Complex Elbow Dislocation with Anteromedial Coronoid Facet Fracture and Ligamentous Injury.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
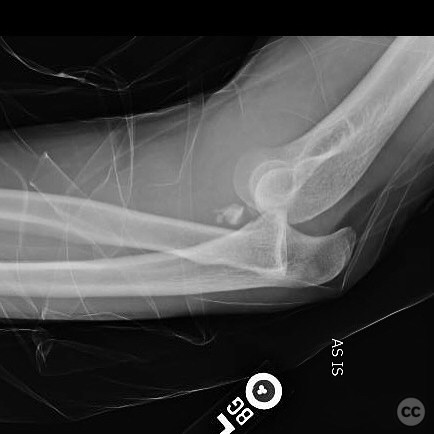
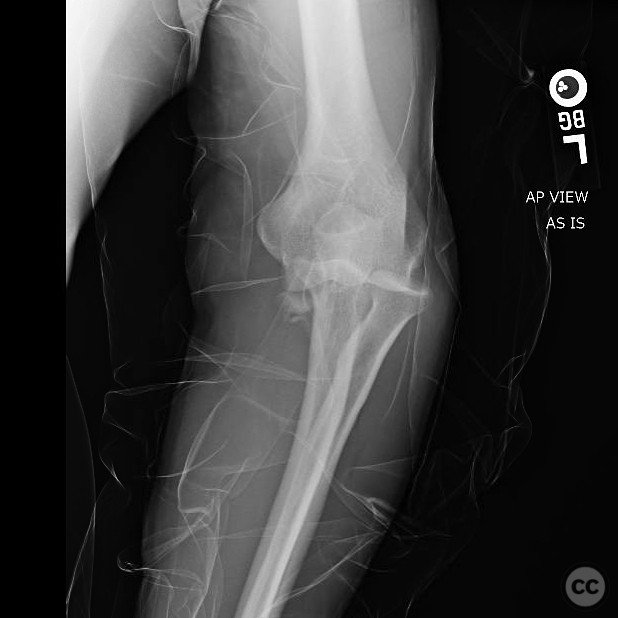
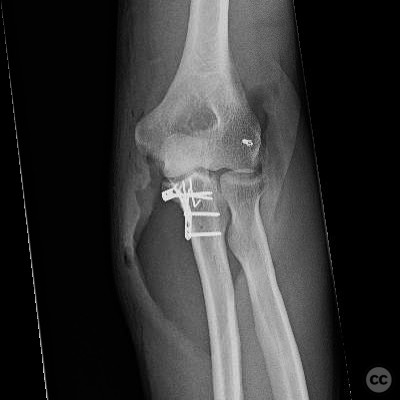
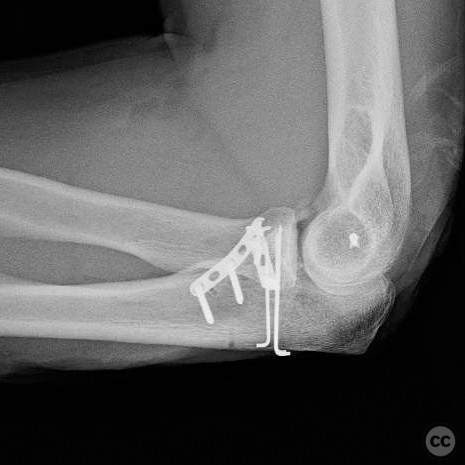
Clinical and radiological findings: A 40-year-old male sustained an injury after being knocked off a table during a bar altercation, landing on an outstretched arm. Initial clinical examination revealed a posterolateral elbow dislocation with significant swelling and tenderness. Radiographs confirmed the presence of an anteromedial coronoid facet fracture and a coronoid tip fracture (type 1), without involvement of the radial head or neck. The injury was suggestive of both posteromedial and posterolateral rotatory instability.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved addressing the coronoid fractures and associated ligamentous injuries. The surgical approach was planned to be through an anteromedial incision to allow direct access to the coronoid process for open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of the anteromedial facet fracture, as well as repair of the lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL).
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with the affected arm placed on a hand table, allowing for full access to the medial and lateral aspects of the elbow.
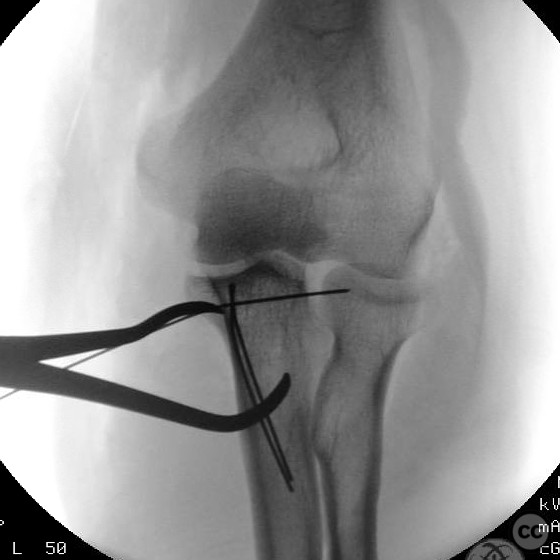
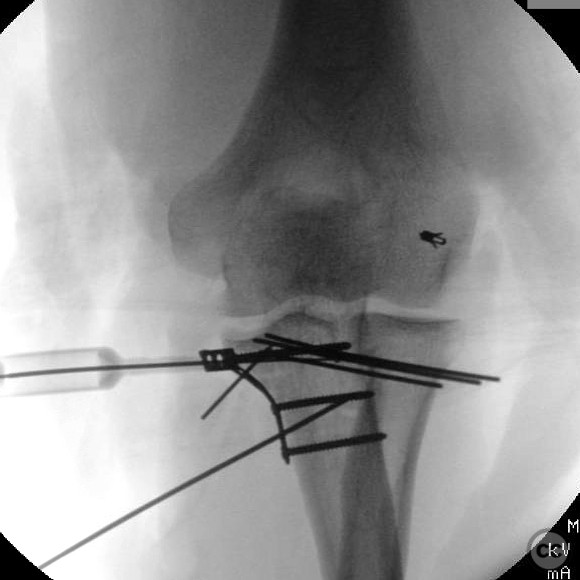
Anatomical surgical approach: A medial approach to the elbow was performed, involving a longitudinal incision over the medial epicondyle. Subperiosteal dissection was carried out to expose the anteromedial coronoid facet. Bone tunnels were created for suture repair of the coronoid tip fracture. ORIF of the anteromedial facet was performed, followed by reinforcement with suture repair of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) through additional bone tunnels. The LUCL was repaired via a lateral approach.
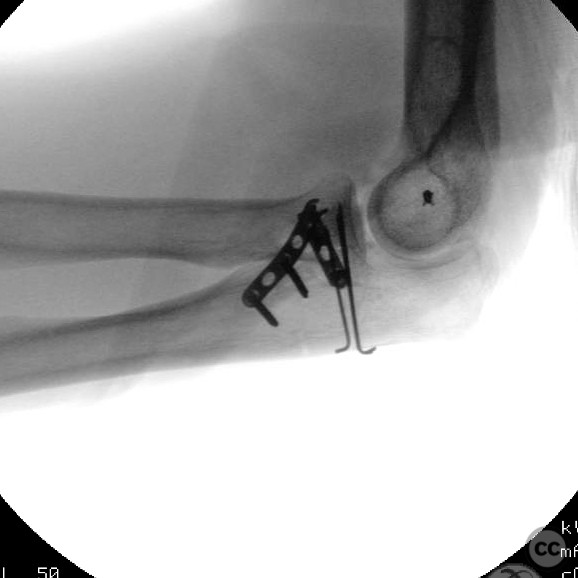
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that despite the complex nature of the injury, successful stabilization was achieved without the need for a static external fixator. The coronoid tip was exploited through the anteromedial facet fracture for suture repair, which was not tensioned or tied until all other repairs were completed. Stability of the elbow was confirmed intraoperatively following repair of the LUCL.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was placed in a hinged elbow brace allowing for early range of motion exercises. Weight-bearing restrictions were maintained for six weeks, with gradual progression to full weight-bearing as tolerated.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included screws for ORIF of the anteromedial coronoid facet and suture anchors for ligamentous repairs.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 186 times
26 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Complex Elbow Dislocation with Anteromedial Coronoid Facet Fracture and Ligamentous Injury.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 19727874 Published Online Jul 26 2025.