Complex Open Upper Extremity Fracture with Vascular and Nerve Injury.
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
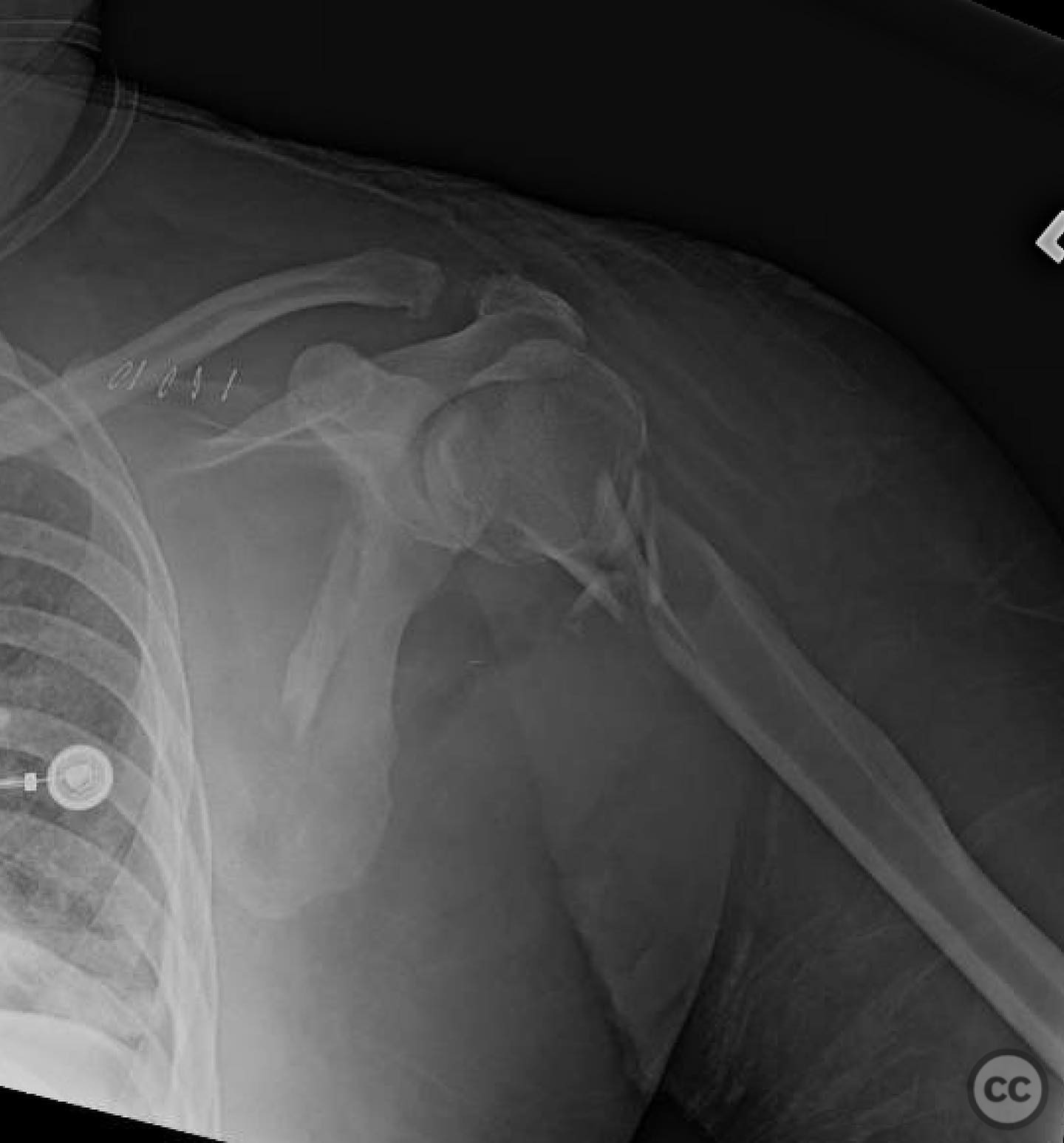
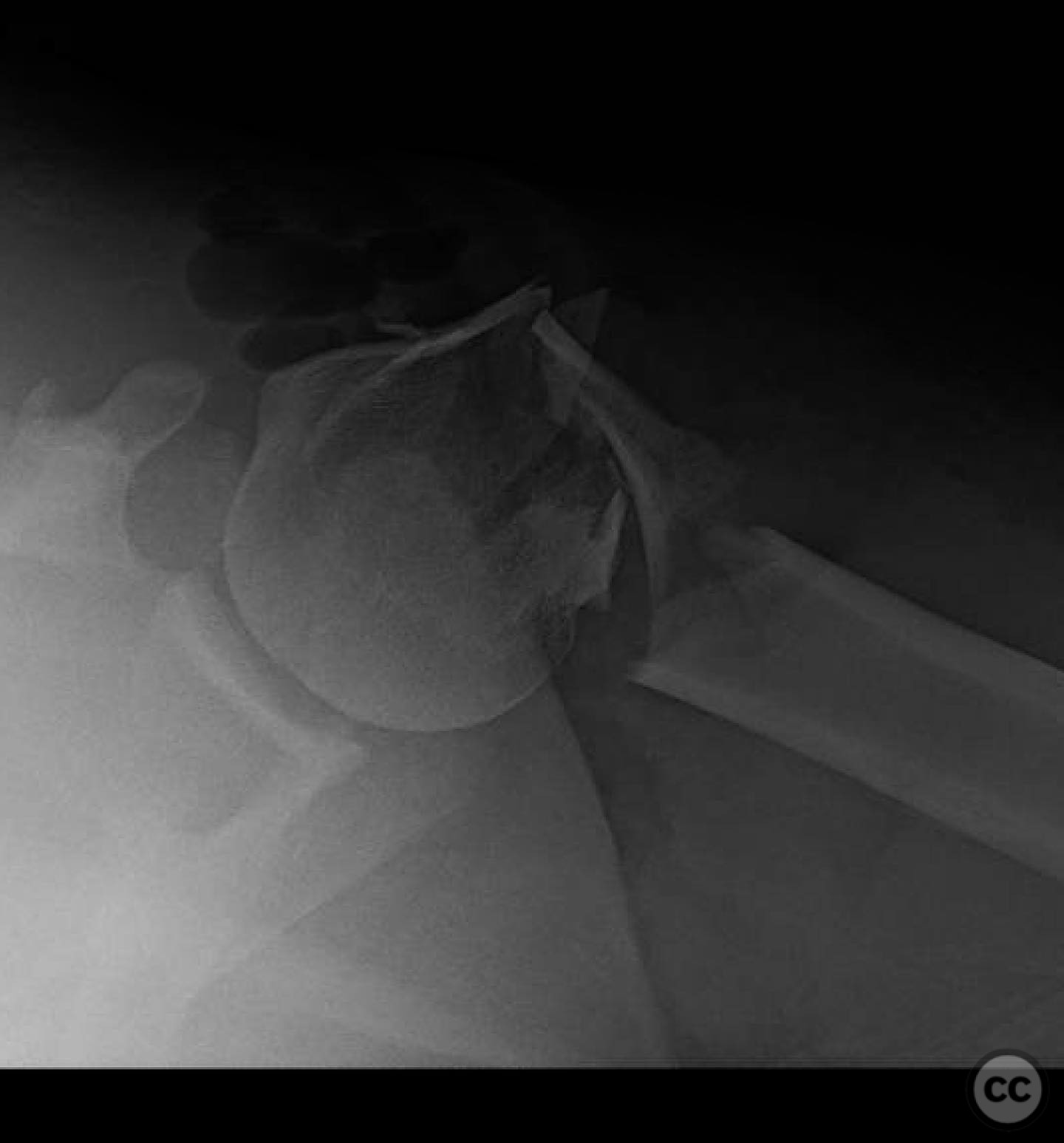
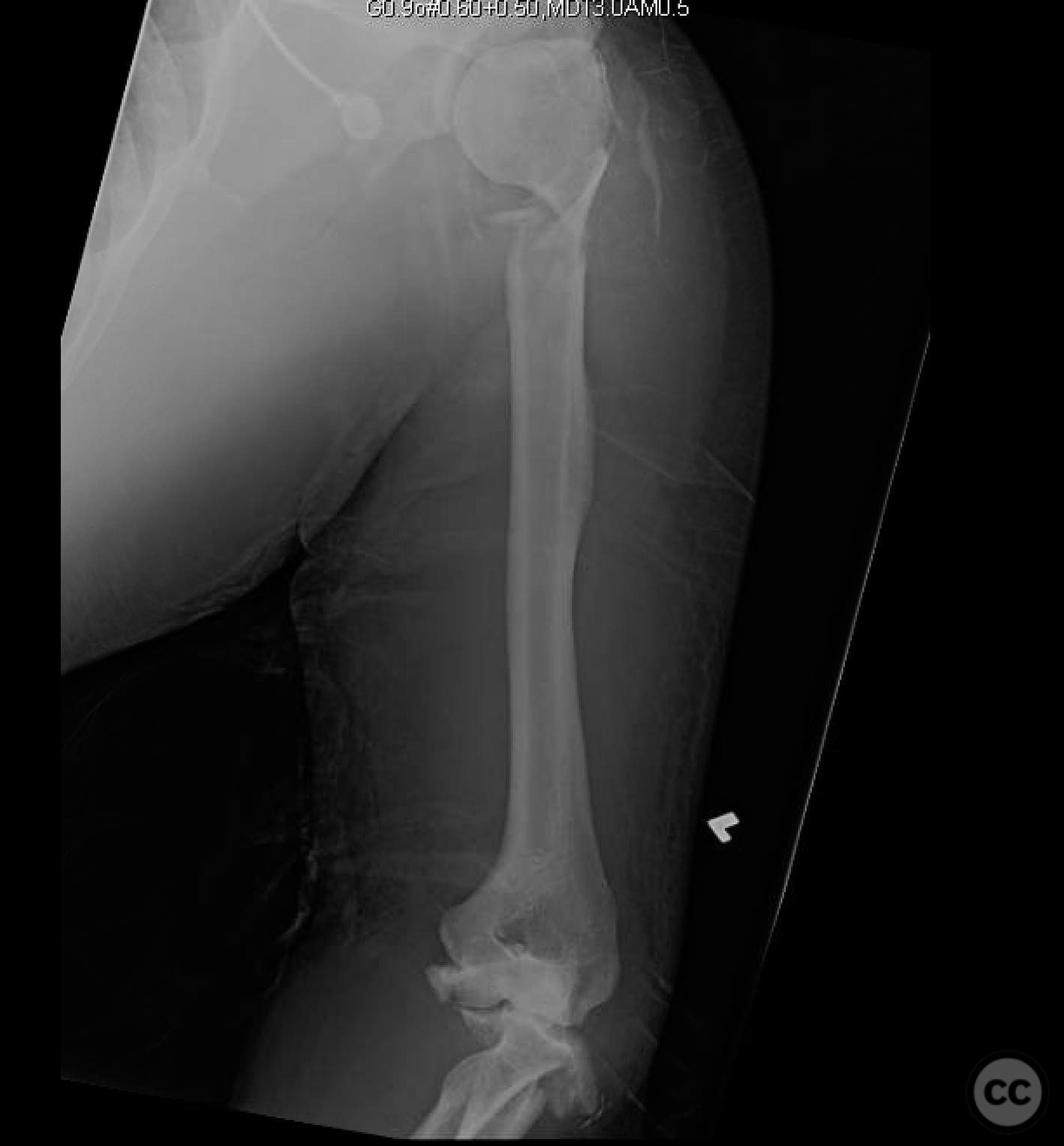
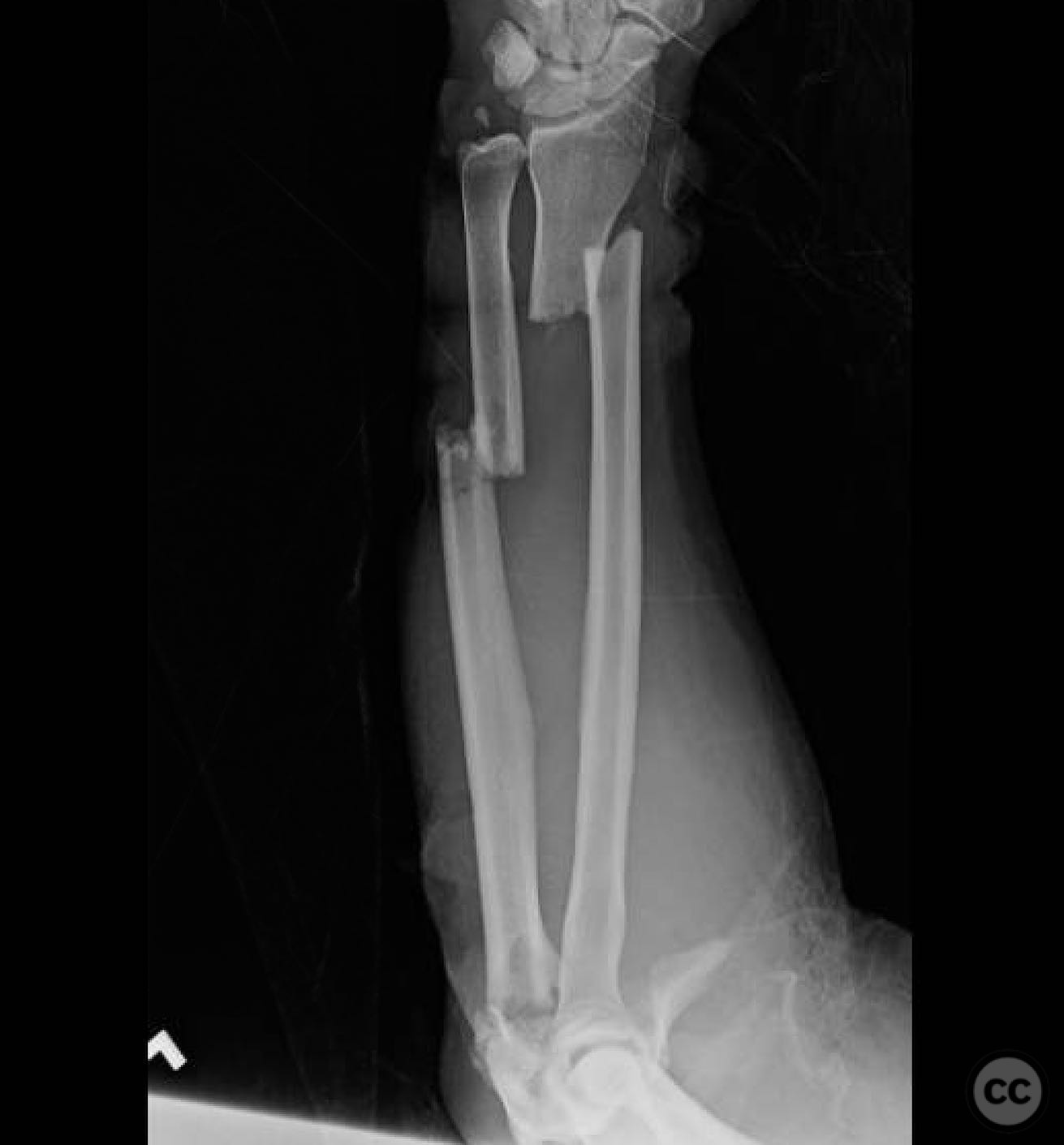
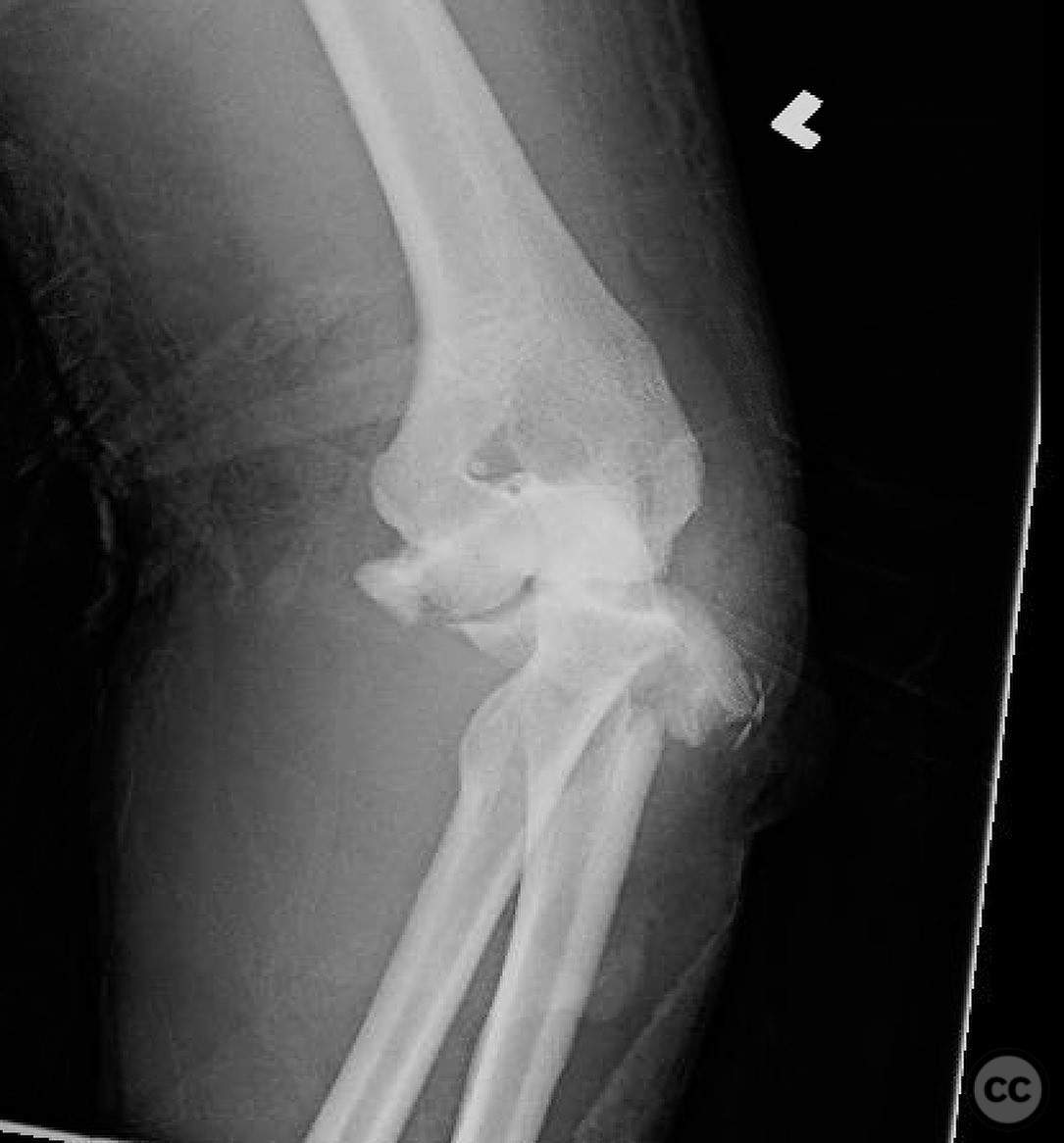
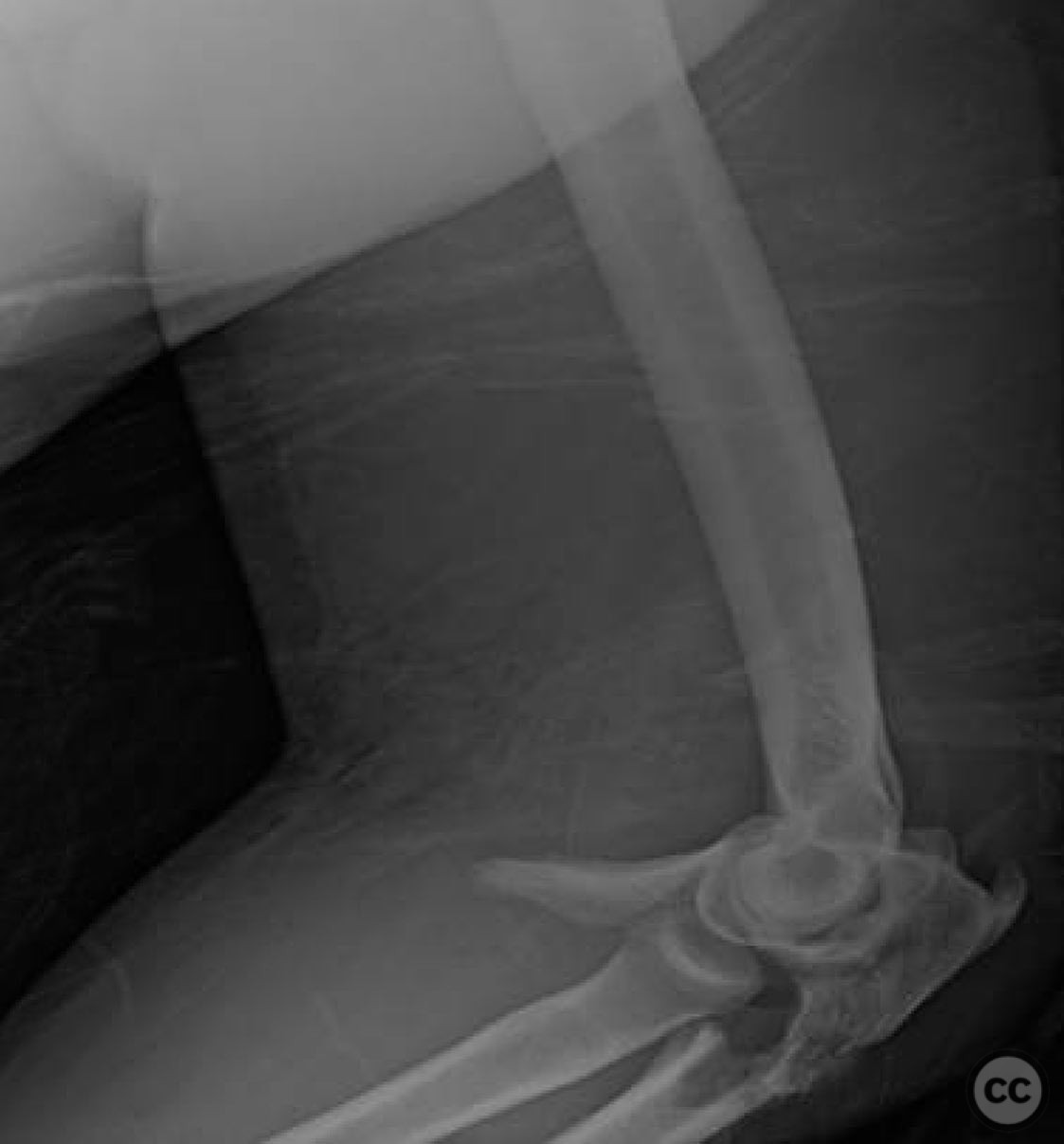
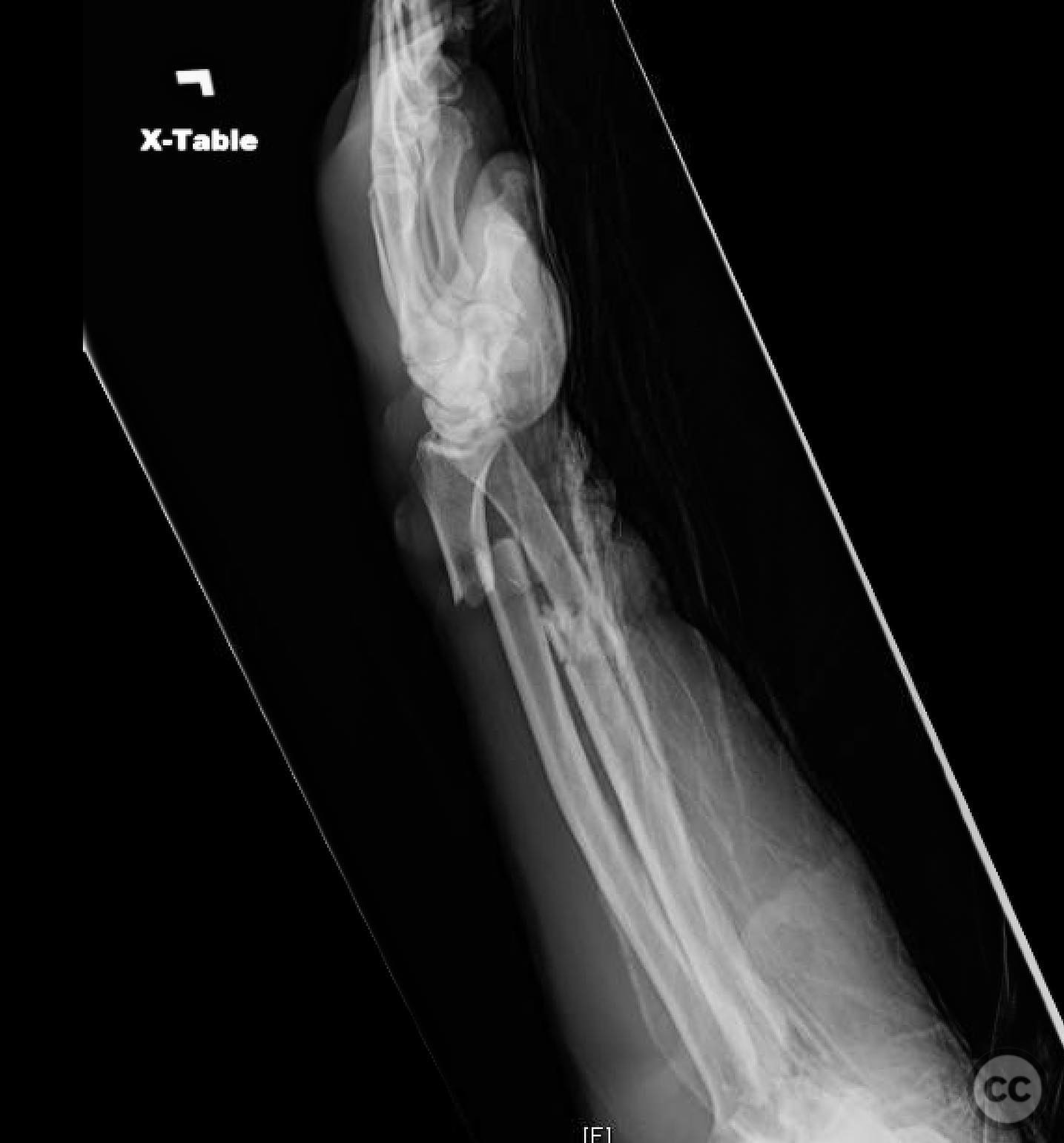
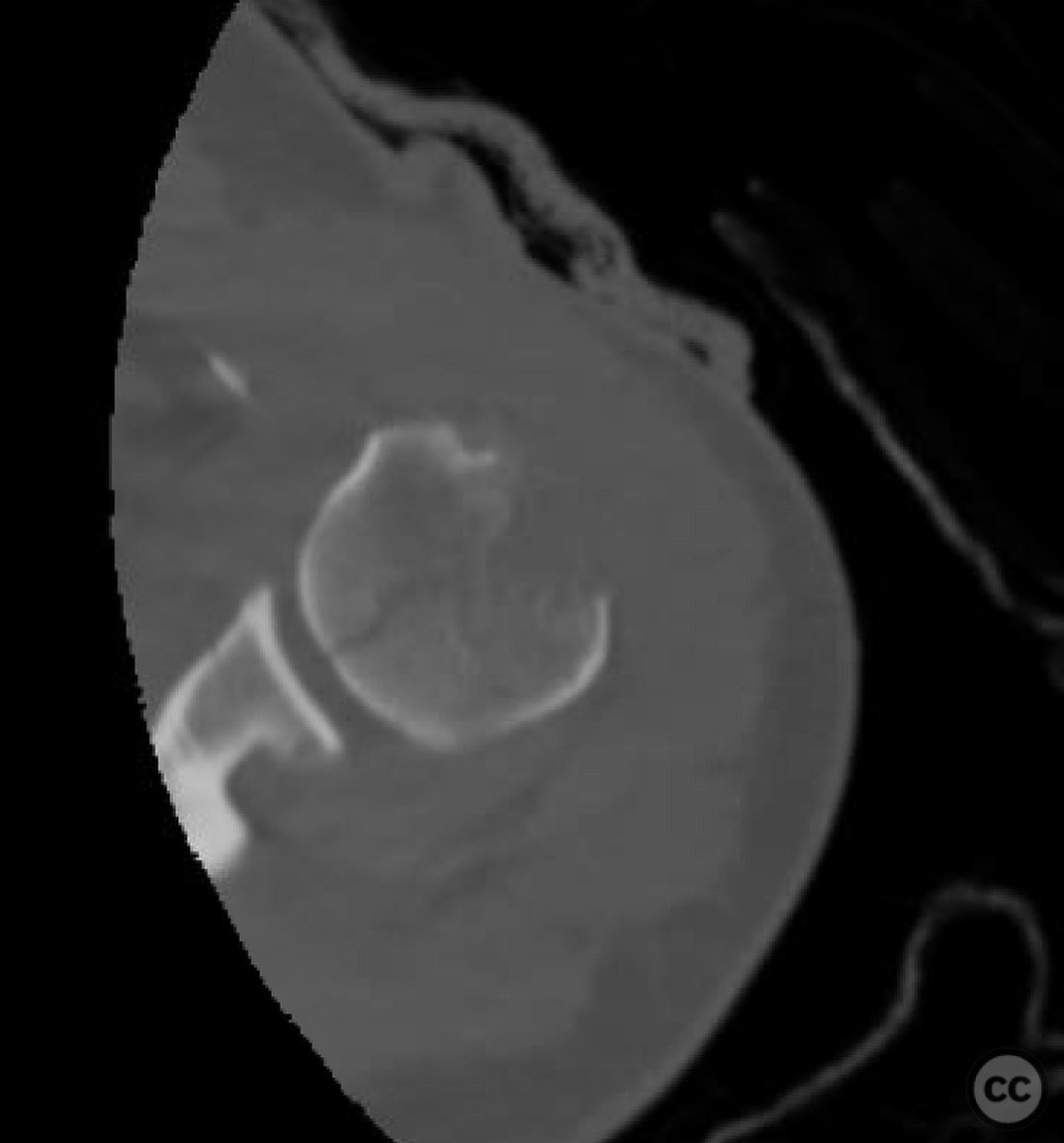
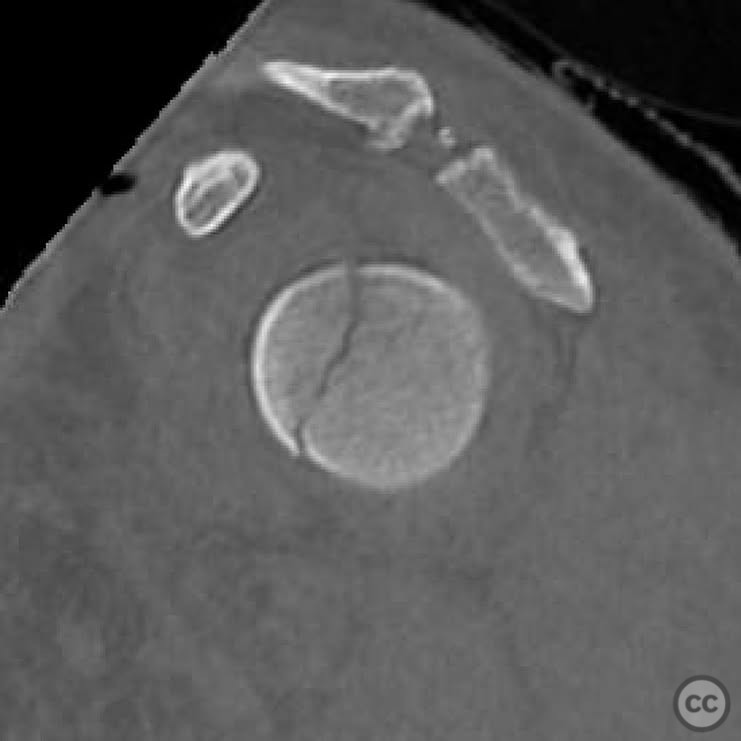
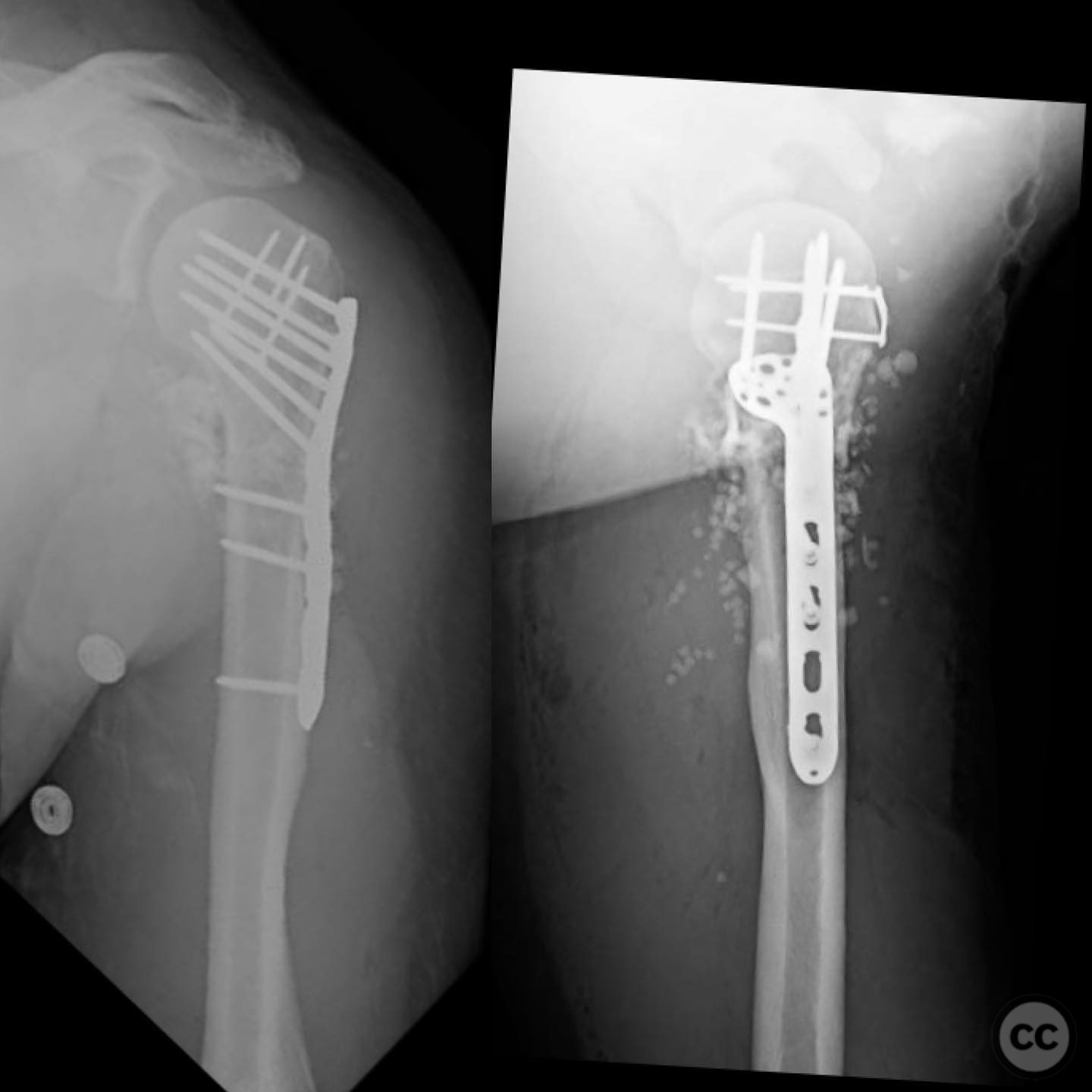
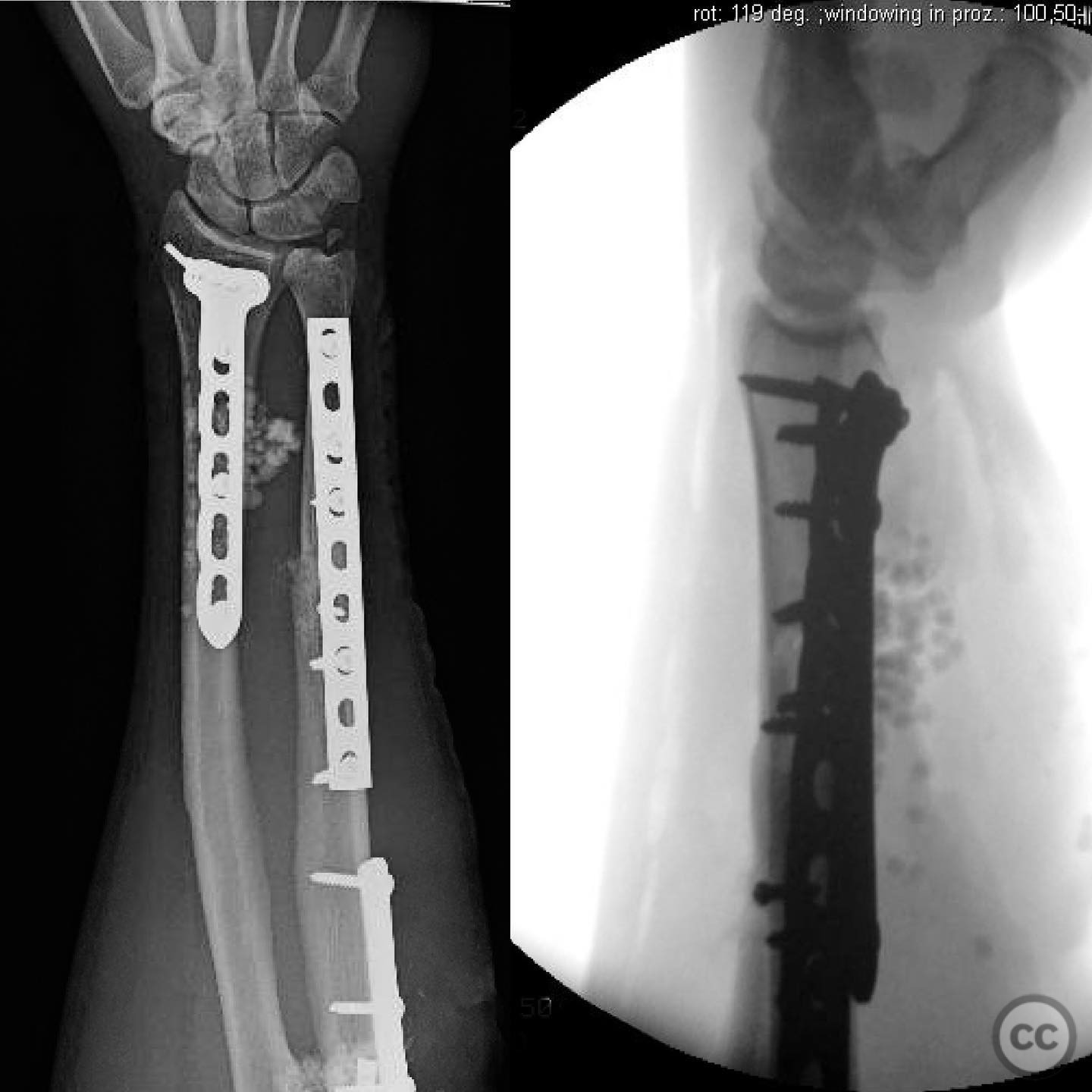
Clinical and radiological findings: A 44-year-old male presented following a motorcycle accident with an "arm vs sign" injury mechanism. Initial management at an outside facility included repair of an axillary artery injury and debridement of open fractures. The patient was transferred with a complete brachial plexopathy and multiple open fractures: an open proximal humerus fracture, an open posterior Monteggia fracture, and open both-bone forearm fractures. The AO/OTA classification for the proximal humerus fracture is 11-C3, the Monteggia fracture is 2U1B3, and the forearm fractures are 22-B3.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a thorough exploration and repeat debridement of all open wounds to address potential contamination and necrotic tissue. The primary focus was on protecting the vascular repair by stabilizing the proximal humerus fracture first. The surgical approach to the humerus would be determined by the fracture pattern, with a potential rotator interval opening for visualization. Subsequent fixation of the forearm and elbow would follow, depending on intraoperative patient stability.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was initially positioned supine for the proximal humerus fixation and forearm procedures. If patient condition allowed, repositioning to a lateral decubitus position was planned for optimal access to the elbow.
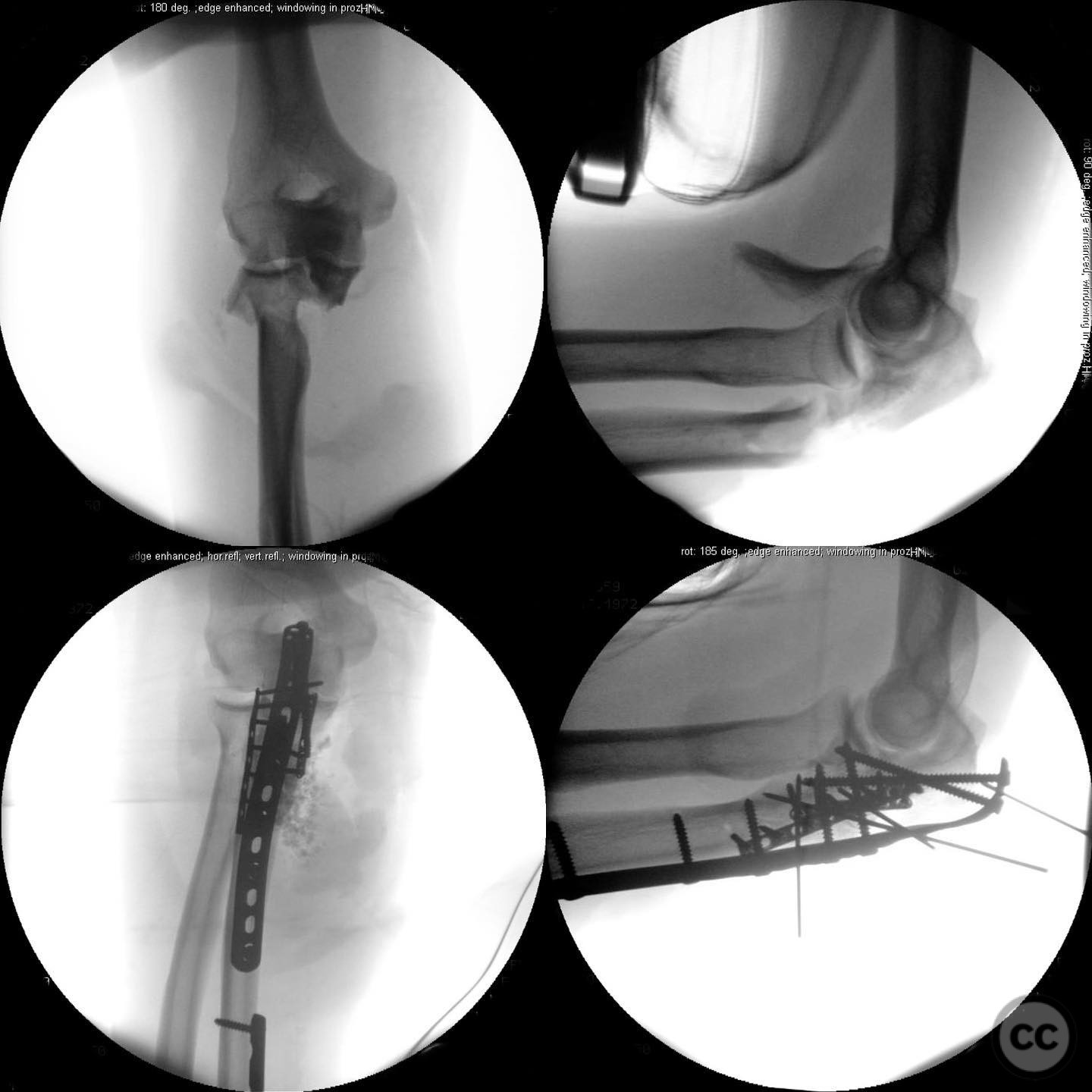
Anatomical surgical approach: The surgical approach to the proximal humerus involved an incision over the deltopectoral interval, with potential extension into the rotator interval for direct visualization of the fracture split in the coronal plane. For the forearm, a standard volar Henry approach was utilized for both-bone fixation. The elbow was accessed via a lateral approach to facilitate reduction and fixation of the Monteggia fracture.
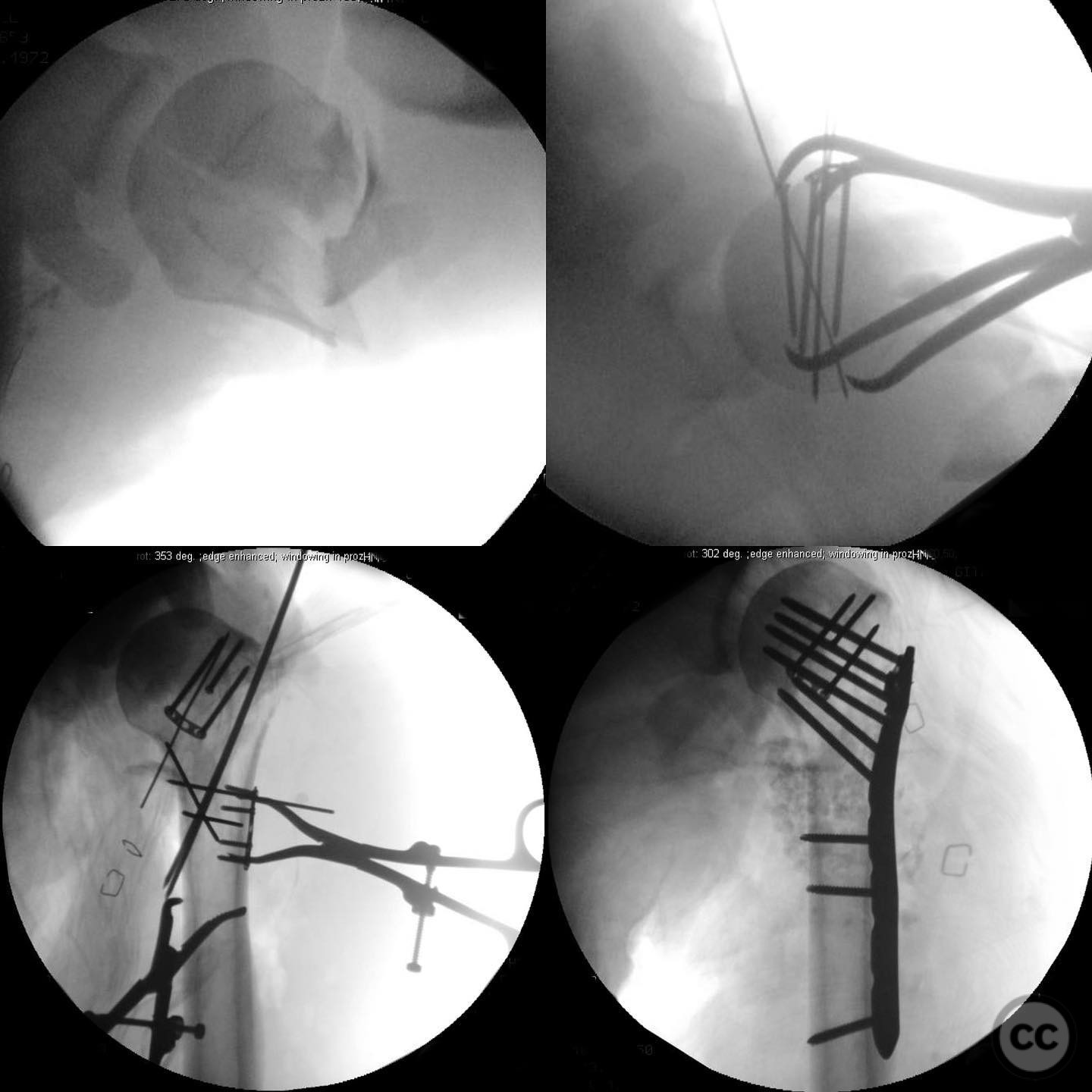
Operative remarks:The surgeon emphasized the importance of verifying all debridement and vascular repairs personally, despite previous interventions at another facility. Fixation of the proximal humerus was prioritized to protect the vascular repair, followed by addressing the forearm fractures. The elbow was considered technically challenging due to its multifragmentary nature, necessitating precise reduction for successful radial head alignment.
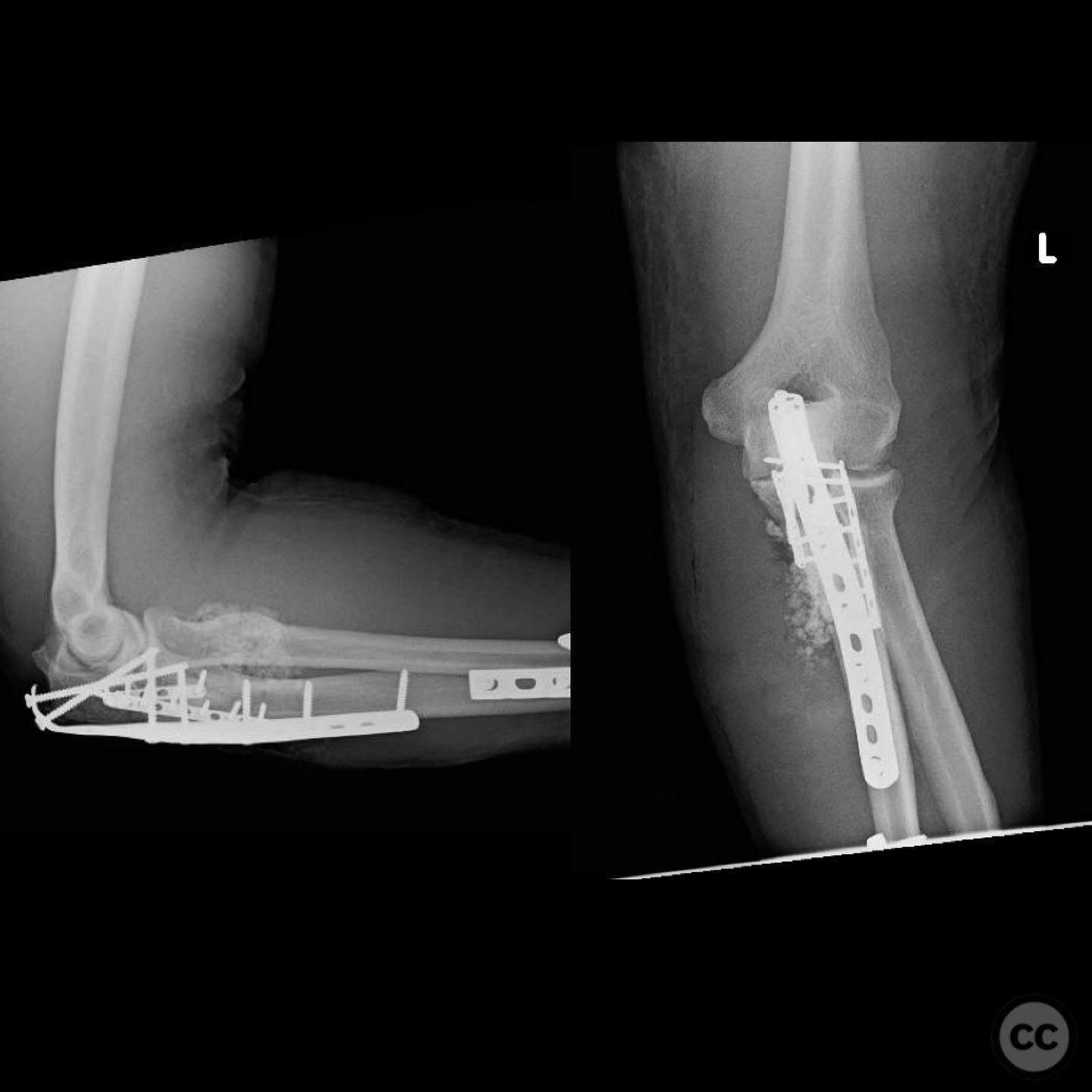
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included immobilization of the upper extremity in a sling for initial protection, with gradual mobilization as tolerated. Emphasis was placed on early passive range of motion exercises to prevent stiffness, with progression to active exercises as healing permitted.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used included locking plates for the proximal humerus and forearm fractures, and a radial head prosthesis or plate fixation for the Monteggia fracture, depending on intraoperative findings.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 173 times
14 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Complex Open Upper Extremity Fracture with Vascular and Nerve Injury.. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 12972078 Published Online Jul 14 2025.