Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture with Plantar Medial Tuberosity Involvement
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
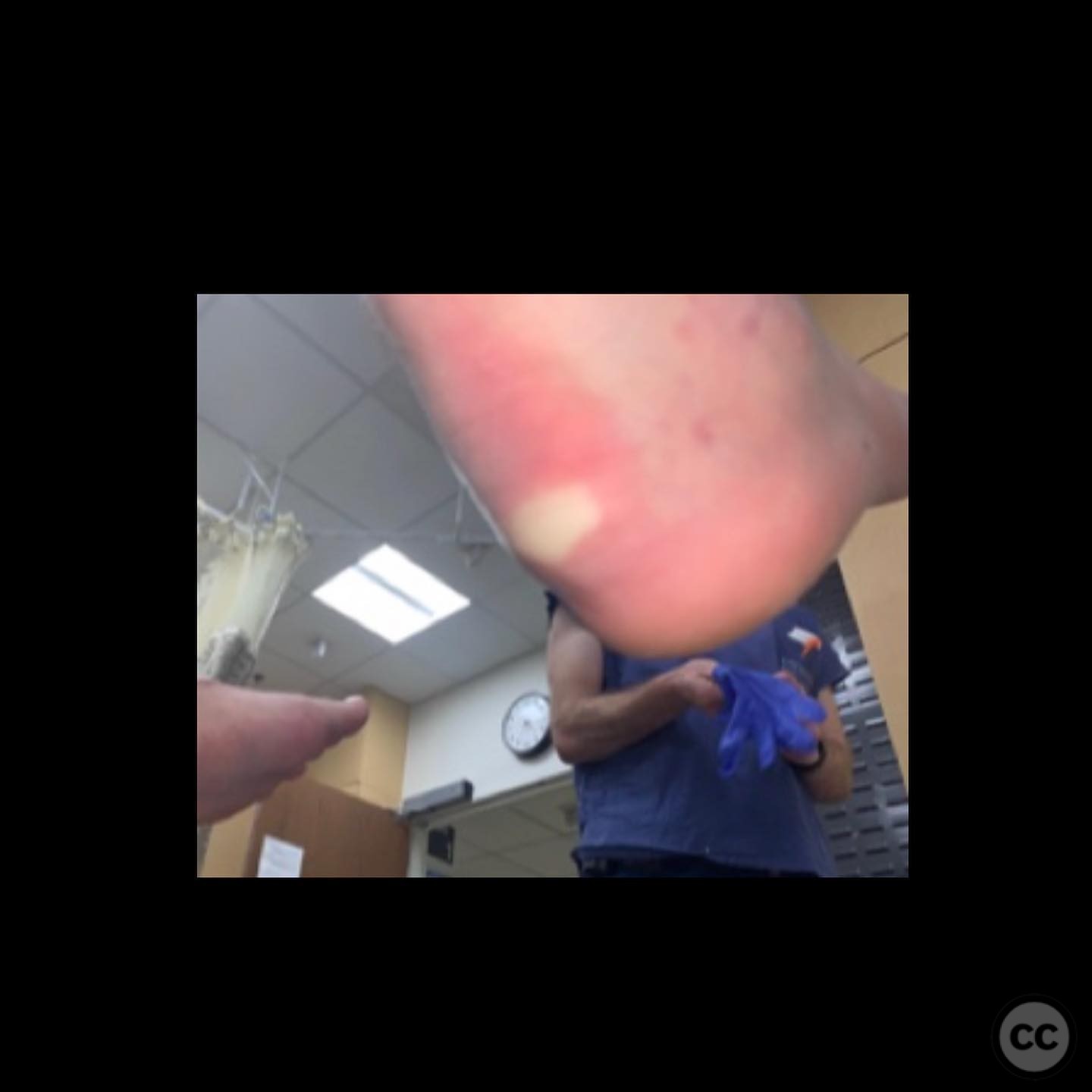
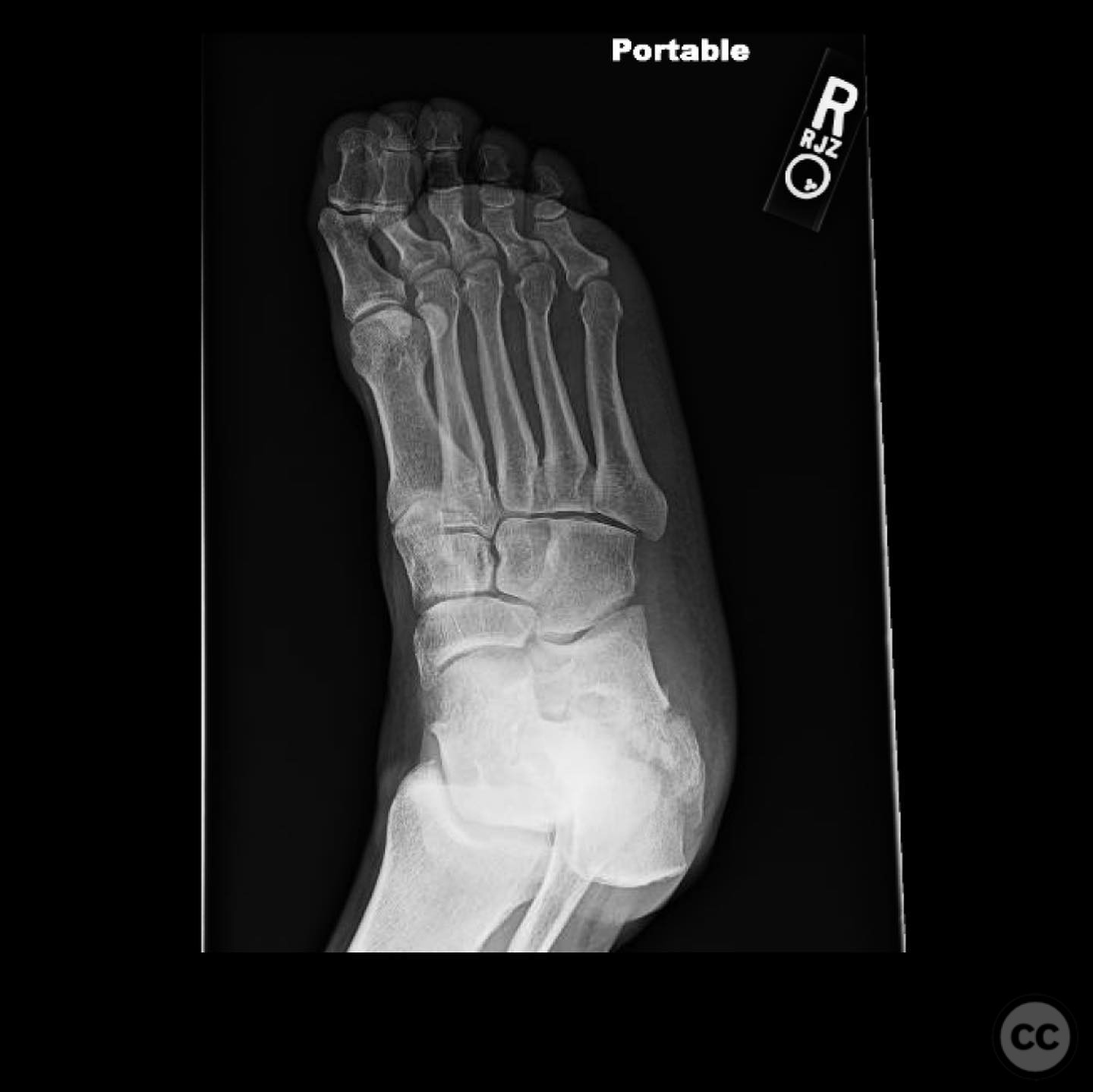
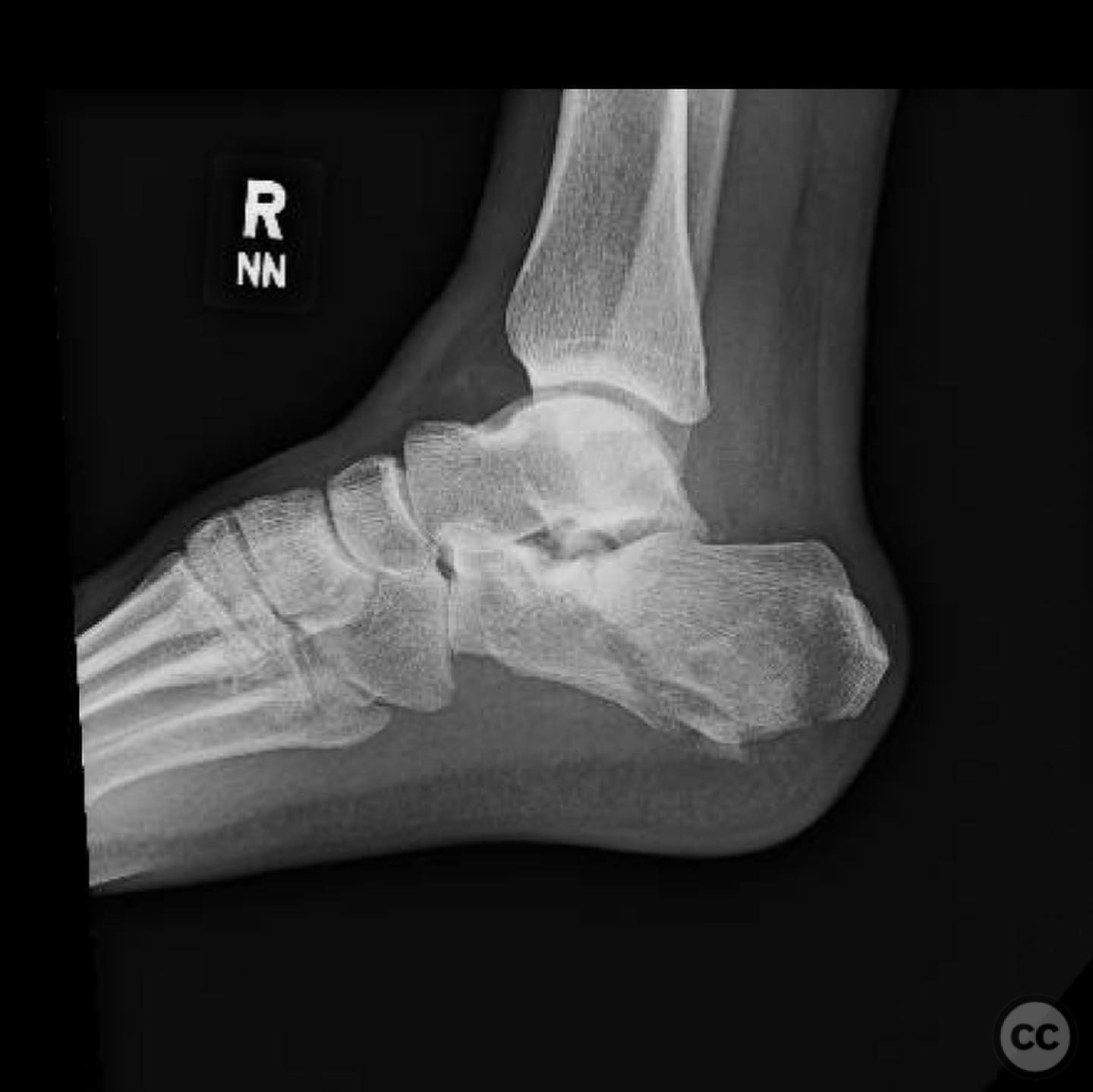
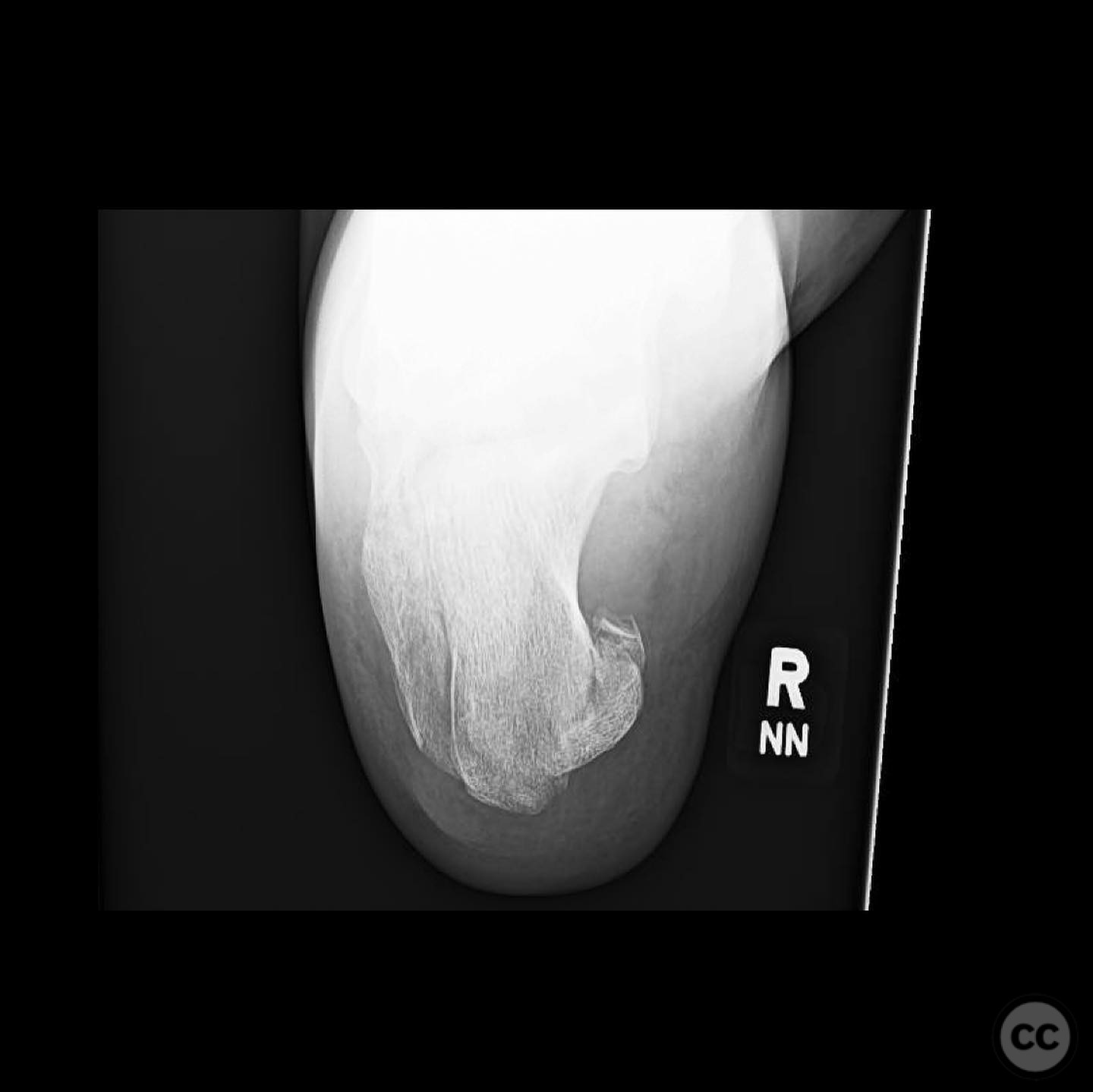
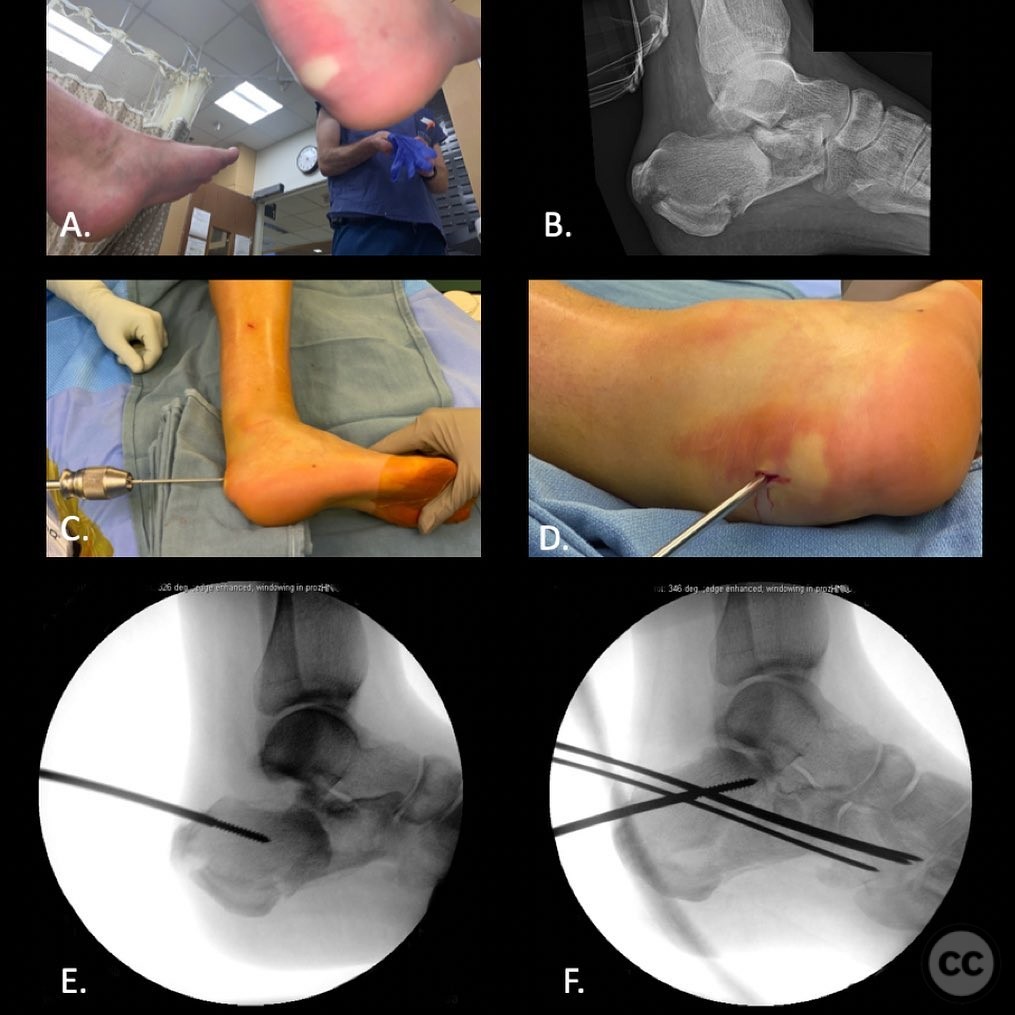
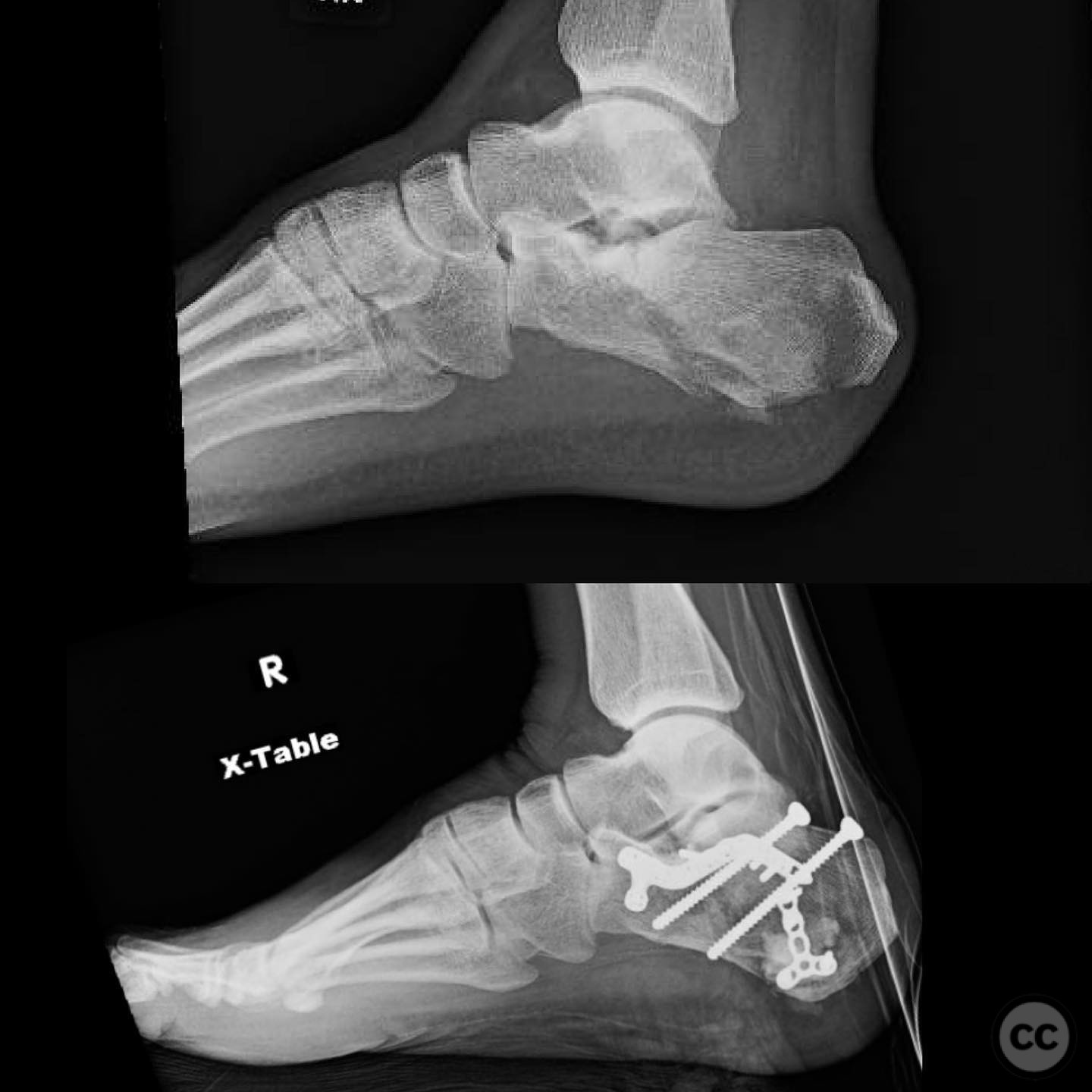
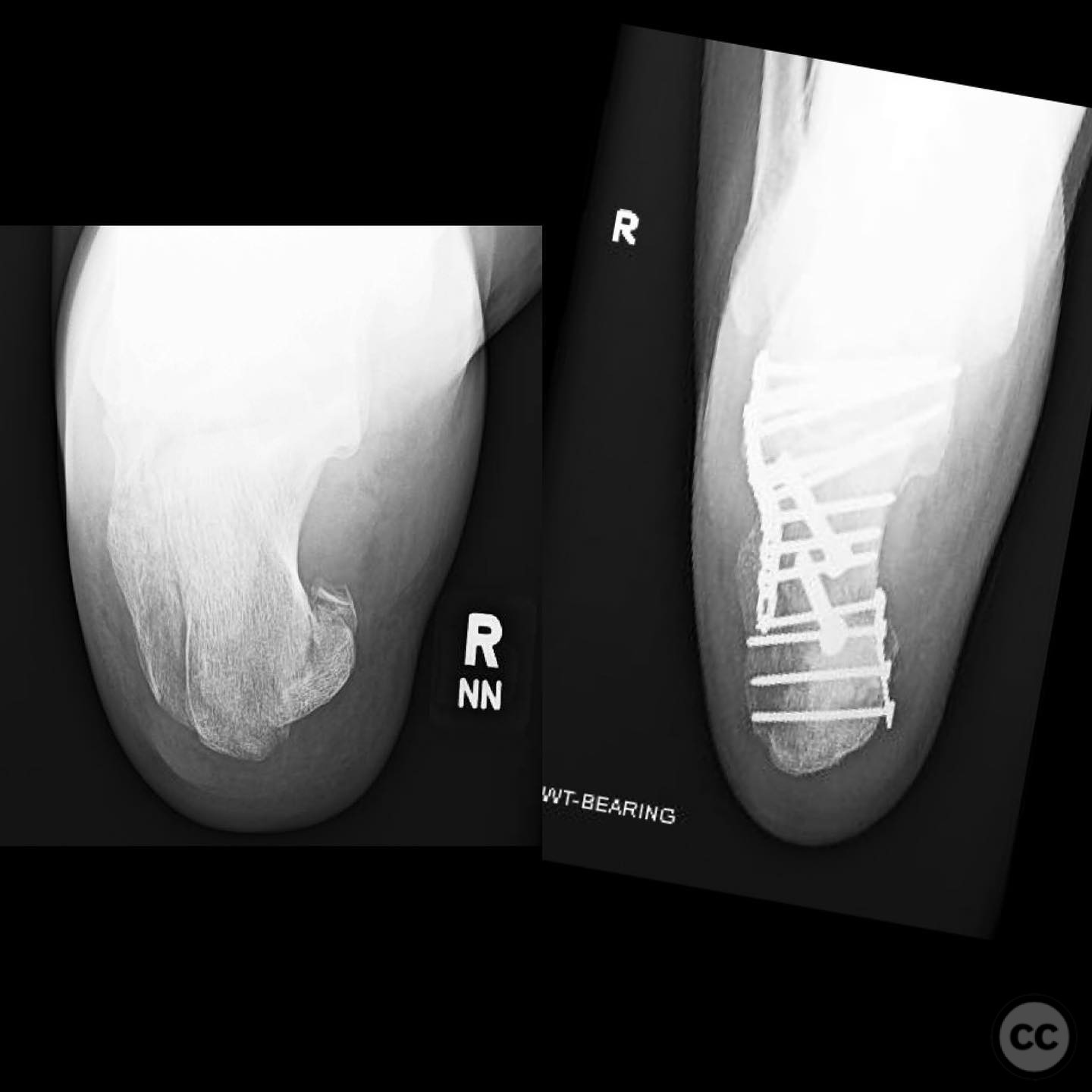
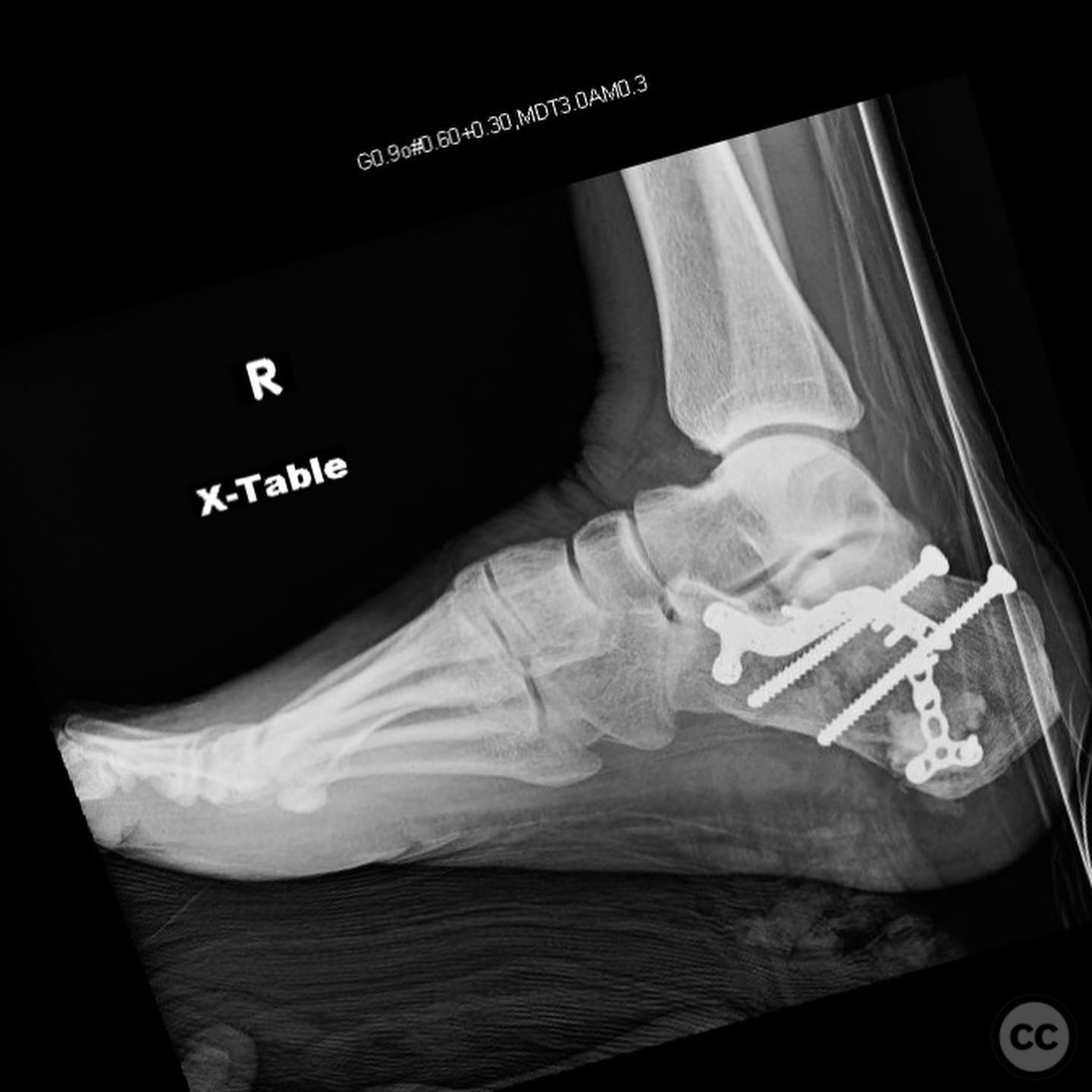
Clinical and radiological findings: A male patient in his 40s, otherwise healthy, sustained a fall from a ladder resulting in a calcaneal fracture. Initial clinical examination revealed significant blanching of the skin overlying the heel, indicating ischemic pressure and necessitating urgent surgical intervention. Radiographs demonstrated a tongue-type calcaneal fracture with modest displacement. The fracture pattern was consistent with a Sanders Type II classification, and the presence of a plantar medial tuberosity fracture was noted.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved an urgent reduction of the tongue-type fracture to relieve ischemic pressure on the skin. A lateral approach to the calcaneus was planned to allow for direct manipulation and fixation of the fracture fragments. The plantar medial tuberosity fragment was also identified for fixation due to its displacement and potential impact on foot biomechanics.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned prone on the operating table to facilitate access to the posterior aspect of the calcaneus.
Anatomical surgical approach: A lateral approach to the calcaneus was performed. A longitudinal incision was made over the lateral aspect of the heel, extending from the posterior superior corner of the calcaneus towards the cuboid. The sural nerve was identified and protected. The peroneal tendons were retracted, and a subperiosteal dissection was carried out to expose the lateral wall of the calcaneus.
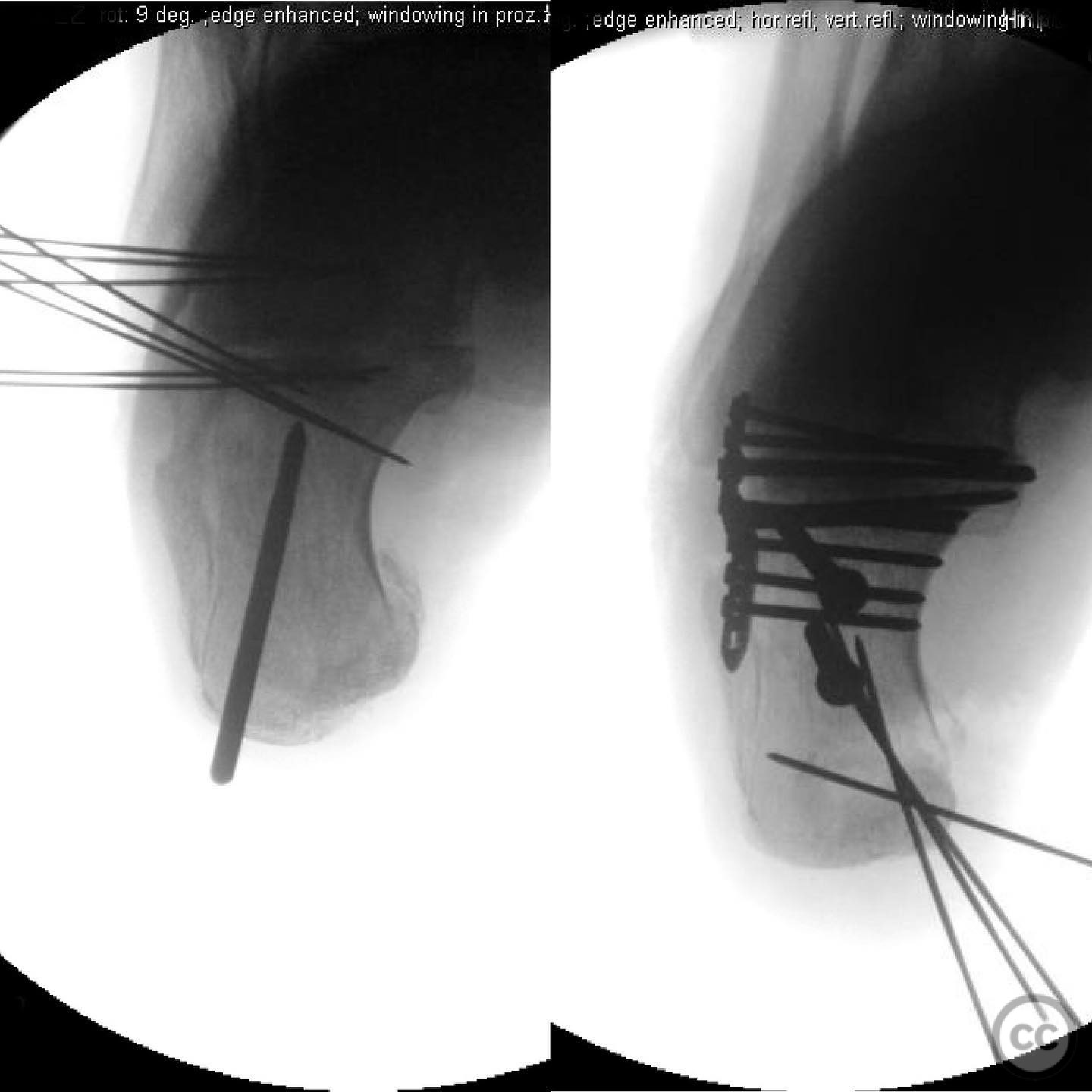
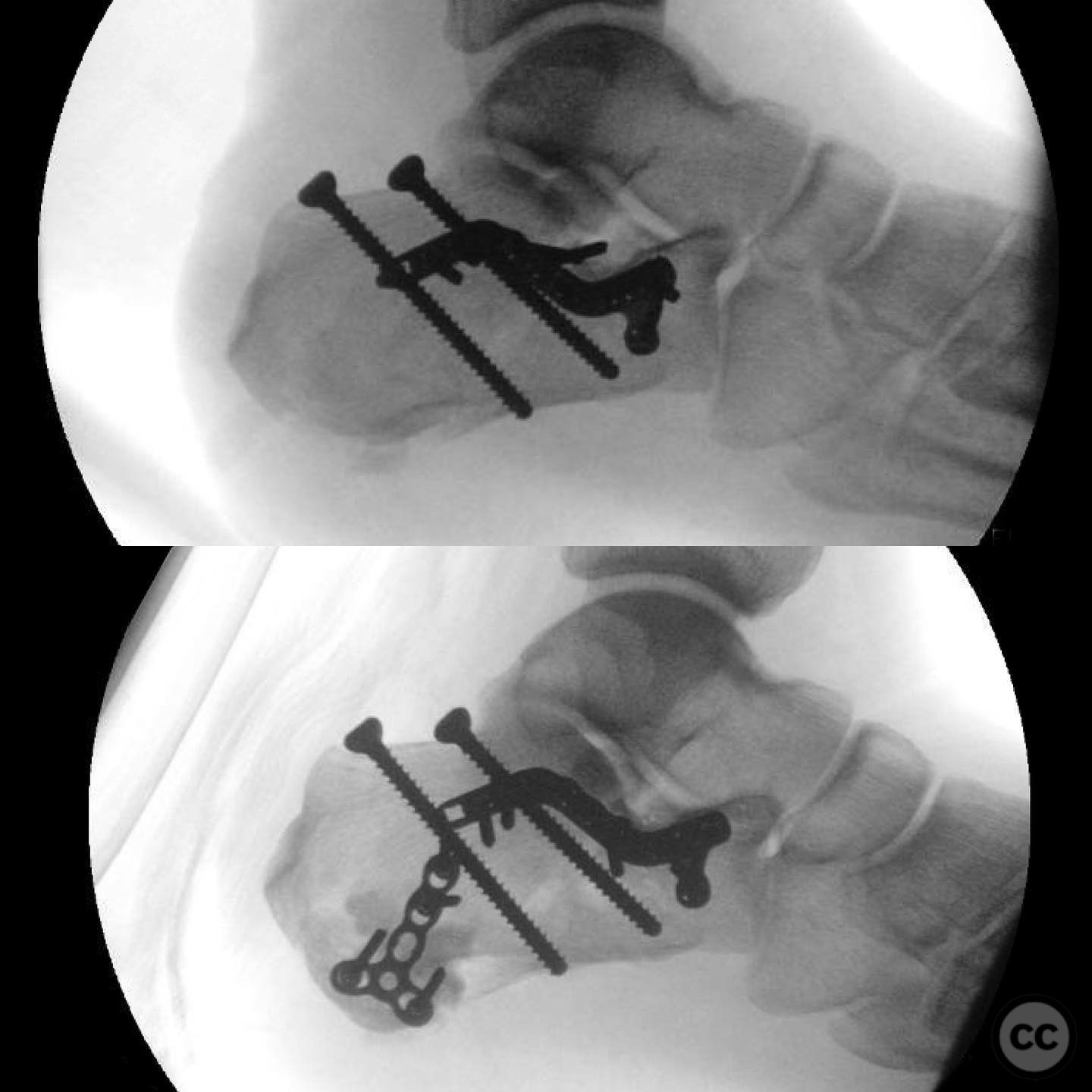
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that the skin blanching indicated an urgent need for reduction to prevent necrosis. A gastrocnemius recession was performed to aid in reduction. A 4.5mm Schanz pin was inserted along the long axis of the tongue fragment, allowing for manipulation and reduction of the fracture. The fragment was then pinned into the cuboid for stabilization. The plantar medial tuberosity fragment, which was large and displaced, was also fixed to restore calcaneal height and prevent biomechanical complications.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was placed in a splint with non-weight bearing status on the affected limb for 6 weeks. Progressive weight bearing was initiated thereafter, with physical therapy focusing on range of motion and strengthening exercises.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: 4.5mm Schanz pin, Kirschner wires for pinning into cuboid.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities


Article viewed 161 times
14 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture with Plantar Medial Tuberosity Involvement. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 14427754 Published Online Jul 14 2025.