Distal Tibia Fracture with Plafond Involvement: Nailing and Plafond Fixation
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
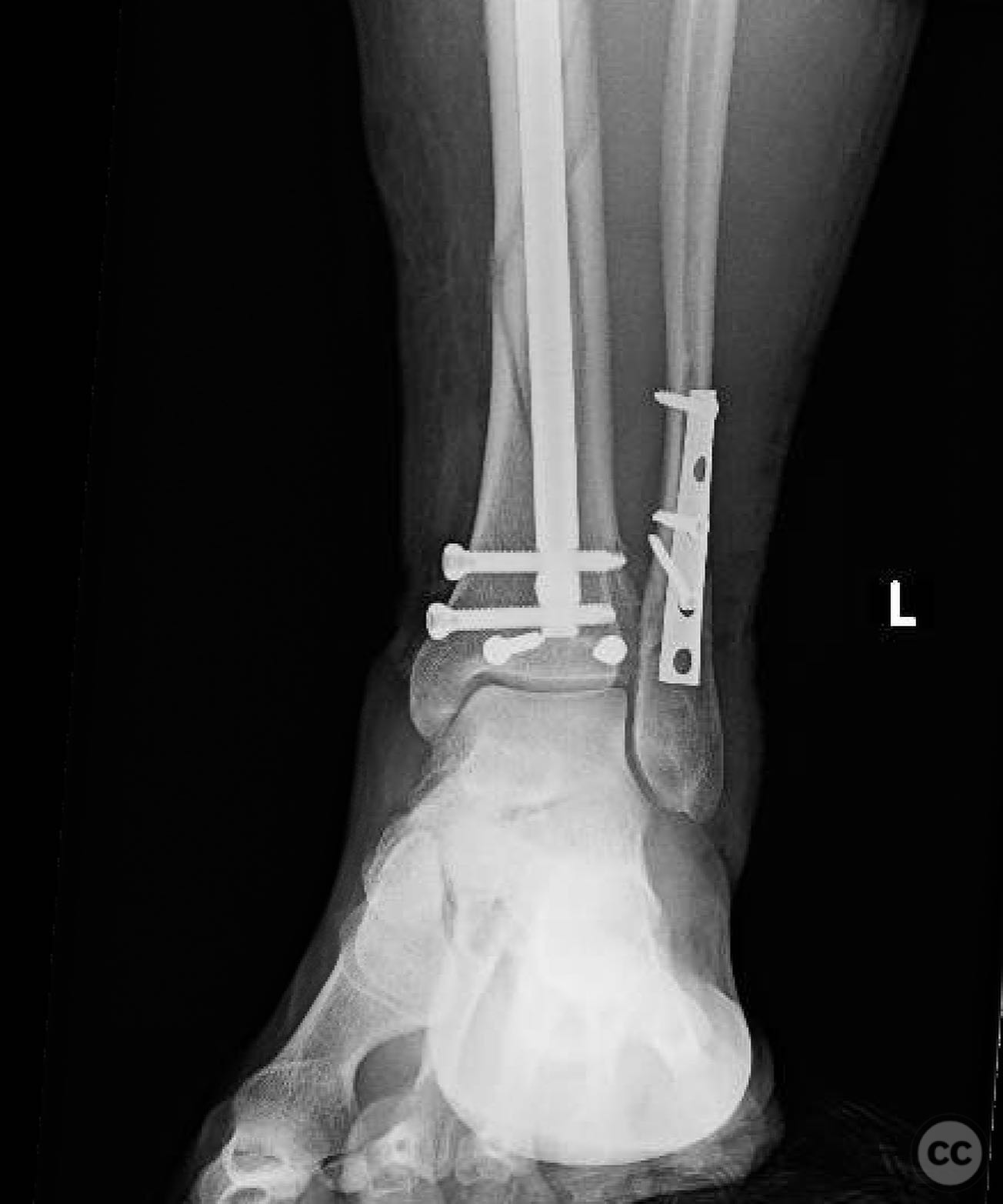
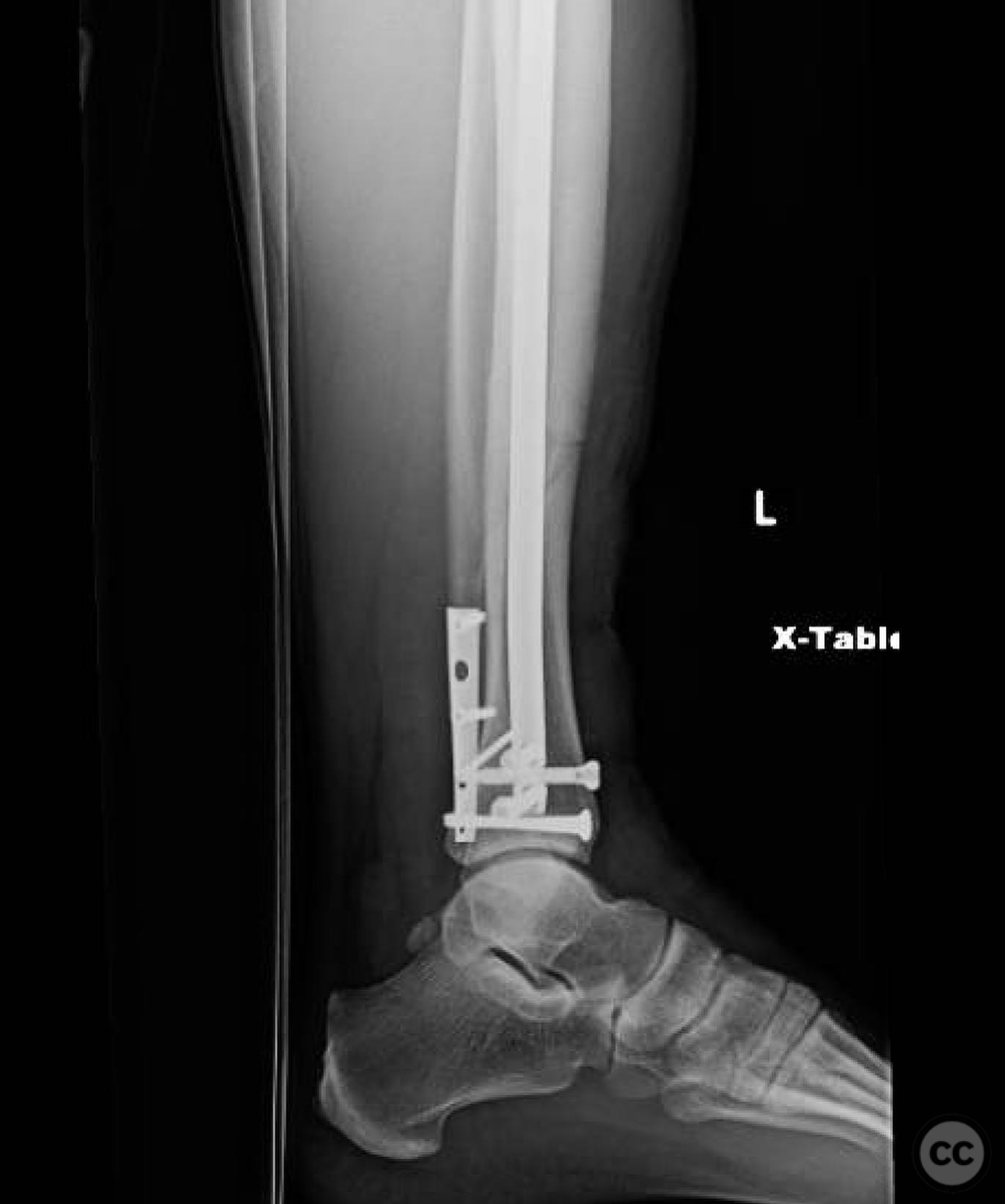
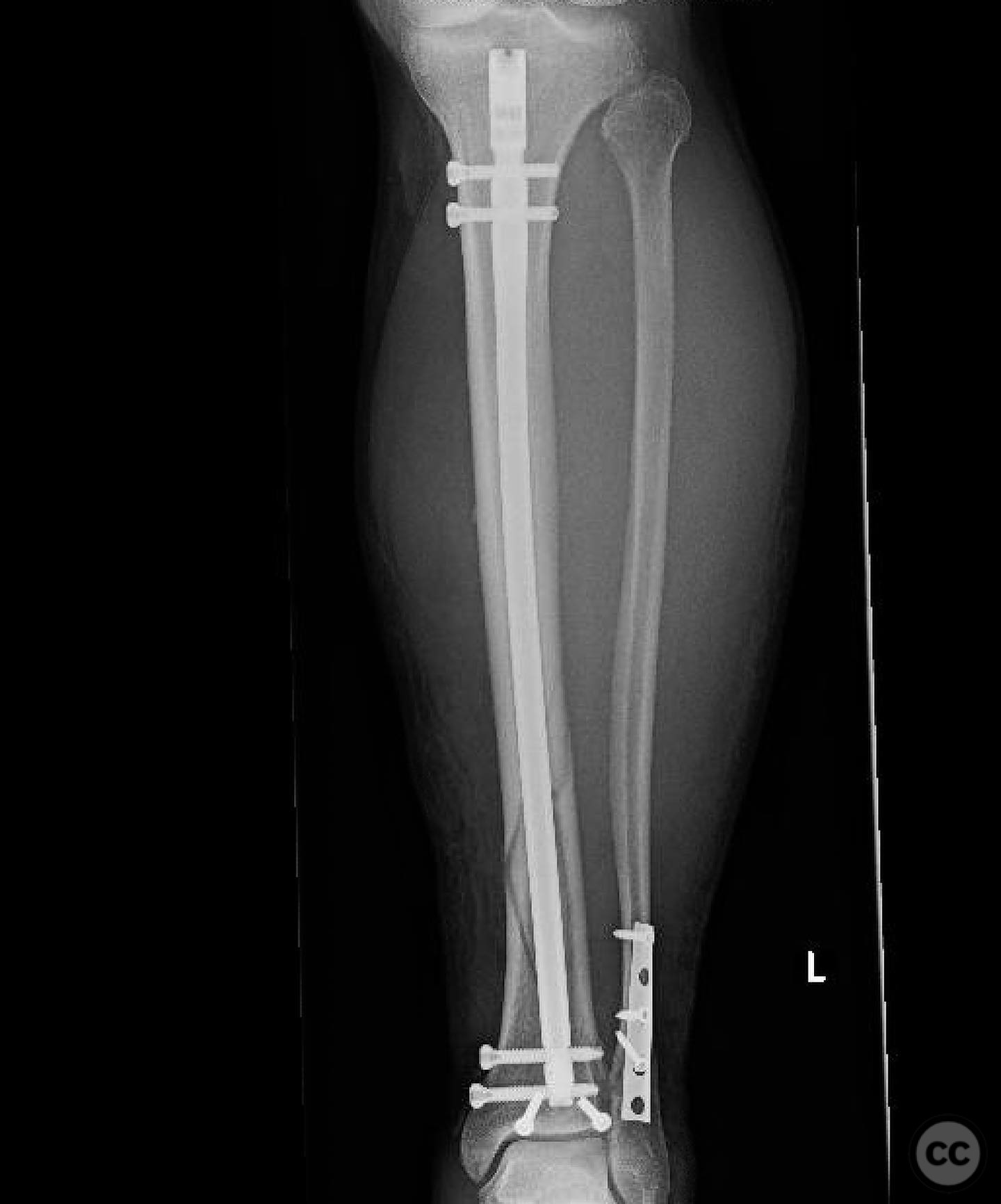
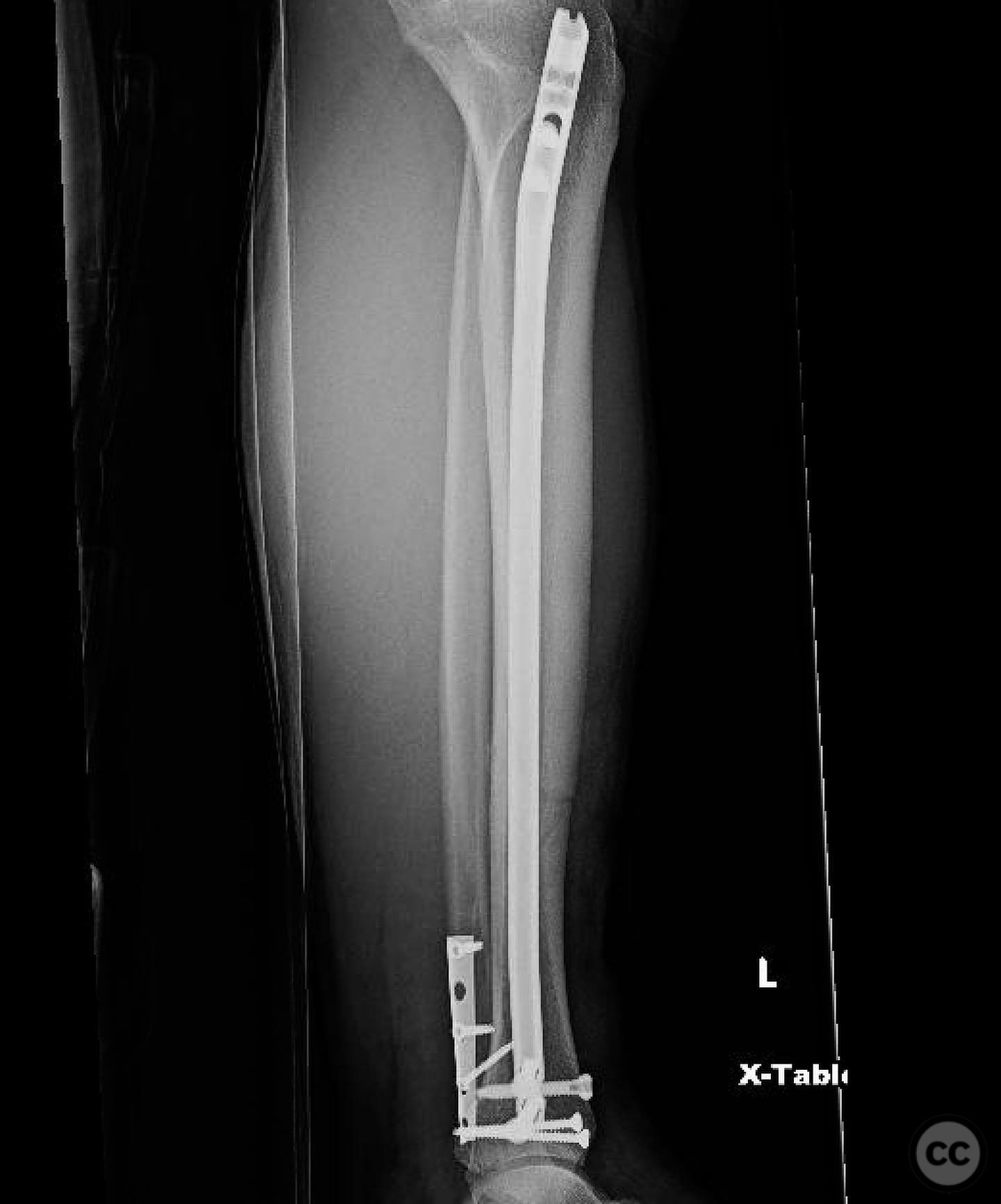
Clinical and radiological findings: A patient presented with an oblique distal third tibia fracture involving the plafond, resulting from a torsional mechanism. Initial radiographs suggested posterior malleolar and ankle involvement, prompting a CT scan for detailed assessment. The fracture was classified as AO/OTA 43-C2, indicating a complex articular involvement.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved treating the tibia and ankle as independent injuries. The tibial fracture required restoration of length, alignment, and rotation with a relatively stable construct to allow secondary bone healing. The ankle necessitated an anatomic reduction and stable fixation to ensure tibiotalar longevity. The plan included placing screws across the plafond prior to intramedullary nailing of the tibia.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with the knee in semi-extension to facilitate a lateral extra-articular parapatellar approach for intramedullary nailing.
Anatomical surgical approach: A lateral extra-articular parapatellar approach was utilized, avoiding instrumentation through the patellofemoral joint. This approach provided access for intramedullary nailing of the tibia while allowing separate fixation of the plafond with screws.
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of treating the tibia and ankle as separate entities despite their mechanical interrelation. The decision to use intramedullary nailing was based on its mechanical advantages and familiarity, although plating was acknowledged as a viable alternative. The surgeon preferred the lateral extra-articular parapatellar approach over retropatellar due to its reduced impact on the knee joint and ease of use during nailing.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was instructed to maintain touch weight-bearing for 4 weeks, progressing to partial weight-bearing by week 5, and full weight-bearing by week 6. Range of motion exercises for the ankle were initiated early to prevent stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Intramedullary nail, screws for plafond fixation.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
_0.jpg)
_2.jpg)
_3.jpg)
_1.jpg)
Article viewed 197 times
14 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Distal Tibia Fracture with Plafond Involvement: Nailing and Plafond Fixation. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 17537515 Published Online Jul 14 2025.