Displaced Pediatric Femoral Neck Fracture in an 8-Year-Old Boy
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
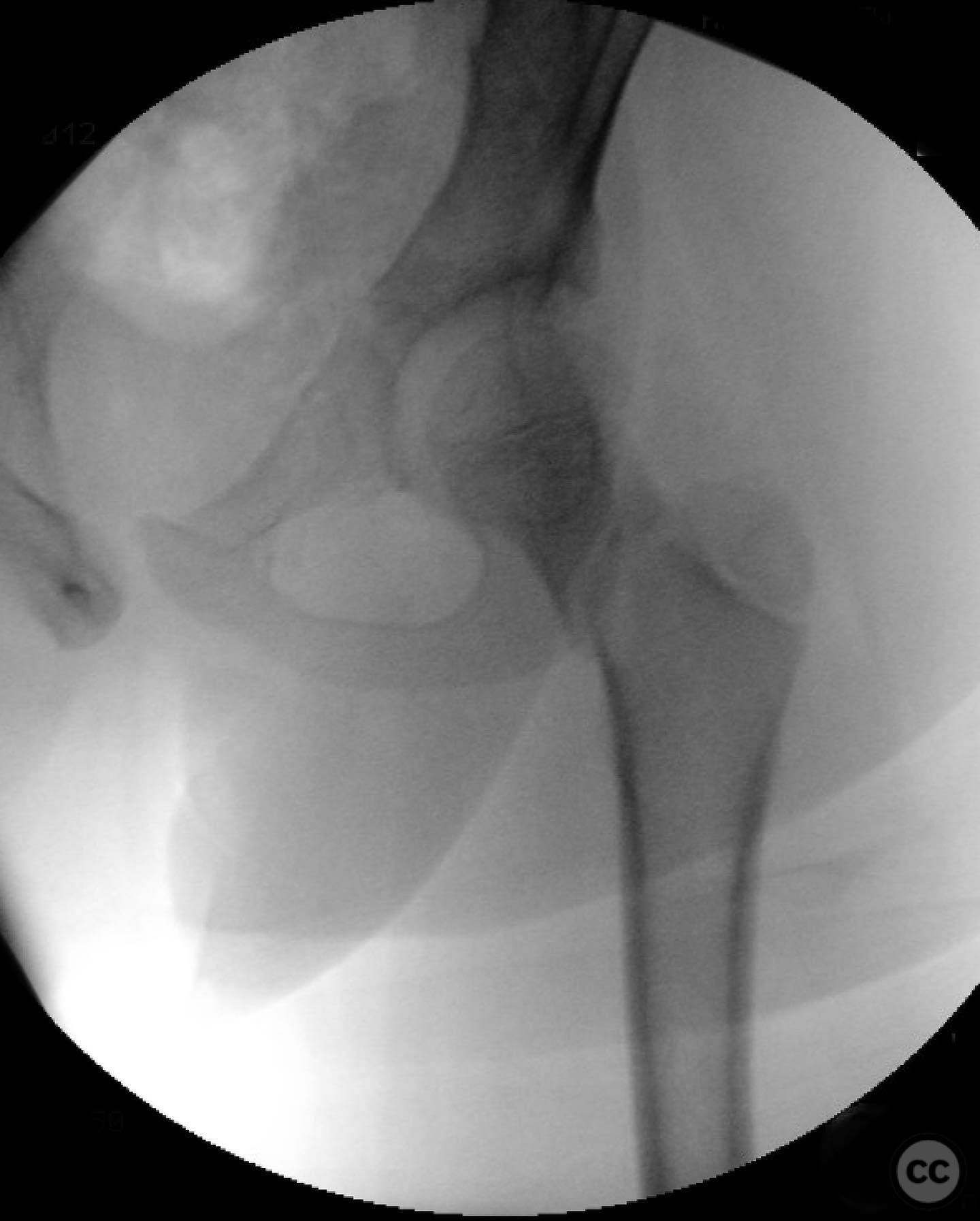
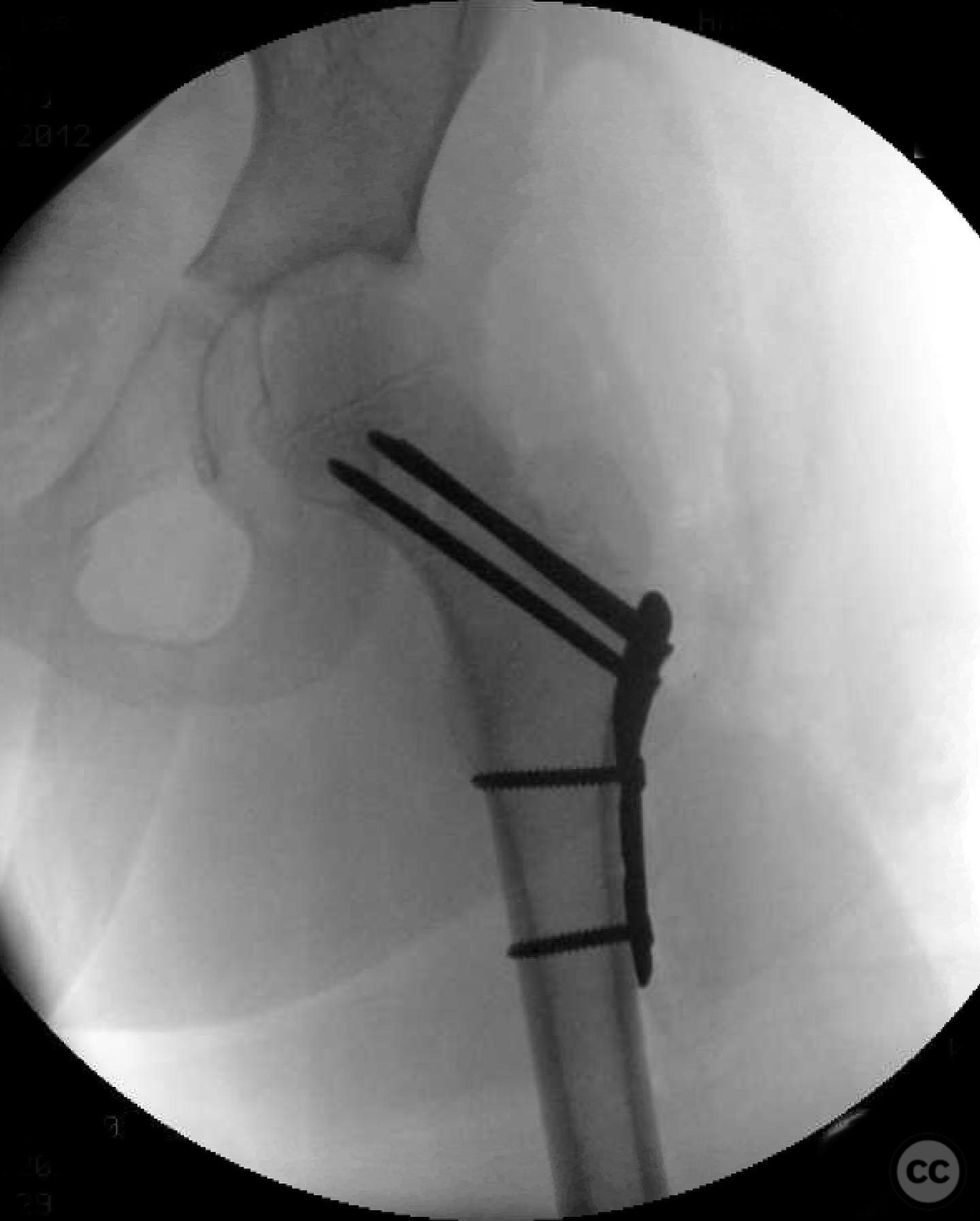
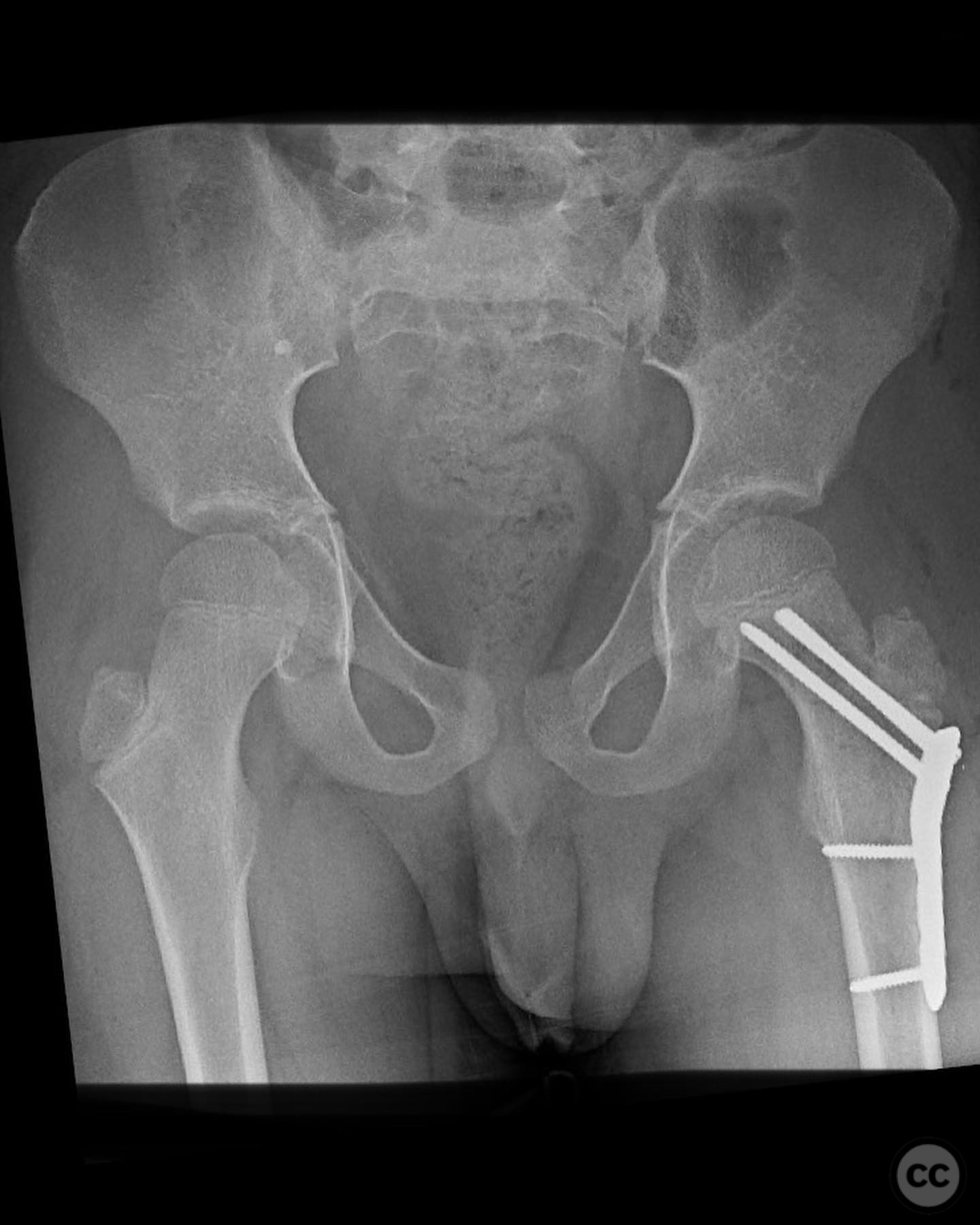
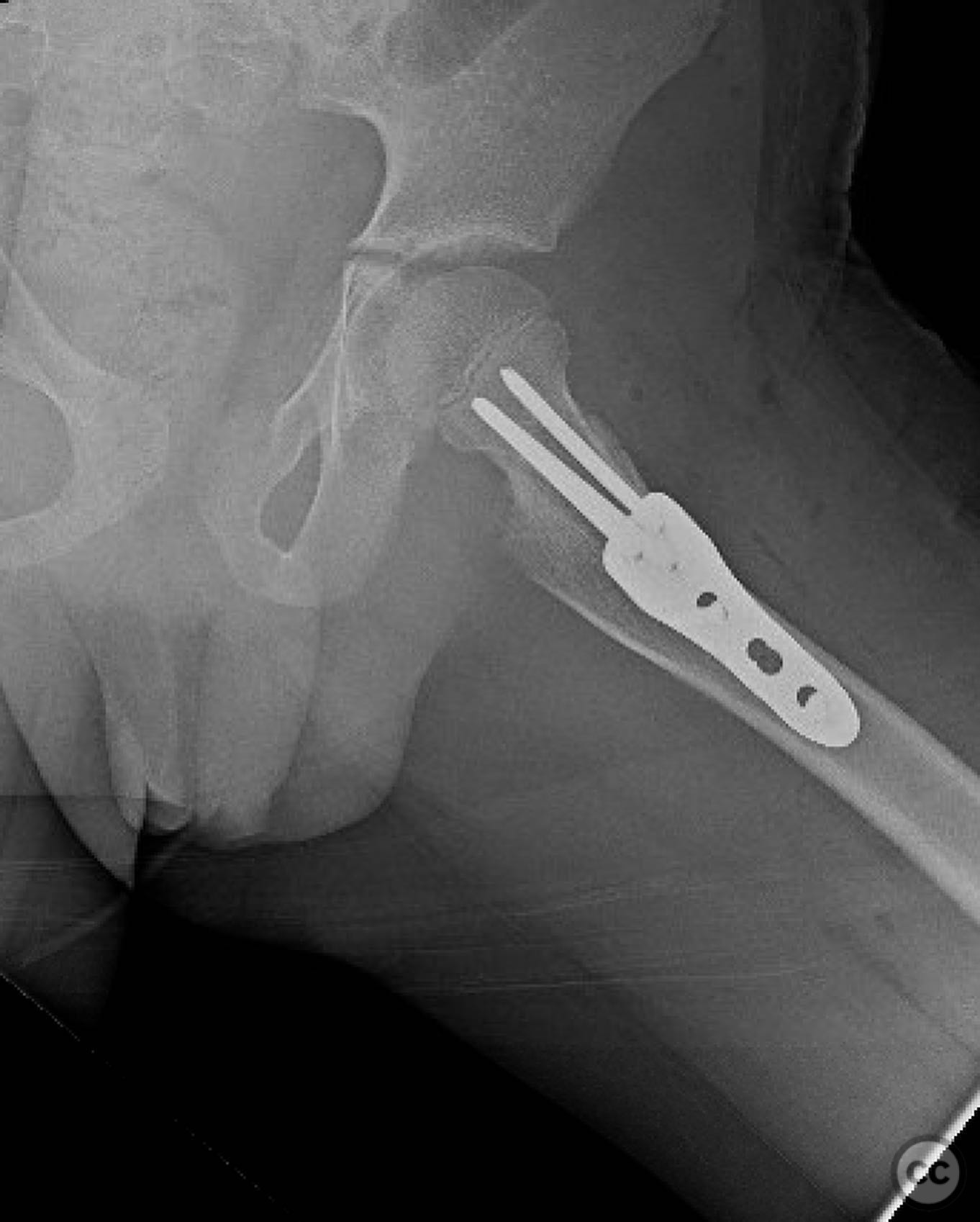
Clinical and radiological findings: An 8-year-old boy fell approximately 15 feet from a treehouse, sustaining a displaced femoral neck fracture. There were no associated injuries to the head, spine, chest, or abdomen. The initial radiological assessment confirmed a displaced fracture of the femoral neck. Neurovascular examination was unremarkable.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved achieving a direct anatomic reduction and stable fixation of the femoral neck fracture. The surgical approach considered was a modified Smith-Petersen approach for optimal visualization and reduction, followed by a separate lateral approach for implant application.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine position on a radiolucent table to facilitate intraoperative imaging and access to the femoral neck.
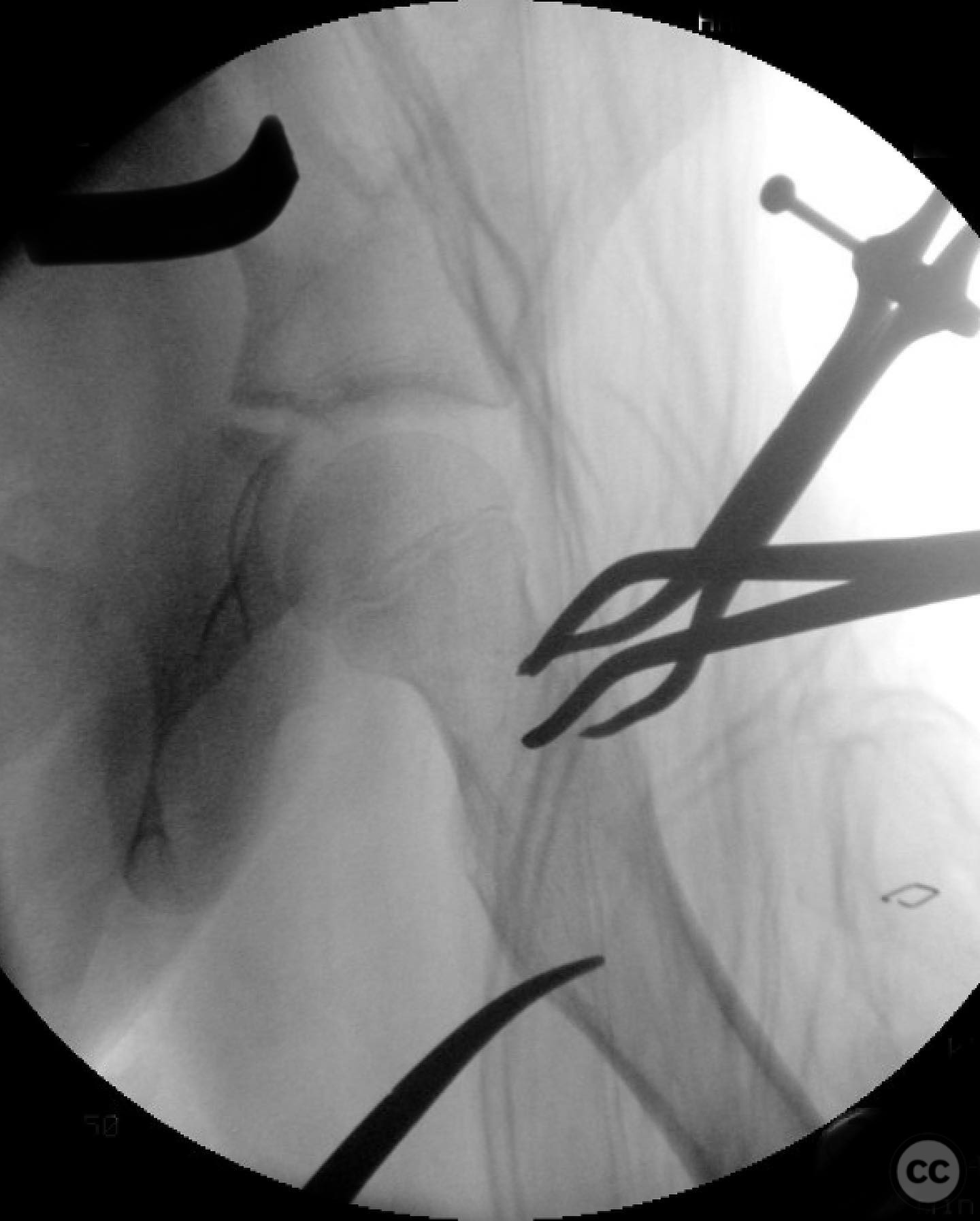
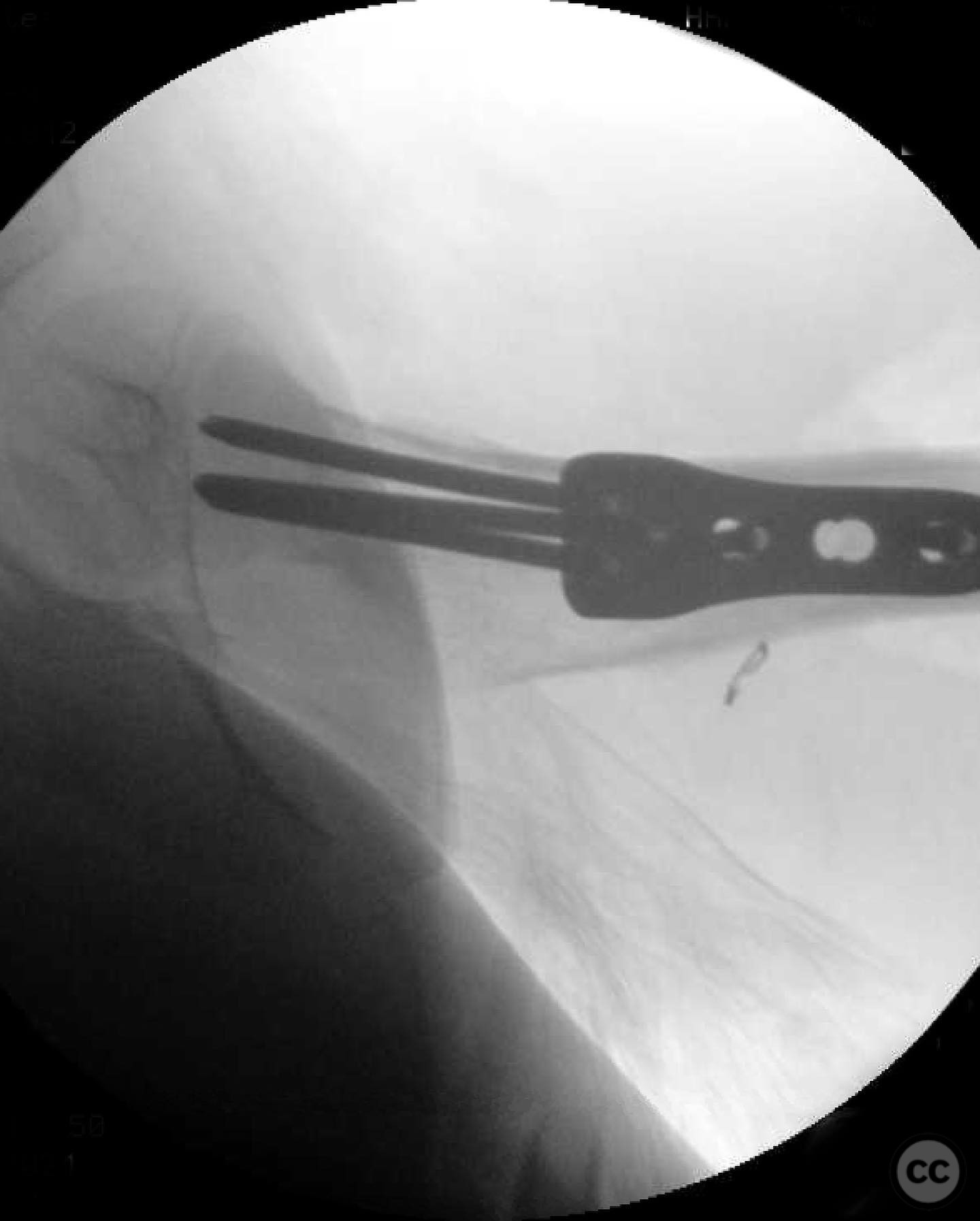
Anatomical surgical approach: A modified Smith-Petersen approach was utilized, involving an incision along the anterior aspect of the hip, allowing for direct visualization of the femoral neck. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the fracture site without compromising the surrounding musculature. A separate lateral approach was employed for the application of fixation devices.
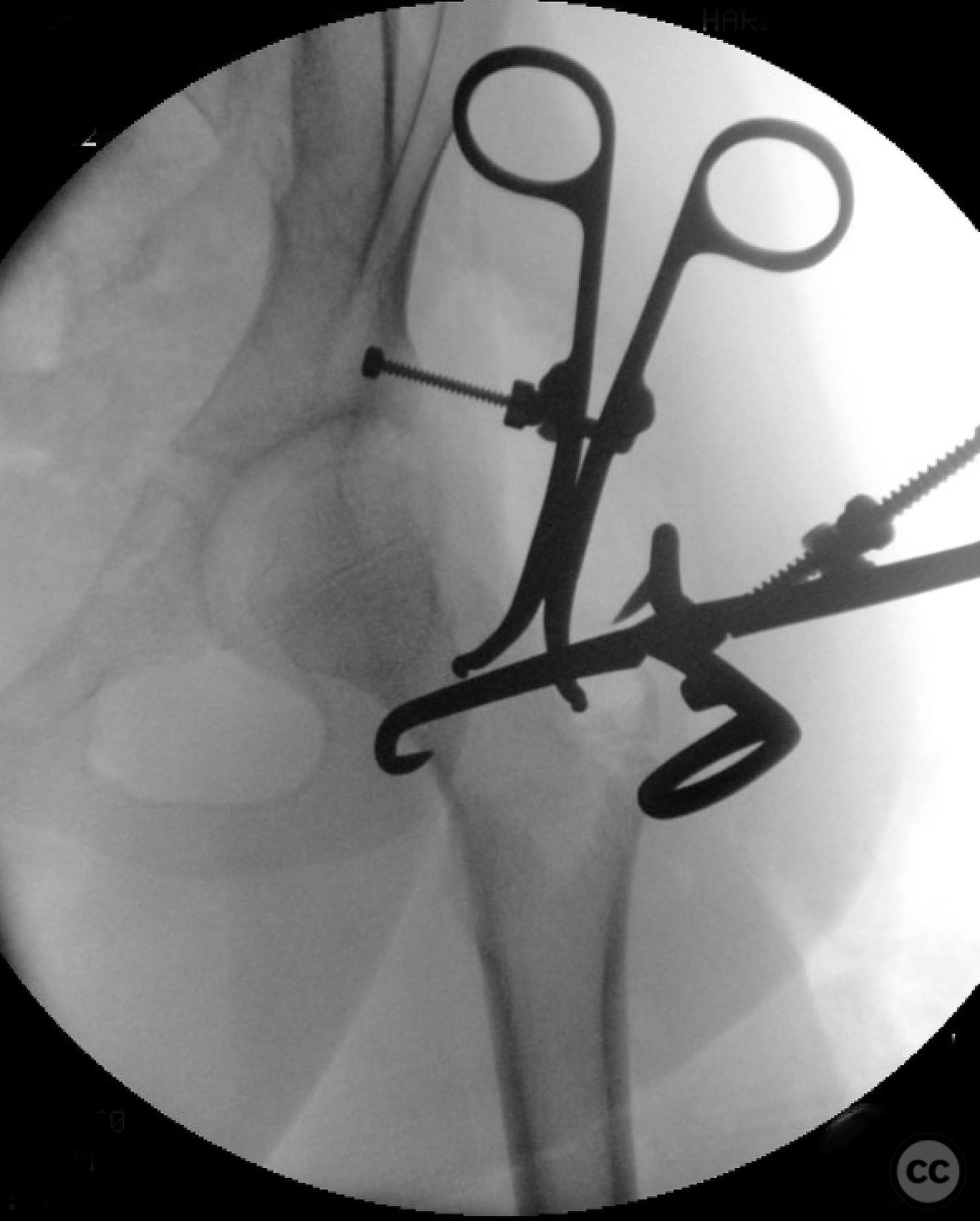
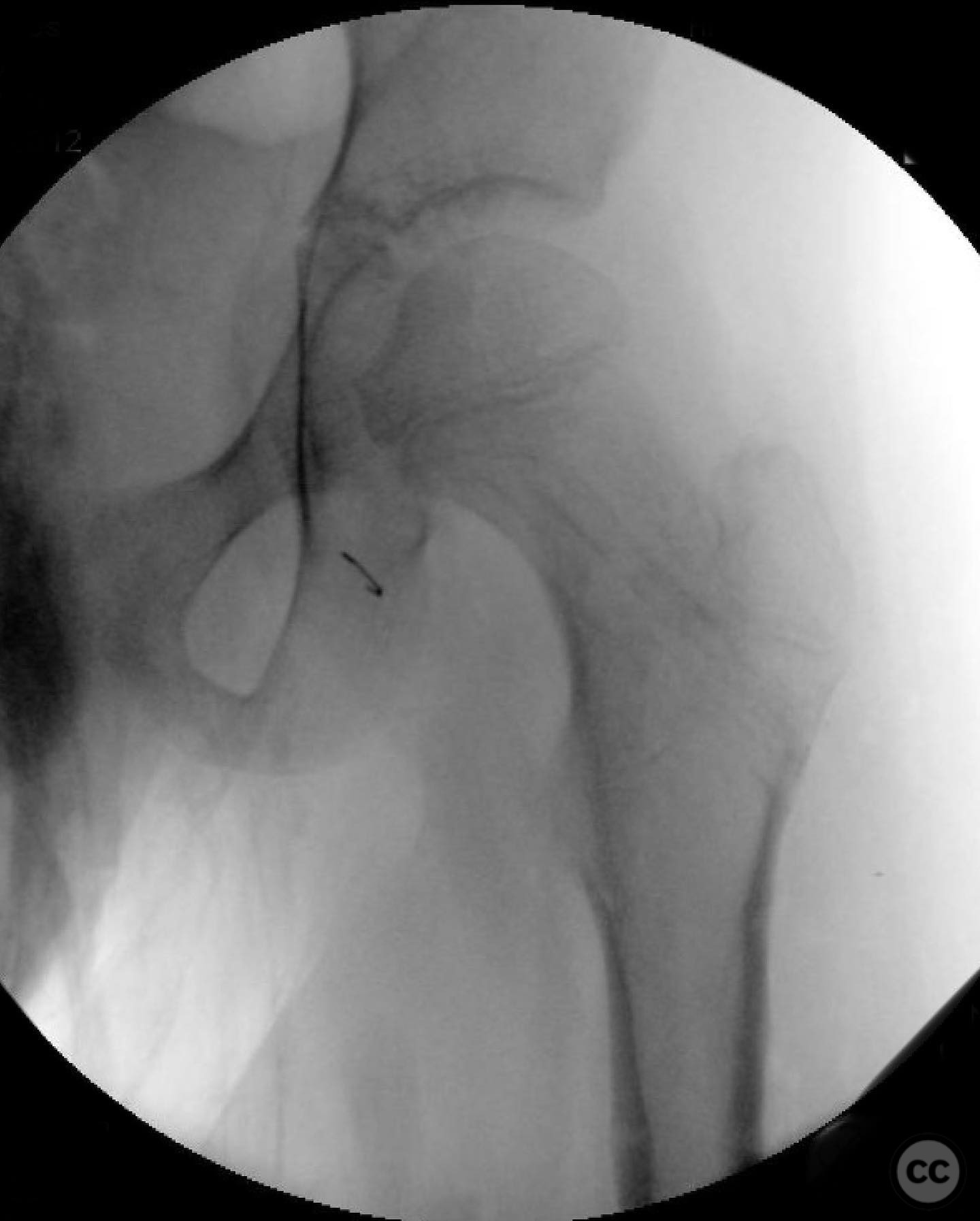
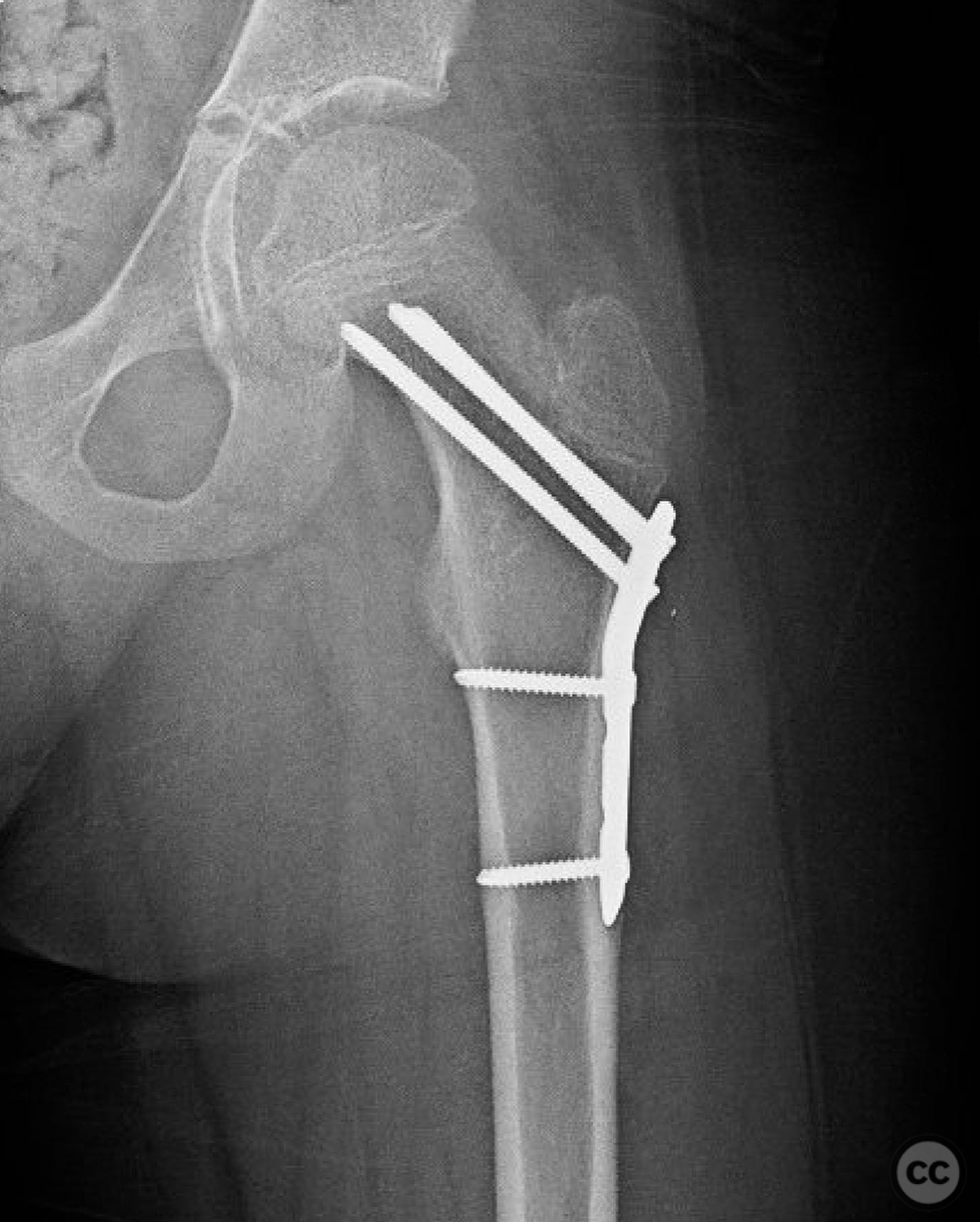
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of achieving a high-quality reduction and stable fixation due to the displacement pattern of the fracture. A meticulous surgical approach was critical to avoid malreduction, which is not well-tolerated in pediatric patients. The modified Smith-Petersen approach provided excellent visualization for anatomic reduction, minimizing soft tissue damage.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included non-weight bearing status initially, with gradual progression to weight-bearing as tolerated. Range of motion exercises were initiated early to prevent joint stiffness.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Angle stable static device (specific brand not mentioned).
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
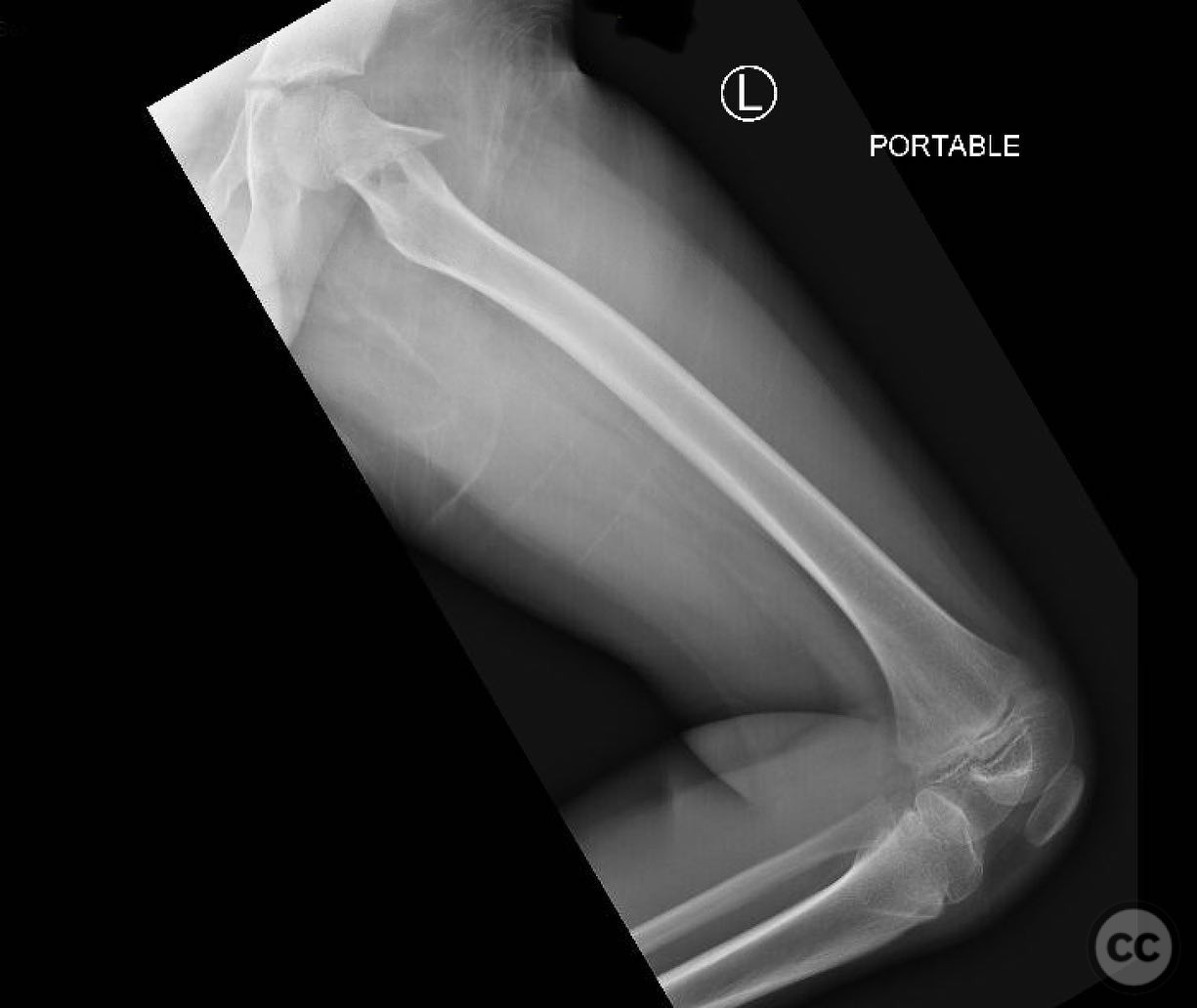
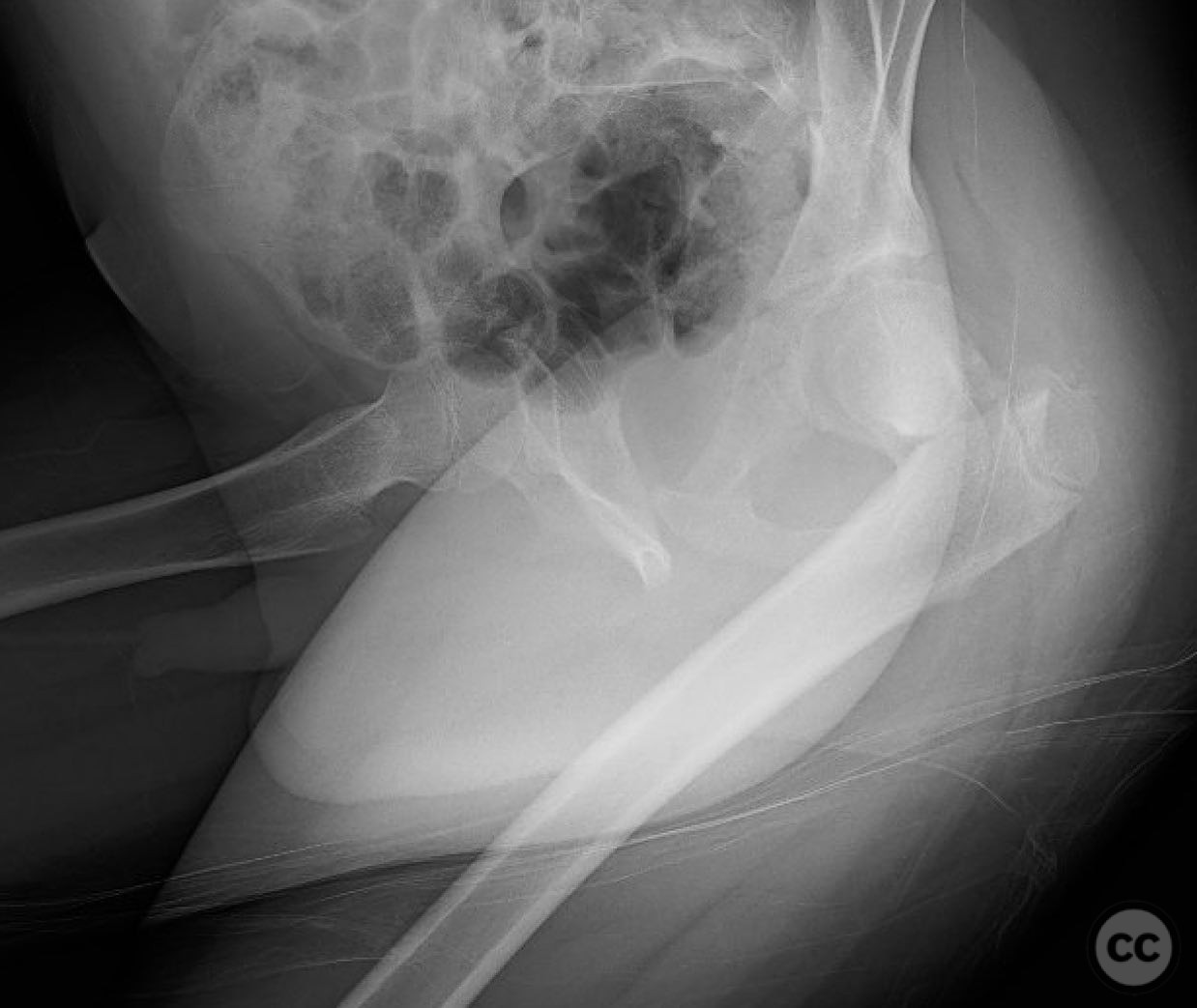
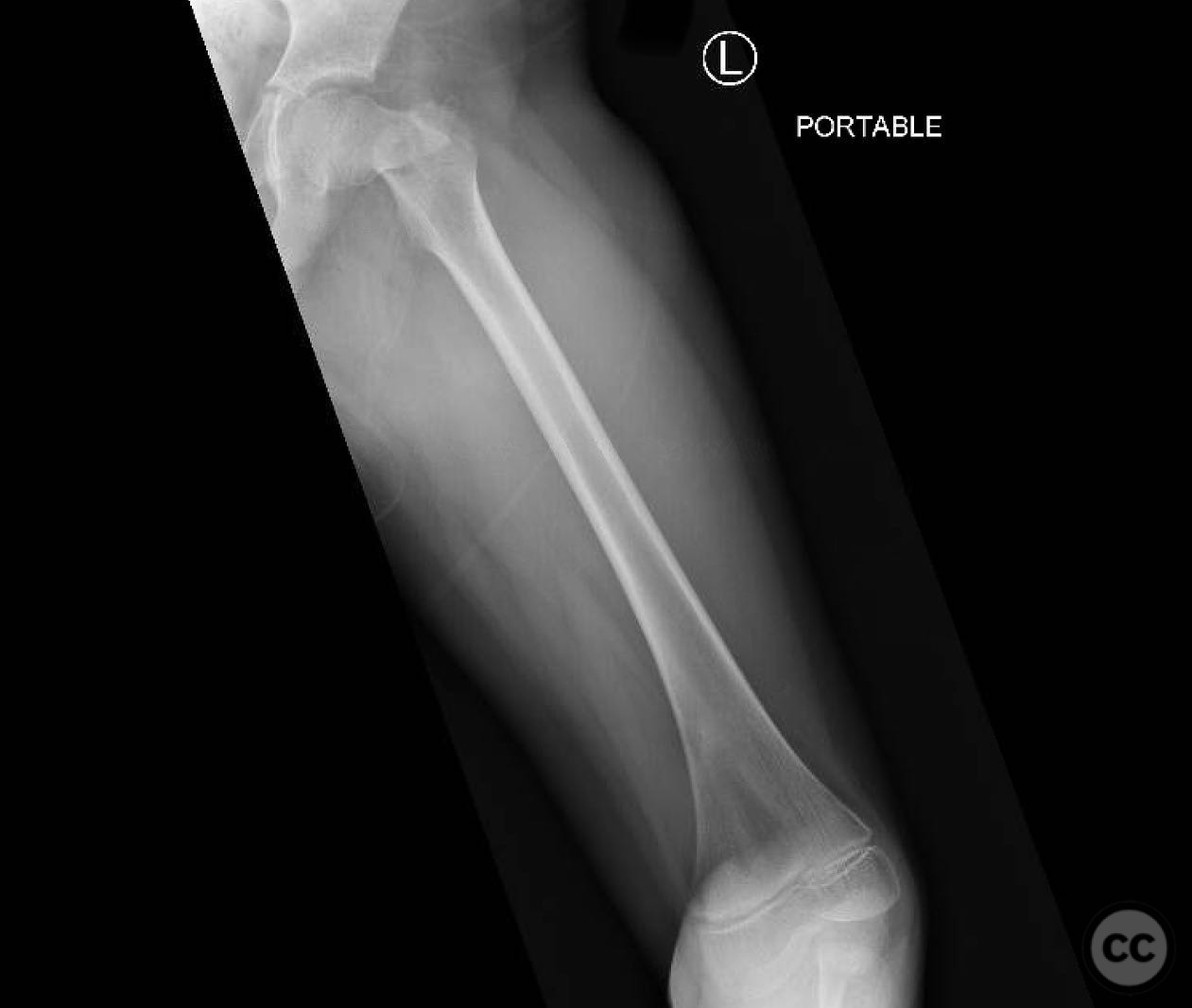
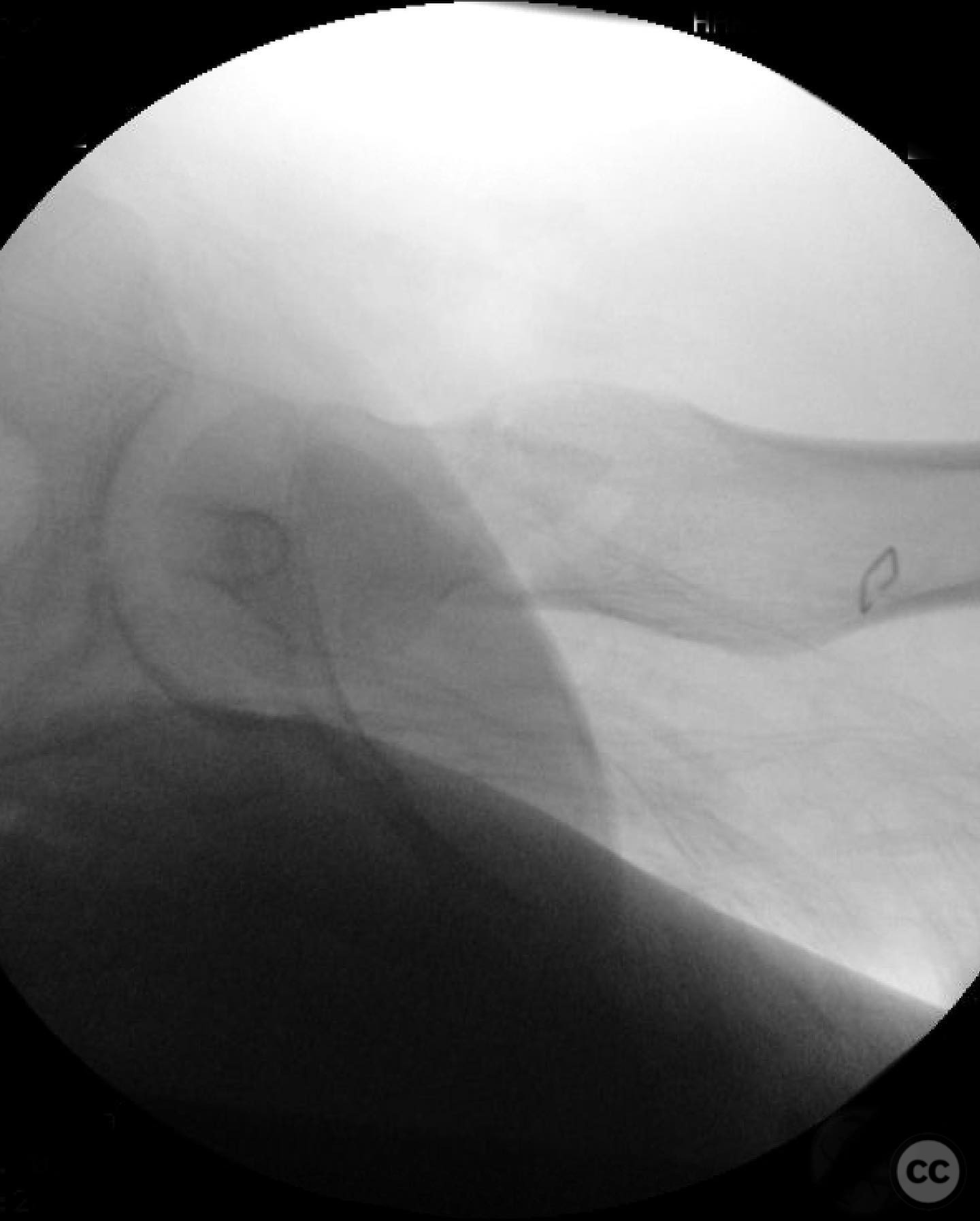
Article viewed 168 times
12 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Displaced Pediatric Femoral Neck Fracture in an 8-Year-Old Boy. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 14330194 Published Online Jul 12 2025.