Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture Treated with Antegrade Reconstruction Nail
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
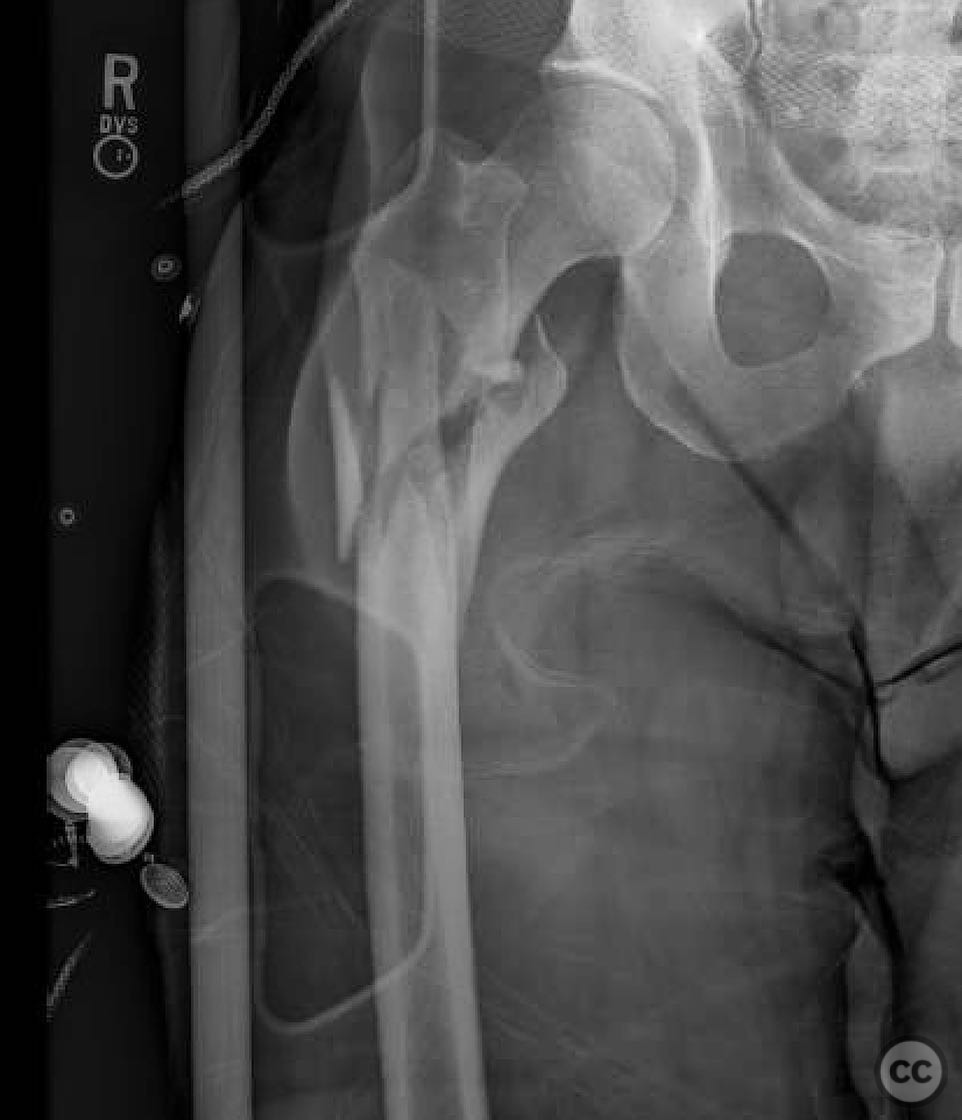
Clinical and radiological findings: A 51-year-old male was involved in a vehicular accident while riding a bicycle, resulting in a subtrochanteric femur fracture. The patient was otherwise healthy, and the injury was isolated with no significant soft tissue damage. Radiological assessment confirmed the subtrochanteric fracture, classified as AO/OTA 32-A3.
Preoperative Plan
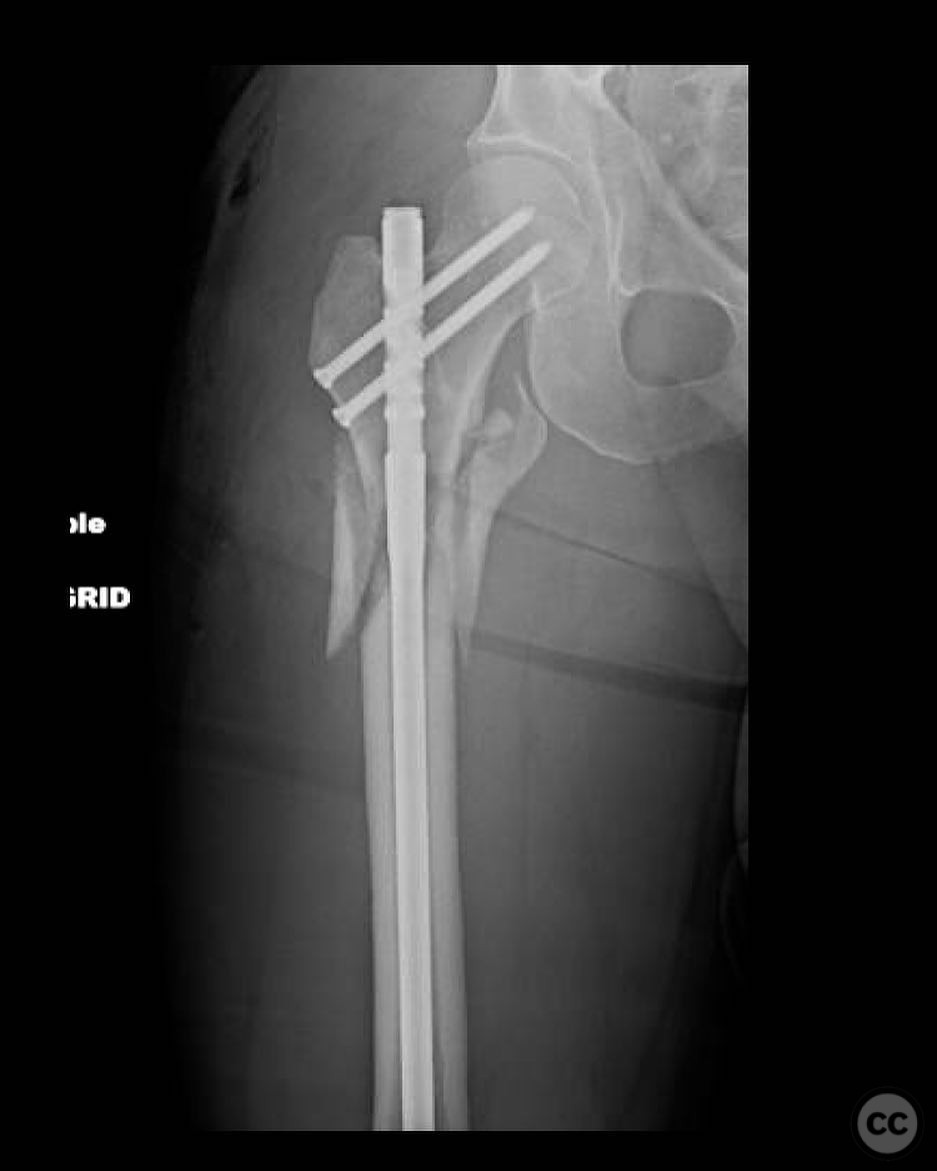
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a reamed piriformis entry antegrade reconstruction nail, statically locked. The surgical approach was planned to utilize the piriformis fossa for nail entry, assuming it remained intact, to minimize the risk of deformity during nail insertion. Closed reduction techniques were prioritized, with percutaneous methods such as bone hooks or schanz pins considered if necessary.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on a fracture table to facilitate traction and alignment during the procedure.
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal incision was made over the proximal femur, with careful dissection to expose the piriformis fossa. The entry point was prepared at the piriformis fossa for the antegrade nail insertion. Closed reduction was attempted first, with percutaneous tools employed as needed to achieve satisfactory alignment.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that closed reduction alone was often insufficient due to the deforming forces on the proximal segment. Percutaneous techniques were employed to aid in reduction. Cerclage wires were not used, as they were deemed unnecessary for maintaining reduction in this case. Preoperative measurements of the contralateral limb were utilized to ensure correct length and rotation.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was encouraged to begin weight-bearing as tolerated on the day of surgery, with progressive mobilization over the following weeks.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Reamed antegrade reconstruction nail, statically locked.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 182 times
26 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture Treated with Antegrade Reconstruction Nail. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 22480970 Published Online Jul 26 2025.