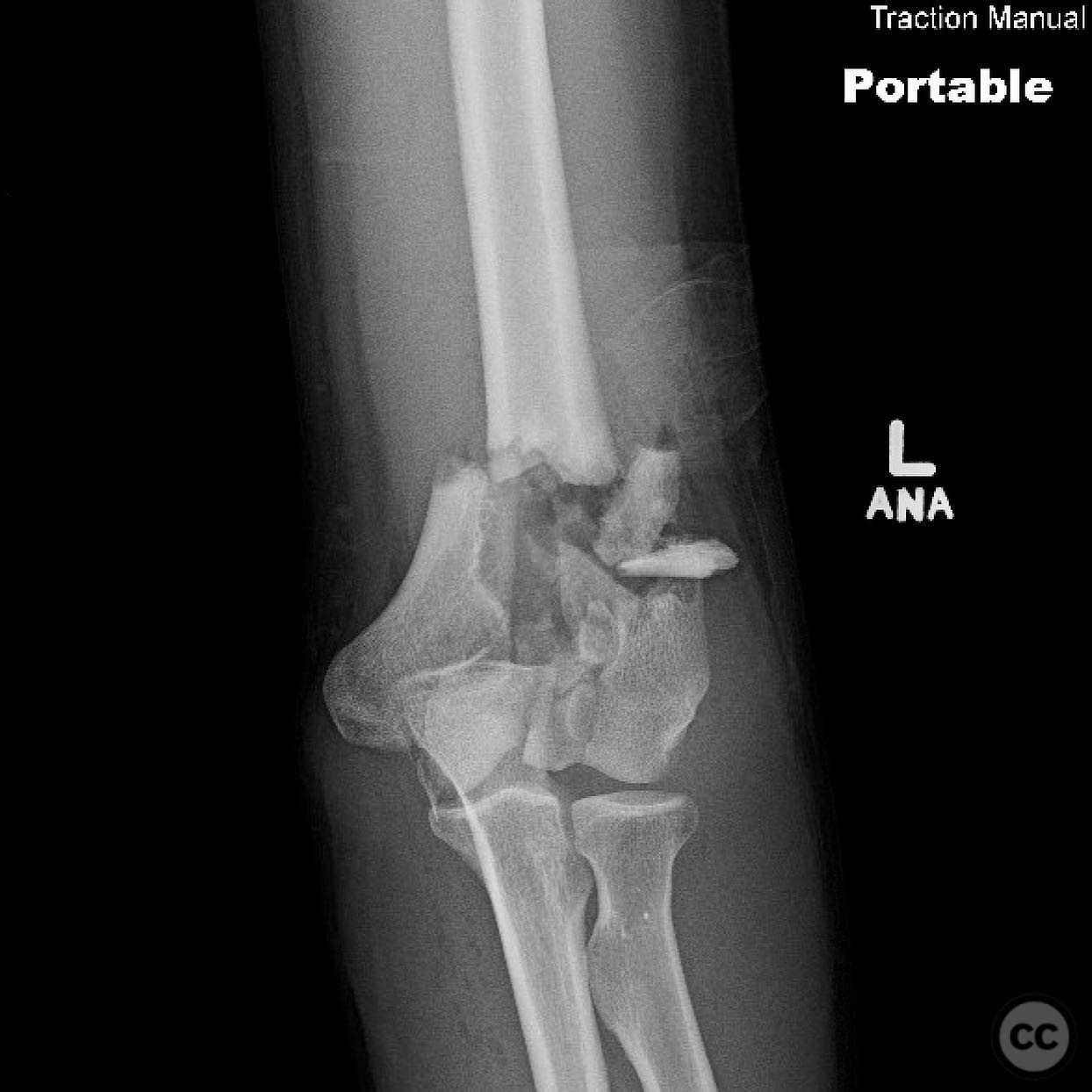
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted significant challenges due to the articular morphological variation and poor metaphyseal bone quality. Fragment-specific fixation was employed using threaded wires and mini fragment screws to reconstruct articular fragments into blocks. These blocks were then stabilized with locking screws through the plates. The surgeon emphasized the importance of being adaptable during the procedure, as initial plans often required modification based on intraoperative findings.
Postoperative protocol: The postoperative rehabilitation protocol focused on early mobilization. No splint was applied, and immediate range of motion exercises were initiated to promote joint function and prevent stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Locking plates, threaded wires, mini fragment screws.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_3.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_4.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_5.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_6.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_7.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_2.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_1.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_8.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguid_9.jpg)
 the idea that doing these case without an osteotomy is _cool_ or _slick_ is misguide(.jpg)
Article viewed 185 times
11 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Type 2 Open Distal Humerus Fracture with Posterior Approach and Osteotomy. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 23661059 Published Online Jul 11 2025.