Proximal Humerus Synovial Pseudarthrosis with Orthogonal Plating and Fibular Grafting
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
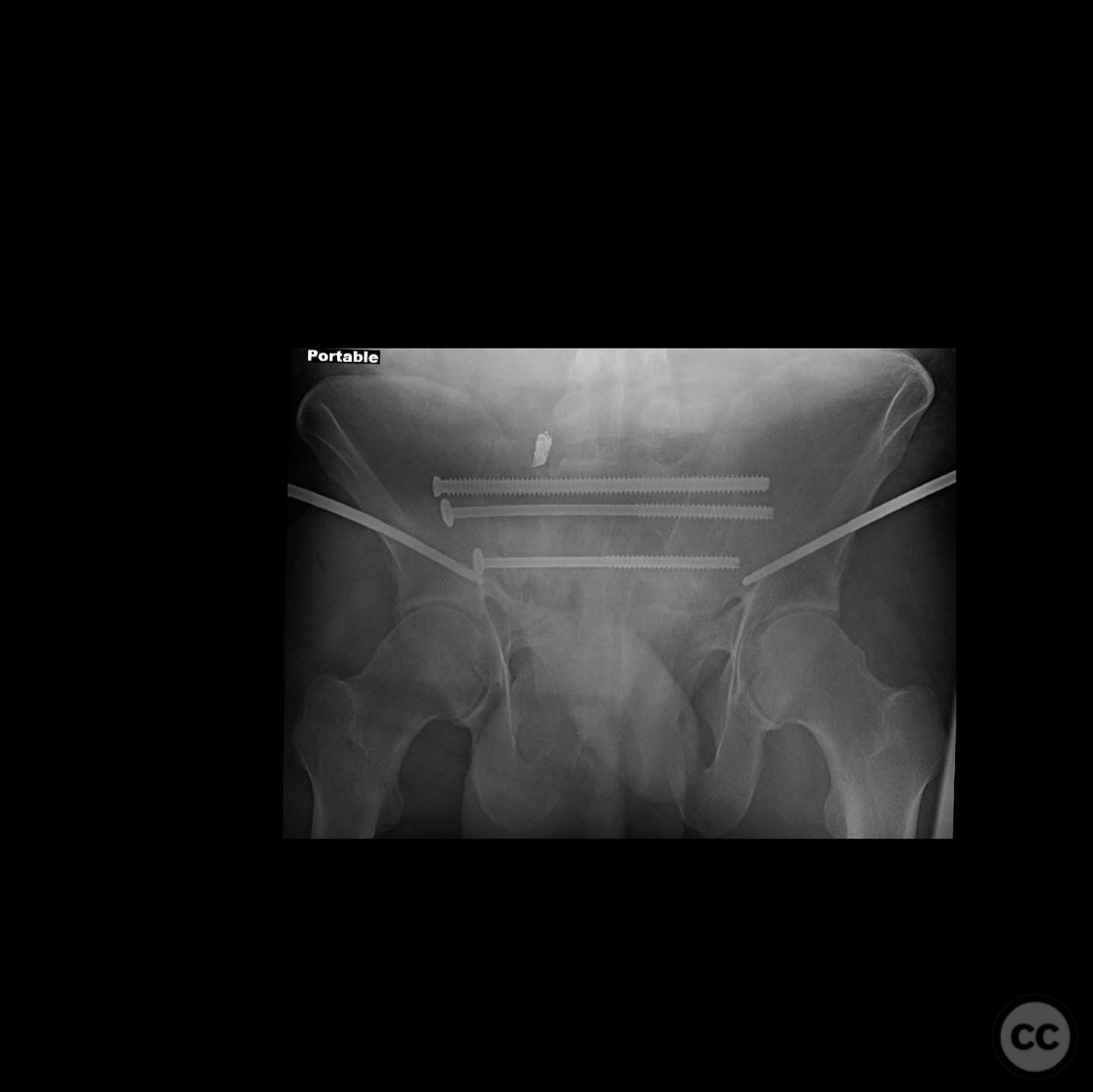
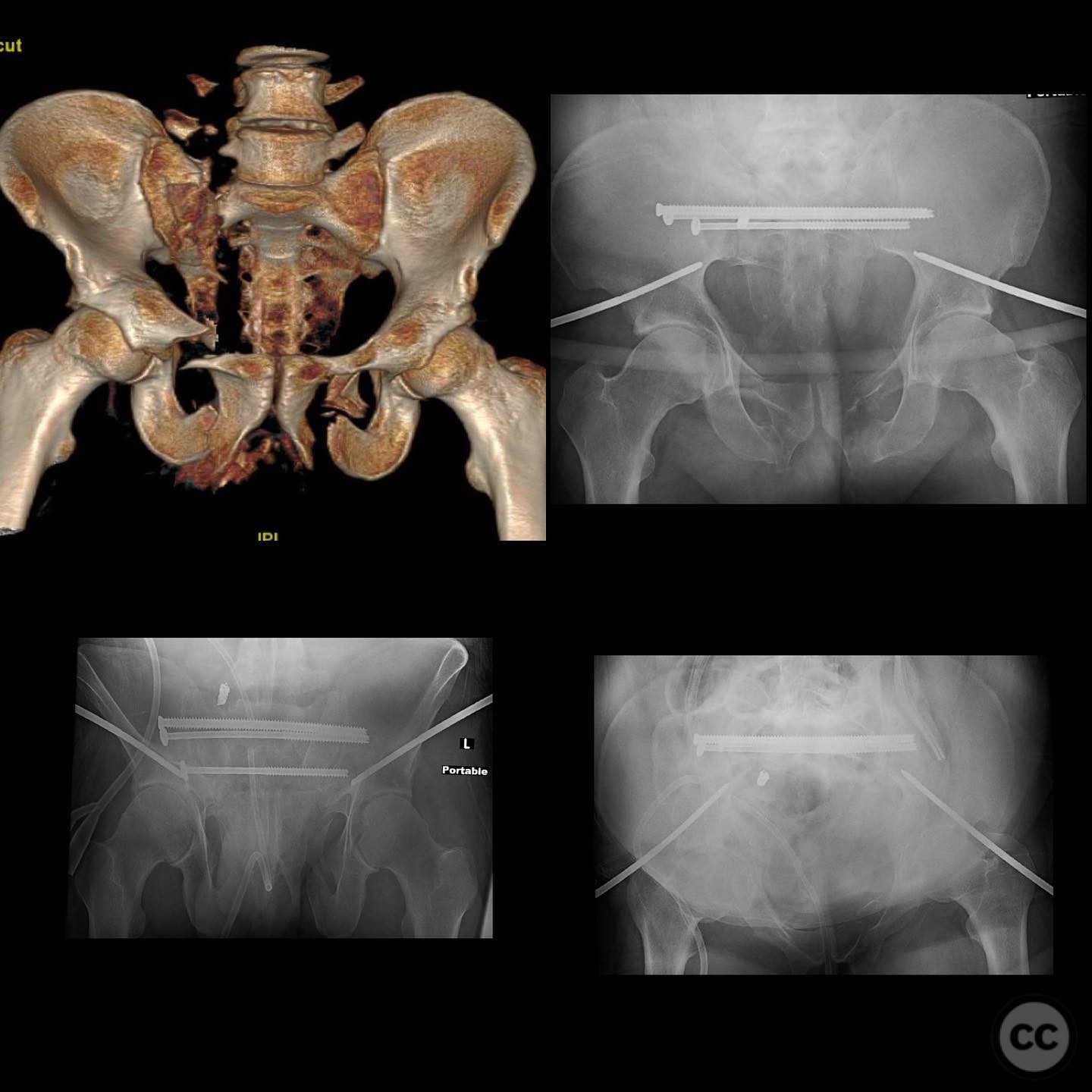
Clinical and radiological findings: A 51-year-old male presented with a painful, limited use of the arm due to a proximal humerus nonunion, 1.5 years post-injury from a fall out of a tree. Initial management was non-operative at an outside facility. Radiological evaluation confirmed a synovial pseudarthrosis, characterized by the formation of a pseudo-joint at the fracture site.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a deltopectoral approach for complete debridement of the pseudarthrosis, fibular grafting to restore the medial column, proximal tibial autograft, and the use of a commercially available osteogenic/osteoinductive graft substitute. Orthogonal plating was planned to achieve absolute stability.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with the arm draped free to allow full access to the shoulder region.
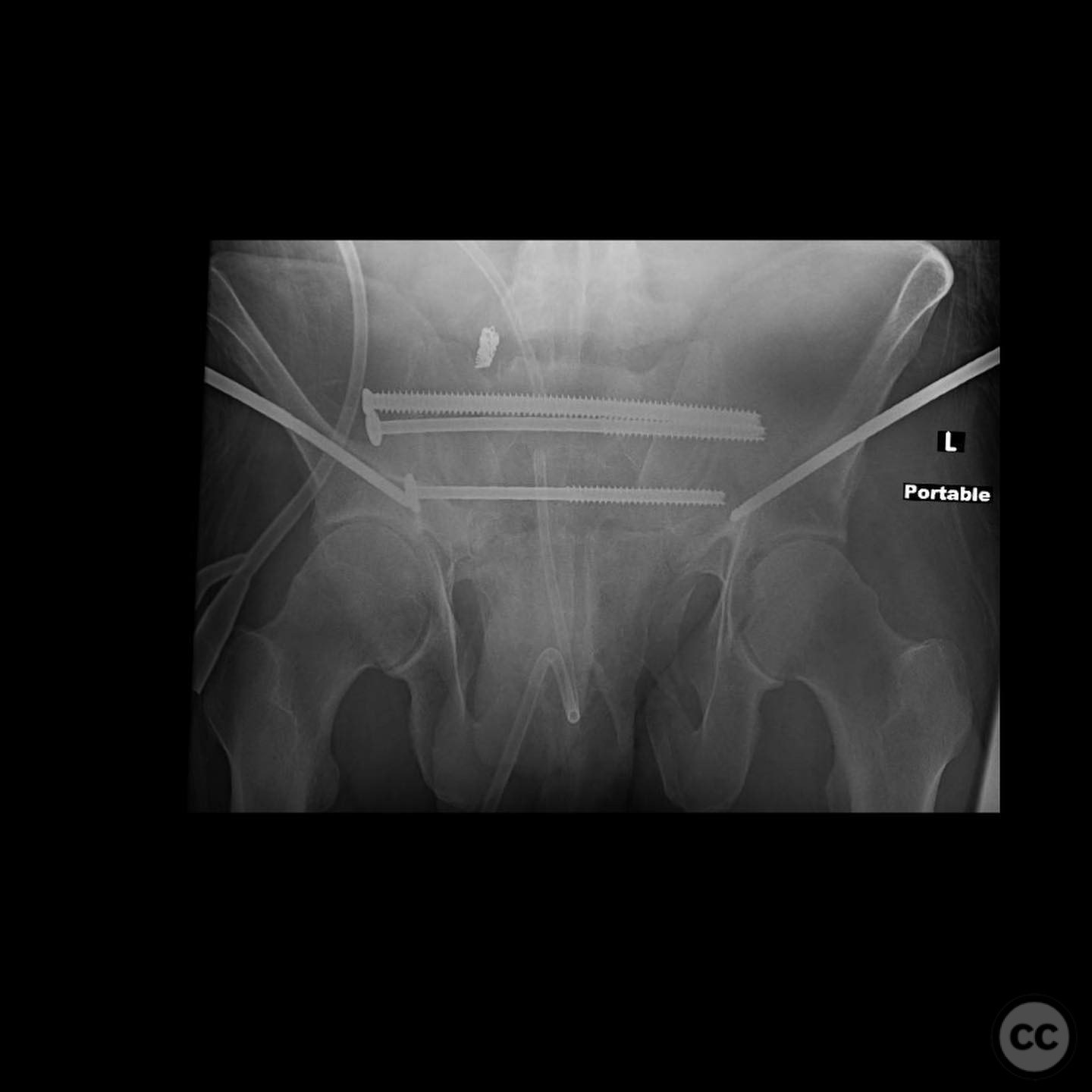
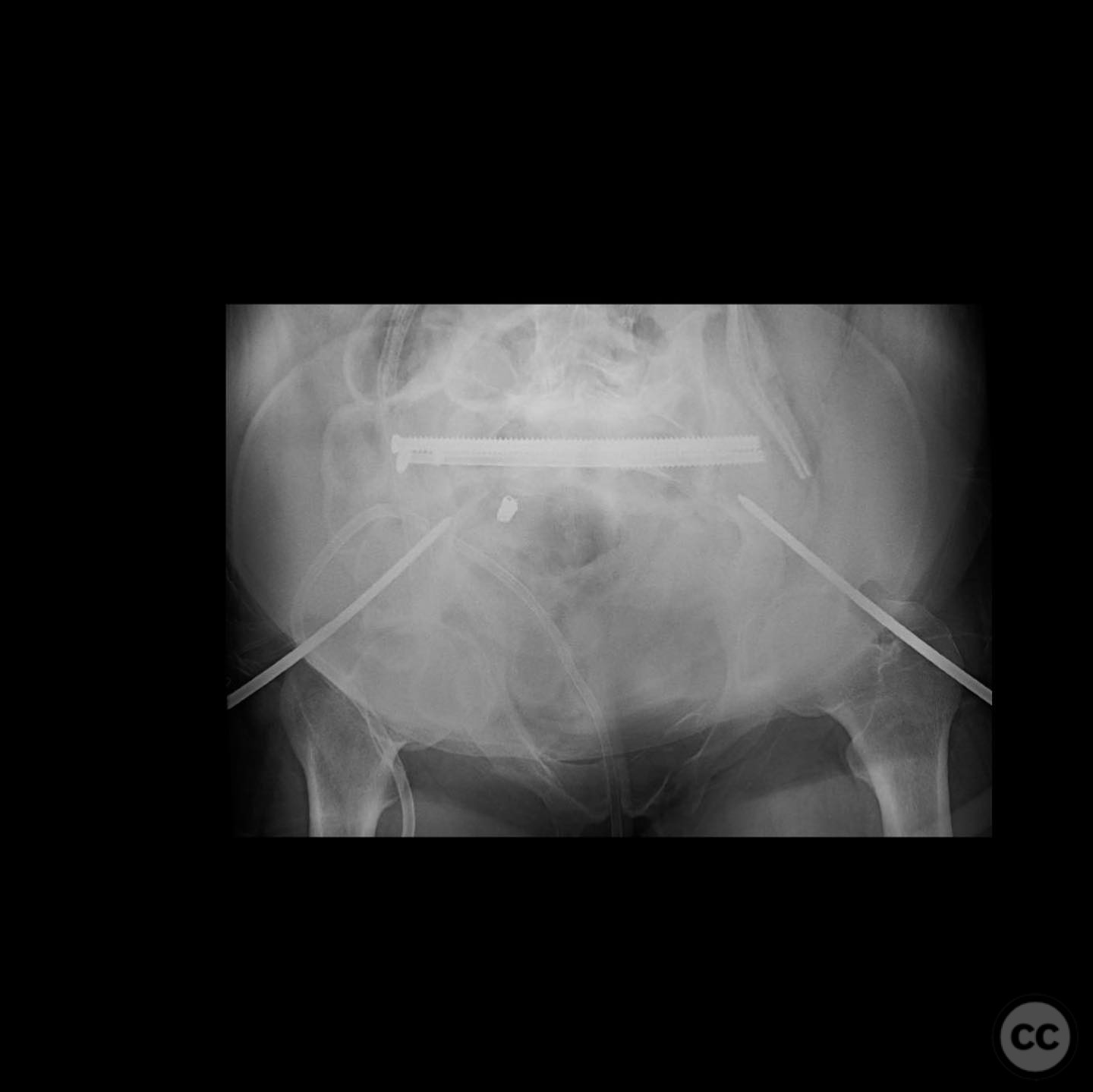
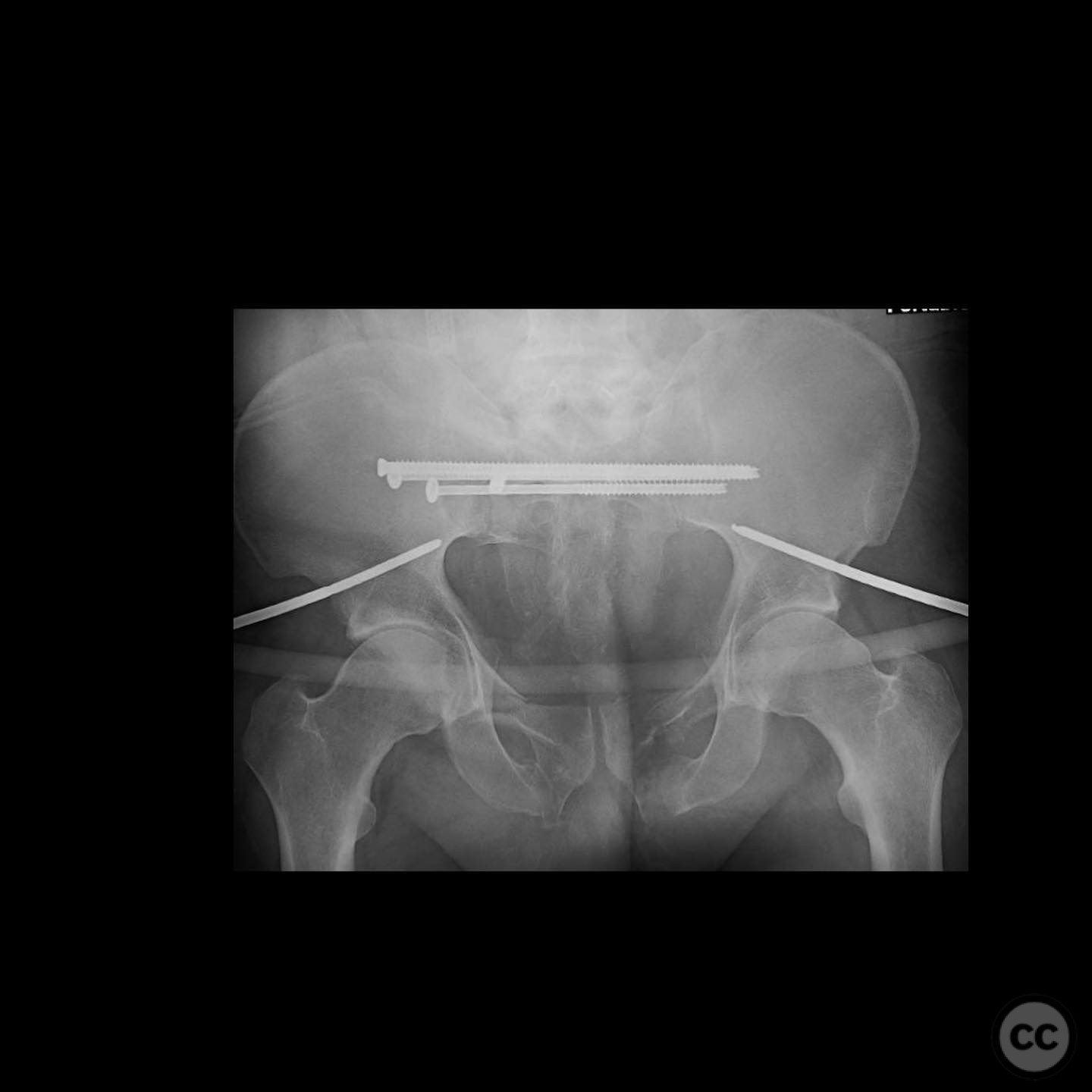
Anatomical surgical approach: A deltopectoral incision was made, and the interval between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles was developed. The pseudarthrosis site was exposed, and complete debridement of the pseudo membrane was performed. The fibula was harvested and used to restore the medial column. Proximal tibial autograft and osteogenic/osteoinductive graft substitute were applied. Orthogonal plating was performed to provide stable fixation.
Operative remarks:The surgeon noted that due to the synovial pseudarthrosis, the patient had been moving through the pseudoarthrosis rather than the glenohumeral joint, resulting in stiffness. Intraoperative examination under anesthesia revealed surprisingly good motion after gentle manipulation.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included early passive range of motion exercises to prevent stiffness, with gradual progression to active-assisted and active exercises as tolerated. Weight-bearing was restricted until radiological evidence of healing was observed.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthogonal plating system, fibular graft, proximal tibial autograft, osteogenic/osteoinductive graft substitute.
Search for Related Literature

orthopaedic_trauma
- United States , Seattle
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 189 times
18 Jul 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Surname, Initial. (2025). Proximal Humerus Synovial Pseudarthrosis with Orthogonal Plating and Fibular Grafting. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 10710572 Published Online Jul 18 2025.